
The Development of Contextual based Accounting E-Module to
Improve Students’ Learning Motivation
Eren Prinstin
1
, Puji Handayati
2*
1
Graduated school of Universitas Negeri Malang
2
Universitas Negeri Malang
Keywords: E-module, Contextual
Abstract: This research and development aimed to create an electronic module of contextual based which able to
improve student's motivation. This development product used the modification of research and development
stages based on Borg and Gill statement, which consists of (1) analysis of initial needs (2) planning (3)
product developing (4) expert validation (5) product revision (6) main field testing (7) final product
revision. Quantitative and qualitative data were used as the type of this research. The content validation was
conducted by using questionnaire of scoring scale based on Likert’s scale. The last product of this research
and development was contextual based e-module which designed to increase students' motivation. Based on
the analysis of the overall validation, the overall percentage average was 89,69% which means valid. Based
on the test of Paired Sample T-Test, it showed that the significance was 0,000 < 0,05. Therefore, it can be
concluded that contextual based e-module is feasible and effective for the learning of accounting.
1 INTRODUCTION
The quality of life of a nation is determined by
educational factors. Education has an important role
in creating a smart, peaceful and democratic life.
Education is a manifestation of a dynamic and
developmental human culture. Therefore, changes or
developments in education are things that should
actually happen in line with changes in the culture of
life. Changes in the sense of improving education at
all levels need to be continuously carried out in
anticipation of future interests (Trianto, 2010: 1).
Recognizing the importance of education, the
government has made various efforts, one of which
is related to the development and improvement of
the curriculum. The 2013 curriculum used today is
the result of improvements and reinforcement of the
previous curriculum. The 2013 curriculum is aimed
at producing productive, creative, innovative and
effective Indonesian people; through strengthening
integrated attitudes, skills and knowledge (Mulyasa,
2014: 65). The 2013 curriculum is implemented at
all levels of school starting from SD / MI, SMP /
MTs, SMA / MA / SMK.
Vocational High Schools (SMK) are educational
institutions that equip students not only with
knowledge but also skills as a life skill. It aims to
prepare graduates as skilled and able to compete in
the world of work. Vocational students as Human
Resources who have superior competencies and
characters are needed in the era of globalization in
order to be able to compete in a healthy manner so
that they are able to develop competencies in their
entirety to survive and exist in this era. Therefore,
teaching materials both applicable theory and
practice must be given early, in the hope that SMK
graduates have the competency according to their
needs. Therefore, adequate education is needed and
designed based on real needs.
Based on this fact, contextual learning feels right
to represent it. Through this design, students will be
accustomed to building their own knowledge based
on real contexts that are meaningful to themselves.
Contextual learning (Contextual Teaching and
Learning) according to (Sanjaya in Sa'ud, 2008: 162)
is a learning approach that emphasizes the process of
full student involvement to be able to find material
that is learned and relate it to real life situations so as
to encourage students to be able to apply it in their
lives. In contextual learning the teacher tries to give
something tangible in accordance with the
environment around the child so that the knowledge
gained by the child in the classroom is the
20
Prinstin, E. and Handayati, P.
The Development of Contextual based Accounting E-Module to Improve Students’ Learning Motivation.
DOI: 10.5220/0008784400200026
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Research Conference on Economics and Business (IRCEB 2018), pages 20-26
ISBN: 978-989-758-428-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

knowledge that is built and owned by themselves.
That way, the application of contextual learning in
schools will be meaningful for students to be able to
solve problems, think critically, carry out
observations, and draw conclusions in the long term.
One aspect that needs to be considered in this
implementation effort can be realized in the form of
adequate teaching materials and in accordance with
the curriculum that applies as a guide in the learning
process. With the existence of teaching materials
will facilitate the learning process of students.
According to Sa'ud (2008: 214) teaching materials or
learning materials are learning materials that are
directly used for learning activities. Teaching
materials are categorized into two, namely printed
and non-printed materials. Printed teaching materials
include textbooks, modules, handouts, and LKS.
While no printed teaching materials such as audio
cassettes, video cassettes, VCD, and films.
Muslich (2010: 30) states that the teaching
materials contained in textbooks circulating in the
market are often biased and stale. This happens
because between the time of the preparation of the
textbook and its usage time is too long even the
teaching material is not in accordance with the
conditions and environment of the students. This is
indicated by the fact that the existing teaching
materials are still based on KTSP. The Electronic
School Book (BSE) provided by the government on
the puskurbuk page, LKS, and existing modules
have not supported the learning expected by the
curriculum now. Circular module form teaching
materials used in schools usually only contain
discussion material and practice questions, so
students cannot develop their creativity.
Whereas the module that is expected now is a
module that not only contains material and exercises
questions, but also contains processes or activities in
learning to acquire and develop various skills.
Currently there are modules available, (1) they are
not contextual, (2) provision of accounting
knowledge and skills still uses a lot of accounting
textbooks, (3) the teaching materials do not use real
business transactions around students, (4) the form is
still conventional or textbook oriented. While the
contextual module will help students in solving
problems, exercises, and assignments in real terms.
Submission of material in the module begins with
phenomena that are close to students. Starting from
special things that are in the environment around
students, after that explained the underlying concept.
The concept received from the module is expected to
be able to be applied by students in the environment.
Research and development related to contextual-
based modules are not the first research done. Dewi
(2014) conducts research and development of
contextual learning module on accounting cycle
material. The development model used the Borg and
Gall development model. Ulfa (2014) conducted a
research and development of contextual learning
modules in the discussion of material processing
journal entries, with the Borg and Gall development
model. Wardani (2016) conducted a research and
development of contextual learning modules on
static fluid material, with Thiagarajan's development
model, the 4D model. Of the three previous studies,
the modules that developed contextual values only
existed at the beginning of the material in the form
of examples of company illustrations and at the end
of the material in the form of independent tasks with
everyday problems. So, the modules that have been
developed are not yet contextual, still seem textual.
Impressed textually because the core material of
teaching materials is still exactly the same as the
books circulating. In addition, it only contains one
competency standard and is still printed or paper-
based.
Print-based or paper-based teaching materials
that are used in learning so far, are static and abstract
which make students feel bored quickly because the
material is dominated by text, in terms of
distribution is relatively long. Paper-based books
that refer to the old curriculum also stuff students
with concepts that must be memorized, and do not
invite students to think as a process of constructing
their knowledge and experience to find their own
concepts that must be understood. That is, existing
paper-based books generally stuff students with
facts, concepts, principles, and procedures that must
be memorized (Komalasari, 2011: 44)
In line with previous research and reviewing the
constraints of existing teaching materials, this study
tries to study the development of contextual based
accounting modules. The module that will be
developed in this study is a digital module or
electronic module or e-module that is easily
accessible via a laptop or personal computer (PC).
This is because the progress of information and
communication technology has shifted the era of
printing machines and replaced them with the digital
era so as to provide opportunities for the world of
education to develop teaching materials that are
more attractive and adaptive in accordance with the
demands of globalization and technological
progress. Like the Readmill study which shows that
people spend more time reading e-books on digital
devices than opening books in general. The ability of
The Development of Contextual based Accounting E-Module to Improve Students’ Learning Motivation
21

technology to send information quickly, precisely
and interestingly in multimedia has also made
learning more enjoyable.
A technology change, especially information
technology, brings a new paradigm in material
learning and learning methods. From previous
research conducted by Pramesti (2014) in the form
of digital modules using flipbook maker software, it
shows that students have increased their learning
outcomes by 87% after using digital modules. In line
with the research, Anori et al (2013) showed that the
use of electronic modules in direct learning models
had a positive influence on student learning
outcomes compared to those who did not use
electronic modules. Andayani et al (2009) also
showed that learning style preferences and
packaging choices of teaching materials for students
(students) accounting programs began to shift from
textbook oriented to digital teaching materials.
Electronic module content can always be accessed
regardless of time and place, can be read on a
personal computer (PC) or e-book reading device
that is easy to carry. Electronic modules are superior
in terms of accessibility, functionality, and cost-
effectiveness.
Computer-based teaching materials also have
advantages and disadvantages. Prastowo (2015: 332)
revealed several advantages, among others: (1) can
display information in the form of text and graphics,
(2) interactive, (3) can manage student responses, (4)
can be adapted as needed, (5) can control other
media hardware. While the shortcomings of
computer-based teaching materials are: (1) need a
computer and program knowledge, (2) need special
hardware for the development process and its use,
(3) incompatible types.
In addition to e-modules as visual teaching
materials, the role of teaching videos as audio-visual
teaching materials is also important in the learning
process. The function of teaching videos in the
learning process is important in improving the
quality of the learning process, especially helping
students to learn because in learning activities the
obscurity of the material delivered can be helped by
using video as an intermediary. The use of animated
videos will attract students' attention and interest in
learning. The sense of sight and hearing of students
can be active together. As explained by Prastowo
(2015: 301) that video is a teaching material that
combines two materials, namely visual and audio
material. Auditive material is intended to stimulate
the sense of hearing, while visual material to
stimulate the senses of sight. In addition, the use of
animated videos can clarify, uniformize, and
streamline the presentation of learning material. So,
the use of animated videos in learning aims to
improve cognitive, psychomotor, and affective
abilities.
E-module with innovative and attention-grabbing
videos is used as a stimulus (stimulation) in the
learning process that is useful to see students'
responses in increasing the curiosity and motivation
of the participants. The more sense devices used to
receive and process information the more likely the
information is understood and can be maintained in
memory. This is supported by previous research
conducted by Purwanto et al. (2015) showing that
teaching materials and learning videos are very
suitable for use and can increase motivation and
learning outcomes.
Based on the above requirements, the
development of contextual-based e-modules will be
made with the help of the Adobe Animate CC
program, due to the small file size with good quality,
easy to integrate with other programs, the evaluation
does not need to use supporting programs, and e-
modules generated also interactive.
The purpose of this research and development is
to produce contextual-based electronic modules that
can increase student motivation in vocational
schools.
2 RESEARCH METHODS
The research model used in this study is a
development research model. Sukmadinata (2013:
164) suggests that research or development research
is a process or steps to develop a new product or
improve an existing product, which can be
accounted for.
This research and development uses the Borg
and Gall (1983) development model that has been
modified and adapted to needs, namely (1) initial
needs collection, (2) planning, (3)product
development, (4) expert validation, (5) revision, (6)
product trials, (7) product revision. Validation
techniques using questionnaires. Data collection
instruments in the form of questionnaires are used to
collect data about assessments from material experts,
design experts, and assessments from students. The
type of questionnaire used was a closed
questionnaire using a Likert scale. The data analysis
technique used in this development is using
percentage descriptive analysis techniques. While
the effectiveness of the product is measured using
the t-Test, namely Paired Sample t-Test. The
subjects of the trial or validator in this research and
IRCEB 2018 - 2nd INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH CONFERENCE ON ECONOMICS AND BUSINESS 2018
22
development are expert groups, namely material
experts and experts in the design of teaching
materials, as well as field trials in class X students
and teachers of Singosari 3 Muhammadiyah
Vocational School majoring in accounting.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Based on the assessment of the product through a
series of trials and revisions that have been carried
out, the product is declared to be valid and feasible
with the acquisition of an overall percentage of
89.69%. The contextual based e-module test results
are summarized in Table 1.
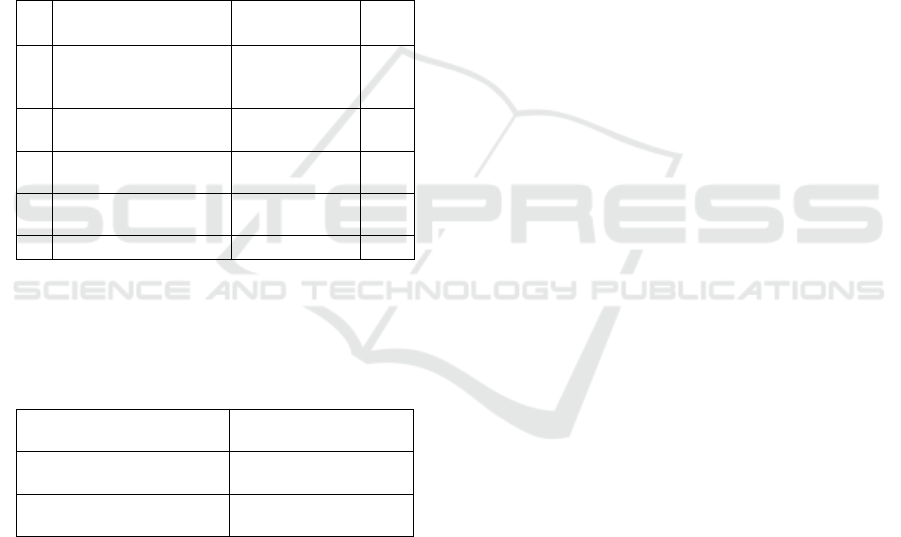
Table 1: Validation Analysis
No Aspect Percentage Note
1 Average of
material expert
validation
90% Valid
2 Average of design
expert validation
96,33% Valid
3 Average user test
(teacher)
84,33% Valid
4 Average user test
(students)
88,10% Valid
Total Average 89,69% Valid
The results of data analysis of student learning
motivation using Paired - Sample t-Test are shown
in Table 2 below
Table 2 Paired-Sample t Test Result
Average motivation to
learn before
64,97
Average motivation to
learn after
72,48
The significance value of
the Paired-Sample T-Test
0,000
Based on Table 2 it can be seen that the
significance value of Paired-Sample t-Test is 0.000
< 0.05, which means that there are differences in
learning motivation between before and after using
contextual-based e-modules. From the results of the
Paired-Sample t Test also known the average student
learning motivation from 64.97 to 72.48 after using
a context-based e-module. Based on the results of
expert validation and field trials, the product
produced is valid and feasible. Paired Sample T-Test
test results also show that the product produced can
increase student learning motivation. So it can be
concluded that contextually based e-modules are
feasible and effective to be used in accounting
learning.
The results of the research and the development
of contextual-based e-modules are: (1) e-modules
are arranged based on the characteristics of the
module, and in the form of soft files that can be read
on a laptop or computer, (2) e-modules containing
accounting material accompanied by images, audio,
video, sample questions, evaluation and assessment,
so that it can help students to learn independently,
(3) there is audio as backsound as well as
illustrations in the form of pictures and videos and
attractive colors aiming to help attract students'
interest in learning material and increase accounting
motivation, (4) material and examples that are
presented briefly, solidly, and clearly based on the
environment around students.
Based on the results of research and
development, the e-module is supported by several
characteristics, namely self-instructional, self-
contained, stand-alone, adaptive, and user-friendly.
1. Self-instructional, indicated by the
presentation of standard competencies and
basic competencies, learning objectives,
instructions for using e-modules. students
can use e-modules according to the
instructions in the e-module. With these
instructions students can learn
independently and not depend on the
teacher.
2. Self-contained, indicated by the
presentation of the material in its entirety.
All learning material from one competency
unit or sub competency learned is contained
in one teaching material in its entirety.
3. Stand alone, the teaching material
developed does not depend on other
teaching materials. This is evidenced by the
material needed by students already
contained in the e-module. The material in
the e-module is also quite complete
according to the learning objectives to be
achieved. In addition, the material is also
accompanied by an example of the problem
and how to solve it that can help students
understand the material. In the evaluation
work also displayed the results obtained as
well as the answer key so that students can
match the answers to the results done with
the aim that students can know their
abilities.
The Development of Contextual based Accounting E-Module to Improve Students’ Learning Motivation
23

4. Adaptive, the e-module that is developed
has high adaptive power to the
development of science and technology.
This is evidenced by the packaging of
materials in the form of service companies
that are developing in the environment
around students, as well as the form of an
electronic module in accordance with
technological developments. Students can
read e-modules with the help of a laptop or
computer anywhere
5. User-friendly, every instruction and
information disclosure that appears to be
helpful and friendly with the user, including
the ease of the user in responding and
accessing as desired. This is evidenced by
students being able to use and learn e-
modules by following the instructions in
this contextual-based e-module.
The following is a review of products that have
been revised and are the final product in
development research conducted by researchers.
3.1 Key Characteristics and E-Module
Components
Selection of good components and proper use of the
products produced are expected to produce or create
products that can improve student learning
motivation. The resulting e-module has a core
component, namely the title, instructions, material,
and evaluation. In addition there are additional
menus, namely references, glossaries and profiles.
This is in accordance with Surahman's statement (in
Prastowo, 2015: 113) that the module is technically
arranged in 4 elements, namely (1) title, (2) general
instructions, (3) material, (4) evaluation.
3.1.1 Instructions
The instructions display contains instructions for
using the product that is equipped with a function
from each button. The instructions placed at the
beginning of the display can make it easier for users
to run and use e-modules based on contextual. In
addition to reading the instructions for use, students
are also advised to read the study instructions.
Instructions for learning to function to provide an
explanation of the competencies and learning
objectives that must be achieved by students after
learning the material contained in the context-based
e-module, and to provide guidance to students about
the order of material to be studied. So that students
learn the material in a coherent way and more easily
understand the material.
This is consistent with Arsyad's (2005: 180)
statement that guidance instructions need to be
informed before learning takes place for students so
that students understand how to operate.
3.1.2 Material
Learning materials are arranged up to date in
accordance with the latest developments. In addition
the module presents examples that are in accordance
with real conditions in the real world. This is so that
students are able to be actively involved in being
able to find material that is learned and relate to real
life situations, so as to provide an overview of
accounting practices in the real world.
E-module developed based on contextual,
including:
1. Constructivism, in this e-module, the
component of constructivism lies in the
appearance of the initial material of the e-
module. There are illustrations and articles
that can help students in constructing
knowledge.
2. Questioning, questions in e-module can
encourage students' curiosity and thinking
skills.
3. The inquiry, after constructing knowledge
and with questions, illustrations and views
about the material in the e-module students
will find facts. So that knowledge and
students are obtained not from the results of
remembering, but the results of finding.
4. Learning community, in this e-module
some activities also require students to
work together with others. Learning
outcomes are obtained from sharing
between friends, between groups, and
between students and the surrounding
environment.
5. Modeling, shown by giving examples in
this e-module are examples that are close to
students' lives. For example, service
companies that are exemplified are GoJek,
Mahameru Jaya Travel, photocopies, and
other service companies that are often
encountered by students. Articles presented
in the e-module are also related to the
material.
6. Reflection is a way of thinking about what
you have just learned or think back about
what you have done in the past. In this e-
module also presented a "Reflection"
IRCEB 2018 - 2nd INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH CONFERENCE ON ECONOMICS AND BUSINESS 2018
24

column to find out the students' response to
the learning that has been done such as
what knowledge is obtained, impressions,
difficulties and suggestions for learning that
has been done in order to improve the next
learning.
7. Authentic Assessment, with group activities
that require students to actively seek
information and work in groups can provide
opportunities for teachers to perform
authentic assessments. Authentic
assessment can be done by the teacher
when students make observations, group
discussions, case study discussions, and
independent assignments.
This is in accordance with the Directorate
General of Primary Education (in Komalasari, 2011:
11) which explains that there are seven components
in the contextual approach, namely (1)
constructivism, (2) questioning, (3) inquiry, (4)
learning community, (5) modeling, (6) reflection, (7)
authentic assessment.
Integration of the contextual approach was put
forward by Blanchard (in Komalasari 2011: 16)
where linking material taught with real-world
situations and encouraging students to make
connections between the knowledge they have with
their application to their lives. Therefore, educators
do not need to change the existing subject matter,
but use the real events and conditions that surround
the students in the subject matter.
The material in the e-module is presented in
brief, concise, and clear. This is done to avoid text
density which will reduce the quality and benefits of
the displayed text. According to Alessi (1991: 368),
pay attention to the aesthetic quality of each display.
The display should be muted, without too much
information being shown at once, and should be
relevant to the goals of the lesson. Meaning, pay
attention to the aesthetic quality of each
presentation. The presentation should be neat,
without too much information being displayed at a
time, and should be relevant to the learning
objectives.
3.1.3 Evaluation
Evaluation is done to find out how far the learning
objectives are achieved. Evaluation of e-module
consists of 2 types of questions, namely multiple
choice questions (with interactive quiz format) and
essay questions. Multiple choice questions were
arranged randomly with the aim of the students as
the trial subjects unable to commit fraud in the work
on the questions. Evaluation results will
automatically appear when the user finishes the
evaluation question.
In essay questions, users can answer questions
directly in the place provided. After filling in the
answer, the user can press the "check answer" button
to see the discussion of the answer regarding the
evaluation that has been done, with the correct
answer, because if the answer is not correct then the
discussion will not appear.
3.1.4 Etc
The glossary is a section that contains the definition
or understanding of terms in the accounting services
company. The reference page is a section that
contains books or other sources that can be used in
studying accounting services companies. The profile
page contains the profile of the developer, which
contains the background of the compiler and mentor
of the contextual based e-module research and
development.
The E-module is equipped with illustrations in
the form of pictures and videos aimed at attracting
students' interests so that it helps students in learning
material and enhancing accounting learning
motivation. E-module with innovative and attention-
grabbing videos is used as a stimulus (stimulation)
in the learning process that is useful for seeing
students 'responses in increasing students' curiosity
and motivation. The more sense devices used to
receive and process information the more likely the
information is understood and can be maintained in
memory. As explained by Prastowo (2015: 301) that
video is a teaching material that combines two
materials, namely visual and audio material.
Auditive material is intended to stimulate the sense
of hearing, while visual material to stimulate the
senses of sight.
This is in accordance with the empirical study
through an experimental method with Paired Sample
t-Test on students of class X Muhammadiyah 3
Vocational School in Singosari. The results showed
that the significance value of the Paired-Sample t-
Test was 0.000 < 0.05. This shows that contextual-
based e-module is proven to increase student
learning motivation. Increased student learning
motivation is known by analyzing differences in the
results of student learning motivation questionnaire
before using e-module with the results of
questionnaires after using e-module.
The Development of Contextual based Accounting E-Module to Improve Students’ Learning Motivation
25

4 CONCLUSIONS AND
RECOMMENDATIONS
Based on the results of expert validation and field
trials, the product produced is valid and the Paired
Sample t-Test results show that the product
produced can increase student learning motivation.
By paying attention to the results of product
development in this study, in order to have benefits
that mean to many parties it is necessary to provide
some related advice. The next suggestion to the
developer is to develop products with other
accounting materials. In addition, the products to be
developed further can not only be operated on
laptops or computers, but also on smartphone
operating systems, such as Android, Blackberry, iOS
(iPhone Operating System), and Windows Phone.
To find out the appearance of the e-module, readers
can contact email erenprinstin@gmail.com
REFERENCES
Andayani, Endang, S., Irafahmi, Diana, T., Sulastri.
2009. Pengembangan Bahan Ajar Mata Kuliah
Praktikum Akuntansi 2 Berbasis CD dengan
Program Microsoft Visual Basic. Laporan
Penelitian Pengembangan. Malang: Lembaga
Penelitian UM
Borg and Gall. 1983. Educational Research: An
Introduction. New York: Longman
Dewi, Shenny Cynthia. 2014. Pengembangan Modul
Pembelajaran Kontekstual pada Mata Pelajaran
Siklus Akuntansi di SMK 2 Muhammadiyah
Malang. Skripsi tidak diterbitkan. Malang:
Fakultas Ekonomi UM
Komalasari. 2013. Pembelajaran Kontekstual
Konsep dan Aplikasi. Bandung: PT Refika
Aditama
Mulyasa. 2014. Pengembangan dan Implementasi
Kurikulum 2013. Bandung: PT Remaja
Rosdakarya Offset
Muslich, Masnur. 2010. Text Book Writing: Dasar-
dasar Pemahaman, Penulisan, dan Pemakaian
Buku Teks. Yogjakarta: Ar-Ruzz Media.
Pramesti , Tysna Diah Ayu. 2014. Pengembangan
Modul Berbasis Digital dalam Pembelajaran
Akuntansi pada Siswa Kelas XI IPS SMA Negeri
3 Malang. Skripsi tidak diterbitkan Malang:
Fakultas Ekonomi UM
Prastowo, Andi. 2015. Panduan Kreatif Membuat
Bahan Ajar Inovatif. Jogjakarta: Diva Press
Purwanto, dkk. 2015. Pengembangan Bahan Ajar
Berbasis Kontekstual Pada Materi Himpunan
Berbantu Video Pembelajaran. Jurnal
Pendidikan Matematika, (Online), ISSN 2442-
5419 Vol. 4, No. 1 (2015) 67-77
(http://fkip.ummetro.ac.id), diakses 4 November
2016
Sa’ud, Udin Saefudin. 2008. Inovasi Pendidikan.
Bandung: Alfabeta
Sukmadinata. 2013. Metode Penelitian Pendidikan.
Bandung: PT Remaja Rosdakarya Offset
Trianto. 2010. Mendesain Model Pembelajaran
Inovatif-Progresif. Jakarta: Prenada Media Grup
Ulfa, Ika Marliana. 2014. Pengembangan Modul
Akuntansi Berbasis Pembelajaran Kontekstual
untuk Kelas X di SMK Muhammadiyah 3
Singosari. Skripsi tidak diterbitkan. Malang:
Fakultas Ekonomi UM
Wardani, Ari Ratna Kusuma. 2016. Pengembangan
Bahan Ajar Fisika Berbasis Masalah
Kontekstual pada Materi Fluida Statis sebagai
Peluang Membangun Kemampuan Pemecahan
Masalah Siswa Sms Kelas X. Skripsi tidak
diterbitkan. Malang: Fakultas MIPA UM
IRCEB 2018 - 2nd INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH CONFERENCE ON ECONOMICS AND BUSINESS 2018
26
