
The Comparison of Ordinary Discussion and Presentation Methods
with the Use of National Geographic Youtube, Screen Shoot Pictures
and Information Gab Approaches to Improve Students'
Communicative Speaking
Al Maghvirah Chan
1
, Ayendi
1
, and Dhiant Asri
1
1
English department, Faculty of Humanities, Universitas Andalas, Padang, Indonesia
Keywords: National Geographic Youtube, screen shoot pictures, information gap, communicative speaking, and
Classroom Action Research.
Abstract: This study aims to explain the extent to which the comparison of presentation methods and ordinary discussion
with the use of National Geographic Youtube, screen shoot pictures, and information Gap approaches can
improve the communicative speaking ability of students taking English II courses in the Department of
History, Faculty of Humanities Andalas University. The research subjects consisted of 30 students. This
research was carried out in the even semester of 2017/2018 academic year. Learning methods apply
Classroom Action Research (CAR) based on the theory of Kemmis and McTaggart (1988) where the
beginning to the middle of the semester (cycle 1) the usual presentation and discussion methods are used,
while from the middle to the end of the semester (cycle 2) National Geographic Youtube, screen shoot
pictures and information gaps are used. The findings obtained from this study suggest that use of National
Geographic Youtube, screen shoot pictures, and information gap, helps most students understand more about
the historical events discussed and use correct vocabulary more precisely because before the presentation
students must watch and hear the videos repeatedly. The results of watching and listening are accompanied
by the absence of written words and sentences from the images, thus causing students to be able to speak
better using natural gestures and using their sentences in explaining historical information discussed. Students
are also more active in discussions because they have engaged during the learning process. This is in contrast
to the previous presentation and discussion classes where students tended to stiffly read powerpoint slides
with long sentences which are the result of the creation of other texts..
1 INTRODUCTION
The English Language Course is a compulsory
subject in the History Department of the Humanities
Faculty and worth 4 credits which is, according to the
curriculum, divided across two semesters, semester 1
and 2. In semester 1, the English language course 1
focuses on grammar mastery. In the second semester,
the learning process in English Language 2 is more
directed at the practice of speaking. The contribution
of the courses prepares students to be able to
communicate and speak in English in general.
The teaching materials provided for the course up
to date is the General English Speaking Text Book, in
which dialog, texts, questionnaires and work
instructions are available so that students could only
follow as instructed. The learning that has been
carried out so far is in the form of monologue
presentations and dialogues in pairs every week.
Lecturers determined the topic of monologue
presentation texts and dialogues for each group at the
beginning of the lecture. In the next meeting, the
individual or each group pair appeared with a
reference that came from reading the text in the
textbook. This was followed by a discussion with
available questions.
The measurement of student learning was in the
form of attendance value, reading the report, present
grade, and activity. Besides that, there was also
midterm and semester exam assessment. For mid and
end semester exams were not conducted in the form
of oral examinations considering the large number of
students (about 40) but in the form of written exams
Chan, A., Ayendi, . and Asri, D.
The Comparison of Ordinary Discussion and Presentation Methods with the Use of National Geographic Youtube, Screen Shoot Pictures and Information Gab Approaches to Improve
Students’ Communicative Speaking.
DOI: 10.5220/0008678400050010
In Improving Educational Quality Toward International Standard (ICED-QA 2018), pages 5-10
ISBN: 978-989-758-392-6
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
5

about understanding previous topics. The weight of
the assessment was as follows;
Presentation : 20%
Attendance : 10%
Active : 10%
Task reading report : 10%
Mid-Term Exam : 25%
Final-Term Exam : 25%
The distribution of the final grades of students, in
general, was C to B based on the experience of
researchers teaching students in 2017. Internal factors
from the students include low motivation and
understanding because they do not like to read, have
a lack of discipline, do not actively ask questions, and
do not prepare to speak before coming to class.
External factors come from the lecturer, in this case,
the researcher himself and include ordinary teaching
methods that mean students are only focused on the
textbook and unable improve and develop
themselves.
2 METHODS
2.1 Learning plan
Learning was designed from the beginning of the
lecture period to the midterm test (cycle 1 of the two
planned cycles) was in the form of group
presentations with students taking turns each week.
Lecturers determined the topic of presentations for
each group at the beginning of the previous lecture.
In the subsequent meetings, each group presented in
turn using power points. This was followed by a
question and answer discussion.
Students prepared Powerpoints according to the
requirements given by the lecturers such as not being
able to use long sentences or complex written
information, especially paragraphs. Information in
the slides was to conveyed using phrases, diagrams,
lists or schemes. Presentation materials consisted of
historical topics relating biographies of heroic figures
and historical events, especially in Indonesia and
West Sumatra.
The learning material used after the mid-semester
test (cycle 2) used National Geographic Youtube,
Screen Shoot Picture, and Information Gap method.
This learning model is an ideal way, according to
researchers, to integrate learning to improve students'
listening and speaking skills. The pleasure of
watching a video certainly increases students' interest
in watching and hearing speech in English.
Furthermore, National Geographic Youtube is an
audio-visual media that describes many phenomenon
in the world including history. On the Youtube
channel, there are illustrations and dialogues or
monologues from experts. Students were expected to
watch from beginning to end repeatedly so that they
understand the content thoroughly and master the
vocabulary used. This activity was done at home so
students have more time explore.
Next, Screen shoot picture is a technology where
an open screen feature can be photographed using a
smartphone. Almost all students had smartphones,
and they were very skilled at using them. Students
used screen shots when watching National
Geographic Youtube taking photos of event
chronologically or explanations of concepts. Students
used these photos in explainations in presentations.
They could no longer use long paragraphs. To be able
to explain these photographs they needed to have
sufficient preparation.
Student communication with lecturers or English
classmates can often be unnatural and ineffective. For
instance, lecturers often ask students or students ask
other students artificial questions with obvious
answers. For example: Do you sleep every day? What
am I doing?
To avoid this Information Gap is a method that
requires students ask something they truly do not
know. As students' are ignorant of much historical
information, it was hoped that student discussions
including information Gap materials would stimulate
natural meaningful communication (Talebinezahd,
1999).
2.2 Development of learning methods
This research was a type of classroom action research
using personal self-intervention to produce
improvements and has special research problems (Mc
Niff et al., 1996) It is a type of practitioner research
used to improve practitioners' practices. The act
implies doing or changing something (Gay and Pete,
2000).
There are four steps in this type of research,
namely 1) formulating problems and planning
actions, 2) monitoring actions and observations, 3)
reflecting the results of observations, and 4) revising
action plans (Kemmis and Mc Taggart, 1988). This
action research was carried out in the form of a cycle.
For one cycle, three topics were used. Topics were
selected for two cycles (16 meetings including
introduction, initial, middle and end tests): for cycle
one (1 topic 2 meetings): Bung Hatta, the Republic of
Indonesia Regional Government (PDRI), and Rohana
ICED-QA 2018 - International Conference On Education Development And Quality Assurance
6

Kudus and for the second cycle, The truth about
Sadam Hussen, American before European
Civilization, and The Pyramids. The work steps of
each cycle were as follows:
1. Planning
a) Make or find three topics related to the history
b) Divide class into groups consisting of three
students
c) Determine the roles of group members, such
as: the group leader, secretary, and other
members.
d) Establish rules for the discussion
e) Prepare research instruments.
f) Collaborate with parallel class lecturers
g) Request approval from the dean
h) Make an agenda before each group meeting.
Step 1: Students watch National
Geographic Youtube at home
Step 2: students take some screen shoot
photos
Step 3: students display photos in
PowerPoint
The role of group leader was to
Lead the group when making presentations
Ensure balanced participation of all
members
Maintain dynamic discussion
Keep time
Ensure group members were focused on the
tasks assigned
Answer questions
The secretary's role was to
• Present
• Make a note of who asked and who gave the
answer
• Create a discussion report
The role of group members was to
• Present
• Record the points raised by students
• Participate actively in group discussions.
• Listen to the contributions of each group
The role of discussion participants was to
• Ask open questions
• Help answer questions from other
participants
• Make a reading report
The role of the research lecturer was to
• Facilitate group interaction
• Consider ways to improve student abilities
• Listen carefully
• Ask
Observe student progress and appearance
2. Action
Classes were carried out according to plan. During the
group meeting it was decided that the discussion stage
should be carried out after the group presentation,
the participants were to ask the questions, and the
answers were not to immediately be answered by the
group but by other discussion participants. At the time
of the discussion the lecturer stimulated the
conversation by asking open ended questions (e.g.
how ...? What ... Why ...? Where ...? that would allow
the group to explore the material in more depth.
3. Observing
a) Researchers monitored groups during
learning activities by walking around or
sitting at the back of the class.
b) Collaborators (other staff members) observe
researchers during the
discussion/presentation process.
c) Collaborators observe, record and record
English activities verbally during the
learning process.
d) Researchers and collaborators evaluate
activities using evaluation instruments that
have been prepared.
4. Evaluating
At the end of the first cycle, researchers and
collaborators analyzed the data collected from
observation sheets/checklists, interviews, and speech
tests to identify weaknesses/problems, and determine
what progress/success had been found in cycle one.
Researchers tried to remedy any weaknesses to
improve the method, and researchers continue to use
the more successful elements in for the next cycle.
2.3 Development of student assessments
There are several categories of student assessments
that include assessment of soft skills, hard skills and
processes. In this project soft skills included attitude,
cooperation and leadership. Hard skill scores were
based on appearance, and listening skills were
assessed from speaking during discussions and
examinations. The process score was taken from
student activity and attendance in class
2.4 Action Research Parameters
Speaking ability assessment depended on the
listening ability to understand audio-visual text.
The Comparison of Ordinary Discussion and Presentation Methods with the Use of National Geographic Youtube, Screen Shoot Pictures
and Information Gab Approaches to Improve Students’ Communicative Speaking
7
The assessment of speaking ability was based on the
Hughes speech test rubric (Hughes, 1983). Five rubric
components were evaluated in the assessment: 1)
grammar, 2) vocabulary, 3) fluency, 4)
understanding, and 5) pronunciation. Each indicator
has 6 levels of proficiency. The final student
assessment grade included soft skills, hard skills and
processes.
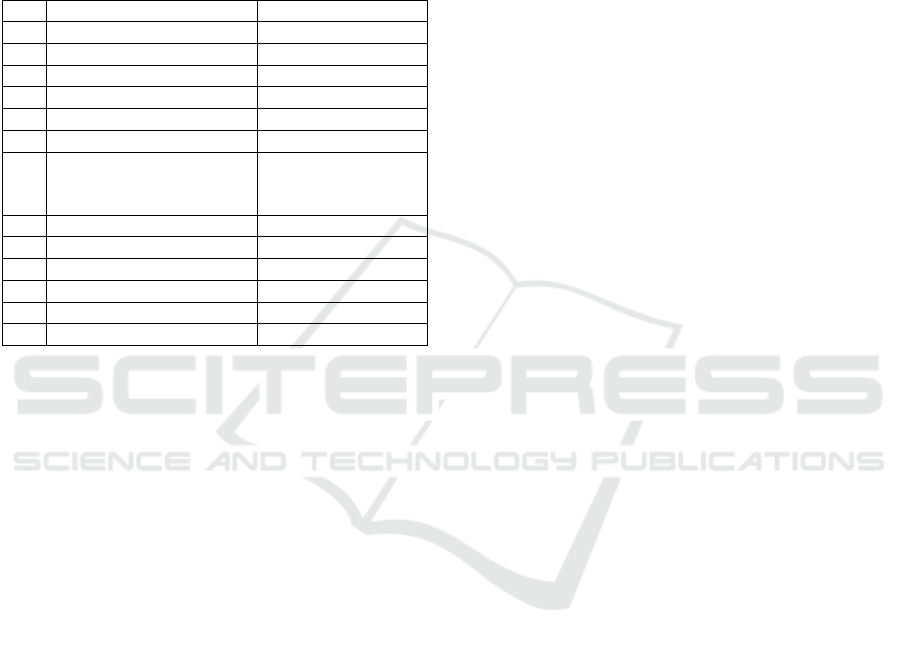
Table 1. Assessment
No
Component
Weight Rating
1
Assessment of soft skills
Attitude
10%
Cooperation
10%
Leadership
10%
2
Assessment of hard skills
Presentation
10%
The listening ability
reflected from the ability
to speak
10%
Oral mid-test
15%
Oral final test
15%
3
Process evaluation
Activity
10%
Presence
10%
Total
100%
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
From the results of the analysis of the implementation
of the ordinary method in the first cycle through
presentation and discussion of topics in the first
meeting until before the midterm examination, it
appears that in the presentation students generally use
existing text/information without using citations,
paraphrasing or summarizing. This means students
rely on plagiarism for their presentations.
Here's one student's powerpoint example of this:
Slide 1: Hamka's Dedication
After that, he was appointed Rector of the Islamic
University, Jakarta and Professor Mustopo
University, Jakarta. From 1951 to 1960, he served
as High Civil Religion by the Minister of Religious
Affairs of Indonesia but resigned when Sukarno
told him to choose between being public servants
or the political spite of the Indonesian Muslim
Shura Council (Masyumi). Buya Hamka is a
figure of self-taught in many areas of science such
as philosophy, literature, history, sociology and
politics, both Islam and the West. With Arabic
language proficiency is high, he can study the
scholars and the Middle East such as Zaki
Mubarak, Jurji Zaidan, Abbas al-Aqqad, Mustafa
al-Manfaluti, and Hussain Haikal. Through the
Arabic language as well, he examines the work of
French scholar, English and German, he is also
familiar with famous figures such as HOS
Tjokroaminoto Jakarta, Raden Mas
Soerjopranoto, Haji Fachrudin, AR Sutan
Mansur, and Ki Bagus Hadikusumo while honed
his talent to become an expert speech reliably.
The results of this method was that students were not
thinking about, formulating, re-reading, concluding,
learning the meaning of difficult words or
summarizing, and this affected the power point
display, understanding, vocabulary mastery,
pronunciation, presentation method, and activity. The
student's powerpoint contained long paragraphs
rather than main points to be discussed, like the
example of the slide given above.
This affected the understanding of students who
did presentations. Because everything was copied, the
students did not read carefully, which meant they did
not to have a frame or organize the ideas to be
conveyed. Because students' lacked understanding
and organization, and had a slideshow with long
paragraphs, then students chose to avoid risk while
presenting by simply reading out the words on the
slides. The student did not face the participants during
the presentation but the slides and had their back to
the participants.
Students also used a limited vocabulary because
they did not try to find out what the new words meant.
Many of the new words readout were mispronounced
because they had not been learned even though
almost all students have a smartphone that has a
dictionary that provides pronunciation. Because of
the limitations of the students' understanding, lack of
vocabulary, and lack of reading, they were less active
in asking questions, giving answers, and
commenting. The results of the student exam are also
less satisfactory than desired with most scoring a B-.
The findings obtained from research from the
second cycle after the first cycle evaluation process in
the second half of the semester were that using
National Geographic Youtube, screen shoot pictures,
and information gap, most students understood more
about the historical events discussed during that time.
They could watch and hear YouTube with visuals or
images and this helped them understand the meaning
of the material.
Pronunciation of new vocabulary used by students
was more accurate because before the presentation
students must watch and listen to the video
repeatedly. They needed to have observed the
pronunciation of the vocabulary they heard and could
watch how often they liked.
ICED-QA 2018 - International Conference On Education Development And Quality Assurance
8

The results of watching and listening and the
absence of many written words and sentences on the
displayed images encouraged students to be able to
explain information using their own words rather than
simply reading the text and use communicative facial
expressions and hand gestures as they faced
participants from their friends.
This was in contrast to with the previous
presentation classes where students tended to read
power point slides which are the result of texts they
themselves did not create. This resulted in the
presentors standing sideways or turning their backs
on the discussion participants and not using facial
expressions or hand movements to communicate.
Students were also more active in discussions
because they had responsibility. The questions were
not just to ask for obvious information for testing but
based on information gaps, things that were not
known. Following are examples of some of the
questions submitted:
1. How was the condition of America when the
colonial arrived?
2. Why did Colombus come to America?
3. Why did Saddam Husen be labeled terrorist by
America?
4. Why did the United States lead the invasion to
take away Saddam Husen Government?
5. Why did the ancient Egyptians construct the
pyramid?
What was difficult for some students was the
availability of internet. Although in general, all
students of that class have smartphones, sometimes
they do not have a data package.
The strengths and limitations found though this
study were that while students who already had
intermediate level English skills could quickly
understand what is being said. , those who lacked
English skills had difficulty understanding the
meaning of what was being conveyed. Most of the
anonymous student comments about the method were
positive but a few were negative. Here are examples:
• "I think this method is constructive in English
because we have to screen shoot and explain the
meaning or purpose of the image".
• "I do not think using Geographic youtube
channel is very effective in the learning process
because it requires an internet data package that
not all people are literate about science and
technology".
• "Yes there is an increase because by explaining
a theme about history, it can improve students'
understanding of the chosen department so that
it can add insight".
• “According to me learning to use this method is
very good because it can train students to dare
to speak and express opinions and be able to
train courage in speaking English".
• “In my opinion, actually this method is
interesting to use, but because this is a new
method especially in English learning that
usually uses PPT plus paper, so it looks
awkward”.
Then below are some photos of research activities:
Figure 1: Students are presenting and discussing the topic
"Saddam Husen"
Figure 2: Students are presenting and discussing the topic
"American before European Civilization."
The comparison of marks from the midterm
examination of the usual presentation and discussion
methods and the end of term exam after using
National Geographic Youtube, screenshots, and
information gaps is shown below.
Category
Pronunciation
Grammar
Vocabulary
Fluency
Comprehension
Mean score for speaking
mid Test
68
75
70
68
66
Mean score for speaking
final Test
76
76
75
77
78
The Comparison of Ordinary Discussion and Presentation Methods with the Use of National Geographic Youtube, Screen Shoot Pictures
and Information Gab Approaches to Improve Students’ Communicative Speaking
9

From the table, it can be seen that the average
speaking test scores on the oral final examinations for
all categories are higher than the midterms and are in
the B + category while the average final semester
exam score after soft skills were added was 81 or A-.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We express thank you to the Unand LP3M who
facilitated and provided financial support so that this
article was realized. We do not forget to say thank you
to all those who have contributed because even the
slightest form of assistance, for us it is significant.
REFERENCES
Gay and Arasian Peter. 2000. Educational Research:
Competencies for Analysis and Application.
Tokyo: Prentice Hall, Inc.
Hughes, Arthur. 1983. Testing for Language.
Cambridge University Press
Kemmis, S & McTaggart, R. 1988. The Action
Research Planner. Victoria, Australia: Deakin
Mc Niff. J., et al. 1996. You and Your Action
Research Project. New York: Hyde
Publications
Talebinezahd, M. 1999. Effective Questions. English
Teaching Forum, 37, 2, pp.20-21
ICED-QA 2018 - International Conference On Education Development And Quality Assurance
10
