
Development of Mathematics Instructional Materials Integrated with
Islamic Sciences
Risnawati
1
, Zubaidah Amir
1
, Depi Fitraini
1
1
Mathematics Education Study Program, Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teacher Training,
UIN Sultan Syarif Kasim Riau
Keywords: Student Activity Sheet, Integrated Islam, Learning Outcomes.
Abstract: The purpose of this research is to produce Student Activity Sheet (SAS) based on Islamic integration in
mathematics instruction. This research is a development research consisting of three stages namely front-
end analysis, prototype, and assessment. Front-end analysis consists of analyzing syllabus and mathematics
textbook and reviewing the literature of concept of integration, Quranic interpretation, and hadith of a
prophet. The prototype stage consists of validation stage and practicality. The assessment stage consists of
predictions by experts and teachers. The SAS is validated by an evaluation expert and obtained a score in
the range of 88% to 100% which means it is very valid. The SAS practicability validated by education
experts and obtained scores in the range of 68% to 87% which means quite valid. The validity of SAS
validated by subject teachers obtained scores in the range of 61% to 80% which means valid. all students
stated that SAS is practically valid enough to use.
1 INTRODUCTION
Islam is the Shari'ah of Allah SWT sent down to a
human on earth so that they can worship him. The
cultivation of belief in God can only be done
through the process of education at home, school,
and community. Islamic education is a human need
because as a pedagogical (educational). Humans are
born with the potential that can be educated to
become a khalifah on earth, as well as supporters
and holders of culture (Majid, 2014). Islamic
education is a system, namely the Islamic education
system that has components that supports the
realization of the Muslim figure "insankamil". This
is meaningful, education is done in accordance with
Islamic ways or review material that has Islamic
values. Theories of Islamic education are of course
based on the Qur'an and Hadith. In decades, much
thought and policy have been taken to integrate
Islamic education in all fields of education including
in mathematics education. Hopefully, the integration
of science education with Islam and other science
can contribute to and describe the significance of
national education. This effort is expected to be able
to educate and develop the potential of learners to
become human beings who believe and cautious to
God Almighty, noble, healthy, knowledgeable,
capable, creative, independent and become citizens
of democratic and responsible.
Based on the aims of national education,
mathematics education should contribute to the
achievement of educational objectives, namely, to
make students who are smart, capable, have a
balance between faith and piety (IMTAK) and
Science and Technology (IPTEK). This is confirmed
in the 2013 curriculum which states that every
subject should contribute to the establishment,
development of knowledge, skills, and attitudes
(Human Resources Development Agency, 2013).
Although the science (general) education curriculum
is often regarded as a secular subject. The purpose of
secular subjects is that public education is
considered totally unrelated to religion. This
assumption shows that the mathematics studied in
schools so far is considered subjects that are not
related to Islamic values. In the case of good moral
or moral formation also develops according to the
environment around the students, one of which is the
school.
Mathematics education program Faculty of
Tarbiyah and Teacher Training UIN Riau is one of
the Islamic educational institutions that develop
insight into Islamic and nationalism high spirit. One
Risnawati, ., Amir, Z. and Fitraini, D.
Development of Mathematics Instructional Materials Integrated with Islamic Sciences.
DOI: 10.5220/0008522503970404
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mathematics and Islam (ICMIs 2018), pages 397-404
ISBN: 978-989-758-407-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
397

of the advantages of this institution is the integration
of general science and religious science. Every
activity including curriculum, teaching should be
integrated with Islamic values either by lecturer,
teacher, and student. Any branch of science,
including mathematics cannot be separated from Al-
Quran. Numbers and counting have been introduced
by God through the Al-quran. Reality field shows
that the integration of mathematics with the science
of religion has not run optimally. During this time
the integration of Islamic values done by lecturers
and teachers is only limited to exemplary attitude.
Lecturers and teachers feel difficult if integration is
done on mathematics material with the concept of
the Qur'an and Sunnah. Whereas Zubaidah (2013)
states that the integration of Islamic values in
learning strategies can be done on 4 aspects, namely:
first, the integration of subject matter. The
integration of the material is done to integrate the
concept or teachings of religion into the material
(theory, concept) of general knowledge that is being
taught. Second, the integration of the process is done
to avoid the learning process that is contrary to the
teachings of religion. Third, integration in choosing
teaching materials. Fourth, integration in choosing
teaching media. Based on this, lecturers, teachers,
and students suggested that the availability of
teaching materials as a guide for the integration of
mathematical science with Islamic science, both
directly related to the Qur'an and Sunnah, including
Islamic moral values.
2 LITERATURE RIVIEW
Mathematics is a part of science so that the nature
that exists in science also applies in mathematics.
Integration is an attempt to make two or more things
into one indivisible entity. Integration, in general,
can be interpreted as an integrated into a unified
whole. Integration is an important process in science
learning such as mathematics, as it teaches students
to monitor, reflect actively, evaluate and modify
knowledge. Integration is the process of scaling up
knowledge and the ability to generate and connect
scientifically the normative idea in explaining
scientific phenomena (Lee & Liu, 2009). Integration
is an important process in science learning such as
mathematics, as it teaches students to monitor,
reflect actively, evaluate and modify knowledge
(Chen & Bradshaw, 2007).
Integration involves applying the process of
pooling knowledge to ideas such as scientific
principles, real-world experiences, classroom
experiences and developing a strong and useful
understanding (Davis, 2004). Integration allows
students to link, evaluate and organize their ideas on
science topics (Liu, Lee, Hofstetter & Linn, 2008).
integration is born from an understanding that
students have the ability to acquire and connect
ideas as a basis for the development of a deep
understanding of science(Lee, Liu, & Linn, 2011).
Integration is a conceptual model and an ontology of
traditional knowledge and science used to create a
system of knowledge (Bohensky & Maru, 2011).
Islam is the religion of Allah brought by the
Prophet Muhammad SAW who guided the Qur'an as
a holy book. Scientific characteristics make science
is a scientific knowledge. Defining science is not
easy, because the various scientists have their own
definition in proving science. For analysts of the
methodology will say that science is a system of
statements that can be reviewed or tested by anyone
and anywhere. Heuristic observers will argue that
science is a further development of the human talent
to determine the orientation of its environment and
determine its attitude toward it. Science can also be
defined as a set of human collective human
rationality, the set of human knowledge of nature
acquired as a consensus of experts. rational
inference of the results of a critical analysis of the
measurement data obtained from observations on
natural phenomena.
While most scientists define science as a result of
experimentation, so to achieve a success must be
through logical conclusions and empirical
observations through scientific methods. From the
above explanation can be concluded that the
integration of Islam and science is an attempt to
unify between Islam and science. Mahfuzoh (2011)
illustrates the forms of scientific integration, namely;
(1) The form of scientific integration based on
classical philosophy, which is trying to explore the
legacy of classical Islamic philosophy, (2) The form
of science integration based on mysticism, namely
Islamization of science or Islamization of knowledge
which means the discussion of science from
interpretation based on ideology, secular phrases, (3)
The form of science-based integration of fiqhie
Islamization of science departed from the fiqh
scholars thought in making the Qur'an and Sunnah
as the peak of truth. Mahfuzoh (2011) reveals the
forms of scientific integration study that are: (1)
Comparative, i.e. comparing the concept or theory of
science with the concept or insight of religion about
the same symptoms, (2) Inductive, that is basic
assumption of scientific theory which is supported
by empirical findings and continued his theoretically
ICMIs 2018 - International Conference on Mathematics and Islam
398

abstract thought toward metaphysical or supernatural
thinking, then connected with religious principles
and the Qur'an about it, (3) Verification, that is
connecting the results of scientific research that
supports and proves the truth of Quran verses.
In integrating value education in learning,
Suwarna (2010) offers several strategies, namely (1)
implicit presentation strategy where in general
textbooks do not present a straightforward and clear
values education but are subtle and implicit (except
for religious education and civic education). in these
circumstances, it is the teacher who must be
sensitive to the analysis of the value education
phenomenon that implicitly arises within it. Any
reading, example, question, an answer should
contain value education. Because the value
education is not presented explicitly, teachers with
students should look for whatever values appear in a
passage, examples, questions, and answers.
Teachers and learners should seek for themselves
an integrated value in learning. If not found, teachers
should be able to develop and insert Islamic values
in the subject matter in context, (2) explicit
presentation strategies in which all values are
presented clearly and decisively. this is called the
method of teaching values or character directly. This
can be seen in the reading, material examples,
problems that directly lead to the education value.
For example, the readings directly presenting the
manners of people entertaining, rights, duties and
obligations of citizens, and love the land of water.
Instant material example refers to servant obligation
to God, obligation of learners, devoted to teacher,
obligation of child to parent. The presentation of
values education explicitly facilitates the learner in
learning the noble values. But learning can happen
to be monotonous because all the material is already
available in the textbook. The teacher only conveys,
the learner appreciates. Therefore, to make learning
more dynamic, creative and efficient, teachers must
be able to develop teaching materials with various
techniques, which are discussing values education
with the rules of life now, practicing values
education, observing the phenomenon of morality
that occurs among children, adolescents, and
community.
Implicit and explicit strategies can lead learners
to learn value education independently. This
independence is demonstrated by the ability to
analyze in various values education phenomenon
which is further presented, discussed, summarized
and internalized in the learner. One purpose of
integrating Islamic values with mathematics is to
improve the learning outcomes of student
mathematics. Nasution (2009) says learning is to
change the behavior of children, so it is about the
character formation of children. Expected results are
not only knowledgeable, but also the understanding,
extent of interest, the appreciation of the norms, and
the abilities that encompass all the characters of the
child. According to Slameto (1991), learning is a
process of effort by a person to obtain a change of
behavior, as a result of his experience in interaction
with his environment. While Suryabrata (2004)
states "Learning is shown by a change in behavior as
a result of experience". The results of learning
mathematics in this study are changes in student
behavior indicated by indicators of achievement
level of learning objectives of mathematics. this
achievement in the form of mastery of cognitive
structure in the form of facts, concepts, and
generalizations after gaining experience in the field
of mathematics.
3 METHOD
This research is a development research. This
research is used to develop Student Activity Sheet
(SAS) based on Islamic integration in mathematics
instruction which is valid and practical for MTs
students. There are three stages of development
carried out in this research, namely; front-end
analysis, prototype stage, and assessment stage. The
research was conducted in three districts, namely
Pekanbaru, Kampar and Kuantan Singingi. The
effectiveness of teaching materials in this study used
a pre-experimental study with the design model
"The One-Shot Case Study".
3.1 Development Procedure
The procedure of development in this research refers
to three development step that is; front-end analysis,
prototype phase, and assessment phase. The three
stages of the research design are described in the
following procedure stages.
Front-end analysis phase: Front-end analysis
phase is conducted to get an overview of the
conditions in the field. This stage consists of
analyzing syllabus and mathematics textbooks to
find out whether the material taught in accordance
with material competence standards and concepts of
integration, Quranic interpretation, the hadist
prophet. Esensi of the integration of Islamic values
begins with the assumption that in teaching
materials, should get the emphasis on mathematical
Development of Mathematics Instructional Materials Integrated with Islamic Sciences
399
relations with Islam both from the Qur'an and
Assunnah.
Prototype phase: The making of this prototype is
done in 2 phases, namely the validation phase and
the phase of practicality. The validation phase
consists of two validation types used, namely
content validation and constructs validation. Content
validation aims to determine whether SAS based on
Islamic integration in mathematics instruction has
been designed in accordance with the syllabus
material. Construct validity aims to see the
suitability of SAS components with predetermined
indicators. The designed SAS will be consulted and
discussed with experts to get suggestion or
validation. Validation activities are carried out by
filling out the SAS validation sheet and discussion
until the SAS is appropriately used. Practicality
steps are taken to see the SAS usage that has been
designed.
Assessment phase: In the assessment phase,
activities are centered on evaluating whether the
prototype (trial version) can be used in accordance
with expectations and effectively to improve the
quality and achievement of student learning. The
effectiveness of SAS based on Islamic integration in
mathematics Instruction is tested to predict whether
SAS is effective according to mathematicians and
education experts. The research procedure is
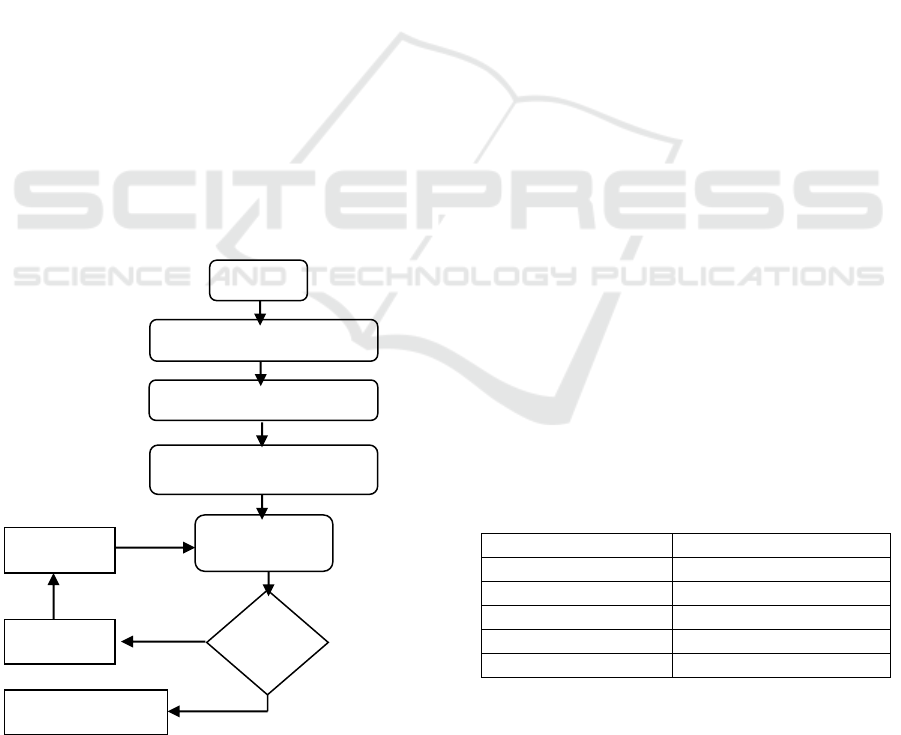
illustrated in figure 1.
Figure 1. Illustration of Research Procedure
3.2 Data Collection Technique
Data collection techniques used in this study are
validation sheets, observation sheets, questionnaires
to assess attitudes and interviews. The validation
sheet is used to determine the SAS and the
instruments that have been designed valid or not.
Riduwan (2005) stated that the observation is to
observe directly to research object to see the
activities done from close range. Observation aims
to know the practicality of the implementation of
SAS and see student activity during the learning
process. The data collection tool used to observe is
the observation sheet. The questionnaire aims to
express the attitude or response of students on
learning using SAS. Interview by Sudjana (2005) is
as an assessment tool used to know opinions,
aspirations, expectations, achievements, desires, and
beliefs as a result of student learning. In this study
interviews used is a free (unstructured) interview
aimed at expressing the practicality of using SAS
based on Islamic integration in mathematics
instruction.
3.3 Data Analysis Technique
Data analysis in this study uses quantitative
descriptive by describing the results of validation
from experts, teachers, and students, which consists
of validity, practicality, the effectiveness of
instruments and products developed. Validation
results from validator to all aspects assessed,
presented in tabular form. Data from the results of
instrument validation assessment and product
validation are then tabulated and the percentage
sought. The percentage results are consulted to the
Conversion Table proposed by Riduwan (2005).
Riduwan's proposed conversion table can be seen in
Table 1.
Table 1: Product and Instrument Conversions
Interval (%)
Criteria
0-20
Invalid
21-40
Less Valid
41-60
Enough Valid
61-80
Valid
81-100
Very Valid
To illustrate the practicality of the
implementation of learning with Islamic-based
mathematics teaching materials, the results of
observations and interviews were analyzed by
descriptive techniques. Data from the attitude
Start
Front-in-Analysis
Prototype Phase
Assessment Phase
Validation
Valid
Revision
Draf
Implementation
No
Yes
ICMIs 2018 - International Conference on Mathematics and Islam
400
questionnaire were analyzed by calculating the score
of students who answered each item according to the
number of items in the questionnaire. Scores that
have been obtained then made a percentage. Data of
learning result analyzed by descriptive statistic is
done by calculating mean, standard deviation, and
percentage. The effectiveness of teaching materials
that have been designed is seen using pre-
experimental research with the design of "The One-
Shot Case Study".
4 RESULTS
To determine whether the product developed is valid
or not, the SAS based on Islamic integration and
assessment instruments are reviewed or assessed by
evaluation experts and learning experts. This
assessment intends to find out weaknesses or
deficiencies that need to be added to the SAS before
being tested further to students. Evaluation and
learning experts who assess these SAS instruments
and products are experts from the State Islamic
University of SulthanSyarif Kasim Riau. The results
of expert research can be seen in the table below.
4.1 Validity of the Instrument by
Expert Evaluation and Learning
Experts
An assessment of the validity of the instrument
intends to see how far the instrument developed is
valid. Assessment is carried out by evaluation and
learning experts. There are six questionnaires
assessed by experts. Expert assessment results can
be seen in Table 2.
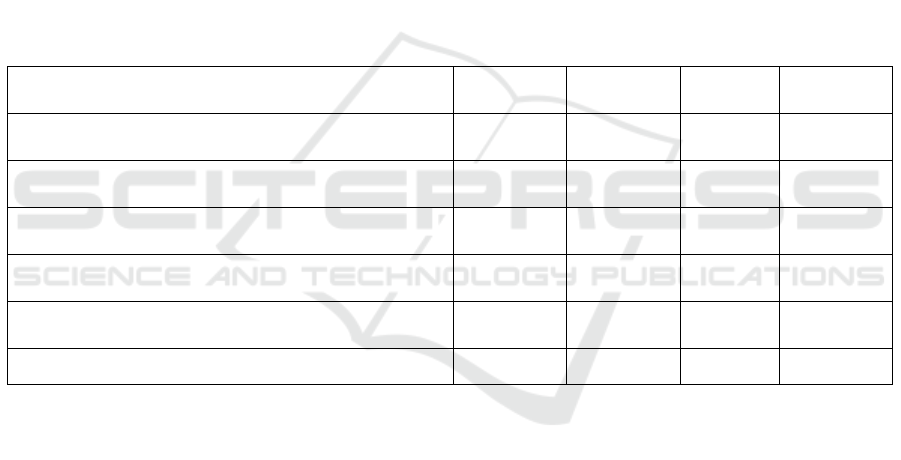
Table 2: Results of validity analysis of validity assessment instruments according to experts
Aspect Assessed
Expert1
(%)
Expert 2
(%)
Mean
Category
The validity of the Self Evaluation Questionnaire on
SAS
100
93.18
96.59
Very valid
The validity of the SAS Practical Questionnaire with
the Respondents are the Teacher
100
93.75
96.87
Very valid
The validity of the SAS Practical Questionnaire with
the Respondents are the Student
100
93.75
96.87
Very valid
The validity of questionnaires to predict SAS
practicality
100
85
92.5
Very valid
The validity of Questionnaire to predict SAS
effectiveness
90
90
90
Very valid
The validity of the interview guide instrument
87.5
90.27
89.21
Very valid
Table 2 illustrates the results of expert judgments
on questionnaires to assess the SAS based on the
Islamic integration. Aspects of the validity of SAS
self-evaluation questionnaires are considered experts
with an average score of 96.65% in a very valid
category. Aspects of the validity of the SAS
practicality questionnaire with teacher respondents
obtained an average score of 96,875 with a very
valid category. Aspects of the validity of the
questionnaire of practicality with student
respondents get the average score of 98,675 with a
very valid category. Aspects of the validity of the
questionnaire to predict the practicality of SAS
obtained the average score 92 with a very valid
category. The aspect of the validity of the
questionnaire to predict the effectiveness of SAS
was obtained with a mean score of 90 with a very
valid category. The aspect of the validity of the
interview guideline instrument was assessed by
experts with an average score of 89.21 with a very
valid category. Scores given by experts show that
the six aspects used as a quality standard for a
product are in a very valid category or worthy of
use. However, expert advice on the instrument needs
to be considered for future research.
4.2 Assessment of The Validity and
Practicality of SAS Based on
Islamic Integration
The products of SAS based on Islamic integration
are assessed by the evaluation and learning experts
in terms of validity, effectiveness and practicality.
Assessment of aspects of product validity aims to
see whether the product being developed is valid or
feasible to use. The predictive aspect of product
Development of Mathematics Instructional Materials Integrated with Islamic Sciences
401
effectiveness is done to see how the product of SAS
based on Islamic integration is effectively applied in
teaching and learning process. The predictive aspect
of practicability aims to see how the product
developed in the form of SAS based on Islamic
integration is practical to use. assessment results can
be seen in Table 3. Table 3 shows the average score
of expert judgment on the validity of the developed
SAS. Aspects of product validity obtained mean
scores of 72.92 with valid categories. Aspects of the
predictive effectiveness of the SAS obtained an
average score of 66.67 with a valid category.
Aspects of the prediction of SAS practices are
obtained with an average score of 66.68 with a valid
category. Based on the evaluation of expert
evaluation and education experts, it can be
concluded that the product of SAS based on Islamic
integration is good or feasible to use because it is
valid.
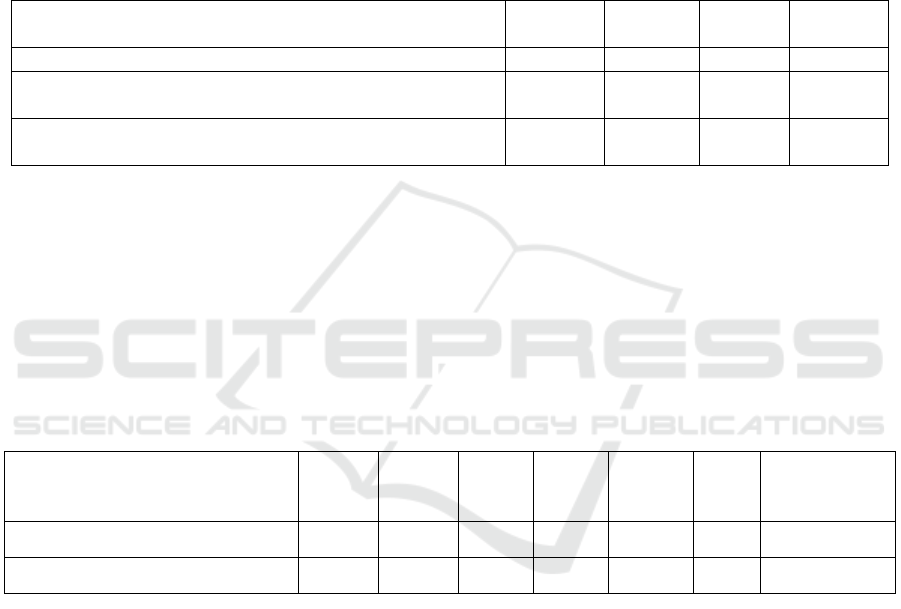
Table 3. Assessment of SAS based on based on Islamic integration by evaluation and learning experts
Aspect Assessed
Expert 1
(%)
Expert 2
(%)
Mean
(%)
Category
Validity of SAS based on Islamic Integration
70.83
75
72.92
valid
Prediction of the effectiveness of the SAS based on based
on Islamic integration
50
83.33
66.67
valid
Prediction of the practicalities of SAS based on Islamic
integration
52
81.35
66.68
valid
4.3 Assessment of the Practicality and
Effectiveness of SAS Based on Islamic
Integration by Teachers of
Mathematics Subjects
Teachers as experts who assess this SAS based on
the integration of Islam is as many as 5 teachers
consisting of Mathematics Teachers MTsN Lipat
Kain, MTsN 1 Pangean Kuantan Singingi, MTsN
Al-Muttaqin Pekanbaru, MTsN Darel Hikmah
Pekanbaru, MTsN Al-Munawarah Pekanbaru. The
assessment is carried out by giving an assessment
sheet consisting of 9 statement items. The results of
the practicality and effectiveness analysis of SAS
based on Islamic integration can be seen in Table 4.
Table 4: Summary of predicted results of the practicality and effectiveness of the SAS.
Aspect Assessed
Expert
1
(%)
Expert
2
(%)
Expert
3
(%)
Expert
4
(%)
Expert
5
(%)
Mean
Category
Practicality predictions of SAS
60
51.11
66.67
60
60
59.56
Enough valid
Effectiveness predictions of SAS
66.64
48.89
62.22
62.22
62.22
60.44
Valid
The table above shows the prediction results of
the practicality and effectiveness of the SAS based
on Islamic integration according to the mathematics
teacher. The practical aspect of SAS based on
Islamic integration is assessed by an expert with a
mean score of 59.56 in the category is quite valid.
The prediction aspect of the effectiveness of the
SAS is considered expert with 60.44 or average in
the valid category. The assessment of the five
experts shows that the SAS based on Islamic
integration is in the valid category or feasible to use.
However, expert advice to improve SAS products
should be considered.
4.4 Assessment of the Practice of
Developing SAS Based on Islamic
Integration by Students
Assessment of the practicality of SAS based on the
Islamic integration assessed by 30 students from 3
districts in Riau Province, i.e. 6 students from MTsN
Lipat Kain in Kampar district, 6 students from
MTsN Pangen in Kuantan Singingi district, 6
students from MTsN Al-Mutaqqin in Pekanbaru
district, 6 students from MTsN Darel Hikmah in
Pekanbaru district, and 6 students from MTsN Al-
Munawaroh in Pekanbaru district. Assessment of the
practicality of SAS is done by giving a questionnaire
ICMIs 2018 - International Conference on Mathematics and Islam
402
to the students. The results of an assessment of the
practicality of SAS based on Islamic integration by
students can be seen in Table 6.
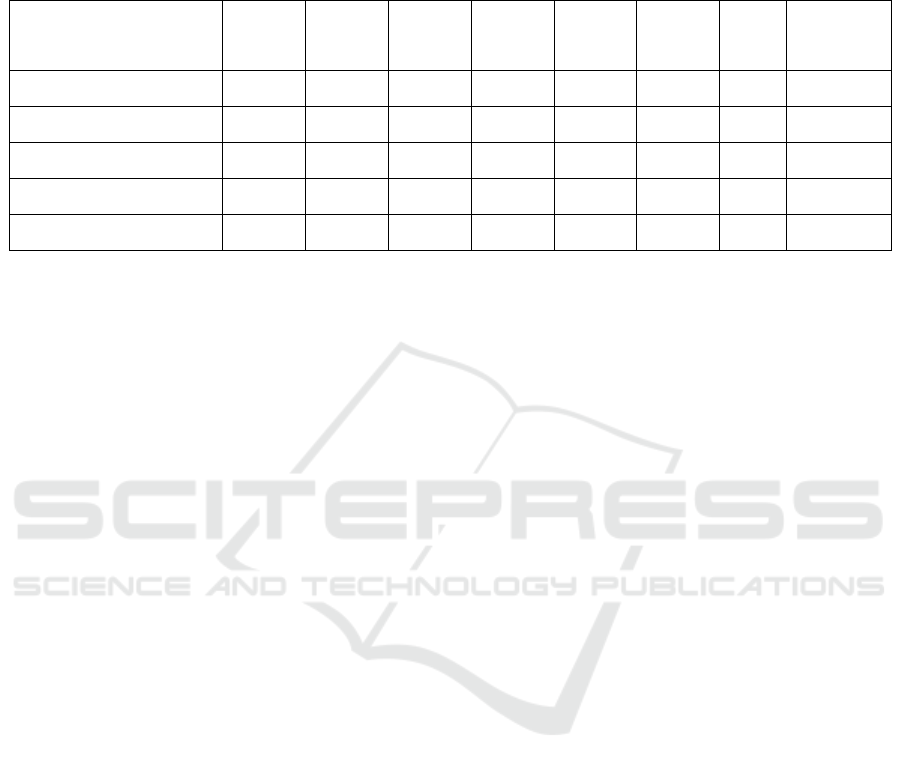
Table5: The results of an assessment of the practicality of SAS based on Islamic integration by students
Practicality of SAS
Student
1
(%)
Student
2
(%)
Student
3
(%)
Student
4
(%)
Student
5
(%)
Student
6
(%)
Avg.
Category
MTsNLipat Kain
66.67
68.75
60.42
66.67
56.25
66.67
64.24
Valid
MTsNPangean
68.75
75
70.83
70.83
68.75
70.83
70.83
Valid
MTsNMuttaqin
68.75
72.92
70.83
66.67
68.75
70.83
69.79
Valid
MtsNDarel Hikmah
70.83
66.67
75
70.83
75
75
72.22
Valid
MTsN Al-Munawaroh
75
64.58
60.42
77.08
70.08
85.42
72.10
Valid
The table above is the result of the practicality of
SAS based on Islamic integration according to 30
students from 3 districts in Riau Province.
Assessment of students of MTsNLipat Kain
obtained an average score of 64.24 with the valid
category. Assessment of MTsN Pangean students
has scored an average of 70.83 with the valid
category. Assessment from students of MTsN Al-
Muttaqin obtained an average score of 69.79 with
the valid category. Assessment of MTsN student
Darel Hikmah obtained an average score of 72.22
with the valid category. Assessment from students of
MTsN Al-Munawaroh obtained an average score of
72.10 with the valid category. All student ratings on
the practicality of the SAS are in the range of 61 to
80 with valid categories, so it can be concluded that
students feel the SAS based on Islamic integration is
practical and worthy of use in the learning program.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of the research it can be
concluded that:
1. According to evaluation and education
experts, the six questionnaires used to assess
SAS are valid. The six instruments developed
are valid and worthy of use for assessing the
SAS based on Islamic integration.
2. The practicality of the SAS based on the
integration of Islam validated by evaluation
and education experts is in the category of
valid or practical use.
3. The practicality of SAS based on Islamic
integration validated by subject teachers in 5
schools in Riau Province is in the category
valid and feasible to use.
4. The result of the practicality of SAS based on
Islamic integration assessed by students from
5 schools in 3 districts is a valid category and
feasible to be used.
5. From the results of qualitative analysis based
on interviews with students, obtained
information that the developed SAS
interesting to use, but need additional time to
implement SAS in the process of learning
mathematics in junior high schools,
especially Madrasah Tsanawiyah.
REFERENCES
Bohensky, E. L., Maru, Y., 2011. Indigenous Knowledge ,
Science , and Resilience : What Have We Learned
from a Decade of International Literature on “
Integration ”?, 16(4).
Chen, C., Bradshaw, A. C., 2007. The Effect of Web-
Based Question Prompts on Scaffolding Knowledge
Integration and Ill-Structured Problem Solving, 39(4),
359–375.
Davis, E. A., 2004. Knowledge Integration in Science
Teaching: Analysing Teachers’ Knowledge
Development, 34, 21–53.
Lee, H., Liu, O. L., Linn, M. C., 2011. Validating
Measurement of Knowledge Integration in Science
Using Multiple-Choice and Explanation Items, (3),
115–136.
Lee, H., Liu, O. U. L., 2009. Assessing Learning
Progression of Energy Concepts Across Middle
School Grades: The Knowledge Integration
Perspective. Science Education.
Liu, O. L., Lee, H., Hofstetter, C., and Linn, M. C., 2014.
Assessing Knowledge Integration in Science :
Development of Mathematics Instructional Materials Integrated with Islamic Sciences
403

Construct, Measures, and Evidence. Educational
Assessment, 13(1), 37–41.
Mahfuzoh. S., 2011. PengaruhIntegrasi Islam dan
SainsterhadapMatematika. Prosiding Seminar
Nasional Matematika dan Pendidikan Matematika.
Yogyakarta
Majid, A., Andayani, D. 2005. Pendidikan Agama Islam
BerbasisKompetensi, Konsep dan Implementasi
Kurikulum 2014. Bandung: PT RemajaRosdaKarya
Nasution., 2009. Berbagai Pendekatan dalam Proses
BelajarMengajar. Jakarta: Bumi Aksara
Riduwan, 2005. Belajar Mudah Penelitian untuk Guru,
Karyawan dan Peneliti Muda. Bandung: Alfabeta
Slameto, 1991. Belajar dan Faktor-Faktor yang
Mempengaruhinya. Jakarta: Rineka Cipta
Sudjana, N. 2005. Penilaian Hasil Proses Belajar dan
Mengajar. Bandung: Remaja Rosda Karya
Suryabrata. S., 2004. Psikologi Pendidikan. Jakarta: Raja
Grafindo
Suwarna, 2010. Strategi Integrasi Pendidikan Budi
Pekertidalam Pembelajaran Berbasis Kompetensi.
Jurnal Cakrawala Pendidikan Volume 12
Zubaidah, A. M. Z, 2013. Integrasi Nilai Pendidikan
Islam dalam Pendidikan Umum Sebagai Revitalisasi
Pendidikan Islam. Jurnal Potensia Fakultas Tarbiyah
dan Keguruan UIN SUSKA RIAU Vol. 12 No.1
ICMIs 2018 - International Conference on Mathematics and Islam
404
