
Analysis of Learning Interest and Learning Outcome for
Mathematics Subject with SCL Approach
Puput Wahyu Hidayat
STKIP Muhammadiyah Muara Bungo
Bungo, Jambi, Indonesia
Keywords: Learning Interest, Learning Outcome, SCL
Abstract: The purpose of the study was to inform about: 1) student’s learning interest; and 2) the learning outcome of
undergraduate student of PGSD STKIP MUHAMMADIYAH at Muara Bungo for the math lesson on the
academic year of 2017/2018. The Research concept used descriptive researching method. This Research
population include all members od second semester undergraduate students which has 4 classes. Meanwhile,
two selected classes made for an example of Research it was Class B and C. Test instruments were used to
describe the learning outcome. Questionnaires were used to describe students' learning interest. The
founding of the research showed that; 1) with SCL approach, student's learning interest for both classes
were in the high category; 2) with SCL Approach, student’s learning outcome of those two classes are on
high category.
1 INTRODUCTION
Learning mathematics is a lesson that must be done
by all people, both young children and parents.
Mathematics is very important to support the lives of
all humans. Without mathematics, humans will find
it difficult to live their lives. Meanwhile, in learning
mathematics, it takes an interest in learning that
comes from within and outside. In learning
outcomes and implementation processes are
influenced by several factors, namely internal factors
and external factors (Slameto, 2003). Internal factors
are factors that exist in individuals who are learning,
while external factors are factors that exist outside
the individual. In this case the internal factors that
influence learning include learning interest. Interest
is one of the very basic factors and is very important
for students in a learning because with the students'
interest in learning, it can determine the success of a
learning. In addition, interest in learning is also a
strong factor in determining one's success.
Therefore, in order to succeed in every effort, one
must cultivate an interest in what is desired, with the
existence of great interest, one will try to obtain
satisfying and maximum results despite the many
obstacles that will be overcome.
Furthermore, argues that interest as a fixed
tendency to pay attention continuously with a sense
of pleasure. Someone who likes something, will get
it to its full potential. One of the learning objectives
to be achieved in a learning activity is an
understanding of the subject (Slameto, 2003).
In addition, interest is defined as a condition that
occurs when a person sees temporary traits or
meanings of a situation that are linked to his own
desires or needs. From some of the above
understanding it can be said that interest is a
tendency to be attracted to something that is
relatively fixed to be more attentive and constantly
remembering followed by a sense of pleasure
(Sardiman, 2011). Interest is the choice of certain
forms of an activity when a person is not under
pressure from outside himself (Nitko, 2007).
Interest is not taken from birth but is obtained
later. Interest in something is learned and influences
further learning and influences the acceptance of
new interests. So, interest in something is the result
of learning and supporting further learning.
Although interest in something is not essential to
being able to learn about it, the general assumption
states that interest will help someone learn it.
Learning interest is a condition, the most convincing
foundation in the success of the teaching and
378
Hidayat, P.
Analysis of Learning Interest and Learning Outcome for Mathematics Subject with SCL Approach.
DOI: 10.5220/0008522203780383
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mathematics and Islam (ICMIs 2018), pages 378-383
ISBN: 978-989-758-407-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

learning process with no pressure on a person
(Slameto, 2003).
Based on some of the meanings above, it can be
concluded that interest is an active mental tendency
which is always related to awareness, attention,
willingness, and pleasure or a feeling of pleasure
towards an object that is related to him, so that
students' interest in learning can foster a sense of
liking and can arouse self-motivation in carrying out
an activity that can be measured through a sense of
love, interest, having attention and involvement in
following the learning process. Lecturer should be
able to convince students that good learning
outcomes is a key to be success. A lecturer should
create a good circumstance in teaching learning
process so that can improve student learning
outcomes (Aunurrahman, 2013).
Learning is a complex action and behavior. As
an action, learning is only experienced by students
themselves. Students are the determinants of the
occurrence or absence of learning processes
(Dimyati, 2013). Learning outcomes are abilities
that students have after receiving their learning
experience (Sudjana, 2004). Meanwhile, according
to Horwart Kingsley in his book Sudjana divides
three kinds of teaching and learning outcomes: Skills
and habits, Knowledge and direction, Attitudes and
ideals (Sudjana, 2004).
Learning outcomes are student achievement
which becomes an indicator of competence and the
degree of change in behavior concerned (Mulyasa,
2005). Competencies that must be mastered by
students need to be stated in such a way as to be
assessed as a form of student learning outcomes that
refer to direct experience. Meanwhile learning
outcomes are changes in behavior not just one aspect
of human potential (Suprijono, 2010).
Based on the understanding of experts, it can be
concluded that the understanding of learning
outcomes is an increase in the ability of students
obtained through the delivery of information and
messages by educators after the learning process
takes place, which is in the form of numbers or
during a certain period. In mathematics learning,
when students are given different questions than
examples, there are still many students who are still
confused in solving the questions given by the
lecturer. So, every student is required to have a
serious interest in learning so that the expected
learning outcomes are better, so that students can
master mathematics learning well.
Meanwhile, based on the teaching experience in
the STKIP Muhammadiyah Muara Bungo
Elementary Teacher Education class (PGSD STKIP-
MB), it was seen when the presentation group was in
front, the students as auditors were noisy in the
discussion. Furthermore, sometimes the time made
to look for answers from the audient is too long so
that students tend to be noisy again. This kind of
time is very unfortunate, because it's wasted.
Furthermore, the time the lecturer has had to
conclude the subject is very little because it has run
out for discussion.
Based on the learning that took place from the
beginning of the lecture until the middle of the
semester it was seen that some students had low
learning outcomes, this was seen in most of the
material taught in the mathematics learning courses
which had very low semester exam scores. When
learning takes place, students are less willing to
convey and ask about the difficulties they face, as
well as in understanding the material and in working
on questions given by the lecturer. Student
initiatives were not seen, it was seen when the
lecturers gave students the opportunity to ask
questions and not be used properly by students. This
is because students are ashamed to ask questions and
or students are ashamed of other friends if they
explain that they do not understand what the lecturer
has said.
Other data found by researchers is that the
learning interest of students in participating in
learning activities is very lacking. This can be seen
from the many students who occupy themselves
behind while other groups are presenting. In this
case, when the moderator is not firm, the audience is
a lot of noise. Students look a lot who play
smartphones and chat with other friends. In fact,
mathematics courses, especially mathematics
learning subjects, students pay attention to lectures
are difficult, especially if the students do not pay
attention to the group and even lecturers who deliver
learning.
Approach in the learning process is important,
student center learning (SCL) that priority
knowledge of learners about influences future
learning. Than assessment SCL provide
opportunities for feedback as learning process
leading and judgment at the end of learning process
(Nicol, 2006).
Students of the second semester of PGSD, have
completed their studies at the high school level, so
they are expected to have authority over elementary
school learning, because they have studied
mathematics from elementary school to high school.
Meanwhile, to find out how far the success of the
PGSD S1 program in improving the quality or
quality of elementary school teachers, especially in
Analysis of Learning Interest and Learning Outcome for Mathematics Subject with SCL Approach
379
terms of interest and learning outcomes of
mathematics, it is necessary to do research. So, with
the existence of these problems, the researchers
intend to conduct research with the title of interest
analysis and mathematics learning outcomes for
undergraduate students of PGSD STKIP-MB.
Based on the background of the problem that has
been described, the formulation of the problem of
this study is:
1.1 How is the students’ learning interest with
student center learning in semester 2 of
academic year 2017/2018?
1.2 How is the students’ learning outcome with
student center learning at semester 2 of
academic year 2017/2018?
2 METHODOLOGY
The design of this study is to use descriptive
research methods. This type of research is
quantitative research. Quantitative research is a
method that emphasizes objective aspects of
measurement of social phenomena and includes
numbers. So, the research design is a design with the
final test of a single group, the one group posttest
(Anggoro, 2007). Which is a research design using
one experimental group, where the measurement is
done once at the end of Test.
This research was carried out in STKIP-MB and
was conducted for one month with six discussion
material for students of Semester II PGSDSTKIP-
MB Study Program Academic Year 2017/2018.
Population and sample from research are all
students of PGSD (Elementary school education
Department) STKIP-MB. Sample: purposive
sampling, select by 2 classes PGSD II B and PGSD
II C.
The research variable is Independent variable
and dependent variable. Independent variable is
student center learning approach, and dependent
variable is learning outcome and learning interest.
Technique of collecting data this research is test
instrument (To measure learning outcomes it
consists of 6 questions), and non-test instrument (a
questionnaire to find out student’s learning interest
consist of 30 statements).
Technique of analyzing data this research is
describing students’ learning interest and describing
the students’ outcome.
2.1 Describing Students’ Learning
Interest
The researcher describes the data about students'
interest in learning mathematics obtained from
instruments in the form of a checklist on a Likert
scale, the data were analyzed with descriptive
statistics. Descriptive analysis is carried out only to
obtain scores of students' interest in learning
mathematics. Furthermore, classified according to
the standard score, the inquiry questionnaire interest
in the study was adjusted according to the number of
questionnaire interest statements. So that with 30
items in the questionnaire, the lowest and highest
score can be determined, so the range of interest
questionnaire has a range of 30 to 150.To determine
the criteria for measurement results used
classification based on ideal average (X
̄
i) and
Standard Deviation (Sbi).
and
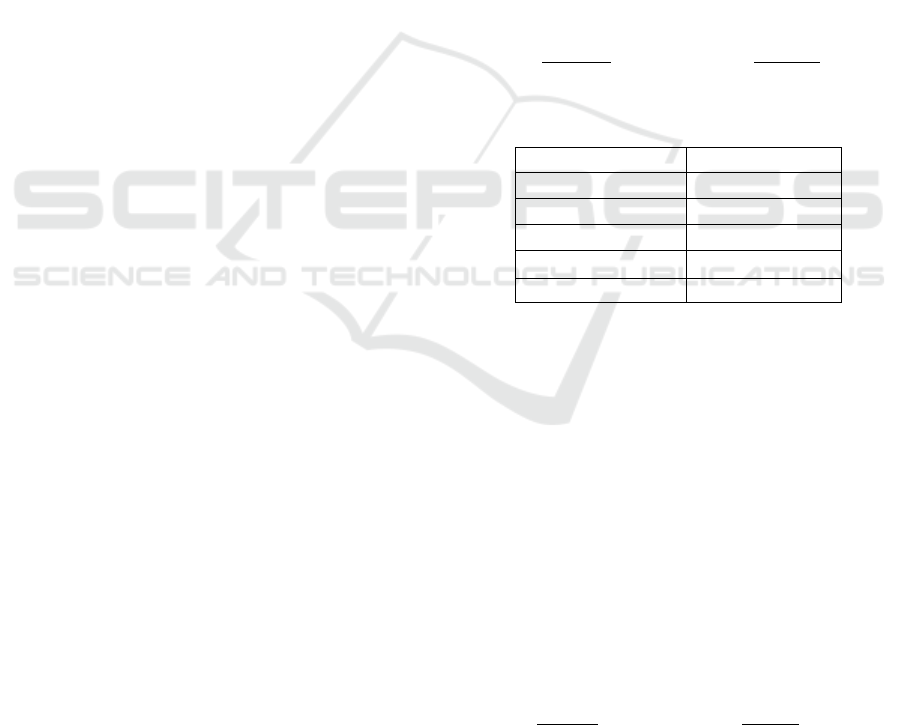
Table 1: Learning interest criteria.
Score (X)
Criteria
X > 126
Very High
102 X 126
High
78X 102
Medium
54 X 78
Low
X 54
Very Low
2.2 Describing Students’ Learning
Outcome
Learning outcomes data were obtained from the
results of tests conducted on two classes in the form
of questions about mathematics learning subjects.
From both classes, the data is analyzed descriptively,
so that the mathematics learning outcomes will be
seen at which level.
So that with 6 items in the questionnaire, the
lowest and highest score can be determined, so the
range of interest questionnaire has a range of 0 to
100. To determine the criteria for measurement
results used classification based on ideal average
(X
̄
i) and Standard Deviation (Sbi).
and
ICMIs 2018 - International Conference on Mathematics and Islam
380
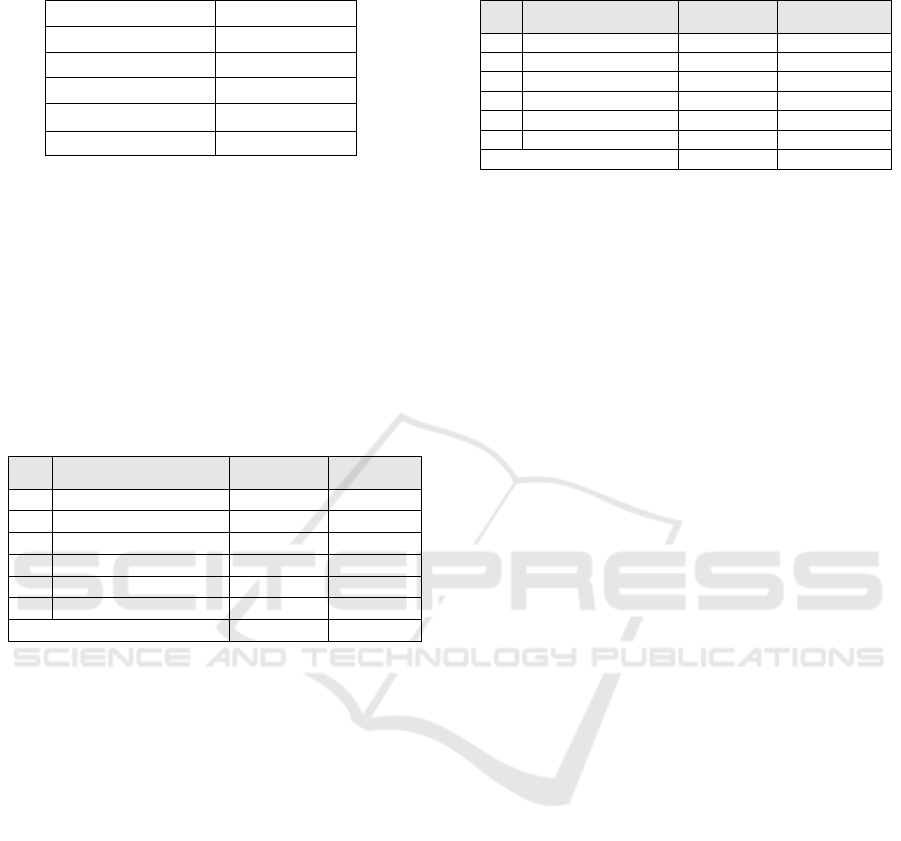
Table 2: Learning outcome criteria.
Score (X)
Criteria
X > 81,2
Very High
62,4X81,2
High
43,6X 62,4
Medium
24,8X43,6
Low
X 24,8
Very Low
Data of student learning interest is described
based on the questionnaire given at the end of the
lesson. Description of data on interest in learning is
a description of the data obtained to support the
discussion in the study. Description of the data
discussed is the result of giving questionnaires given
to research subjects, namely Class B students and
Class C PGSD STKIP-MB Study Program second
semester.
Table 3: Learning interest data.
No
Description
Class B
Class C
1
Average score
106,59
104,06
2
Maximum score
131
119
3
Minimum Score
71
87
4
Deviation standard
13,19
8,59
5
Ideal Maximal Score
150
150
6
Ideal Minimal Score
0
0
Total
45
26
Based on Table 3, information is obtained that
the average number of questionnaire scores of
students' interest in learning mathematics in
Semester II class B is 106.59, while for Class C
Semester II students is 104.06. Both are in the high
category.
Meanwhile, for learning outcome are described
based on the tests given at the end of the learning in
the form of 6 essay questions about mathematics
learning subjects. Description of learning outcome
data is a description of the data obtained to support
the discussion in the study. Description of the data
discussed is the result of giving the test given to the
research subject, namely Class B students and Class
C PGSD STKIP-MB Study Program second
semester.
Based on Table 4, it was obtained information
that the average number of test scores of the second
semester students' mathematics learning outcomes in
class B was 78.07, while for class C students in
Class C was 78.42. Both are in high criteria.
Table 4: Learning outcome data
No
Description
Class B
Class C
1
Average score
78,07
78,42
2
Maximum score
88,38
88,04
3
Minimum Score
63,55
60,74
4
Deviation standard
5,21
5,90
5
Ideal Maximal Score
100
100
6
Ideal Minimal Score
0
0
Total
45
26
3 RESULT AND ANALYSIS
3.1 Description of Student Learning
Interest Categories
In describing student interest learning categories, the
researchers describe the data through the results of
the instruments given to students in the form of
questionnaires which are checklist on a Likert scale,
the data are analyzed descriptively with the help of
Microsoft Excel.
Descriptive analysis is carried out only to obtain
scores of students' interest in learning mathematics.
Furthermore, classified according to the standard
score, the inquiry questionnaire interest in the study
was adjusted according to the number of
questionnaire interest statements. So that with 30
items in the questionnaire, the lowest and highest
score can be determined, so the range of interest
questionnaire has a range of 30 to 150.
After obtaining the data quantitatively, the
researchers analyzed the data according to the
criteria achieved by the Semester II Regular Class
Study Program students of PGSD STKIP-MB and
categorized into very high, high, medium, low or
very low levels. In this study, it is known that before
giving a questionnaire on interest in learning,
students are given student-centered learning with
group presentations. Treatment in both classes uses
the same learning methods, namely student-centered
learning with group presentations. The results of the
analysis of learning interest in learning in Class B of
Second Semester Study Program Students of PGSD
STKIP-MB are that most students have interest in
learning in the high category, namely 25 students or
55.56%, medium category 13 students or as much as
28.89%, low category there were 2 students or
4.44%, very high there were 5 students or 11.11%,
while for the very low category none of the students
had a learning interest in that category.
From the data that has been described above, the
highest average student interest in learning is in the
Analysis of Learning Interest and Learning Outcome for Mathematics Subject with SCL Approach
381

high category, namely as many as 25 students or
55.56%. In learning outcomes and process activities
are influenced by several factors, namely external
and internal factors, all learning by students is
influenced by internal and external factors (Slameto,
2003).
Meanwhile, for the description of the data on the
learning interest at Class C of Semester II Students
of the PGSD STKIP-MB Study Program, the
majority of students also have an interest in learning
in the high category, namely 13 students or 50%, the
middle category is 10 students or 38.46%, and a very
high category of 3 students as much as 11.54%,
while there were no students in the very low and low
categories.
From the data that has been described above, the
highest average student learning interest is in the
high category, namely as many as 13 students or
50%. This is in accordance with what was expressed
by (Slameto, 2003), in learning outcomes and
process activities are influenced by several factors,
namely external and internal factors, all learning by
students is influenced by internal and external
factors.
Based on the results of the discussion of data
descriptions in both classes, the learning interest of
PGSD students in STKIP-MB is in the high
category. However, this category is a minimum high
category, namely 106.59 and 104.06. Student
learning interest in the high category is between 102
and 126. So, from the description of the data, the
researcher hopes that there will be special actions to
improve the learning interest for PGSDSTKIP-MB
Study Program students in the very high category or
high category at the maximum limit.
3.2 Description of Student Learning
Outcome Categories
Data of students' mathematics learning outcomes are
described based on the tests given at the end of the
learning. The test consisted of 6 essay questions
about Mathematics Learning subjects. Description of
learning outcome data is a description of the data
obtained to support the discussion in the study.
Description of the data discussed is the result of
giving the test given to the research subject, namely
Class B students and Class C PGSD STKIP-MB
Study Program second semester.
After obtaining quantitative data, the researchers
analyzed the data according to the criteria achieved
by the Semester II Regular Class students of the
PGSD STKIP-MB Study Program and categorized
them into very high, high, medium, low or very low
levels. In this study, it is known that before giving a
learning outcome test, students are given student-
centered learning with group presentations. The
treatment in both classes uses the same learning
method, namely student-centered learning with
group presentations.
For the PGSD STKIP-MB Study Program class
B, the data obtained after conducting the learning
outcomes test were the students with the highest
number in the high criteria, which were 33 students
or 73.33%, at very high criteria of 12 students or 26,
67%, and the criteria are very low, low and there are
no students.
In addition to this, when viewed globally, the
lowest value in class B is 63.55, while the highest
value is 88.38, and has an average of 78.07. The
average value if seen from the criteria table, then the
ability of class B students of PGSD STKIP-MB
study program is on high criteria.
Meanwhile, for the C class students of PGSD
STKIP-MB Study Program, the data obtained after
testing the results of the learning outcomes is the
value of students with the highest number in the high
criteria, just like class B, which is 15 students or
57.69%. In the Medium criteria as many as 1 student
or as much as 3.85%, on Very High criteria there
were 10 students or 38.46%, in the low and very low
criteria there were no students.
In general, for class C the lowest value is 60.74,
while the highest value is 88.04, and has an average
of 78.42. The average value if seen from the criteria
table, then the ability of class B students of PGSD
STKIP-MB study program is in the high criteria,
which has a range between 62.4 and 81.2.
In addition, based on the discussion of the results
of research on mathematics learning outcomes for
students of Semester II PGSD STKIP-MB, for both
classes the average is not in very high criteria. For
class B has a high criterion, so also for class C is on
the high criteria.
Based on the results of research conducted in
STKIP-MB especially the PGSD study program,
researchers feel that the learning that has been
carried out must be further enhanced by combining
student-centered learning with the development of
learning models and methods. So that, student
interest and learning outcomes can be increased
again.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The result showed that: 1) with SCL approach,
student's learning interest for both classes were in
ICMIs 2018 - International Conference on Mathematics and Islam
382

the high category; 2) with SCL Approach, student’s
learning outcome of those two classes are on high
category.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This Research was supported by LP3M STKIP-MB
and, we thank our colleagues from Class B and
Class C in PGSD STKIP Muhammadiyah Muara
Bungo.
REFERENCES
Anggoro, T., 2007. Metode penelitian. Jakarta,
Universitas Terbuka.
Aunurrahman, 2013. Belajar dan pembelajaran.
Bandung, Alfabeta.
Dimyati & Mudjiono, 2013. Belajar dan
pembelajaran. Jakarta, PT. Rineka Cipta.
Mulyasa, E., 2005. Menjadi guru professional
menciptakan pembelajaran kreatif dan
menyenangkan. Bandung, Remaja Rosdakarya.
Nicol, D. J. & Macfarlane-Dick, D., 2006.
Formative assessment and self-regulated
learning: a model and seven principles of good
feedback practice. Studies in Higher Education
Vol. 31(2), 199-218.
Nitko, A. J. and Brookhart, S. M., 2007. Educational
assessment of students 5
th
edition. Upper Saddle
River, New Jersey: Pearson Merrill Prentice
Hall.
Sardiman, A. M., 2011. Interaksi dan motivasi
belajar mengajar. Jakarta, Rajawali Press.
Slameto, 2003. Belajar dan faktor-faktor yang
mempengaruhinya. Jakarta, PT. Rineka Cipta.
Sudjana, N., 2004. Dasar-dasar proses belajar
mengajar. Bandung Sinar Baru Algensido
Offset.
Suprijono, A., 2010. Cooperative learning: teori dan
aplikasi PAIKEM. Yogyakarta, Pustaka Pelajar.
Analysis of Learning Interest and Learning Outcome for Mathematics Subject with SCL Approach
383
