
The Increasing Students’ Mathematical Creative Thinking Ability
using Treffinger Model of Indonesian Lower Secondary Students
M. Duskri
1
, Khairatul Ulya
2
, Rauzatul Munawarah
3
1
Mathematics Education Department, UIN Ar-Raniry, Banda Aceh, Indonesia
2
Mathematics Education Department, IAIN Langsa, Langsa, Indonesia
3
MTs Oemar Diyan Aceh Besar, Aceh Besar, Indonesia
Keywords: Treffinger Model, Creative Thinking
Abstract: One of mathematics teaching goals is to improve students’ mathematical creative thinking ability as they are
able to solve problems in variety ways. The purpose of this study was to analyze the increasing of students’
mathematical creative thinking ability by using Treffinger at student lower secondary school. Treffinger
Model is a collaborative learning using divergent and convergent thinking processes. The research method
used in this study was a quasi-experimental research design using pre-test and post-test design. As a sample,
there were two groups of students grade VII SMPN 2 Unggul Mesjid Raya Aceh Besar that was chosen
randomly. The study results showed that students’ mathematical creative thinking ability taught by using
Treffinger model is better than students’ mathematical creative thinking ability taught by conventional
model. There was an increasing of each students’ mathematical creative thinking ability indicator in
experimental group, namely, flexible increased significantly from 0.00% to 70.69%, fluency raised from
50.00% to 89.66%, and elaboration grew from 20.69% to 77.59%.
1 INTRODUCTION
Thinking skills consist of recall thinking, basic
thinking, critical thinking, and creative thinking (S.
Krulik and Rudnick, 1999). Recall thinking and
basic thinking are categorized to lower order
thinking, while critical thinking and creative
thinking are categorized to higher order thinking.
Mathematical creative thinking is a reflective
pure thinking that produces a complex product
(Alimuddin, 2009). Prasetiyo et al. (2014) stated that
a creative thinking is a usual thinking related to
intuition that encourage imagination and give a
novel possibility which produce great ideas that is
not expected. As a result, a creative thinking is a
thinking process that produces variety ideas to solve
a problem.
A creative thinking skill is an integral part in
education. Permendikbud (2016) stated that
authentic learning in mathematics focuses on (1)
process and product oriented in solving problem (2)
a reasoning to improve logic, critical, analytic and
creative. A creative thinking is added as
instructional strategy and lesson plan as well.
Mathematics is able to train the thinking to
improve reasoning. As the result, logical, critical,
analytic and creative thinking will improve as well.
However, in practices, students’ activity and
achievement is not quite good yet. Based on
preliminary study on SMPN 2 Unggul Mesjid Raya
Aceh Besar, it was found that a mean score of each
indicator of students’ creative thinking ability is low
namely flexible indicator 8%, fluency indicator
reached 64% which no one can produce an original
idea in solving problem, and elaboration indicator
39%. The problem faced is needed to solve by using
instructional model that is able to explore students’
creative thinking. One of model used is Trefingger
Model. Trefingger model is a model that combines
two domains of learning namely cognitive and
affective domain. Moreover, the model describes
level of learning start from basic level to complex
level
There are 3 levels of Treffinger Model namely
basic tools, practice with process, and working with
158
Duskri, M., Ulya, K. and Munawarah, R.
The Increasing Students’ Mathematical Creative Thinking Ability using Treffinger Model of Indonesian Lower Secondary Students.
DOI: 10.5220/0008518701580161
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mathematics and Islam (ICMIs 2018), pages 158-161
ISBN: 978-989-758-407-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

real problems. Level 1 (basic tool) consist of
divergent thinking skills and creative technique. As
introduction, divergent function consists of the
improving of fluency, flexibility, originality,
elaboration. Level 2 (practice with process) is a
chance given for students to practice the skills that
have been learnt in level I. Level 3 (working with
real problem) is applying skills learnt in two level
toward a challenge in real world (Nisa, 2011)
Study of model Treffinger showed that students’
mathematical creative thinking ability taught by
using Treffinger model is better than students’
mathematical creative thinking ability taught by
conventional model. In addition, there is a positive
response of students toward applying Treffinger
model in mathematics learning (Rohaeti, 2016).
From the background, it is a need to study about
“The influences of Treffinger Model towards
students’ mathematical creative thinking in lower
secondary school”. There are some research
questions (1) How is students’ mathematical creative
thinking in lower secondary school after applying
Treffinger Model? and (2) How is students’
mathematical creative thinking in lower secondary
school after applying Treffinger Model and
conventional model.
2 METHOD
Quasi Experimental design using pre-test and post-
test with qualitative approach was used in this study.
The Sample is students grade VII SMP Negeri 2
Unggul Mesjid Raya Aceh Besar year 2017/2018.
Grade VII-1 was chosen as experiment group and
grade VII-2 as control group. The primary
Instrument is creative thinking ability item with its
rubric. While supporting instrument is lesson plan
and students’ worksheet.
3 RESULT STUDY
Students’ Mathematical Creative
Thinking Ability
This analysis was used to determine the influences
of students’ mathematical creative thinking before
and after applying Treffinger Model. The picture
below showed that students’ mathematical creative
thinking before applying Treffinger model. It is clear
that students’ mathematical creative thinking is low
level.
Based on the answer on Figure 1, it is seemed
that the indicator flexible, CS got score 2. It means
that she is able to give one-way answer with correct
computation. The answer that she gave is correct. In
the case of the fluency indicator, she got score 4. It
means that she is able to give relevant ideas and
correct answer without doing a mistake. In addition,
the elaboration indicator, CS got score 3 because she
is only able to give a correct answer, but the answer
given is not detail. Moreover, the original indicator,
she got score 0 because the answer given is similar
to other friends in his class.
Figure 1: Students’ pre-test of students’ mathematical
creative thinking.
Based on the answer given on Figure 2, it is
found that RN got score 1 on the flexible indicator.
It means that he is able to give one-way answer even
though there are some mistakes given. However, R
got score 2 on fluency indicator because he is only
able to give a relevant idea, but the answer given is
not fully correct. In the case of elaboration indicator,
RN got score 1 because he did some mistakes on
answering and the answer, he gave is not detail.
Moreover, original indicator, he got score 0 because
the answer given is similar with other students in is
classroom.
Figure 2: A student (RN) pre-test answer of creative
thinking.
From the answer given on Figure 3, it is found
that RN got score 4 on flexible indicators. It means
that he is able to give more than one answer with
correct computation. Like flexible indicator, RN got
score 4 on fluency indicator. It means that he is able
The Increasing Students’ Mathematical Creative Thinking Ability using Treffinger Model of Indonesian Lower Secondary Students
159
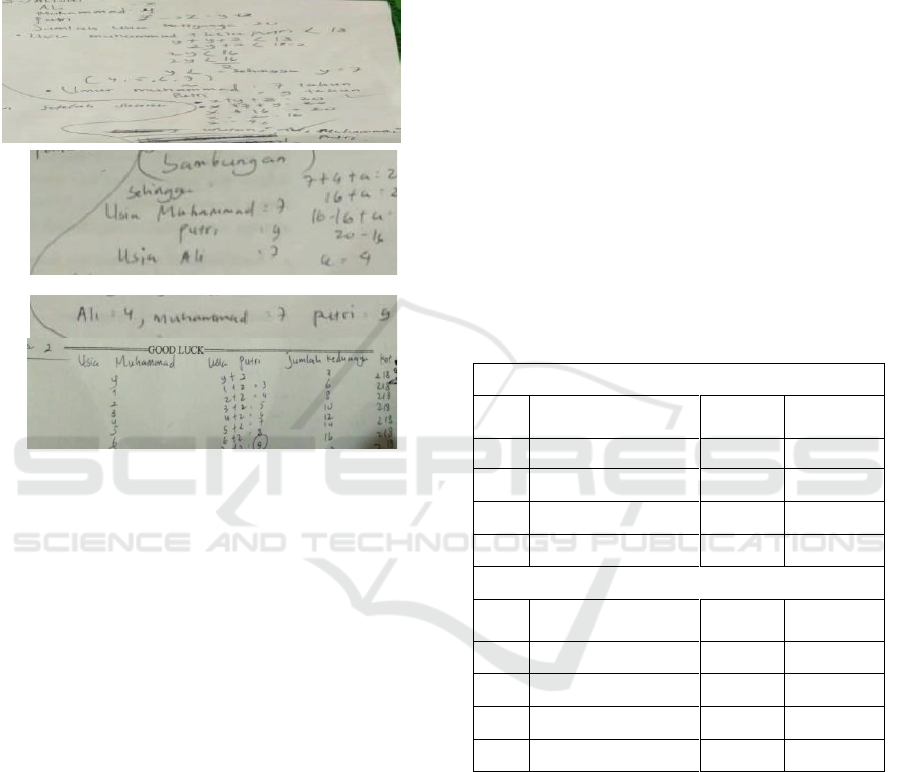
to give a relevant idea with a correct solution.
However, CS got score 3 on elaboration indicator, it
means that she is able to give a correct answer
without detail. Like the answer before, the original
indicator could not reach by the student, and he got
score 0 because the answer give is similar to other
students in her classroom.
Figure 3: A Student (RN) pre-test answer of creative
thinking.
Treffinger model enables students to develop
their creative thinking ability since in the first level,
it uses open-ended questions to encourage students
to think flexibly, originally and fluently. In addition,
in the second level, both students are encouraged to
have a role in working groups. In this level, they will
be given complex questions. The purposes of these
activities are to encourage students to think
creatively with working-learning activity.
Moreover, the third level, the model used is
creative thinking technique. In this level, student
was asked to answer non-routine question relate to
their real world. The students were asked to get
solution of the problem given to encourage them to
think creatively.
The data analysis in Table 1 showed that the
creative thinking indicator is increasing in each
indicator except original indicator. As the result, it is
concluded that Treffinger Model has a positive
impact towards students’ mathematical creative
thinking.
4 DISCUSSION
Students’ Mathematical Creative Thinking
After applying Treffinger Model on learning
process, there is an increasing of students’
mathematical creative thinking of each indicator
except original indicator. In original indicator, both
pre-test and post-test, the student’s achievement is
categorized as low ability. It is caused by some
reasons: (1) the topic of learning is less effective to
develop original indicator (2) original indicator is
one of the difficult indicators to improve because
students need to find the solution that is not similar
with other students. Moreover, the original indicator
needs more time to develop. However, the
researcher conducts 3 meeting classes, for the
reason, it is predicted that the original indicator did
not increase.
Table 1: Students pre-test and post-test achievement on
creative thinking ability.
Experiment Group Post-Test
No
Observing Aspect
Low
Good/
Excellent
1.
Originality
100%
0.00%
2.
Flexibility
29.31%
70.69%
3.
Fluency
10.34%
89.66%
4.
Elaboration
22.41%
77.59%
Control Group Post-Test
No
Observing Aspect
Low
Good/
Excellent
1.
Originality
100%
0,00%
2.
Flexibility
75%
25,00%
3.
Fluency
30%
70,00%
4.
Elaboration
50,85%
49,15%
It was predicted that the original indicator would
not increase in this research. There are three reasons
why the indicator did not increase. Firstly, the
Acehnese students do not have a habit to think
dependently. it means that students are still thinking
as their habitual thinking. For this case, further
research needs to conduct in order to focus on
encouraging students to think “out of the box”.
Secondly, the students feel afraid or not feel
confidently in asking or answering the question from
the teacher. The culture of “ a shame” is affected in
creating original ideas because the students choose
ICMIs 2018 - International Conference on Mathematics and Islam
160

being silent rather that asking or answering the
question.
In other hand, the different thing happens to 3
other indicators. The flexible indicator increases
from low level with 100% to 29.31%, while good or
excellent categorized increase 0% to 70.69%. For
fluency indicator fluency, the number of students
with low categorized decrease from 50.00% to
10.34%, on the other hand, students reached good
and excellent categorized increase from 50.00 %
89.66%. The last indicator, elaboration, the number
of low achievement student decrease from 79.31%
to 2.41%, while students who reach good/excellent
categorized increase from 20.69 % to 77.59%.
Treffinger Model is one of learning models that
is reliable, visible and applicable model in teaching
and learning (Supriyono, 2011). In addition, the
model has success in order to teach learners in
achieving divergen thinking (Wirahayu, Purwito,
Juarti, 2018). Morever, there are stated that
Treffinger model is able to improve students’
creativity (Pomalato, 2006; Siswati, 2011; Haryono,
2009).
5 CONCLUSION
This study showed that Treffinger model has a good
impact on students’ creative thinking ability.
Moreover, it is claimed that students’ creative
thinking ability taught by Treffinger model is better
than students’ creative thinking ability taught by
conventional model.
REFERENCES
Alimuddin, 2009. Menumbuh Kembangkan Kemampuan
Berpikir Kreatif Siswa melalui Tugas-Tugas
Pemecahan Masalah. Jurnal Universitas Negeri
Yogyakarta, Februari, p. 2.
Haryono, Ary D., 2009. Pembelajaran Treffinger untuk
Menumbuhkan Kreatifitas dalam Pemecahan Masalah
Operasi Hitung Pecahan Siswa Kelas V SD Islam
Bani Hasyim Singosari. Thesis, Unpublished, Malang:
Postgraduate Program State University of Malang.
Kementerian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan, 2016. Silabus
Mata Pelajaran Sekolah Menengah Pertama/
Madrasah Tsanawiyah (SMP/MTs). Jakarta.
Krulik, S. and Rudnick, 1999. Innovative Task to Improve
Critical and Creative Thinking Skills. Developing
Mathematical Reasoning in Grades K-12, pp.138-145.
Nisa, Titin Faridatun, 2011. Pembelajaran Matematika
dengan Setting Model Treffinger untuk
Mengembangkan Kreativitas Siswa, Pedagogia Vol.
1, No. 1, December, p. 35-50.
Pomalato, Sarson W. Dj., 2006. Mengembangkan
Kreativitas Matematik Siswa dalam Pembelajaran
Matematika Melalui Pendekatan Model Treffinger.
Mimbar Pendidikan No. 1/XXV, pp.22-25.
Prasetiyo, A. D. and Mubarokah, L., 2014. Berpikir
Kreatif Siswa dalam Penerapan Model Pembelajaran
Berdasar Masalah Matematika. Jurnal Pendidikan
Matematika STKIP PGRI Sidoarjo Vol.2, No.1, pp. 9-
18.
Rohaeti, I. T., Priatna, B. A., and Dedy, B., 2013.
Penerapan Model Treffinger pada Pembelajaran
Matematika untuk Meningkatkan Kemampuan
Berpikir Kreatif Siswa SMP. Jurnal Online
Pendidikan Matematika Komtemporer Vol 1 No. 1,
journal.fpmipa.upi.edu/index.php/jopmk/article/
view/41.
Siswati, Anna, 2011. Meningkatkan Kemampuan Berpikir
Kreatif Matematika melalui Pembelajaran Model
Treffinger pada Siswa Kelas VII SMPN 1 Singosari,
Thesis, Unpublished, Malang: Postgraduate Program
State University of Malang.
Supriyono and Hardika, 2011, Model Pembelajaran
Transformatif Berbasis Learning How to Learn:
Pengembangan dan Uji evektifitas Model untuk
Peningkatan Kreativitas Belajar Mahasiswa dalam
Mengeksplorasi Kompetensi Akademik untuk
Kehidupan. Research Report, Malang: LP2M UM
Malang.
Wirahayu, Y. A., Purwito, H., and Juarti, 2018, Penerapan
Model Pembelajaran Treffinger dan Ketrampilan
Berpikir Divergen Mahasiswa, Jurnal Pendidikan
Geografi: Kajian, Teori, dan Praktik dalam Bidang
Pendidikan dan Ilmu Geografi Tahun 23, Nomor 1,
January.
The Increasing Students’ Mathematical Creative Thinking Ability using Treffinger Model of Indonesian Lower Secondary Students
161
