
Ethnomathematics: The Exploration of Learning Geometry at Fort
Rotterdam of Makassar
Sri Sulasteri, Fitriani Nur, Andi Kusumayanti
Department of Mathematics Education, Universitas Islam Negeri Alauddin Makassar, Indonesia
Keywords: Learning Geometry, Ethnomathematics, Historical Objects.
Abstract: The needs of math in various aspects of life prove that through math, human can understand and solve the
problems. Basically, learning math has never been separated from daily lives, especially the culture, but
most of students assume that math and culture have no any much correlation. This may occur because
almost all teaching media used by the teachers have not given any real examples yet on the relation between
math and culture that we have. One of the ethnomathematical objects that can be used as learning media are
the historical objects at Fort Roterdam. The study aims to deeply explore and dig the concept of learning
geometry bases on any kinds of ethnomathematics that can be used as the sources or learning math on
Junior High School level. This field study shows that based on the exploration, observation, and
documentation results as well as the literature study, it was found the geometry concept on the historical
objects at Fort Roterdam. Learning math based on ethnomathematics can be implemented in order to
introduce the cultures to the students as well as to give more interesting learning.
1 INTRODUCTION
Indonesia is an archipelago consisting of various
ethnic groups, languages, arts and cultures, and
various kinds of natural wealth. With those
Indonesia’s ethnicity and culture diversities, it is not
such an easy job to keep and preserve it on the
rapidly increasing globalization. Nowadays, the
presence of a combination between education and
culture gives positive impact on the cultural
development in Indonesia. It is expected that our
nation’s successors will continue maintaining their
cultural preservation even on the rapidly increasing
globalization someday. One of math learning
alternatives that are currently viral in math education
matter is by linking math learning with daily life
based on the local culture. Math and culture are two
interrelated things. A student can start learning math
from the concrete things that he has known such as
exploring the information on what he has gained in
his daily life relating to the math that he is learning.
Learning math related to the local culture is a
good model to be continually developed so that the
math learning become more fun, interesting, and
familiar for the students because every activity done
by the students always prioritizes their cultural
background. It is in line with (Turmudi, 2018),
(Marsigit, Setiana, & Hardiarti, 2016), (Zayyadi,
2017), (Ekowati, Kusumaningtyas, & Sulistyani,
2017). In general, said that the obe way to conclude
mathematics learning is related to local culture.
Other thatD'Ambrosio’s point of view in Marsigit et
al. (2018) that "the term requires a dynamic
interpretation because it describes concepts that are
themselves neither rigid nor singular-namely, ethno
and mathematics" (D’Ambrosio, 2011). The term
‘etno’ describes everything that creates culture of a
group, namely, language, code, values, jargon,
beliefs, food and clothing, habits, and physical traits.
Meanwhile, according to Gerdes (1994) in Wahyuni,
he states that Ethno-mathematics is the math
implemented by a certain cultural group, group of
workers / farmers, the children from certain class
community, professional classes, and so forth
(Wahyuni, 2016).
As a matter of fact, on the contrary, almost all
students especially in Makassar still think that math
cannot be related to daily life so that the students fail
in understanding the basic concept of math. Another
reason of it is because most of the devices used by
the teachers have no link between the students’
learning and their daily lives, whereas math learning
should be associated with the concrete things that
Sulasteri, S., Nur, F. and Kusumayanti, A.
Ethnomathematics: The Exploration of Learning Geometry at Fort Rotterdam of Makassar.
DOI: 10.5220/0008518601510157
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mathematics and Islam (ICMIs 2018), pages 151-157
ISBN: 978-989-758-407-7
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
151

the students have known. The concrete things known
by the students are the knowledge bridges to
understand the math abstractness. The knowledge
bridge that is meant is by implementing the media of
ethno-mathematics.
It is in line with D’Ambrosio’s point of view
(1985) in Hardiarti that on the other hand, there is a
reasonable amount of literature on this by
anthropologists (Hardiarti, 2017). Making a bridge
between anthropologists and historians of culture
and mathematicians is an important step towards
recognizing that different modes of thoughts may
lead to different forms of mathematics; this is the
field which we may call ethnomathematics. It means
that creating a bridge between culture and math is
necessary step to recognize various thinking ways
that can create mathematical forms; it is what is
called as ethno-mathematics. It can be interpreted
that various concept of math can be explored and
found in the culture so that it clarifies that the math
and the culture are interrelated; math can be created
from the culture, and math can be explored in the
culture so that it can be used as one of concrete
learning sources existed around the students. It is in
line with (Wahyuni, 2016), (Fajriyah, 2018), (Putri,
2017), (Hardiarti, 2017) and (Maryati & Prahmana,
2018) in general said that mathematics should be
associated with daily life based on local culture.
One of the historical objects that can be used as
learning media is the relic of historical object in Fort
Ujung Pandang or more known as Fort Rotterdam
located in the center of Makassar city. Fort
Rotterdam is one of the legacies of Gowa kingdom
and has a lot of relics of historical objects. Some of
buildings and historical objects at Fort Rotterdam
seem have similarity with the math concepts
especially geometry material. The learning sources
derived from those historical objects can be used to
introduce forms of shapes and surface area. Marsigit
et al. (2018) state that ethno-mathematics serves to
express the relation between the culture and the
math. Therefore, ethno-mathematics is a science
used to understand how the math is adapted from a
culture.
Through math learning resources derived from
the socio-cultural environment, it is expected to
facilitate students in understanding the basic
concepts of math because the learning process that is
carried out starts from informal math knowledge as
well as to develop the students’ insight on the
culture diversity that they have especially the local
culture. The math learning based ethno-mathematics
is one of alternatives that can make learning more
meaningful, contextual, interesting, and fun. it is in
line with Putri’s explanation (2017) in her research
that the exploration on the cultural studies related to
the math is able to give new information about local
culture diversity and it is easier to understand the
math learning because it is not perceived as an ‘odd’
thing by the students anymore.
Based on the above descriptions, it can be
concluded that this study aims to explore and
describe the geometrical concepts found in the
historical objects at Fort Rotterdam and how to
utilize the math concepts in math learning on those
historical objects at Fort Rotterdam.
2 METHOD
The study used qualitative research with
ethnographic approach. Ethnographic research is
also often referred to as field research. According to
Lawrence Neuman, ethnography is the extension of
field research. Meanwhile, according to Roice
Singleton, ethnography provides answers to the
question on what the culture of an individual group
is. The qualitative research is used by the researcher
in order to be directly involved in getting what
information needs to be known.
The research instrument in the qualitative
research with ethnography approach is the
researcher himself/herself (human instrument) which
means that the researcher acts as the main
instrument that cannot be replaced by others. The
role as the main instrument is setting the research
focus, selecting the informants as data sources,
collecting library data, interviewing, observing, and
documenting.
Data analysis techniques were carried out by
changing the data obtained from both the informants
and those obtained by the researcher in the form of
recordings or images into writing or report by
selecting which data needed in the study.
ICMIs 2018 - International Conference on Mathematics and Islam
152
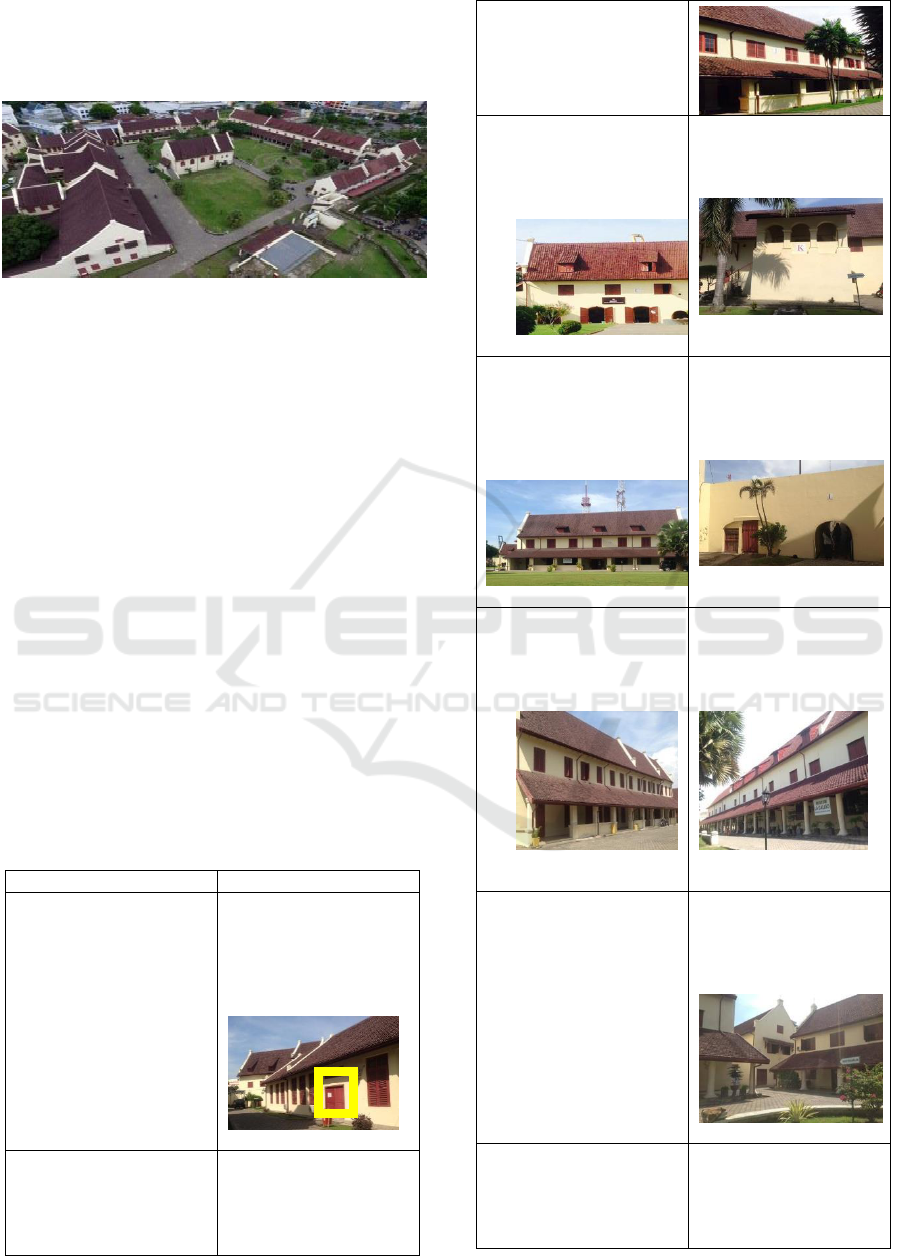
3 FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 The Area of Fort Rotterdam
Figure 1: The Area of Fort Rotterdam
(makassar.tribunnews.com)
Fort Ujung Pandang which is now called as Fort
Rotterdam was firstly established by the 9th King of
Gowa, Daeng Matanre Karaeng Manguntungi
Tumapparisi Kalonna, in 1545 (Natsir, 2017). The
purpose of this establishment was to strengthen the
base defense of Gowa Kingdom along the coast of
Makassar in order to face the expansion of VOC
power (the Dutch eastern company) that continues to
expand its influence in the field of politics and
economy in the eastern Indonesia.
When the Dutch conquered Gowa kingdom in
1667, Bungayya Treaty was made in which one of
its contents was yielding Fort Ujung Pandang to the
Dutch then it was further changed into Fort
Rotterdam.
The total area of the building in Fort Ujung
Pandang is 12.999,57 m
2
. There are 15 buildings that
were entirely built by the Dutch, and 1 building was
built during the Japanese occupation.
Table 1: The Buildings at Fort Rotterdam
Building A-H
Building I-P
Building A
It was a place to receive
guests from Bone.
Building I
It was built by the
Japanese as the office of
language and farming
research.
Building B
The top part of it was
used as a place of trade
representatives and the
bottom part of it was used
Building J
It was functioned as the
office for the
bookkeeper.
as prison.
Building C
It was functioned as the
guest house for the guests
from Buton.
Building K
It was functioned as city
hall office.
Building D
The back was functioned
as the hospital for the
Dutch then changed as
public building for the
army.
Building L
It was functioned as
prison.
Building E
It was the residence place
for the leaders of trade
and priest.
Building M
It was functioned as
warehouse and trade
office of the Dutch.
Building F
It was the residence place
for the Dutch.
Building N
It was functioned as the
place for the guests from
Bacan.
Building G
It was the place for
carpentry.
Building O
It was used as the
governor office of South
Sulawesi and its
surrounding area.
Ethnomathematics: The Exploration of Learning Geometry at Fort Rotterdam of Makassar
153

Building H
It was the place for the
guests from Ternate.
Building P
It was a church.
Nowadays, the buildings at Fort Rotterdam are
partly functioned as the offices of Cultural Heritage
Conservation Center of South Sulawesi and
museum. One of them is building D and M which
are functioned as the La Galigo Museum building.
La Galigo museum has collections as many as about
4999 historical relics consisting of prehistoric
collection, numismatic, foreign ceramics, history,
manuscript, and ethnography. The ethnography
collections consist of various kinds of technology
results, arts, living equipment, and other objects
created and used by four ethnics in South Sulawesi,
namely, Buginese, Makassarese, Mandarese, and
Torajaist. The museum also has the objects coming
from the local kingdoms and the weapons that were
once used during the independence revolution.
Table 2: Some Collections in La Galigo Museum
The Collection
Figure
Archipelago Collection:
In the form of replica of
some sites or cultural
heritage in Indonesia and
also the custom objects of
the Archipelagic
kingdom.
Ceramic Collections:
Consist of various kinds
of ancient ceramics
coming from different
countries.
Traditional Tools of
Agriculture, Fisheries,
and Marine:
In the form of harvesting
tools
Bike
Equipment of traditional
weaving and fabric
The Royal Seals of Bone
Kingdom
3.2 Geometry Learning Concept of
Junior High School in the
Historical Objects at Fort
Rotterdam
The ethno-mathematics is one of the bridges that
help the students in understanding the math lesson
related to each local culture. The roles of ethno-
mathematics also give positive impact on the
development of math learning in Indonesia
especially related to the learning media. The teacher
can develop many ideas on utilizing learning media
related to the students’ daily lives, the more the
students’ experiences in understanding their
cultures, the easier they understand the math
concepts in their learning. Zayyadi (2017) states that
to create a concept: it needs a number of experiences
with the similarities. Those similarities are trusted as
the initial concepts that can bridge the students’
knowledge on the math concepts. One of the cultural
inheritances that have the concept similarities with
ICMIs 2018 - International Conference on Mathematics and Islam
154

the math learning in Makassar, South Sulawesi are
the buildings and the cultural objects in Fort
Rotterdam. The similarities of buildings and the
cultural objects can be used as the media in learning
math especially related to the geometrical materials.
The buildings and the cultural objects make the
students easier in shaping the concrete initial
concepts and make the students easier in
constructing their understanding.
Based on the field observation result conducted
at Fort Rotterdam on April 17
th
, it was found some
building images and historical objects in La Galigo
Museum and related to ethno-mathematics. It was
found that there are a lot of historical objects that
can be used as ethno-mathematics media. Some of
them are inscription stone from Sri Sultan
Hamengkubuwono, Salokoa (the Crown of Gowa
Kingdom), bridal bracelets, batik, and harvesting
tools. Those objects were then analyzed to get the
representation of what kind of geometry concepts
consisted in those historical objects. After being
analyzed and taxonomy, it was found that the
historical objects related to geometry concept are as
follows:
3.2.1 Two-Dimensional Figure
No.
Object Images
Longitudinal section
1.
Building O have
similarities with
several plane figure,
namely rectangle,
square and equilateral
triangle.
Rectangle
Square
Equilateral triangle
2.
Epigraphy has
similarities with one
of plane figures such
as parallelogram.
Parallelogram
3.
South Sulawesi’s
Batik has similarities
with several plane
figures, namely
isosceles triangle and
circle.
Isosceles triangle
Circle
4.
Phinisi miniature has
similarities with
several plane figure,
namely Equilateral
triangle and trapezoid.
Equilateral triangle
Trapezoid
5.
Ceramic as
similarities with one
of the plane figure
such as a circle.
Circle
Ethnomathematics: The Exploration of Learning Geometry at Fort Rotterdam of Makassar
155

3.2.2 Space Form
No.
Object Image
Longitudinal section
1.
Monument has
similarities with
several geometry
figure, namely cuboid
and cube.
Cuboid
Cube
2.
Archipelagic has
similarities with
several geometry
figure, namely cone
and cylinder.
Cone
Cylinder
3
3
3
3
3
The crown has
similarities with
several geometry
figure, namelycone
and cylinder.
Cone
Cylinder
4.
Building P has
similarities with
several geometry and
plane figure, namely
prism, cuboid,
rectangle and semi-
circle.
Prism
Cuboid
Rectangle
Semi-circle
5.
The Royal Seals has
similarities with one
of geometry
figuressuch as sphere.
Sphere
3.3 The Alternatives of the Historical
Objects Use in Geometry Learning
Let’s observe!
Figure 2. Building P Figure 3. Monument Figure 4. King Crown
Figure 6. Archipelagic Figure 7. Fisheries
Pay attention to the images above!
Let’s give question!
Based on some images that you have observed,
make questions about space form!
Let’s try it out!
Based on the questions that you have made, find a
space form that is similar to the image! On your own
opinion, what kind of the space form image it is?
Let’s associate!
Based on the space form that you have mentioned,
draw the longitudinal section of the image!
Let’s communicate!
Make conclusion about the activity that you have
done.
Let’s think about!
The image above is one of the
jewelries used by Buginese –
Makassarese when
conducting wedding
ceremony. The bracelet is
used hereditary by Buginese.
If it is assumed that the bracelet is similar to a space
form, what kind of the space form if it? Please draw
ICMIs 2018 - International Conference on Mathematics and Islam
156

the longitudinal section of it! Furthermore, if it is
known that the bracelet height is 20 cm with
diameter of 2 cm, determine the surface area of the
bracelet.
Some of the above explanation shows that there
is ethno-mathematics concept in the historical
objects at Fort Rotterdam. The ethno-mathematics
concept existing in those historical objects is seen on
the shapes that resemble to the shapes of two-
dimensional form and space form.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the above several analysis and discussion,
it can be concluded that there are ethno-mathematics
concepts found on the historical objects at Fort
Rotterdam such as: 1) two-dimensional form:
parallelogram, triangle, isosceles triangle, circle,
rectangle, and trapezoid, 2) space form: cube, beam,
tube, cone, pyramid, and ball, 3) the historical
objects that resemble the two dimensional forms and
the space forms can be used as knowledge bridge in
learning math. By using learning based local culture,
the learning activity in the classroom will be more
meaningful and interesting because the learning
comes from the local knowledge so that the students
are easier in understanding the abstract math to be
more concrete.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The writers address incredible thanks to Andi
Halimah, A. Sriyanti, Andi Dian Angriani, Suharti,
and Nina Agustina who have been involved in this
research.
REFERENCES
D’Ambrosio, U., 2011. Ethnomathematics. Link Between
Traditions and Modernity. In Rotterdam: Sense
Publisher.
Ekowati, D. W., Kusumaningtyas, D. I., & Sulistyani, N.,
2017. Ethnomatematica dalam Pembelajaran
Matematika (Pembelajaran Bilangan dengan Media
Batik Madura, Tari Khas Trenggal, dan Tari Khas
Madura). Jurnal Pemikiran Dan Pengembangan SD,
5(2), pp. 716–721.
Fajriyah, E., 2018. Peran Etnomatematika Terkait Konsep
Matematika dalam Mendukung Literasi. In Jurnal
Prisma 1, Prosiding Seminar Nasional Matematika
(pp. 114–119).
Hardiarti, S., 2017. Etnomatematika: Aplikasi Bangun
Datar Segi Empat Pada Candi Muaro Jambi. Jurnal
Aksioma, 8(2).
Marsigit, Setiana, D. S., & Hardiarti, S., 2016.
Pengembangan Pembelajaran Matematika Berbasis
Etnomatematika. Prosiding Seminar Nasional
Etnomatnesia (pp. 20-38).
Maryati, & Prahmana, R. C. I., 2018. Ethnomatematics:
Exploring the Activities of Designing Kebaya Kartini.
Jurnal MaPan: Jurnal Matematika dan Pembelajaran,
6(1), 11–19.
Natsir, M., 2017. Acara Plesiran: Seri Kerajaan Gowa,
Eps 4. In Balai Pelestarian Cagar Budaya Sulawesi
Selatan.
Putri, L., 2017. Eksplorasi Etnomatematika Kesenian
Rebana Sebagai Sumber Belajar Matematika Pada
Jenjang MI. Jurnal Ilmiah”PENDIDIKAN DASAR”,
4(1), 21-31
Turmudi, 2018. Kajian Etnomatematika: Belajar
Matematika Dengan Melibatkan Unsur Budaya.
Prosiding Seminar Nasional Etnomatnesia (pp. 38–
53).
Wahyuni, I., 2016. Eksplorasi Etnomatematika
Masyarakat Pesisir Selatan Kecamatan Puger
Kabupaten Jember. Jurnal Fenomena, 15(2), pp. 225–
238.
Zayyadi, 2017. Eksplorasi Etnomatematika pada Batik
Madura. Jurnal ∑igma, 2(2), 35–40.
Ethnomathematics: The Exploration of Learning Geometry at Fort Rotterdam of Makassar
157
