
The Effect of Leadership and Organizational Climate on Turnover
Intention Mediated by Job Satisfaction
Nancy Natawijaya, PM Budi Haryono, Saparso and Hery Winoto
Master of Management Study Program, Faculty of Economics and Business, Krida Wacana Christian University,
Jakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Leadership, Organizational Climate, Job Satisfaction, Turnover Intention, and 2018.
Abstarct: This research is a quantitative descriptive study that discusses leadership and organizational climonate
whether they affect turnover intention through job satisfaction. The purpose of this study was to analyze the
influence of leadership and organizational climate on turnover intention mediated by job satisfaction. The
research sample is 60 respondents who work for more than 1 year at a Head Office and Warehouse. Data
were collected through questionnaires distributed to selected respondents by purposive random sampling
method. Data analysis technique used is Structural Equation Model (SEM) with SmartPLS program version
3.2.7. Analytical methods use a measurement model (validity and reliability test), structural model (R-
Square), t test, and mediation effect test. Period of research is April 2
nd
- 29
th
, 2018.
1 BACKGROUND
In the current era of technological development,
every company must have a comparative advantage
in order to compete both in the local and
international business world. It is important for the
organization or company to understand what causes
employees to have the intention to look for another
job as an alternative in a different place and choose
to leave the old workplace (turnover intention).
Turnover is defined as the proportion of the
number of members of the organization who are
voluntarily and non-voluntarily leaving the
organization within a certain period of time. This
is generally stated in one year. Turnover should
not be more than 10% per year (Ridlo, 2012).
Turnover volunteers are those who have a reason to
resign. Conversely, non-turnover volunteers must
resign because of decisions made by the company,
such as termination of employment. In general,
turnover volunteers are a measure used to compare
companies with one another.
High turnover rates in companies are often a
problem. Besides taking a lot of time to recruit new
employees, the costs incurred to attract candidates to
apply are not small. The entry and exit of employees
in a company cannot be avoided because it is a
natural thing; even a profitable company goes
through this because the company can get better
employees. The company will be harmed if
employee turnover occurs too often or large in
number.
The following is a table that shows Turnover
Data (TO) 2012 - 2017.
Table 1: Data of Employee Turnover (TO) 2012 – 2017.
Year
Employees
Early in the
Yea
r
In Out
Employees
End in the
Yea
r
TO
(%)
2012 64 31 14 81 19.3
2013 81 18 22 77 27.8
2014 77 18 11 84 13.66
2015 84 7 8 83 9.58
2016 83 2 14 71 18.18
2017 71 6 8 69 11.43
Source: PT Spektrum Krisindo Elektrika (2018)
Based on the above table, the average turnover
rate of PT Spektrum Krisindo Elektrika employees is
over 10% each year, meaning that it is very high.
Turnover intention is influenced by leadership. If
the leadership of a company is good, then the
turnover rate is low. Reduced job satisfaction on
leadership in the company where you work, can
bring up even increase employee turnover intention.
At PT Spektrum Krisindo Elektrika, in 2014 there
Natawijaya, N., Haryono, P., Saparso, . and Winoto, H.
The Effect of Leadership and Organizational Climate on Turnover Intention Mediated by Job Satisfaction.
DOI: 10.5220/0008492002890295
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Entrepreneurship and Business Management (ICEBM Untar 2018), pages 289-295
ISBN: 978-989-758-363-6
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
289

were additional Directors (Project Directors) who
helped develop Project Division. This affects the
turnover intention of employees of PT Spektrum
Krisindo Elektrika. It can be seen from the high
turnover fluctuations from 2013 to 2014.
Turnover intention is also influenced by the
organizational climate. If the organizational climate
of a company is good, then the turnover rate is low.
At PT Spektrum Krisindo Elektrika, in 2012 there
were new additional divisions (Product Support,
Project, and several adjustments on other divisions),
so the number of recruits that year was the highest
compared to the following years. This is also a new
thing for leaders and employees who have been
there before. In 2013 the number of employees who
came out was more than those who entered, because
adapting to the project work system and many new
products was not easy. These difficulties affect the
work atmosphere that creates the organizational
climate, which in turn affects turnover intention.
The more dissatisfied someone is about his/her
job, the stronger the urge to turnover. Conversely,
the more satisfied someone is towards his/her job,
the weaker the urge to turnover (Ritonga et al.,
2013).
Job satisfaction mediates the influence of leadership
and organizational climate on turnover intention. If
employee job satisfaction is achieved with
leadership and a good organizational climate, then
the turnover intention will certainly be lower. At PT
Spektrum Krisindo Elektrika, macro and micro
economic conditions make the leader need to
implement several policies that certainly affect the
job satisfaction of several employees. But
organizational climate is formed quite well, because
good communication is established between
employees.
2 RESEARCH PROBLEM
1. Does Leadership affect Job Satisfaction?
2. Does the Organizational Climate affect Job
Satisfaction?
3. Does Leadership affect Turnover Intention?
4. Does the Organizational Climate affect Turnover
Intention?
5. Does Job Satisfaction affect Turnover Intention?
6. Does Job Satisfaction mediate the influence of
Leadership on Turnover Intention?
7. Does Job Satisfaction mediate the influence of
the Organizational Climate on Turnover
Intention?
3 LITERATURE REVIEW
3.1 Leadership
According to Northouse (2015),
"Leadership is a process whereby an individual
influences a group of individuals to achieve a
common goal".
Which means leadership is the process by which a
person influences a group of individuals to achieve a
common goal.
Another definition states
"
Leadership is the ability to influence a group
toward the achievement of vision or set of goals."
(Robbins and Judge, 2011). Leadership is the
ability to influence a group towards achieving a
vision or set of goals.
The definition of leadership is influence, art, or the
process of influencing someone so that they will try to
achieve the group's goals with willingness and
enthusiasm (Saidi, 2008).
Leaders have four paradigms in looking at and
handling organizations, subordinates, and the world.
These four paradigms are analytical, humanist,
political, and visionary. In addition, there are two
dimensions of leader behavior, namely employee
centered and job centered.
3.2 Organizational Climate
Robbins and Judge (2011) argue that
“The psychological climate is strongly related to the
level of job satisfaction, involvement, commitment,
and individual motivation. A positive work climate
will have an impact on higher customer satisfaction
and good financial performance. Organizational
climate refers to the shared perceptions organizational
members have about their organization and work
environment. This aspect of culture is like team spirit
at the organizational level. … One meta-analysis
found that across dozens of different samples,
psychological climate was strongly related to
individuals’ level of job satisfaction, involvement,
commitment, and motivation. A positive overall
workplace climate has been linked to higher customer
satisfaction and financial performance as well.”
According to Swastha (2008),
"Organizational climate is the quality of the
interaction process in an organization to achieve
the stated goals so that employees will make
assessments about the company and form their
own perceptions about the climate of the
organization in which they work. If employees
perceive that the company applies a regulation that
does not conform to their value, then this condition
ICEBM Untar 2018 - International Conference on Entrepreneurship and Business Management (ICEBM) Untar
290
can lead to job dissatisfaction. Conversely, if
employees perceive that the company applies
regulations that are in line with their values, then
job satisfaction will be created. "
Organizational climate which is also called
organizational atmosphere is a series of work
environments around the workplace that affect the
behavior of a person in carrying out work that
ultimately makes the goals of organization be
quickly achieved (Cahyono, 2014).
Organizational climate is the quality of the
organization's internal environment that is
relatively continuously experienced by members of
the organization, influencing their behavior (Putra
et al, 2014). Organizational climate is a
characteristic that distinguishes one organization
from another which can influence employees so
that they are willing to work willingly without
being forced (Kusmaningtyas, 2013).
3.3 Job Satisfaction
Ridlo (2012) stated that employees who perform
turnover, generally found a reason because they
feel dissatisfied with the company's management,
the quality and nature of the working conditions,
the amount of wages, the feeling of being treated
unfairly by the company and the quality of
inadequate supervision.
Job satisfaction is influenced by a lot of variables,
such as: organizational structure, employee
characteristics, work motivation, work design,
organizational climate, leader behavior or
leadership (Irsan, 2008).
Based on Ahmad etc. (2013),
“Several factors contribute to job satisfaction,
including wages, benefits, achievements,
independence, recognition, communication,
working conditions, work colleagues,
professionalism, organizational climate,
relationships, support from superiors, job security,
work flexibility, and team environment.”
According to Handoko (2011),
“Job satisfaction is a pleasant or unpleasant
emotional state by which employees view their
work. Job satisfaction reflects a person's feelings
about his work. This appears in the positive
attitude of employees towards work and everything
faced in the work environment. The personnel
department or management must always monitor
job satisfaction, spirit at work, complaints, and
other vital personnel issues.”
Job satisfaction can be indicated through the comfort
of work with the support of colleagues, a good
compensation system based on job suitability,
quality of supervision and promotion opportunities.
3.4 Turnover Intention
Based on Dessler (2013), “turnover is the rate at which
employees leave the firm.”
According to Abdillah (2012),
“Turnover intention is a situation where
employees have intentions that are done
consciously to look for another job as an
alternative in a different organization and turnover
is the movement out of workers from the place of
work”
“Turnover intention is also defined as a factor that
mediates the desire and action of stop from the
organization itself” (Glissmeyer et al., 2008).
From some definitions of turnover, in summary,
the definition of turnover is the cessation of
individuals from membership in an organization
within a certain period of time which is not more
than 10% per year (Ridlo, 2012).
3.5 Research Hypothesis
The hypotheses proposed in this study are:
H1: Leadership affects Job Satisfaction.
H2: Organizational Climate affects Job
Satisfaction.
H3: Leadership affects Turnover Intention
H4: Organizational Climate affects Turnover
Intention.
H5: Job Satisfaction affects Turnover Intention.
H6: Job Satisfaction mediates the effect of
Leadership on Turnover Intention.
H7: Job Satisfaction mediates the effect of
Organizational Climate on Turnover Intention.
Figure 1: Construction of Research Path Diagrams, 2018.
4 RESEARCH METHODS
4.1 Conceptual Framework
Based on the background of the problem, literature
The Effect of Leadership and Organizational Climate on Turnover Intention Mediated by Job Satisfaction
291
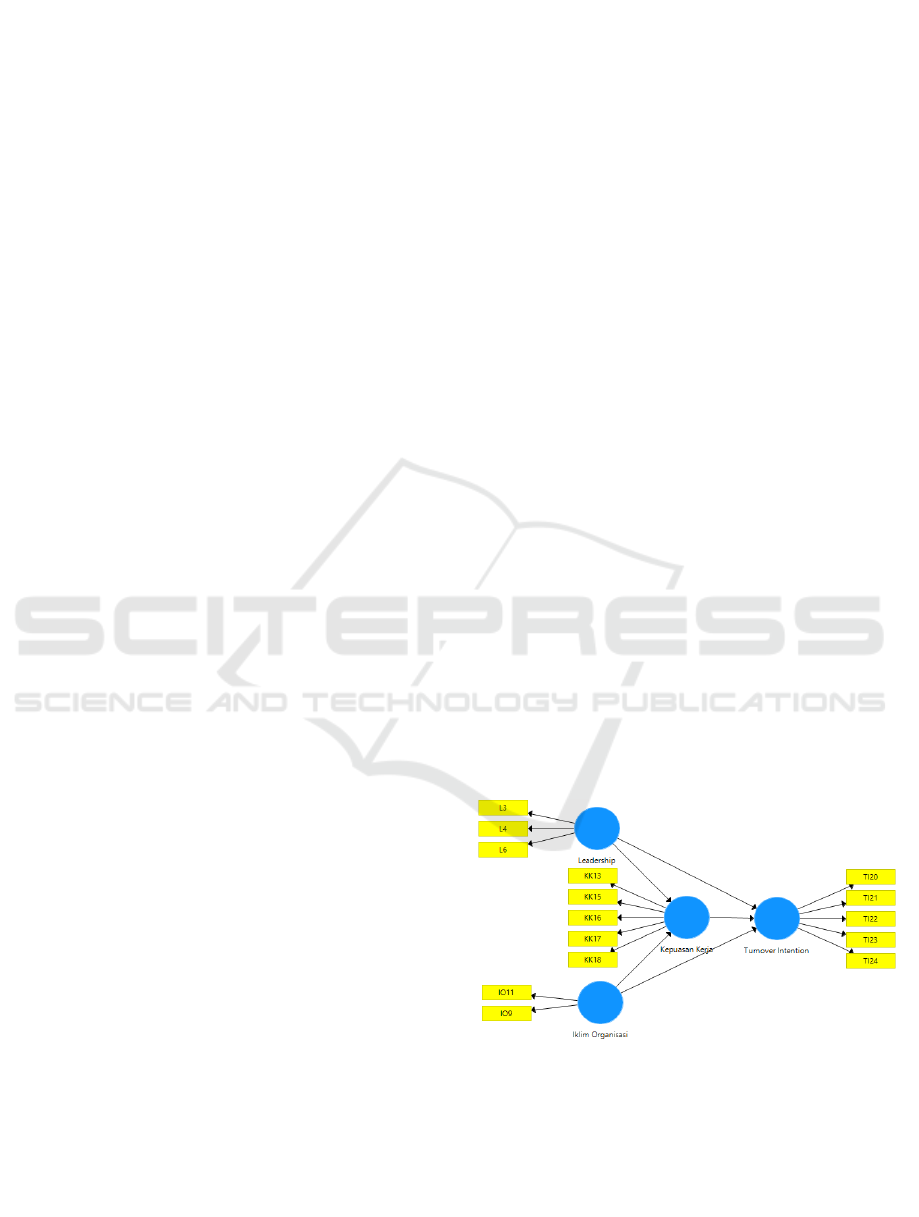
review and previous research that has been
described, the conceptual framework in this study
can be seen in the following figure:
Figure 2: Conceptual Framework.
4.2 Data Collection Technique
Collecting data from the total population in this
study uses primary data sources (Interviews and
Questionnaires) and secondary data sources
(Literature Study). Primary data sources are data
sources that directly provide data to data collectors,
and secondary data sources are sources that do not
directly provide data to data collectors, for example:
through other people or documents.
4.3 Data Analysis Technique
Data analysis techniques in quantitative research
use statistics. This study uses descriptive statistics,
namely statistics used to analyze data by
describing or describing data that has been
collected as it is without intending to make
conclusions that apply to the general or
generalization (Sugiyono, 2016).
The quantitative analysis technique used is the SEM
(Structure Equational Modeling) analysis technique.
The data obtained will be processed statistically
using SmartPLS software (v.3.2.7), as a tool for
processing statistical data professionally and
computerized.
5 RESULTS AND CONCLUSION
After doing research on influence of Leadership
variables and Organizational Climate on Turnover
Intention mediated by Job Satisfaction, we have
found the following results and conclusions.
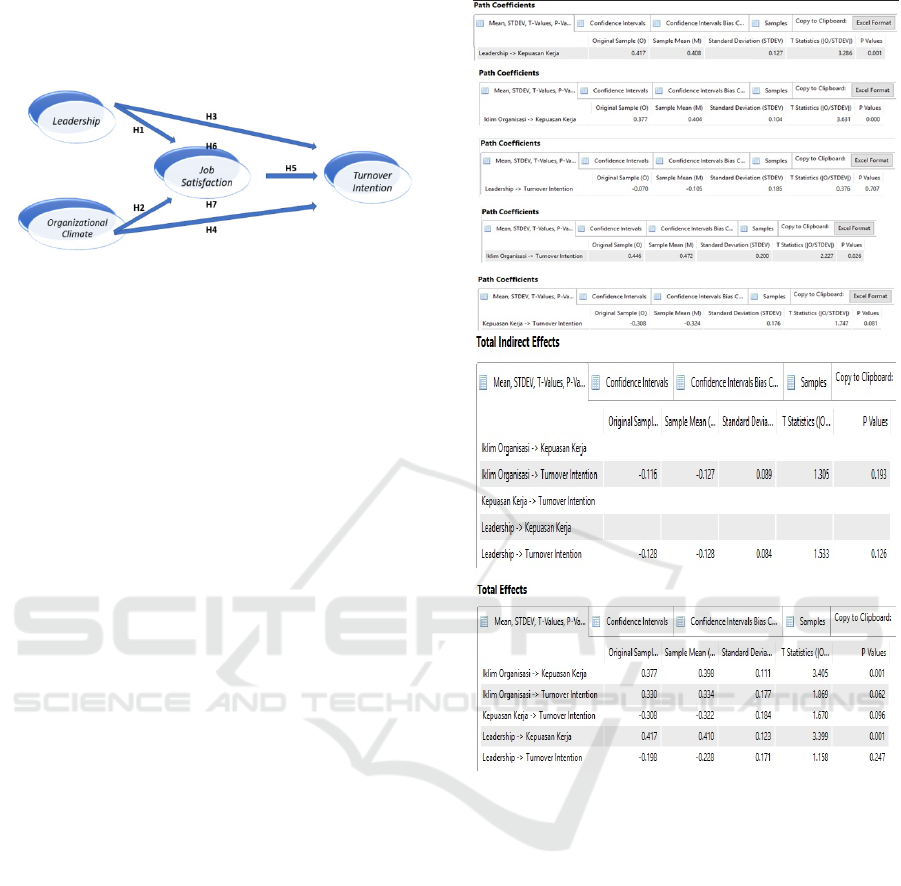
Leadership has a significant positive effect on
job satisfaction. This means that if leadership
improves, then job satisfaction will improve.
Organizational climate has a significant positive
effect on job satisfaction. This means that if the
organizational climate improves, job satisfaction
also improves.
Figure 3: Output of SmartPLS (v.3.2.7), 2018.
Leadership does not significantly affect turnover
intention. This means that there is not enough
evidence that leadership has a negative effect on
turnover intention.
Organizational climate has a significant positive
effect on turnover intention. This means that the
better the existing organizational climate, the
turnover intention will also be better.
Job satisfaction significantly negatively affects
turnover intention. This means the higher the level
of job satisfaction, the smaller the effect on turnover
intention.
Job Satisfaction does not significantly mediate
the negative effect of Leadership on Turnover
Intention. This means that there is not enough
evidence that the variable of job satisfaction
significantly mediates the negative influence of
leadership on turnover intention. The higher the
ICEBM Untar 2018 - International Conference on Entrepreneurship and Business Management (ICEBM) Untar
292

level of satisfaction on leadership leads to the
smaller the effect on turnover intention.
Job Satisfaction significantly mediates the
negative effect of the Organizational Climate on
Turnover Intention. This means that the higher
satisfaction of the organizational climate in the
company, the smaller the effect on turnover
intention.
6 RECOMMENDATION
Leadership has a significant positive effect on job
satisfaction and does not significantly negatively
affect turnover intention. It is recommended that
leaders continue to learn. The way of
communicating to employees needs to be adjusted to
the conditions and background of each, because it
cannot be generalized.
Organizational climate has a significant positive
effect on job satisfaction and turnover intention. It is
recommended for organizational climate to be
maintained and even developed to be even better.
Job satisfaction significantly affects turnover
intention, does not significantly mediate the negative
effect of Leadership on Turnover Intention, and
significantly mediates the negative effect of the
Organizational Climate on Turnover Intention. The
role of Leadership in mediating influence is not yet
visible. It is recommended to pay more attention to
or improve the above indicators so that job
satisfaction can be created.
Turnover Intention will decrease if Job
Satisfaction is achieved. To make employees more
satisfied, the insight of leaders and all employees
needs to be improved and knowledge added
continuously.
The purpose of this study was to analyze the
influence of leadership and organizational climate
towards turnover intention mediated by job
satisfaction.
6.1 For Company
The implication of this study is to become an
inspiration for companies for implementing
leadership and the right organizational climate. This
is done order to prevent the increase of turnover
intention in number and frequency.
All of this is for job and employee satisfaction so
that the company can survive and progress.
Employees should feel fit to work there and the
result is the reduction of labor turnover /
management turnover, which will also create
conducive organizational climate.
6.2 For Further Research
Likewise, in subsequent studies, it is recommended
to add new and distinct indicators and find other
mediating variables that affect turnover intention,
because the R-square in this study is only 14.3%,
which means that 85.7% consists of factors not
included in this study, such as motivation.
It is expected that testing of the influence of
leadership factors, organizational climate, job
satisfaction, or others on turnover intention will be
more reliable and significant. In addition, it is also
expected to enrich the model or conceptual
framework of subsequent research.
To increase the likelihood of getting more
accurate results, it is recommended to conduct
research on larger companies.
REFERENCES
Abdillah, Fuad. 2012. Hubungan Kohevitas Kelompok
Dengan Intensi Turnover Pada Karyawan. Journal of
Social and Industrial Psychology, 1(2):52-58.
Abelson, M.A. 1986. Strategic Management of Turnover:
a model for the health service administrator, Health
Care Manage Review, Vol.11 (2), pp 61-71.
Ahmad, Abd Rahman., Mohd Nazir Mohd Adi., Haris Md
Noor., Abdul Ghafar Abdul Rahman., & Tan
Yushuang. 2013. The Influence of Leadership Style on
Job Satisfaction among Nurses. Asian Social Science,
9 (9):19112025.
Amri, Ulil, Agustina M., and Steven Riyanto. 2017.
Pengaruh Kepuasan Kerja, Stres Kerja, dan Komitmen
Organisasi terhadap Turnover Intention pada Head
Office PT. Thamrin Brothers Palembang. Jurnal
Kompetitif, Vol.6 No. 1 Ed. Januari – Juli.
Ardana, Komang, Ni Wayan Mujiati, dan Anak Agung
Ayu Sriathi. 2008. Perilaku Keorganisasian. Cetakan
Pertama. Yogyakarta: Graha Ilmu.
Brahmasari, Ida Ayu and Agus Suprayetno. 2008.
Pengaruh Motivasi Kerja, Kepemimpinan dan Budaya
Organisasi Terhadap Kepuasan Kerja Karyawan serta
Dampaknya pada Kinerja Perusahaan (Studi kasus
pada PT. Pei Hai International Wiratama Indonesia).
Jurnal Manajemen dan Kewirausahaan, Vol.10, No. 2,
September: 124-135.
Awang, Zainudin, Junaidah Hanim Ahmad, and Nazmi
Mohamed Zin. 2010. Modelling Job Satisfaction And
Work Commitment Among Lecturers: A Case Of
UiTM Kelantan. Journal of Statistical Modelling and
Analytics, 1(2):45-59.
Cahyono, Eko Aprihadi. 2014. Pengaruh Gaya
Kepemimpinan, Motivasi Kerja dan Iklim Organisasi
Terhadap Prestasi Kerja Karyawan Bagian
The Effect of Leadership and Organizational Climate on Turnover Intention Mediated by Job Satisfaction
293

Engineering Pada PT. Arabikatama Khatulistiwa
Fishing Industry Denpasar. E-Jurnal Manajemen
Universitas Udayana, 3(9):2784-2798.
Dessler, Gary. 2013. Human Resource Management.
Thirteenth Edition. England: Pearson Education
Limited.
Dewi, Kadek Sintha. 2013. Pengaruh Gaya
Kepemimpinan Transformasional Terhadap Kepuasan
Kerja Karyawan dan Komitmen Organisasi pada PT.
KPM. Jurnal Manajemen, Strategi Bisnis, dan
Kewirausahaan Vol. 7, No. 2, Agustus 2013: 116-125.
Diharjo, Wulandari Puspa and Khuzaini. 2017. Pengaruh
Kepemimpinan dan Learning Organization Terhadap
Kepuasan Kerja dan Turnover Intentions Karyawan.
Jurnal Ilmu dan Riset Manajemen, Sekolah Tinggi
Ilmu Ekonomi Indonesia (STIESIA) Surabaya,
Volume 6, Nomor 4, April 2017 ISSN : 2461-0593.
Eslami, Javad and Davood Gharakhani. 2012.
Organizational Commitment and Job Satisfaction.
ARPN Journal of Science and Technology, 2(2):85-
91.
Ghozali, Imam. 2011. Aplikasi Multivariate dengan
Program IBM SPSS 19, BP Undip: Semarang.
Ghozali, Imam dan Hengky Latan. 2015. Partial Least
Square Konsep, Teknik dan Aplikasi Menggunakan
Program SmartPLS 3.0 Untuk Penelitian Empiris.
Semarang: Badan Penerbit Universitas Diponegoro,
ISBN: 979.704.300.2.
Glissmeyer, M., Bishop J. W., and Fass, R. D. 2008. Role
conflict, role ambiguity and intention to quit the
organization: The case of law enforcement. Academy
of Management Journal, 40(1):82-111.
Handoko, T. Hani. 2011. Manajemen Personalia dan
Sumber Daya Manusia. Edisi ke 14. Yogyakarta:
BPFE.
Irsan. 2008. Pengaruh Kepemimpinan, Disain Pekerjaan,
dan Iklim Organisasi Terhadap Kepuasan Kerja
Tenaga Penunjang Akademik di Universitas Negeri
Medan. Jurnal Manajemen Pendidikan, 363-376.
Kumar, Naresh, and Vandana Singh. 2011. Job
Satisfaction and its Correlates. International Journal of
Research in Economics & Social Sciences, 1(2):11-24.
Kusmaningtyas, Amiartuti. 2013. Pengaruh Iklim
Organisasi dan Kepemimpinan Terhadap Kepuasan
Kerja Karyawan PT. Persada Jaya Indonesia di
Kabupaten Sidoarjo. Jurnal Ekonomi dan Manajemen
Bisnis, 4(1):107120.
Matalia. 2012. Pengaruh Kepemimpinan Dan Hubungan
Kerja Terhadap Pengembangan Karir Dan Kepuasan
Kerja Pegawai. Jurnal Manajemen, Strategi Bisnis dan
Kewirausahaan, 6(2):185-194.
Meilano, Muhammad Reza Anugrah and Rini Nugraheni.
2017. Analisis Pengaruh Lingkungan Kerja dan
Kompensasi terhadap Turnover Intention dengan
Kepuasan Kerja sebagai Variabel Intervening (Studi
pada Karyawan Laksana Baru Swalayan Majenang).
Universitas Diponegoro. Semarang.
Northouse, Peter G. 2015. Introduction to Leadership:
concepts and practice. Third Edition. Western
Michigan University. United Kingdom: SAGE
Publications, Inc.
Pepe, Michael. 2010. The Impact Of Extrinsic
Motivational Dissatifiers On Employee Level Of Job
Satisfaction And Commitment Resulting In The Intent
To Turnover. Journal of Business & Economics
Research, 8(9):99108.
Putra, Agung Utomo, Endang Siti Astuti and Djamhur
Hamid. 2014. Pengaruh Iklim Organisasi terhadap
Eustress dan Kepuasan Kerja Karyawan (Studi Pada
Karyawan Perum Jasa Tirta I Malang Jawa Timur).
Jurnal Administrasi Bisnis, 14(1):1-10.
Putra, Kadek Bayu Satrio Maha and I Gusti Made
Suwandana. 2017. Pengaruh Iklim Organisasi terhadap
Turnover Intention dengan Kepuasan Kerja sebagai
Variabel Mediasi. E-Jurnal Manajemen Unud, Vol. 6,
No. 5: 2417-2444.
Ridlo, Ilham Akhsanu. 2012. Turn Over Karyawan
“Kajian Literatur”, Upload Pertama, Surabaya:
PHMovement Publications.
Ritonga Ferdiansyah, Fitri Apriliyani Zein. 2013.
Hubungan Antara Gaya Kepemimpinan, Kepuasan
Kerja Dengan Intensi Keluar Auditor Yang Bekerja Di
Kantor Akuntan Publik. Journal and Proceeding Feb
Unsoed. Vol 3 No 1.
Robbins, Stephen P. and Timothy A. Judge. 2011.
Organizational Behavior. Global Edition. Fourteenth
Edition. New Jersey 07458: Pearson Education, Inc.,
publishing as Prentice Hall.
Saidi, Wahyu and Sofia Hartati. 2008. Kewirausahaan.
Jakarta: Enno Media.
Saklit, I Wayan. 2017, Pengaruh Gaya Kepemimpinan dan
Pengembangan Karir Terhadap Intensi Turnover:
Kepuasan Kerja Sebagai Mediator. Jurnal Manajemen,
Volume XXI, No. 03, Oktober 2017: 472-490.
Soetopo, Hendyat. 2010. Perilaku Organisasi; Teori dan
Praktek di Bidang Pendidikan. Bandung: Remaja
Rosdakarya.
Sugiyono. 2016. Metodologi Penelitian Kuantitatif,
Kualitatif, dan R&D. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Suhanto, Edi. 2009. Pengaruh Stres Kerja dan Iklim
Organisasi terhadap Turnover Intention dengan
Kepuasan Kerja sebagai Variable Intervening (Studi di
Bank Internasional Indonesia). Universitas
Diponegoro. Semarang.
Sutanto, Eddy M., and Carin Gunawan. 2013. Kepuasan
Kerja, Komitmen Organisasional dan Turnover
Intention. Jurnal Mitra Ekonomi dan Manajemen
Bisnis, 4(1):76-88.
Swastha, Basu. 2008. Manajemen Pemasaran Modern.
Yogyakarta: Liberty.
Teh, Goi Mei. 2014. Impact of Organizational Climate on
Intentions to Leave and Job Satisfaction. World
Journal of Management, 5(2):14 – 24.
Zhao, Erdong and Liwei Liu. 2010. Comments of
Development of Job Embeddednes About Study to
Turnover and Exploration Into Application in
Enterprises. Asian Social Science, 6(6):63-64.
ICEBM Untar 2018 - International Conference on Entrepreneurship and Business Management (ICEBM) Untar
294

Umar, Husein. 2008. Desain Penelitian MSDM dan
Perilaku Karyawan. Jakarta: Rajawali Pers, PT
RajaGrafindo Persada.
Undang-Undang No. 13 Tahun 2003 Tentang:
Ketenagakerjaan, Pasal 68 “Pengusaha dilarang
mempekerjakan anak”.
The Effect of Leadership and Organizational Climate on Turnover Intention Mediated by Job Satisfaction
295
