
Is Financial Distress Cost Important for Determining Firm
Performance ?
Estu Widarwati
1
, Dewi Sartika
2
1
ISTIE Sutaatmadja Subang, Jl. Otista 76, Subang, Indonesia
2
Akademi Sekretari dan Manajemen (ASMI)Persada Bunda, Jl. Diponegoro No. 42, Riau, Indonesia
Keywords: Financial Distress Cost, Firm Performance, Sales Growth, Stock Return.
Abstract: The global financial crisis provides the importance in developing model to monitor, identify and asses
potential risks that can threat business sustainability. Financial Distress Cost (FDC) seems to be one of early
signal about early risk of decreasing of firm performance such as sales growth and stock return. Futhermore
it give early signal to firm reducing the loss possibility before it lead to firm’s bankruptcy. This research aims
to explain the evidence of FDC in Indonesia’s industry and its impact to firm performance. The data use
financial reports of 107 firms of manufacture industry listed in Indonesia Stock Exchange (IDX) for 2011 –
2017 and all analyzed using panel regression for presenting FDC’s impact. The descriptive analysis show that
Indonesia’s manufacture industry have higher FDC and lower sales growth after based year of crisis. There
is a negative impact of FDC to firm’s sales growth. The result proposes that FDC can be used as an early
determinant for reducing loss possibility of firm’s market share.
1 INTRODUCTION
Environmental changes become an important part
of firm’s business strategies for managing the
performance. Economic expansion will create better
operational activity for better growth opportunity, but
recession may bring a probability of failing and
liquidation of firm that may caused by raising of cost
from distressed condition (John, 1993). The global
crisis in 2013 have still impacted to business stability
in some countries of Asia. Nikkei Releases on
December 2016 reported a decline in new foreign
business both volume and export since November
2015 where client demand weakened. Then leading
the ASEAN’s manufacturing industries to buy fewer
inputs in a third week of December and causing pre-
production stocks to fall in 16 last month. Other fact
in Indonesia for period 2014-2016, Indonesia Stock
Exchange (IDX) suspended 28 firms in their trading
stock caused by several things such as disruption of
company's sustainability, no income, and other
business management issues.
The uncertainty of this economic improvement
makes firm have greater pressure opportunity in
industrial competition. Investment activities make a
high probability of economic uncertainty risk which
will affect firm’s financial performance. A firm have
potential decreasing of it when management have
been unable to anticipate the impacts. This
phenomenon referred as financial distress that occurs
before liquidation (John, 1993).
The financial distress can occur in all industries
and have been an early signal of firm bankruptcy such
as in service (Smith and Graves, 2005) and
manufacture (Smith and Liou,2007). In distressed
firm, there is a cost incurred called by Financial
Distress Cost (FDC) and it is suffered by the firm as
impact of weakening of financial position or business
disruption (Bulot et al, 2017).
The firms tend to increase following cash flow
realization which may be lower in economic crisis
(Hann et al, 2013). Then that will damage firm
performance such as loss of market share and also
cause inefficiency. Opler and Titman (1994) found a
loss of firm’s market share was caused by distress
period of highly leveraged firm.
The importance of FDC still receive less attention
in its consequency to firm performance. In previous
studies, some researchers have been interesting to
analysis the factors of it and there is many different
estimation for measuring such growth of invested
capital (Chen and Marvile, 1999), and firm’s debt
(Korteweg, 2007). Opler and Titman (1994) captured
540
Widarwati, E. and Sartika, D.
Is Financial Distress Cost Important For Determining Firm Performance.
DOI: 10.5220/0008442305400545
In Proceedings of the 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference (SEABC 2018), pages 540-545
ISBN: 978-989-758-387-2
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

financial distress debt which based the indicators
assuming that the higher firms leverage will make
higher it. Other studies such Pindado and Rodrigues
(2005) and Bulot et al (2017) also captured
opportunity cost that refer to the cost lowered as a
result of decreasing financial conditions. This loss is
calculated as the difference between firm sales
growth and the sectors of sales growth. A positive
result will demonstrate that firm bear opportunity loss
and underperform as industry performance
comparison in term of sales growth.
The paper gives an insight when financial distress
occurs, mostly a pressure is directed toward firm
performance. In distressed firm, there is an indication
that management has an option to reduce budgets for
remaining of competitive because it may affect their
cost and this decision can damage its performance. It
captured that industry’s FDC in Indonesia
descriptively based distress period in Opler and
Titman’s study. The argumentation that the level of
firm’s financial distress is different between before
and after occure global crises in 2013, so it resulted
FDC and performance difference. Furthermore, for
completing our descriptive analysis, the FDC’s data
test of all sample firms to performance. Using
Pindado and Rodrigues’s model measurement
through opportunity loss, mean opportunity cost
which refer FDC and then tested the impact to firm
performance. It also estimated that firm leverage,
size, and firm age have influenced to firm
performance. This study shows that opportunity loss
as Financial Distress Cost’s proxy impact to firm
performance .
This paper provides more attention on the matters
that have not fully described but it is critical in
financial distress research that is FDC and its
implication to firm performance. Refering to previous
researchs, loosing opportunity as FDC’s
measurement, and firm performance proxied by sales
growth and stock return. The argumentation using
both of them as firm performance indicators can
reflect financial distress consequency in resource
management, and also in the effort to describe its link
to FDC. Furthermore, this study describes
descriptively about the difference of firm
performance in two years before based year of
occured global crisis in 2013 and four years after it.
The hyphotesis tested FDC have negative affect to
firm performance by using some control variables
such as firm size, leverage, and firm age in the
regression model of all samples are expected more
clarify the FDC’s impact to performance.
For easier explanation, we manage the systematic
of this paper as below: part 2 describes literature
review, then part 3 explains the data, including
variables, also empirical model. Part 4 talks about
descriptive analysis and regression result, and finally
part 5 discussion that includes the limitation and
suggestion.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Financial Distress Cost
In finance, a firm that use more debt in its
operation will get more risk of financial distress.
When firm have difficulty making payments to
creditors, it categorized as distressed firm. The firm
should pay some costs that associated with financial
distress such indirect cost, cost of capital, and
bankruptcy cost.
Financial Distress Cost (FDC) is a special
argument in main financial problems of a firm that
related with capital structure, firm valuation, and risk
management. If firm takes more debt, it give more
risk for firm being unable to meet the creditor’s
obligation. Previous research argue that FDC only
occurs in small percentage and temporary but on the
other side, there are some results find FDC is
significant impact to firm (Altman and Hotchkiss,
2006).
FDC appears as result of costs that occur when
firm unable to fulfil its responsibility because
financial decreasing (Altman and Hotchkiss, 2006).
The firm have difficulty in payment to its creditors
may cause by several reasons, such as decreasing of
profitability which Earning Before Interest and Tax
Depreciation of Assets (EBITDA) is lower than
financial costs incurred (Opler and Titman, 1994) and
poor management (Venkataramana et al., 2012).
Some of previous studies employ different
estimations in assessing FDC, such using firm
liabilities (Korteweg, 2007), and loose opportunity
(Pindado and Rodrigues, 2005). This study uses sales
as part to evaluates FDC according Pindado and
Rodrigues (2005) and Bulot et al. (2017), because it
less affected by firm characteristic According In
context of Indonesian firms, management tends more
attention to internal factors such as human labor and
sales growth. Therefore, sales used in measuring FDC
which opportunity loss or profit can be detected as
activities output. It calculated by comparison sales
growth and sales sector.
However, the FDC discussion is important to
understand the impact of control function for their
strategic decisions in improvement firm performance.
It may lead to bankruptcy (Altman and Hotckiness,
Is Financial Distress Cost Important For Determining Firm Performance
541

2006), so this paper assumes that FDC costs that
occurs as result of financial decresing which will
impact to market share loss, growth opportunity, and
firm return, therefore causes firm inability to fulfill its
responsibilities.
2.2 Firm Performance
The firm achievement in certain period reflects
the level of its performance. Using financial
statements, management and investors can analyze
firm performance and evaluate it. The information of
firm’s financial performance needed for getting better
investment decision making, and risk management.
Financial distress risk is one of things that firm should
needs to pay attention to. As Opler and Titman (1994)
states that financial distress is costly. The market
share decline impacts to firm income, therefore sales
growth be an important ratio to measure firm ability
for maintaining its position in economic and
industrial growth. In addition, firm performance in
distress conditions also impact to rate of return in the
market. Some results show evidence that firm earns
lower return when there is decreasing financial such
finding of Lamont et al. (2001) and Campbell et al
(2008). On the other side, some research also find that
firm ability of environment adapting make financial
distress for firm but it unrelated impact to rate of
return. The gap among these findings show there is an
optimum implementation of strategy that FDC is
managable well by effectively ways and not the
contrary, increasing high cost which may decline firm
performance.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 The Data
This research analyzes financial report of firms
listed in IDX of 2011-2017. The samples are 107
manufacture firms with total of 749 observations in
Indonsia’s industry covering the subsectors of basic
processing and chemical; pharmacy; textile and
garment; miscellaneous industries; automotive; cable
and electricity; cosmetics; and consumers goods. The
data consist of FDC, sales growth, and stock return
processed using panel data regression. In order to
attain required sample, firms observation having zero
sales and also merger firms are excluded.
FDC used as independent variable which
measured by opportunity loss following Pindado and
Rodrigues (2005) and Bulot et al (2017). Then
dependent variables are firm performance which
proxied by sales growth and stock return (Opler and
Titman,1994). Furthermore, we take firm size,
leverage, and firm age as variable control in this
research.
First, firms analyzed descriptively about their
FDC, sales growth, and stock return over five-year
periods between 2011 and 2017. It described
previously that distressed firm have market shares
loss possibility that impacted by uncertainty
economic such global krisis. Then dividing period in
two group are before and after crisis in 2013. As
known, there is Yunani’s crisis also impacted to many
countries including Indonesia.
Second, the link between FDC and firm
performance tested without crisis period because the
insight of this paper that financial distress make a
pressure to firm performance only. Then capturing
the differences during crisis in Indonesia
descriptively and focusing in FDC’s impact to firm
performance. Therefore it is not exploring the other
determinants. After that proposing regression model
in which is influenced by FDC formula as below:
SG
it
= β
0
+β
1
FDC
it
+ LEV
it
+ SIZE
it
+AGE
it
+
it
(1)
SR
it
= β
0
+β
1
FDC
it
+ LEV
it
+ SIZE
it
+AGE
it
+
it
(2)
SG
it
represents firm performance which can be
measured by sales growth and SR
it
is stock return as
another proxy of firm return, and FDC
it
measured
using opportunity loss as comparison sales growth of
firm and sales sector, LEV
it
is leverage of firm
measured by total debt to total assets, SIZE
it
is firm
size measured using ln assets, and AGE
it
is firm age.
4 RESULT AND ANALYSIS
4.1 Descriptive Statistics
Table 1 shows descriptive statistic results for each
variable in all samples of manufacture sector. The
lowest sales growth is 3,34% and the highest FDC is
21,23%. The statistics for each observation year for
all sample of firms in which the lowest average of
sales growth and stock return for overall samples are
-26,6% in 2017 and -3,45% in 2013 and FDC as
independent variable is the highest average of overall
samples in 2017 with 26,6%.
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
542
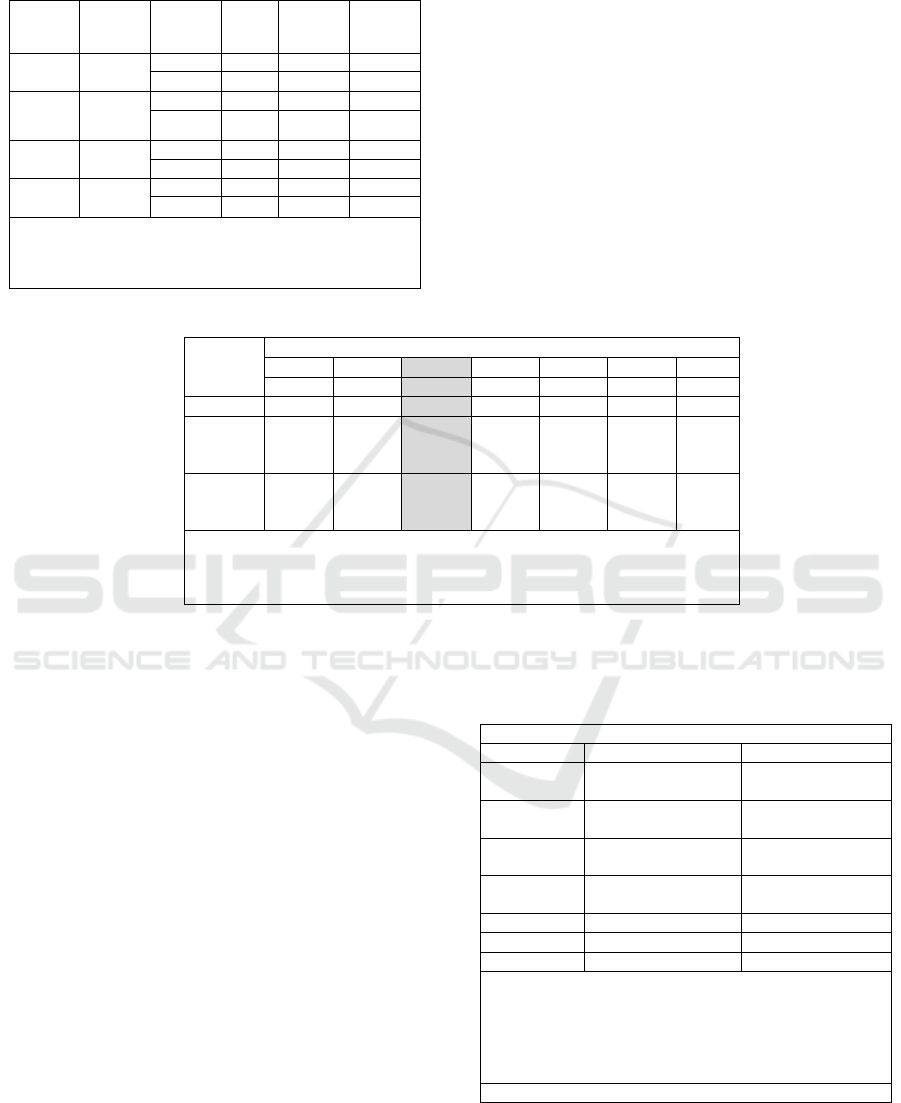
Table 1: Descriptive Statistics Manufacture Sector
Sample
Firms
Statistic
FDC
Sales
Growth
Stock
Return
Full
Sample
107
Mean
0.0478
-0.0312
0.1967
Stdev
1.0944
1.0957
1.1641
Basic
&Chemi
cal
44
Mean
0.1184
-0.1017
0.1972
Stdev
1.4895
1.4910
1.505
Aneka
Industry
34
Mean
-0.0168
0.0334
0.1788
Stdev
0.2249
0.2263
0.7688
Consum
ption
29
Mean
-0.0311
0.0478
0.2123
Stdev
0.4974
0.4986
0.5419
This table presents the descriptive statistic of variables in which FDC
is Financial Distress Cost that measure by opportunity loss as
comparison sales growth of firm and sales growth in its sector. (%),
Sales growth and stock return are proxy of firm performance (%)
To provide background for the remainder of the
analysis, tabel 2 presents the result of all samples
before, during, and after the base year of global crisis
in 2013 for FDC, sales growth, and stock return.
Apart from showing how firms perform and the table
also shows how their performance changes over time.
This study finds that manufacture industry in
Indonesia have highest of FDC in 2017 then firms
take down in sales growth level since global crisis’s
year until four year after. It is an early indication that
firms may reduce budgets for remaining of
competitive when economic crisis and it may affect
their cost then it damage firms performance.
Tabel 2: Comparation the average of FDC and Firm Performance of all samples in 2011-2017
4.2 Regression
Against this background, the remainder of this
study investigates the impact of FDC to firm
performance. We employ panel least square
regression to explain these, controlling for a number
factors such firm size, leverage, and firm age that
might help to explain it.
The two dependent variables used to capture FDC
are sales growth, and stock return. Cash flow
problems of distressed firm may also retard firm
competitiveness in product market for various
reasons. Creditors may be unwilling to extend credit
to them fearing that they may go bankrupt before
clearing their debts. Distressed firm may be unable to
take advantage of cash discounts, and customers may
be reluctant to buy durable goods from weak firms,
which might not be in business to provide after sales
service. Decreasing of obligation fulfilment ability
due to increase FDC that lead to return decline for
investors.
Table 3: Regression Result of Financial Distress Cost and
Firm Performance
Dependent Variabel ; Firm Performance
Model 1 - SG
Model 2 - ST
FDC
-0,202*
[0,000]
-0,225
[0,5730]
LEV
-0,020
[0,1741]
0,1493**
[0,1001]
SIZE
0,0061
[0,3132]
-0.0634
[0,3095]
AGE
0,0004
[0,1475]
0,000018
[0,9945]
Method
Panel (LS)
Panel (RE)
Observations
749
747
R-squared
0,052
0,005
This table presents the result of LS on SG and SR. SG is sales
growth and SR is stock return in percent, which FDC is Financial
Distress Cost that measure by opportunity loss as comparison
sales growth of firm and sales growth in its sector (%), LEV is
measured by total debt to total asset, SIZE is firm size computed
from total asset ln TA, and AGE is firm age.
*significant at 1% **significant at 10%
As expected, this study finds negative and
significant on the impact of FDC to sales growth.
Firms with higher FDC decrease sales growth
meaning firm lose more market share. This result
Variables
Research Periode
2011
2012
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
t-2
t-1
T
t+1
t+2
t+3
t+4
FDC
-0.0050
-0.0300
-0.1292
-0.0198
0.1232
0.1296
0.266
Sales
Growth
SG
0.1216
0.0795
0.0796
0.0198
-0.123
-0.1296
-0.266
Stock
Return
SR
0.2420
0.2969
-0.0345
0.1324
-0.158
0.6547
0.2425
This table presents the descriptive statistic of variables in which FDC is Financial
Distress Cost that measure opportunity loss as comparison sales growth of firm and
sales growth in its sector (%), Sales growth and stock return are firm performance
proxies (%)
Is Financial Distress Cost Important For Determining Firm Performance
543

support the hypothesis. As presented in Table 3, on
contrast, stock return not impacted by FDC although
it is significant by using size and firm age as control
variables. This finding shows an important role of
FDC as early signal for better managing of firm
performance.
This study also finds that firm size and firm age
has no role in controlling relation between FDC and
firm performance, but leverage level does. It
supported the finding of Opler and Titman (1994) that
leverage caused loss of firm’s market share.
5 CONCLUSION
The conceptualization of FDC shows that
Financial Distress Cost may appear as decreasing of
firm’s financial condition caused by economic crisis.
This paper focuses on explain the evidence of FDC in
Indonesia industries and its impact to firm
performance. This analysis proposes that sales growth
and stock return as firm performance proxies may be
better capture the impact of FDCs.
Firstly, this paper describes that there is difference
of firm performance before, during, and after the base
year of global crisis in 2013. From the descriptive
analysis, it is known that average FDC before the
crisis occurs lower with average sales growth is
greater than after the crisis occurred. This is in line
with the statement of Opler and Titman (1994) that
when a crisis occurs, there will be a loss of market
share in terms of lower sales growth.
Secondly, we examine the effect of FDC to firm
performance in all research periods with all samples.
The result show negative effect of FDC to sales
growth, but not find the FDC’s impact to stock return.
This is assumed due to the different Indonesian
industry characteristics that tend to be based on the
cost of human labor as the dominant determinant of
corporate costs. In addition, Indonesian industrial
investors may also have greater external
considerations than the internal factors of the
company, so it is necessary to explore further the link
between FDC and stock return.
Other result of test also finds evidence that firm
age has been as better controller on FDC’s impact to
firm performance, but none in firm size dan firm age.
Pindado and Rodrigues (2005) and Bulot et al (2017)
find the significant role of firm size in FDC. This
inconsistency finding needed to be explore more in
next research.
These all results have a theory implication that
enriching evidence of the FDC’s as one of firm
performance determinants. Furthermore, we also
reveals the relationship between leverage level on
management risk decision in improvement of
business performance. This study also offers an
practical implication for firms that the FDC’s role is
important as determinant of firm performance
especially in crisis period. Therefore, a firm can
choose preventive strategy for managing its growth
opportunity through FDC’s controling so the
decreasing probability of firm performance can be
minimized.
As limitation of this study, we only analyse
descriptively the differences of FDC and firm
performance before during, and after crisis base year
without examine it in regression. Then we use only
one proxy of FDC’s which measured based of
Pindado’s research. Those make this study’s result
can not generalized and we suggest future research
will explore the relation of FDC and firm
performance using a regression model which include
dummy function of FDCs difference in period
categories of crisis, so that firm performance can
reflected at different level of industry and research
period. Furthermore, next research also can combine
many proxies of FDC and use other proxies of firm
performance such Tobin’s Q, so its will explain better
about the impact FDC on firm performance.
Acknowledgements
We give appreciate thank to the anonymous
referees and all collegas in our affiliations for their
helpful and support in finishing this research. This
paper will be presented at 4th Sriwijaya Economics,
Accountings, and Business Conference (SEABC
2018) held in Palembang (Indonesia), November 8-9,
2018.
REFERENCES
Altman, E.I., Hotchkiss. 2006. Corporate Financial
Distress and Bankruptcy: Predict and Avoid
Bankruptcy, Analyze and Invest In Distressed Debt. 3rd
Edition. Wiley Finance: North America.
Bulot, N., Salamudin, N., Aziz, R.A. 2017. The Size
of Indirect Financial Distress Costs : Which Variable is
Reliable Important ? Jurnal Intelek, 12, 1, 12-29
Campbell, J.Y., Hilscher, J., Szilagyi, J. 2008. In Search of
Distress Risk. The Journal of Finance, 68, 6, 2899-
2939.
Chen, G.M., Marville, L.J. 1999. An Analysis The
Underreported Magnitue of the Indirect Financial
Distress Cost, Review of Quantitative Finance and
Accounting, 12, 277-293
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
544

Hann, R.N., Ognea, M., Ozbas, O. 2013. Corporate
Diversification and the Cost of Capital. The Journal of
Finance, 68, 5,1961-1999
John, T.A. 1993. Accounting Measures of Corporate
Liquidity, Leverage, adn Costs of Financial Distress,
22, 3, 91-100.
Korteweg, A.G. 2007. Financial Distress Cost across
Industries. www.ssrn.com.
Lamont, O., Polk, C., Saa-Requejo J. 2001. Financial
Constraints and Stock Returns. Review of Financial
Studies, 14, 2, 529-554.
Opler, T.C., Titman, S. 1994. Financial Distress and
Corporate Performance. The Journal of Finance, 49, 3,
1015–1040.
Pindado, J., Rodrigues, L. 2005. Determinants of Financial
Distress Costs. Swiss Society for Financial Market
Research, 19, 4, 343–359.
Smith, M., Graves, C. 2005. Corporate Turnaround and
Financial Distress. Managerial Auditing Journal, 20, 3,
304 – 320.
Smith, M., Liou, D.K. 2007. Industrial Sector and Financial
Distress. Managerial Auditing Journal, 22, 4, 376 –
391.
Venkataramana, N., Azash, S.Md., Ramakrisnaiah K.
2012. Financial Performance and Predicting the Risk of
Bankrupcty: A Case of Selected Cement Companies in
India. International Journal Of Public Administration
and Management Research (IJPAMR), 1, 1, 40-56
Is Financial Distress Cost Important For Determining Firm Performance
545
