
An Antecedent of E-Invoice User Behavior with Behavioral
Intention as an Intervening Variable
Maya Qodarsi, Syamsurijal A. Kadir and Luk Luk Fuadah
Sriwijaya University, Palembang, Indonesia
Keywords: Performance Expectacy, Business Expectacy, Behavioral Intention, User Behavior, E-Invoice, Tax payers
Abstract: E-Invoice is the development of the information and public administration system of the tax sector that has
only been prevalent in the last 3 years in 2018. The objective of this study is to explore the factors that
might motivate the citizens to adopt the public service of e-Invoice provided by the Indonesian government.
The insight of this study will help the government to plan public services effectively. This study surveyed
282 respondents living in the South Sumatra region, especially taxpayers registered at the Tax Services
Office (TSO) of Palembang. This study uses an analysis of exploratory factor that matches the validity of
the theoretical model on the data collected, a confirmation analysis to extract latent factors and both
multiple regression and Structural Equation Modeling - Partial Least Square to test the research hypothesis.
The finding of this study reveals that performance expectacy is the strongest predictor of the behavioral
intention to use e-Invoice services and greatly influences the users’ behavior. Business expectations do not
affect the behavioral intentions and the behaviors of the users. And the behavioral intentions significantly
affect the user behaviors. The practical implication is that when the government knows the main factors that
influence the adoption of e-Invoice services in Indonesia, it can maximize its profits on the investment in
ICT infrastructure by providing efficient services that can be adopted by the citizens. For the future study, it
is recommended that the area of research object be expanded in the area of the Directorate General of Tax of
the Ministry of Finance.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the taxation sector, the state’s revenues cannot be
separated from the system used by the government
in collecting taxes. Currently there are 3 systems
applied in tax collection, namely official assessment
system, self assessment system, and with holding tax
system. The current tax payment system is based on
a tax collection system that gives authority, trust and
responsibility to the Taxpayers to calculate, to pay,
and to report on their own the amount of tax to be
paid, known as a self assessment system. One of the
Indonesian tax collections is Value Added Tax
(VAT) imposed on each production process and is
charged directly to the final buyer/consumer. At
present, each VAT imposition is provided with a
proof in the form of a tax invoice as stipulated in the
Indonesian Act No.42 of the Year 2009 as a proof of
tax collection and also as a means to credit input
taxes. According to the Indonesian Act No. 28 of the
Year 2007 the tax invoice must be filled in correctly,
completely and clearly because a slight error in the
issuance of a tax invoice will be subject to a fine of
2% per error so that the input tax invoice can be
credited.
For this reason, the government launched an e-
invoice information system as a means of issuing tax
invoices for taxable entrepreneurs, the use of e-
invoices as a means of issuing tax invoices that are
integrated with the DJP portal so that every time the
tax invoice issuance will be validated by the central
DJP, PKP will avoid mistakes according to the
Indonesian Act No. 28 of the Year 2007, the
Government will easily find cases of Invalid Tax
Invoice, Tax Invoice based on non-actual
transactions, and the Entrepreneurs who have not
been confirmed as PKP cannot issue invoices.
However, behind all the advances in
technology, innovation and ease in the field of e-
invoice applications, software applications
themselves face problems related to the adoption at
the user or taxpayer level. The development of
Information Technology does not necessarily
positively influence the adoption of the software
itself at the user level. Related to the low level of
adoption of software technology, some previous
394
Qodarsi, M., A. Kadir, S. and Fuadah, L.
An Antecedent of E-Invoice User Behavior with Behavioral Intention as an Intervening Variable.
DOI: 10.5220/0008440603940401
In Proceedings of the 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference (SEABC 2018), pages 394-401
ISBN: 978-989-758-387-2
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
researchers have explored social and psychological
theories to explain the factors that cause this
problem, among them (Venkatesh et al. 2003)
(Venkatesh, 2008) (Heijen, 2004) (Ajzen, 2005).
Even so, the existing technology acceptance theories
are still limited in their use in the context of
organizations or companies. The study that covers a
more individual context such as the acceptance of
the information technology context on the user's side
is currently very limited (Venkatesh, 2012).
Based on these conditions, it is necessary for the
Directorate General of Taxes to be able to know the
factors that influence the behavioral intention of the
taxpayers and the behavior of the taxpayers to utilize
the e-invoice application facilities, so that the use of
e-invoices can be sustainable according to the
government directives. This kind of activity is
considered important because with the previous
study, the Director General of taxes who provides e-
invoice services is able to get a clear picture of what
factors are capable of encouraging the behavioral
intentions and the behaviors of the taxpayers to
utilize e-invoices, so that the final result is
encouraging the taxpayers to be constantly
motivated to use e-invoice applications and the
public services become effective.
2 LITERATURE STUDY
2.1 Theoretical basis Unified Theory of
Acceptance and Use of Technology
(UTAUT)
UTAUT is one of the latest technology acceptance models
developed by Venkatesh, Morris, and Davis. This model is
based on basic theories about the behavior of technology
users and the technology acceptance model. UTAUT
combines the successful features of eight leading
technology acceptance theories into one theory, namely
the Theory of Action reason (TRA) from Ajzen and
Fishbein 1977, Technology acceptance model (TAM)
from Davis 1989, Model Motivational (MM) Davis et al
1992, Theory Ajzen 1991 planned behavior (TPB), Taylor
and Todd 1995 combination of TAM and TPB (C-TAM-
TPB), PC Utilization Model (MPCU) Thompson et al
1991, Rogers 2003 Innovation Diffusion Theory (IDT)
and Social Cognitive. UTAUT proved to be more
successful than the other eight theories in explaining up to
70 percent of user variants. After evaluating the eight
models, Venkatesh, et al. found seven constructs that
seemed to be a significant direct determinant of behavioral
intentions or user behavior in one or more of each model.
Constructs are performance expectations, business
expectations, social influences, facilitating conditions,
attitudes and self-confidence. After further testing, they
found four main constructs that play important roles as
direct determinants of behavioral and user behavior
intentions, namely, performance expectations, business
expectations, social influences, and facilitating conditions.
While the others are not significant as a direct determinant
of intention and behavior. Besides that there are also four
moderators namely gender, age, experience and
volunteerism which are positioned to moderate the impact
of the four main constructs on behavioral intentions and
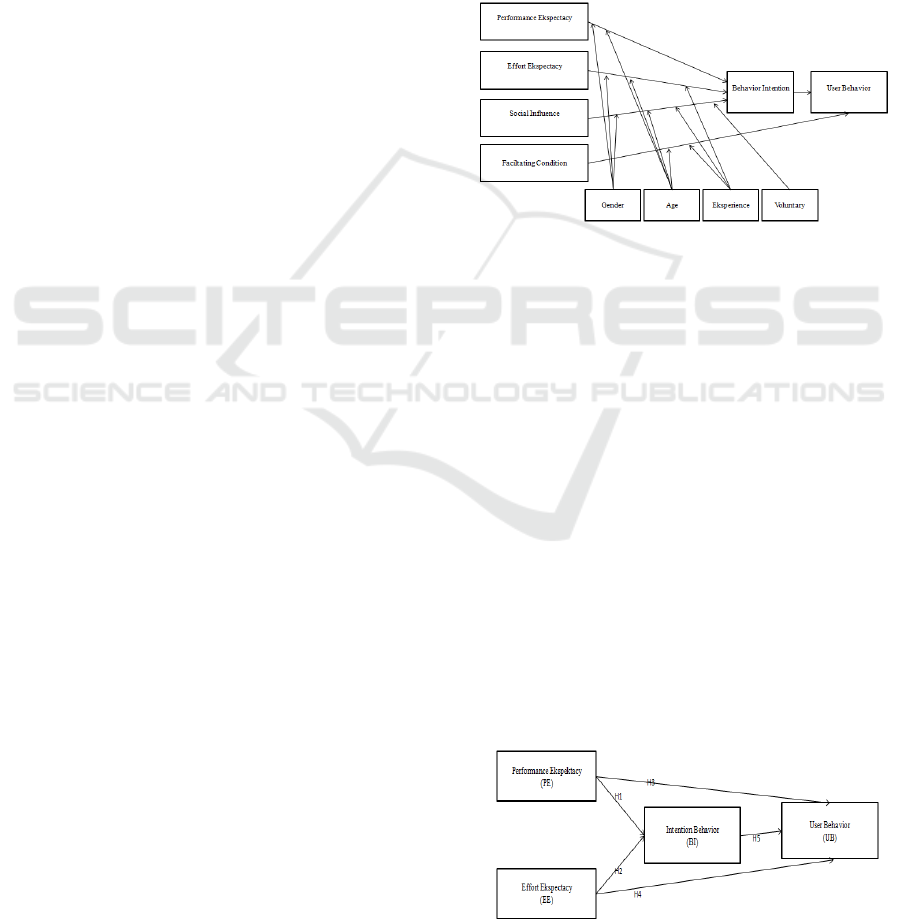
user behavior. Figure 1 shows the links between these
determinants and moderators.
Figure 1: UTAUT Model (Venkatesh, Moris, Davis 2003)
The UTAUT model was chosen in this study
because of its capacity to effectively summarize the key
aspects of technology acceptance from a variety of
existing models, which emphasizes its ability to provide a
comprehensive perspective that has been widely tested in
empirical research. Furthermore, we add that the Trust
variable on government and hedonic motivation is very
important to consider in the context of the learning
environment. Because most technology acceptance models
are proposed for the work environment, the greater scope
and analytical capabilities of the UTAUT model make it
suitable for the study of technology acceptance in e-
Invoice.
2.2 Framework
The frame of mind made in the form of schematic
drawings to further explain the relationship between
independent variables, dependents, and intervening
variables. For this reason, in this study it was formulated
in the framework of the picture as follows:
Figure 2: Framework
An Antecedent of E-Invoice User Behavior with Behavioral Intention as an Intervening Variable
395

2.3 Literature Review
Davis, Bagozzi, Warshaw (1989) developed a
Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) to examine
the determinant factors of the use of Information
Systems by the users. The results of Davis's study
indicate that the interest in the use of information
systems is influenced by the Perceptions of Use and
the Perception of Convenience. Venkatesh, Morris,
Ackerman (2000) conducted a study to see gender
differences in social factors and their role in the
acceptance of technology and the behavior of the
users of e-services with the technology acceptance
model. The object of this study is the companies in
the fields of telecommunications, entertainment,
banking, and public administration that use
Information System mandatorily and voluntarily.
This study was conducted to review and combine
several information system acceptance models and
hypothesize performance expectations, business
expectations, and social factors that have an effect
on the interest in using information systems and the
conditions that facilitate users to influence the use of
information systems. The results of the study show
that the interest in using information systems and the
conditions that facilitate the users affect the use of
information systems.
The next study by Venkatesh et al. (2003)
reviewed and combined several Information Systems
acceptance models. The result of the formulation of
several previous research models is known as the
combined theory of acceptance and use of
technology (Unified theory of acceptance and use of
technology) or abbreviated as UTAUT. This study
only hypothesizes and categorizes four variables that
play a major role in the interest and use of
information systems, namely performance
expectations, business expectations, and social
factors that have an effect on the interest in using
Information Systems. While the interest in using
Information Systems and the conditions that
facilitate users affect the use of Information
Systems. This study was conducted in the
communication, entertainment, banking and public
administration industries that use information
systems mandatorily and voluntarily
Wang et al. (2003) studied the
determinants of the user acceptance of internet
banking in commercial banks in Taiwan. The
variable of the study used was intention behavior as
the dependent variable. While the independent
variables used were computer self-efficacy,
perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and
perceived credibility. The result of the study showed
that computer self-efficacy had a significant positive
effect on the perceived usefulness and the perceived
ease of use, and a significant negative effect on the
perceived credibility. The other result of the study
was that computer self-efficacy had a significant
positive effect on the behavioral intention.
Pikkarainen et al. (2004) studied the factors that
affect the acceptance of online banking systems by
the customers in banking companies in Finland. The
variables used were perceived usefulness, perceived
ease of use, perceived enjoyment, security and
privacy, internet connection and amount of
information. The results of this study indicated that
perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use,
perceived enjoyment, security and privacy, and the
amount of information had an effect on the
acceptance of the online banking system. While the
internet connection did not have a significant effect
on the acceptance of the online banking system.
The study conducted by Amroso and Gardner
(2004) was about the interest in using the internet.
The results of the study, among others are as
follows: (a) The experience in using the internet
influences perceptions of usefulness and behavioral
interest in the internet usage; (b) Volunteerism is
also found to correlate with the behavioral interest in
the internet use; (c) Complexity Perception of using
the internet can be a significant relationship of the
perceived usefulness (as in the perception of ease)
and directly affects the perception of use; (d) Gender
can have an important role in the variables of "trust"
(Perception of Usability and Perception of Ease) as
well as its direct role in the Perception of Internet
Use.
According to Isais and Lencastre (2017)
the Performance Expectations and Business
Expectations have a positive influence on one's
behavior to accept a technological update. The study
conducted in Indonesia such as those conducted by
Puspitasari (2013), Prasetyo (2017) show that the
construct of the theory of Unified Theory of
Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) has a
positive effect on the Intention and the Behavior to
use technology. While for a short period, the study
produces a low level of significance (Sarbani and
Astuti, 2016).
3 METHOD
This study is a quantitative study, a study to test
certain theories by examining the relationships
between variables (Juliansyah, 2011). The reason for
using the quantitative study is that this study aims to
determine the effect of Performance Expectacy,
Business Expectacy, on the Behavior of E-Invoice
User with the Behavioral Intention as an intervening
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
396

variable, so that the quantitative study is compatible
with this study. According to Sugiyono (2014), this
type of study uses a descriptive method with a
quantitative approach, meaning that the study
conducted emphasizes numerical analysis or
numerical data. While a descriptive method is a
method used to describe and analyze a research
result but it is not used to make broader conclusions.
So, it can be concluded that the method used in this
study is a descriptive method with a quantitative
approach, in which the results of the study are
processed and analyzed and then the conclusions are
drawn. This means that the result of the study is
processed by emphasizing the analysis of numerical
data (numbers), so that a significant relationship
among these variables is known and the object under
study can be clarified. This study was conducted at
the Office of Tax Services of Palembang. The
subject of the study was the corporate taxpayers
which are registered at the Office of Tax Services of
Palembang registered as a Taxable Entrepreneur
(TE) and the taxpayers who took the tax invoice
serial numbers through e-nova.
The data for this study were collected by
distributing questionnaires. The questionnaire in this
study uses scaling (provides answer choices),
namely the Likert scale. The likert scale used is 1 to
represent strongly disagree, 2 to represent disagree,
3 to represent rather disagreeing, 4 to represent
agreeing, and 5 to represent strongly agree. This
questionnaire is called a fixed-alternative
questionnaire or a close-ended questionnaire, which
is a questionnaire that has an answer choice.
(Zikmun et al. 2010).
The population of this study is corporate
taxpayers registered at the Office of Tax Service of
Palembang which has used the E-Invoice system to
issue tax invoices. The reason for the researcher to
take corporate taxpayers was due to the fact that
corporate taxpayers at the Office of Tax Services of
Palembang had been required to use e-invoices since
June 2015, so that they have adapted to the new
system for more than one year.
In determining the sample size, this study uses
the Slovin’s formula to determine how many
samples will be taken. The formula used is as
follows (Sugiyono, 2014):
2
9471
947
e
n
= 282
Based on the result of the calculation of the
Slovin’s formula, this study uses 282 corporate
taxpayers that are used as the respondents. The
sampling follows the probability sampling theory by
using proportional stratified random sampling
technique (random samples with respect to the type /
category). The samples are grouped into 4 groups,
namely trading companies, manufacturing
companies, service companies and other categories
of companies. The determination of the proportion
of each type of business is based on the percentage
of the number of the companies in each sample
category (Prasetyo, Bambang, 2012).
The number of samples of 282 respondents that
are spread can be used in the analysis of this study.
The principle of sample selection in this design is
that each element in the population has the same
opportunity to be selected (Kuncoro, 2013). The
following table lists the number of respondents:
Table 1:Number of Samples based on Business Category
No
Business
Category
Number of
Taxpayers
Number
of
Samples
Percentage
1.
Trading
406
122
42.87%
2.
Service
389
115
41.09%
3.
Manufacturing
81
24
8.55%
4.
Other Category
71
21
7.49%
Total
947
282
100%
Source : Processed Data, 2018
The data presented in Table 3.1 reveal that the
taxpayers engaged in trading are the largest number
of taxpayers totalling 42.87%; The second position
is occupied by those engaged in the service
companies of 41.09%, the third position is occupied
by those engaged in manufacturing companies of
8.55%; And the fourth position is occupied by
those engaged in other business enterprises of 7.49.
4 FINDINGS
4.1 Taxpayer Behavior Model
Structure in using E-Invoice
Source: Processed data using version 3.0 SmartPLS
Figure 3: PLS Model.
An Antecedent of E-Invoice User Behavior with Behavioral Intention as an Intervening Variable
397

Table 2: Estimation of Parameters and Path
Significance Test
Variables
Original
Sample
Sample
Mean
T-Statistic
P.Value
Performance
Expectancy >
Behavioral Intention
0.205
0.201
3.45
4
0.00
1
Business
Expectancy>
Behavioral Intention
-0.116
-0.110
2.15
9
0.03
1
Performance
Expectancy >
Behavior
0.330
0.330
3.79
3
0.00
0
Business
Expectancy >
Behavior
-0.031
-0.025
0.52
9
0.59
7
Intention >
Behavior
0.319
0.314
4.16
0
0.00
0
Source : Data of significance test with SmartPLS
version 3.0
The results of the significance test above show
that there is a positive and significant effect of the
variable of Performance Expectancy (PE) on
Behavioral Intent (BI). This can be seen in table t
statistics > 1.96 (3.454) and has a positive value in
the p-value table (0.001 ), meaning that the first
hypothesis (H1) is accepted. There is a significant
positive effect of the Business Expectancy (EE)
variable on the Behavioral Intent (BI) as can be seen
from table t statistics > 1.96 (2.159) and has a
positive value on the p-value table (0.031), meaning
that the second hypothesis (H2) is rejected.
Then the Performance Expectancy (PE) variable
has a significant positive effect on the Taxpayers'
Behavior in using e-invoice of 3.793 > 1.96 which
means that the third hypothesis (H3) is accepted.
And the Business Expectancy variable does not have
a significant effect on the behavior of the taxpayers
in making tax invoices using e-invoice because the t
statistic value is smaller than 1.96, so that hypothesis
4 (H4) is rejected. And the Variable of Behavioral
Intention on the Behavior has a positive and
significant effect. This is shown by table t statistics
of 4.160 > 1.96, so that hypothesis 5 (H5) is
accepted.
5 HYPOTHESIS DISCUSSION
H1: The Effect of the Performance Expectancy
on the Intention of the Taxpayers' Behavior
in Using E-Invoice
The test results on the parameters of Performance
Expectancy on the Behavioral Intention of the
Taxpayers in using E-Invoice that can be seen from
the original sample value of PE → BI shows that
there is a positive effect of 0.205 (20.5%). While the
significance level is seen at the t statistic value of
above 1.96 (> 1.96) of 3.454 and the p.value is
below 5% (α = 0.05) which is 0.001, so that the
results of this study accept the first hypothesis (H1).
Based on the results of this study, it can be
concluded that Performance Expectancy has a
significant positive effect on the behavioral intention
of the taxpayers in using e-invoices. This shows that
the higher the trust / confidence of the taxpayer in
using the e-invoice, the more positive the
Performance Expectancy will become, so as to form
behavioral intentions to use e-invoices. And on the
contrary, the lower the trust or the confidence of the
taxpayers in using e-invoice, the lower the
behavioral intention to use it becomes.
The results of this study are consistent with the
studies conducted by Yahia et al (2016), Azis, Saliza
Abdul (2014), Costa, Silva (2014), Isaias, et al
(2017), Preeti tak (2017), McKeown, Tui & Mary
Anderson (2016), Yusup, Maulana. & Hardiyana.,
(2015), Yusof, Raja Jamilah Raja. & Irum Inayat.,
(2017), Mahzan, Nurmazilah., Andy Lymer., (2014).
This study supports the theory of unification of
acceptance and use of technology (Unified Theory
of Acceptance and Use of Technology).
Performance Expectancy is the extent to which the
taxpayers believe that if they use an e-invoice
system, it will help them to improve the performance
in his work (Venkatesh et al., 2003) When taxpayers
believe that this technology will help them to get a
better job or a lot of benefits, it will increase their
hopes to perform better professionally. In line with
the attribution theory that increasing expectations is
a part of the feeling experienced by the taxpayer that
he is able to internally influence behavioral intention
through his abilities, expertise and efforts.
H2: The Effects of the Business Expectations on
the Behavioral Intention of the
Taxpayers in Using E-Invoice
The second hypothesis states that Business
Expectations negatively affect the Taxpayer's
Behavioral Intention in using the e-invoice system
which can be seen from the original sample of -
0.116, although the significance level is seen at t
statistics above 1.96 (> 1.96) of 2.159 and p value
below 5% (α = 0.05) which is 0.031, so that the
results of this study reject the second hypothesis
(H2). Based on the results of this study, it can be
concluded that the Business Expectations negatively
affect the intention of the taxpayer behavior in using
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
398

e-invoices. This shows that the low the trust / the
confidence of the taxpayer in using e-invoice will
result in low business expectations so as to form the
behavioral intentions to use e-invoices.
The results of this study are consistent with the
results of the studies conducted by Indipenrian, Baiq
Nensi Veni, Bambang Subroto & Rahman (2015),
Kuciapski (2017), Handayani, Trie & Sudiana
(2015), Lee et al (2010). Business Expectations
imply the level of ease associated with the use of
technology (Venkatesh et al., 2003). In the case of
the use of e-invoices, the taxpayers find it difficult
to use the technology. This is because the e-invoice
program is currently still in the development stage.
When the taxpayer starts adapting to the use of e-
invoice version, the government issues the latest
version again. When the taxpayers feel that this
service is easily accessible and they do not have to
spend a lot of effort in utilizing the technology, their
tendency to use e-invoice services increases.
H3 : The Effects of the Performance Expectations
on the Taxpayer’s Behavior in Using E-
Invoice
The test results on the parameters between
Performance Expectancy on the Taxpayer’s
Behavior in using E-Invoice that can be seen from
the original sample value of PE → PWP shows that
there is a positive effect of 0.330 (33%). While the
significance level is seen at the statistic value above
1.96 (> 1.96) of 3.798 and the p. value of below 5%
(α = 0.05) which is 0.000, so that the results of this
study accept the sixth hypothesis (H6). Based on the
results of this study, it can be concluded that
Performance Expectations have a significant positive
effect on the taxpayer behavior in using e-invoices.
This shows that the higher the trust / the confidence
of the taxpayer in using e-invoice, the more positive
the performance expectations will be, so as to shape
the behavior to use e-invoices. And on the contrary,
the lower the trust or the confidence of the taxpayer
in using e-invoice, the lower the behavior to use it
becomes.
The empirical studies have shown that certain
behaviors can be predicted well enough by the
measures of compatible behavior towards the
questionable behavior (Ajzen and Fishbein, 2005).
In this paper, the use of behavior towards technology
has been included in the UTAUT model to improve
its ability to explain the technology acceptance as
well as the attribution theory. The definition of
behavior towards technology relates to the perceived
benefits and the pleasures experienced by users
when using it (Toh, 2013). Behavior consists of
positive or negative feelings towards certain
performance (Gilbert, 2015). Therefore, a person's
behavior towards the use of technology reflects an
affective reaction to the use of technology in general
(Kusuma & Puspaningsih, 2014). The study by
Ursavaş (2013) in Priyadi, Daryanto, & Hermadi.
(2017) argues that the significant role of behavior in
the general variance of the user's intention to use
technology and relevant correlational behavior has a
variety of variables that are usually used in
technology acceptance.
H4: The Effect s of Business Expectations on the
Behavior of the Taxpayers in Using E-
Invoice
The seventh hypothesis states that Business
Expectations negatively affect the Taxpayers'
Behavior in using an e-invoice system which can be
seen from the original sample of - 0.031, with a
significance level seen at statistical t value below
1.96 (> 1.96) of 0.529 and p value below 5% (α =
0.05) namely 0.597, so the results of this study reject
the seventh hypothesis (H7).
Business expectations are considered by some
studies as a positive influence on the behavior of
technology use as stated by Mahzan, Nurmazila
(2014), Kuciapski. (2017), Awwad, Mohammad
Sulieman (2016), Indipenrian, Baiq Nensi Veni,
Bambang Subroto & Rahman (2015) Yi, Ching Suk,
Chung Yee Ting & Dee Chia Young (2016) who
also argued that business expectations can be used to
assess behavior significantly. However, in this study
Business Expectations did not affect the behavior of
the taxpayers in using e-invoice services. It is
probably due to the fact that this service is still in the
development stage and it has entered the third year
since its enactment in June 2015 based on the decree
of Kep-08 / PJ / 2015 (Ministry of Finance of the
Republic of Indonesia, 2015).
H5: The Effect of the Behavioral Intention on the
Taxpayers' Behavior in Using E-Invoice
The test results of the parameters between the
Intention of the Taxpayer Behavior in using the E-
invoice that can be seen from the value of the
original sample of BI → PWP shows that there is a
positive effect of 0.319 (31.9%). While the level of
significance is seen at the t-statistical value above of
1.96 (> 1.96) of 4.160 and the p.value of below 5%
(α = 0.05) that is 0.000, so that the results of this
study accept the eleventh hypothesis (H11). Based
on the results of this study, it can be concluded that
the Taxpayer's Intention has a significant positive
effect on Taxpayer Behavior in using e-invoices.
This shows that the higher the trust / confidence of
the taxpayer in using e-invoice, the more positive
intention to shape the behavior of the taxpayer to use
An Antecedent of E-Invoice User Behavior with Behavioral Intention as an Intervening Variable
399

e-invoices. And on the contrary, the lower the trust
or the confidence of the taxpayers to use the e-
invoice, the lower the taxpayer's behavior to use it.
The user behavior was found to be
important in the actual use of technology (Chen et
al., 2008). In consistency with all drawing models of
the psychological theories, which argue that
individual behavior can be predicted and influenced
by the individual intentions. This study supports the
theory of unification of acceptance and use of
technology (Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use
of Technology) which argues and has proven that
User Behavior has significant influence on the use of
technology (Venkatesh et al. 2003), (Venkatesh,
Zhang, 2010). The intention to use refers to the
strength of the intensity of e-invoice program users
with their desire to use digital information resources
for their work. Therefore, the intention to use plays
an important role in predicting the future use of
electronic tax invoicing (Abdul Rahman et al. 2011).
This study also supports the study of Venkatesh and
Davis (2000), Venkatesh and Morris (2000) that the
causal relationship between Intention and Behavior
is empirically proven.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The findings of this study on the factors that
influence citizens' behavioral intentions for e-invoice
services in Indonesia are largely consistent with the
findings of the previous studies. This validates the
use of the modified UTAUT model in this kind of
analysis.
This study revealed that the Performance
Expectancy is the strongest predictor of the
behavioral intention and taxpayer behavior to use e-
invoice services. However, the business expectation
does not affect the behavioral intention and the
behavior of the taxpayers to use e-invoice services.
This study also proves that the Behavioral Intention
influences the Behavior of the taxpayers in adopting
the e-services. Having this insight, the government
will be more capable to strengthen citizens' intention
to use e-invoice services, and then keep using this
service in the future.
However, this study has certain limitations. The
main limitation in carrying out this study is the
problem of reaching the desired number of samples
for questionnaire-based surveys. In addition, the
independent variables used in this study are still
limited to 2 UTAUT variables from Venkatesh et al.
2003, so that if this study is used as a reference for a
further study, other variables must be added to get
optimal results. And the future study can expand the
area of study objects such as the Directorate General
of Tax, Ministry of Finance.
REFERENCES
Ajzen, I. (2005). Attitudes Personality and Behaviour
Scond Edition. Two Penn Plaza, New York USA.
Awwad, Mohammad Sulieman, S. M. A.-M. (2016).
Electronic Library Services Acceptance and Use, An
empirical validation of unified theory of acceptance
and use of tecchnology. The Electronic Library, 33(6),
1100–1120.
https://doi.org/10.1108/09574090910954864
Azis,Saliza Abdul, K. M. I. (2014). Does design matter in
tax e-filling acceptance ? Scinecedirec.
https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.11
.102
Davis, F. D., Bagozzi, R. P., & Warshaw, P. R. (1989).
User Acceptance of Computer Technology : a
Comparison of Two Theoretical Models *, 35(8).
Gilbert, P. (2015). The Evolution and Social Dynamics of
Compassion. Social and Personality Psychology
Compass, 6, 239–254.
Handayani, T., & Sudiana. (2015). Analisi Penerapan
Model UTAUT Terhadap Perilaku Pengguna Sistem
Informasi (Studi Kasus: Sistem Informasi Akademik
Pada STTNAS Yogyakarta. Prosiding Seminar
Nasional ReTII Ke-10, 688–696.
Heijen, H. Vander. (2004). User Acceptance of Hedonic
information System, 28(4), 695–704.
Indipenrian, Baiq Nensi Veni., Bambang Subroto., A., &
Rahman, F. (2015). Analysis of behavioral intention
on ABC system adoption: Model of information
systems technology and success acceptance. Journal
of Economics, Business & Accountancy Ventura,
18(3), 403. https://doi.org/10.14414/jebav.v18i3.510
Isaias, P., Reis, F., Coutinho, C., & Lencastre, J. A.
(2017). Empathic Technologies for Distance and
Mobile Learning : An Empirical Research Based on
Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology
(UTAUT). Interactive Technology and Smart
Education, 14(2), 159–180.
https://doi.org/10.1108/ITSE-02-2017-0014
Kementerian Keuangan Republik Indonesia. (2015). Kep-
08/PJ/2015.
Kuciapski, M. (2017). A model of mobile technologies
acceptance for knowledge transfer by employees.
Journal of Knowledge Management, 00–00.
https://doi.org/10.1108/JKM-03-2016-0136
Kuncoro, M. (2013). Metode Riset Untuk Bisnis &
Ekonomi. Jakarta: Erlangga.
Kusuma, D. H., & Puspaningsih, A. (2014). Model
Penerimaan User dalam Implementasi SAP (System
Application and Product ) dengan Menggunakan
Model UTAUT. Aplikasi Bisnis, 15(9), 1799–1822.
Mahzan, Nurmazilah., A. L. (2014). Examining the
adoption of computer-assisted audit tools and
techniques. Managerial Auditing Journal, 29(4), 327–
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
400

349. https://doi.org/10.1108/MAJ-05-2013-0877.
McKeown, T., & Anderson, M. (2016). UTAUT:
capturing differences in undergraduate versus
postgraduate learning? Education + Training, 58(9),
945–965. https://doi.org/10.1108/ET-07-2015-0058
Prasetyo, Bambang, L. M. J. (2012). Metode Penelitian
Kuantitatif Teori dan Aplikasi (Edisi 1 Ce). Jakarta:
RajaGrafindo Persada (Rajawali Pers).
Priyadi, R., Daryanto, A., & Hermadi, I. (2017). Perilaku
Penggunaan Portal E-office di Bank XYZ Dengan
Pendekatan Model UTAUT. Jurnal Aplikasi Bisnis
Dan Manajemen, 3(2), 185–195.
https://doi.org/10.17358/jabm.3.2.185
Sugiyono. (2014). Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif Kualitatif
dan R & D (Cetakan ke). Bandung: Alfabeta Bandung.
Toh, P. K. (2013). A Competition-Based Explanation Of
Collaborative Intention Within The Firm. Academy of
Management Journal, 51(2), 315–334.
https://doi.org/10.1002/smj
Venkatesh, V. (2008). Technology Acceptance Model 3
and a Research Agenda on Interventions (Vol. 39, pp.
273–315).
Venkatesh, V. (2012). Consumer Acceptance and Use of
Information Technology : Extending the Unified
Theory (Vol. 36, pp. 157–178).
Venkatesh, V., Morris, M. G., & Ackerman, P. L. (2000).
A Longitudinal Field Investigation of Gender
Differences in Individual Technology Adoption
Decision-Making Processes. Organizational Behavior
and Human Decision Processes, 83(1), 33–60.
https://doi.org/10.1006/obhd.2000.2896
Venkatesh, V., Morris, M. G., Davis, G. B., & Davis, F.
D. (2003). User, Acceptance of Information
Technology. Toward a Univied View (Vol. 27, pp.
425–478).
Yahia, Imene Ben., Abdelfattah Mohamed Triki., dan L.
C. (2016). Understanding citizens’ adoption of e-filing
in developing countries: An empirical investigation.
Journal of High Technology Management Research,
27(2), 161–176.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hitech.2016.10.006
Yi, Ching Suk, Chung Yee Ting, Dee Chia Young, N. S.
Y. (2016). Determinants of Continuance Usage
Intention of Social Network Services in Malaysia. A
Research Project Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of
the Requirement for the Degree, (April).
Yusof, Raja Jamilah Raja., Irum Inayat., A. Q. (2017).
Student real-time visualization system in classroom
using RFID based on UTAUT model. International
Journal of Information and Learning Technology,
34(3), 274–288. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJILT-03-
2017-0018.
Yusup, Maulana., A., & Hardiyana., I. S. (2015). User
Acceptance Model on E-Billing Adoption: A Study of
Tax Payment by Government Agencies. Asia Pacific
Journal of Multidisciplinary Research, 3(4), 150–157.
An Antecedent of E-Invoice User Behavior with Behavioral Intention as an Intervening Variable
401
