
Environmental Management Accounting, Quality of Decision
Influence on Environmental Performance in Indonesia
Luk Luk Fuadah, Rochmawati Daud, and Burhanuddin
Universitas Sriwijaya
Keywords: environmental management accounting, quality of decision, environmental performance
Abstract: The aim of this study is to examine the link between environmental management accounting, quality of
decision and environmental performance. The data is obtained from the survey. The natural resource based
view theory and decision theory used in this study. The results research show both environmental
management accounting and quality of decision have a positive and significant effect on environmental
performance. The more companies implementation environmental management accounting, the higher
environmental performance. This is similar to the higher quality of decision, higher environmental
management accounting. The first limitation of this study is a low response rate supports this idea, even
though the company contacted in this study is all ISO 14001 certified companies that have achieved
environmental management system standards. Future research should research qualitative research. Second,
this study only focuses on two variabels impacts on environmental performance. Future research can use
other variables.
1 INTRODUCTION
The company's social and environmental
responsibility has been the focus of attention by the
media and globally in currently, because the
company concerns about environmental hazards,
such as climate change, greenhouse gas emissions
and partly because the company's current
performance is measured in not only financial
performance but also environmental performance
(Stefan Schaltegger, Gibassier, & Zvezdov, 2013).
Thus, stakeholders encourage managers to focus
more on environmental issues and evaluating
environmental performance (Burritt, Schaltegger, &
Burritt, 2010; Rodrigue, Magnan, & Boulianne,
2013).
Environmental Management Accounting is "a
technique for improving, analyzing and using
financial and non-financial information, with the aim
of improving the environment and corporate
environment, economic performance and
contributing to sustainable business" (Schaltegger,
Bennet, Burrit, & Jasch, 2009).
The Government, through the Environment and
Forestry Ministry since 2002, formed a Corporate
Performance Rating Assessment Program in
Environmental Management (PROPER). Initially
PROPER was one of the policy tools developed by
the Environment and Forestry Ministry in order to
encourage compliance with the business and / or
activity responsible for various laws and regulations
in the environmental field. PROPER provides
information about the performance of each company
to all stakeholders on a national scale (mnlh.go.id).
Staniskis & Stasiskiene, (2006) research
environmental management accounting in Lithuania.
The finding reveals there is a positive relationship
between environmental management accounting and
environmental performance. The companies used
environmental management accounting to improve
their decision making including environment and
economics (Staniskis & Stasiskiene, 2006).
Environmental management accounting is useful for
monitoring environmental costs and environmental
performance recordings (Burritt & Saka, 2006).
Furthermore, Henri & Journeault (2010) conclude
that managers depend on indicators of
environmental performance in the evaluation of
performance and decision making.
The implementation of ISO 14001, the standard
used by companies to implement, maintain and
improve their environmental management systems
(Solovida & Latan, 2017).
Fuadah, L., Daud, R. and Burhanuddin, .
Environmental Management Accounting, Quality Decision Influence on Environmental Performance in Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0008440003390346
In Proceedings of the 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference (SEABC 2018), pages 339-346
ISBN: 978-989-758-387-2
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
339

Indonesia is a country in Southeast Asia and has
a complex geographical environment; Deforestation
problems are serious according to a 2013 report
from the Indonesian Ministry of Environment and
Forestry. However, research in Southeast Asia and
Indonesia is still rarely carried out that reflects the
empirical gap (Derchi, Burkert, & Oyon, 2015).
This shows that environmental issues in Indonesia
are very important to study.
This research focuses on the link environmental
management accounting, quality of decision and
environmental performance to companies listed in
Indonesia Stock Exchange especially for companies
received ISO 14001 certification.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Natural Resources Based View
Theory
Natural resources based view theory, argues
competitive advantage can be maintained only if the
company has the ability to realize profits that are
supported by resources that are difficult for
competitors to follow (Hart & Dowell, 2011). Hart
& Dowell, (2011) to evaluate the theory of Natural
Resources Based View Theory based on existing
empirical research and conclude that most of Hart,
(1995) propositions are supported. However, there
has been no further exploration of how the
combination of company resources affects
environmental performance.
Natural Resources Based View Theory proposed
by (Hart, 1995; Hart & Dowell, 2011), which
determines that the company's strategy will improve
its environmental performance. Thus, this study uses
the Natural Resources Based View as a theory that
explain the influence of environmental management
accounting on the environmental performance
(Aragón-Correa, Hurtado-Torres, Sharma, & García-
Morales, 2008; Christ & Burritt, 2013).
Natural Resources Based View Theory argues
that competitive advantage can be maintained only if
there is the ability to create profits that are supported
by resources that are not easily duplicated by
competitors. This consists of three interrelated
strategies, namely: (1) pollution prevention; (2)
product stewardship; and (3) sustainable
development. They have different driving force in
the environment, which builds different key
resources, and they have different sources of
competitive advantage. For example, removing
pollutants from the production process can increase
efficiency by (a) reducing the input needed, (b)
simplifying the process, and (c) reducing costs and
compliance obligations Hart & Dowell, 2011)
2.2 Decision Theory
Decision theory is a theory about a decision.
Based on decision theory that highlights the
important role of information in decision making
processes (Hansson, 2005). In particular, with the
use of Environmental Activity Management will
facilitate better environmental assessment and
decision quality because of the provision of more
detailed and accurate environmental information that
is likely to assist the manager's decision-making
process, thereby increasing the quality of
environmental decisions, and in turn, leads to
improved environmental performance. Thus, in this
study propose the link between quality of decision
and environmental performance.
Based on decision theory there are two central
questions, namely the prescriptive and descriptive
approach. First, our prescriptive (rational) approach
asks how rational decisions must be made. Second,
with a descriptive approach (behavior) we model the
actual decisions made by individuals (Hens &
Rieger, 2016). Furthermore, decision theory that
studies choices between alternatives that involve risk
and uncertainty. Risk means here that decisions lead
to consequences that cannot be predicted precisely,
but follow a known probability distribution.
Uncertainty or ambiguity means that this probability
distribution is at least partially unknown to the
decision(Hens & Rieger, 2016).
2.3 Environmental Management
Accounting
Environmental Management accounting has
received considerable attention for academic,
international organization, professional accounting
organizations and business entities. It is reflected in
many scientific journals articles, books and also
working papers (Stefan Schaltegger et al., 2013).
There are several potential benefits associated
with the use of Environmental Management
Accounting. These include reducing costs,
increasing product prices, attracting human
resources, and increasing reputation (Burrit, Rogger,
Hahn, & Schaltegger, 2002). The study also notes
that the implementation of environmental
management accounting usually benefits
organizations by giving them different information
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
340

for decision making (Burrit et al., 2002). Such
information can reveal hidden opportunities, such as
better waste management processes, energy
reduction and consumption of materials or
opportunities for material recycling. From an
environmental perspective, this information can also
be used in developing more efficient processes and
thus leading to innovation.
Burrit, Rogger, Hahn, & Schaltegger, (2002)
reveals that environmental management accounting
is distinguished between ad hoc and routine
information when focusing on past, present or future
time frames and short and long term. Based on this
environmental management accounting information
dimension, Burrit, et.al., (2002) have suggested a
framework of environmental management
accounting. Furthermore, Business entities use
environmental management accounting can improve
environmental and financial performance (Gibson &
Martin, 2004)
Burritt & Saka, (2006) investigate the link
between environmental management accounting and
eco-efficiency measurement in Japan. They
promoted to business entities in Japan to concern to
the environment on their process and consumption
of their products. Moreover, Staniskis & Stasiskiene
(2006) imply SMEs in Lithuanian implement
environmental management accounting and
innovation of Cleaner production. They also report
base on projects of cleaner production and increase
concern from policy makers, industrialists and
practitioners.
There are no regulations on environmental
disclosure in Spain, but this study reveals that the
elaboration of a large number of environmental
accounting information used by internal parties is
useful for decisions on the implementation of
environmental management systems (Masanet-
Llodra, 2006). The use of environmental
management accounting can improve the companies
performance, one of that is environmental
performance (Tsui, Christophor, Lee, & Kee, 2014).
It is also better to manage the cost of environment
and improve process of production (Tsui et al.,
2014).
Solovida & Latan (2017) the use of
environmental management accounting as an
intangible asset has benefited companies by
providing information on their operational activities,
especially as related to the environment and the
results of good environmental performance. Qian et
al., (2018) reveals that the implementation of
environmental management accounting has a
significant positive impact on the company's carbon
management and the quality of its disclosure.
2.4 Environmental Performance
The Government, through the Environment and
Forestry Ministry since 2002, formed a Corporate
Performance Rating Assessment Program in
Environmental Management (PROPER). The
Company Performance Rating Program (PROPER)
is a program used by the Indonesian Environment
and Forestry Ministry together with the Environment
Agency to monitor and assess the company's
environmental performance. Initially PROPER was
one of the policy tools developed by the Ministry of
Environment and Forestry in order to encourage
compliance with the business and / or activity
responsible for various laws and regulations in the
environmental field. PROPER is closely related to
the dissemination of information on the performance
of each company to all stakeholders on a national
scale (mnlh.go.id).
Solovida & Latan (2017) explained that
PROPER (Program of the corporate performance
rating) members are assessed on a 5 (five) color
scale ranging from the highest, gold, down to green,
blue, red, and black. Gold and green rating gave to
companies that go beyond mere compliance and
include three criteria: (1) implementing an
environmental management system, one of that is
the certificate of ISO 14001, (2) using resources, and
(3) carrying out community development.
2.5 Hypothesis Development
2.5.1 Environmental management
accounting (EMA) and environmental
performance (EP)
Environmental management accounting is one of
the tools of environmental management that is useful
for tracking environmental costs as well as physical
environmental flows (Burritt & Saka, 2006). Based
Natural Resources Based View Theory argue that
there is the combination of company resources
affects environmental performance (Hart, 1995).
One of the company resources is environmental
management accounting. In this study proposed that
environmental management accounting has relation
with environmental performance. The higher
environmental management accounting implement
in the company, the higher environmental
performance.
Environmental Management Accounting, Quality Decision Influence on Environmental Performance in Indonesia
341
Previous studies include Aragón-Correa,
Hurtado-Torres, Sharma, & García-Morales (2008),
and Henri & Journeault (2010) showed that eco-
efficient practices are positively related to company
performance. Henri & Journeault (2010) use 303
respondents for their analysis. Empirical evidence
shows that the use of environmental management
accounting has a positive and significant on
company's environmental performance (Solovida &
Latan, 2017). Solovida & Latan (2017) analyzed
from 68 respondents from the survey conducted.
The more sophisticated the use of management
accounting practices, namely environmental
management accounting, the better the process of
control and decision making influences the
environmental management control system on
environmental performance (Solovida & Latan,
2017).
Furthermore, other study revealed that there is a
positive and significant influence between
organizational resources, the use of environmental
management accounting, and the company's
environmental performance (Latan, Chiappetta
Jabbour, Lopes de Sousa Jabbour, Wamba, &
Shahbaz, 2018). Latan, Chiappetta Jabbour, Lopes
de Sousa Jabbour, Wamba, & Shahbaz (2018)
analyzed 107 respondents using an online survey.
Based on the argument above, the hypothesis
proposed is in the following:
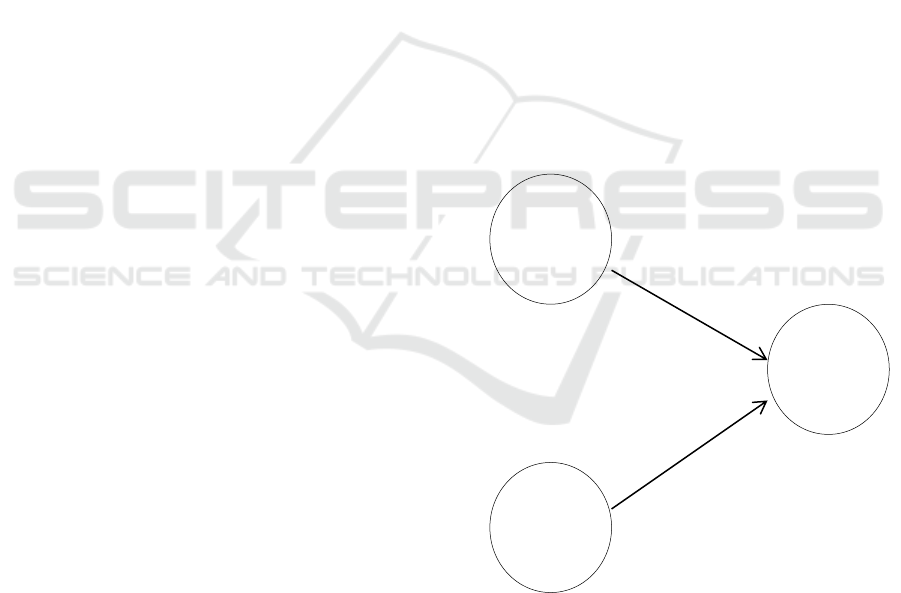
H1: Environmental Management Accounting
have a positive impact on Environmental
Performance.
2.5.2 Quality of decision (QD) and
Environmental performance
Quality of decisions are decisions taken
accurately and in detail specifically related to the
environment in this study. Decision theory is a
theory about a decision. Based on decision theory
that highlights the important role of information in
decision making processes (Hansson, 2005). Thus,
better environmental assessment and decision
quality due to the provision of more detailed and
accurate environmental information that is likely to
assist the manager's decision-making process,
thereby increasing the quality of environmental
decisions, and in turn leads to improved
environmental performance. The higher quality of
decision, the higher environmental performance.
Phan, Baird, & Su (2018) reveal that the
management of environmental activities towards the
quality of decisions and environmental performance
of the company. The study was conducted in
Australia to test the management of environmental
activities related to Activity Based Costing. The
more sophisticated the use of management
accounting practices (in this case environmental
management accounting), the better the process of
control and decision making and the more solid the
impact of environmental management control
system on the company's environmental
performance. Phan, Baird, & Su (2018) research
environmental activity based costing and
environmental performance through the quality of
decision.
It is expected that the quality of their
environmental decisions will be improved, which in
turn will have a positive impact on environmental
management in terms of improving environmental
performance. One of the main difficulties in
environmental management is the identification and
calculation of the costs of organizational activities
and processes (Sarkis, Meade, & Presley, 2006). The
higher quality of decision, the higher environmental
performance as well. Thus, our hypothesis is
proposed in the following:
H2: Quality of decision have a positive effect on
environmental performance.
Figure 1: Research Framework
Environmental
Management
Accounting
Quality
of
Decision
Environmental
Performance
H1
H2
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
342
3 METHOD
3.1 Sample
The sample in the study are all companies that
have ISO 14001 certification. This is because the
company is more concerned than other companies
about environmental issues and tends to have a
strong commitment to environmental responsibility.
The sample in this study as respondents were
general managers, operations managers, financial
managers and environmental managers in the sample
company.
3.2 Instruments
3.2.1 Environmental management
accounting
This study uses environmental management
accounting instruments are 12 items of
environmental management accounting (Ferreira,
Moulang, & Hendro, 2010). This study uses seven
Likert point scales which indicate 1 "do not do it at
all" up to 7 "has been done".
3.2.2 Decision Quality
The measure for decision quality is a five-item
instrument derived from (McIntyre, 1982). This
study uses seven Likert point scales which indicate
that from 1 "not at all applied" to 7 "very applied".
3.2.3 Environmental Performance
This study uses 13 environmental performance
instruments of the company (Henri & Journeault,
2010). This study uses seven Likert point scales
which indicate 1 "do not at all" up to 7 "to great
extent".
3.3 Data Collected Technique
The collection technique is by collecting by the
survey. Before the survey was conducted, a pilot
test has been carried out. Data obtained from an
online survey to companies received ISO 14001
certificate listed Indonesian Stock Exchange. The
total company received ISO 14001 around 200
companies. The data use in this study is 56
respondents from the result of the survey.
3.4 Analysis
The hypotheses developed were examined by
using Partial Least Square (PLS).
The model of this study is:
EPi,t = α + β1 EMAi,t, + β2 QDi,t + t
(1)
Where:
i, t = sector i, Year t,
= intercept
Β = independent variable coefficient
= error term
EMA = Environmental Management Accounting
QD = Quality of decision
EP = Environmental performance
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Result
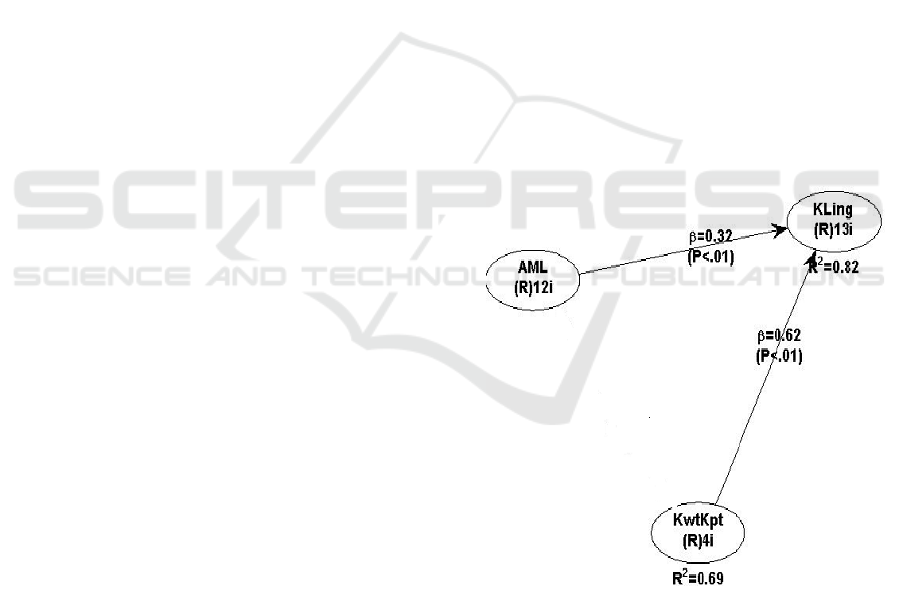
Figure 1: The result of research
Environmental Management Accounting, Quality Decision Influence on Environmental Performance in Indonesia
343

Table 1: The hypothesis Result
Hypothesis
Coefficient
p Value
Result
H1
0,32
< 0.01
Supported
H2
0,62
< 0.01
Supported
It can be seen in figure 1 and table II. Based on
the results the explanation in the following:
1. The first hypothesis, the link between
environmental management accounting and
environmental performance. It shows that p= <
0.01. It means that the first hypothesis is
accepted at the level below 1 %. The
coefficient 0,32. It shows a positive
relationship.
2. The second hypothesis states quality of
decision has a positive effect on environmental
performance. It is also suported. Because p= <
0.01, it is less than 1%. The coefficient (β =
0,62). It means the quality of decision has a
positive link with environmental performance
4.2 Discussion
The first hypothesis (H1) which states
environmental management accounting have a
positive effect on environmental performance.
Result research shows H1 is accepted. The results of
this analysis indicate that the company's
environmental performance is influenced by
environmental management accounting. The more
often environmental management accounting is used
in a company, the higher the environmental
performance of the company. This finding is in line
with previous studies by (Aragón-Correa, Hurtado-
Torres, Sharma, & García-Morales, 2008). The
finding support Natural resource base view theory.
This finding in line to Solovida & Latan (2017);
Latan, Jabbour, Lopes de Sousa Jabbour, Wamba, &
Shahbaz, (2018).
The argument for the acceptance of the first
hypothesis is as follows; the implementation of
environmental management accounting has
encouraged companies to improve their
environmental performance. The finding supports
the Natural Resources Based View Theory, that
explain the influence of environmental management
accounting on the environmental performance
(Aragón-Correa, Hurtado-Torres, Sharma, & García-
Morales, 2008; Christ & Burritt, 2013).
The second hypothesis (H2) which states
Decision Quality has a positive effect on
Environmental performance. The result of the
research shows H2 is accepted. The findings
indicate that the quality of decisions has an impact
on environmental performance. In particular,
information on environmental costs is very
important in assisting internal decision makers in
various production decisions and resource allocation
(Deegan, 2008). Therefore, it is very important for
organizations to assess correctly environmental costs
to provide better product cost estimates with
increasing costs Environmental protection must be
passed on to customers through an accurate pricing
policy. This finding support (Phan et al., 2018).
The argument for the acceptance of the second
hypothesis is as follows; the quality of decision
improves their environmental performance. This
study supports the decision Theory.
5 CONCLUSION
Both environmental management accounting and
decision quality have a positive impact on
environmental performance. The more companies
implementation environmental management
accounting, the higher environmental performance.
The higher the quality of decision, the higher
environmental management accounting.
One of the roles of environmental management
accounting on business in a company is to disclose
both financial information and non-financial
information. In addition, it is to improve information
about the environment and the corporate
environment, the economic performance of the
company. This environmental management
accounting also contributes to sustainable business.
However, the quality of decision is a decision taken
by a company that has the quality where in decision
making requires information not only financial
information but also non-financial information
especially information related to the environment in
company.
This study support two theory that used includes
Natural Resources Based View Theory and decision
theory. This research also has important implications
for the management of the company with regard to
environmental management accounting and the
quality of decisions that can improve environmental
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
344

performance. The actions that can be taken by
companies is managing waste and improving all
activities that are environmentally friendly which
can contribute to environmental performance.
There are several limitations in this study that
must be considered. First, this study uses a relatively
small sample: many companies are reluctant to
provide it information related to environmental
performance, because most companies treat this
information as "confidential." Information relating to
the strategy, use of environmental management
accounting and environmental performance are thus
not known to the public. A low response rate
supports this idea, even though the company
contacted in this study is all ISO 14001 certified
companies that have achieved environmental
management system standards. Second, this study
only focuses two variables impacts on
environmental performance. Future research can use
other variables.
Acknowledgment
Author thank to Universitas Sriwijaya, we can
get Competitive Research grant (Penelitian
Unggulan Kompetitif Universitas Sriwijaya) in
2018.
REFERENCES
Aragón-Correa, J. A., Hurtado-Torres, N., Sharma, S., &
García-Morales, V. J. (2008). Environmental strategy
and performance in small firms: A resource-based
perspective. Journal of Environmental Management,
86(1), 88–103.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2006.11.022
Burrit, Rogger, L., Hahn, T., & Schaltegger, S. (2002).
Towards a comprehensive framework for
environmental management accounting - Links
between business actors and environmental
management accounting tool. Australian Accounting
Review, 12(2), 39–50. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1835-
2561.2002.tb00202.x
Burritt, R. L., & Saka, C. (2006). Environmental
management accounting applications and eco-
efficiency: case studies from Japan. Journal of
Cleaner Production, 14(14), 1262–1275.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2005.08.012
Burritt, R. L., Schaltegger, S., & Burritt, R. L. (2010).
Sustainability accounting and reporting : fad or trend ?
https://doi.org/10.1108/09513571011080144
Christ, K. L., & Burritt, R. L. (2013). Environmental
management accounting: The significance of
contingent variables for adoption. Journal of Cleaner
Production, 41, 163–173.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2012.10.007
Deegan, C. (2008). Environmental costing in capital
investment decisions: Electricity distributors and the
choice of power poles. Australian Accounting Review,
18(1), 2–15. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1835-
2561.2008.0002.x
Derchi, G. B., Burkert, M., & Oyon, D. (2015).
Environmental management accounting systems: A
review of the evidence and propositions for future
research. Studies in Managerial and Financial
Accounting (Vol. 26). Emerald Group Publishing
Limited. https://doi.org/10.1108/S1479-
3512(2013)0000026006
Ferreira, A., Moulang, C., & Hendro, B. (2010).
Environmental management accounting and
innovation: an exploratory analysis. Accounting,
Auditing & Accountability Journal, 23(7), 920–948.
https://doi.org/10.1108/09513571011080180
Gibson, K. C., & Martin, B. A. (2004). Demonstrating
value through the use of environmental management
accounting. Environmental Quality Management,
13(3), 45–52. https://doi.org/10.1002/tqem.20003
Hansson, S. O. (2005). Decision Theory A brief
introduction. Sweden: Upsala University. Swedia:
Upsala University.
https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203112991
Hart, S. (1995). A Natural-Resource-Based View of the
Firm. Academy of Management Review, 20(4), 986–
1014. https://doi.org/10.5465/AMR.1995.9512280033
Hart, S. L., & Dowell, G. (2011). A natural-resource-
based view of the firm: Fifteen years after. Journal of
Management, 37(5), 1464–1479.
https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206310390219
Henri, J. F., & Journeault, M. (2010). Eco-control: The
influence of management control systems on
environmental and economic performance.
Accounting, Organizations and Society, 35(1), 63–80.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aos.2009.02.001
Hens, T., & Rieger, M. O. (2016). Decision Theory. In
Financial Economics (pp. 15–88). London, UK:
Springer Text Book in Business and Economics.
https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203932025
Latan, H., Chiappetta Jabbour, C. J., Lopes de Sousa
Jabbour, A. B., Wamba, S. F., & Shahbaz, M. (2018).
Effects of environmental strategy, environmental
uncertainty and top management’s commitment on
corporate environmental performance: The role of
environmental management accounting. Journal of
Cleaner Production, 180, 297–306.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.106
Masanet-Llodra, M. J. (2006). Environmental
management accounting: A case study research on
innovative strategy. Journal of Business Ethics, 68(4),
393–408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-006-9029-1
McIntyre, S. H. (1982). An Experimental Study of the
Impact of Judgment-Based Marketing Models.
Management Science, 28(1), 17–33.
https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.28.1.17
Phan, T. N., Baird, K., & Su, S. (2018). Environmental
activity management: its use and impact on
environmental performance. Accounting, Auditing and
Environmental Management Accounting, Quality Decision Influence on Environmental Performance in Indonesia
345

Accountability Journal, 31(2), 651–673.
https://doi.org/10.1108/AAAJ-08-2016-2686
Qian, W., Hörisch, J., & Schaltegger, S. (2018).
Environmental management accounting and its effects
on carbon management and disclosure quality. Journal
of Cleaner Production, 174, 1608–1619.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.11.092
Rodrigue, M., Magnan, M., & Boulianne, E. (2013).
Stakeholders’ influence on environmental strategy and
performance indicators: A managerial perspective.
Management Accounting Research, 24(4), 301–316.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mar.2013.06.004
Sarkis, J., Meade, L., & Presley, A. (2006). An activity
based management methodology for evaluating
business processes for environmental sustainability.
Business Process Management Journal, 12(6), 751–
769. https://doi.org/10.1108/14637150610710918
Schaltegger, S., Bennet, M., Burrit, R. L., & Jasch, C.
(2009). Eco-Efficiency in Industry and Science
Environmental Management Accounting for Cleaner
Production. Vienna: Springer.
Schaltegger, S., Gibassier, D., & Zvezdov, D. (2013). Is
environmental management accounting a discipline? A
bibliometric literature review. Meditari Accountancy
Research, 21(1), 4–31.
https://doi.org/10.1108/MEDAR-12-2012-0039
Solovida, G. T., & Latan, H. (2017). Linking
environmental strategy to environmental performance
Mediation role of environmental. Sustainability
Accounting, Management and Policy Journal, 8(5),
595–619. https://doi.org/10.1108/SAMPJ-08-2016-
0046
Staniskis, J. K., & Stasiskiene, Z. (2006). Environmental
management accounting in Lithuania : exploratory
study of current practices , opportunities and strategic
intents. Journal of Cleaner Production, 14, 1252–
1261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2005.08.009
Tsui, C. S. K., Christophor, Lee, S. K. T., & Kee, S.
(2014). A Literature Review on Environmental
Management Accounting (EMA) Adoption. Web
Journal of Chinese Management Review, Vol. 17(3),
No. 3.
Tsui, (2014), A literature review on Environmental
Management Accounting, (EMA) adoption, Chinese
Management Review, Vol. 17, No. 3, 1- 19.
www.mnlh.go.id
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
346
