
The Impact of Fundamental Factors and Inflation on Abnormal
Return on Registered Service Company on the Indonesia Stock
Exchange
Yusmita Kumala, Taufiq and Sa’adah Siddik
Universitas Sriwijaya, Palembang, Indonesia
Keywords: Abnormal return, return on asset, debt to equity ratio, current ratio, inflation
Abstract: This research was conducted to examine the impact of fundamental factors and inflation on abnormal return
on service companies listed on the IDX. The aim of this research is to test and analyze the effect of
fundamental factors and inflation on abnormal return on service companies listed in the Indonesia Stock
Exchange in 2011 up to 2015. Dependent variables in this study are abnormal returns, while independent
variables in this study are return on asset, debt to equity ratio,current ratio, and inflation as a control
variable.The population of this research is a service company listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange (IDX)
in 2011- 2015. Total sample of this research is 87 companies determined by purposive sampling. The data
were analyzed using the classic assumption test, multicollinearity test, normality test, heteroscedasticity test,
data analysis using multiple linear regression, determination coefficient test (R
2
), statistical test t and
statistical f test, and test the control variable using covariance analysis.Partial test results (t test) indicate that
return on assets, debt to equity ratio, current ratio have a significant positive effect on abnormal return.
The test results together (f test) shows that return on assets, debt to equity ratio, current ratio together have
an effect on abnormal return. While the results based on the results of covariance analysis, return on assets,
debt to equity ratio, current ratio influenced by inflation control variables together become insignificant to
abnormal returns.
1 INTRODUCTION
The capital market is a market that is used for
various long term financial instruments and
transactions, such as bonds, stocks and mutual
funds. The capital market can be one of the
alternatives that can be used to obtain funding
sources for other companies or institutions and as a
means of investment for investors. he capital market
has two functions, namely: (1) for the company as a
means of obtaining funds from the investors
(investors) for the financing of the enterprise
business, and (2) for the public as a place to invest in
profit through financial instruments, such as stocks,
bonds, and mutual fund.
Investors who invest in capital market by buying
company shares will expect a good return in the
future from stock investment that has been invested
in the capital market. Efficient market is the speed
and completeness of a securities market price in
responding to relevant information. The efficient
capital market is the price of a stock that has
reflected an information related to the company's
management activities and prospects in the future
and when new information about the company
appears, the stock price will change reflects the
information (Zaenal, 2005). One way that investors
can use in assessing a company's stock, which is by
observing the fundamental factors that companies
are issuing shares in the capital market. One of the
information available in the market is earnings in the
income statement. Virginia, Manurung, &
Muliawati(2012) Earnings information that raises
the reaction of the investor market is said to assess
the content of information. This reaction can be
measured using abnormal return.Research
conducted by Purbawati, Arifati, & Andini, (2016)
to determine the effect of stock split before and after
announcement of average abnormal return and
trading volume activity before and after the stock
split announcement date. The results showed a
significant increase in the Average Abnormal Return
(AAR) following a stock split policy. Then the
Kumala, Y., Taufiq, . and Siddik, S.
The Impact of Fundamental Factors and Inflation on Abnormal Return on Registered Service Company on The Indonesia Stock Exchange.
DOI: 10.5220/0008439803190329
In Proceedings of the 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference (SEABC 2018), pages 319-329
ISBN: 978-989-758-387-2
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
319

research done by Randina & Fachrizal(2016) with
the results of the research that there is a significant
difference in stock trading volume of companies
between the period before and after the ISRA award
2012-2014period.
The phenomenon of abnormal return is known
from using the calculation of the difference between
the actual return (actual return) occurs with the
expected return (expected return). Positive abnormal
return indicates that the actual return of the stock
during the period of the event is greater than the
expected return expected by the investors. Negative
abnormal returns indicate that the actual return in the
stock of the event period is lesser than the
expectation return expected by the investor.
In addition to the phenomenon of abnormal
return, then the other phenomenon that affects is a
fundamental factor consisting of return on assets,
debt to equity ratio and current ratio. Fundamental
analysis is one of the ways to evaluate stocks by
studying or observing various indicators related to
macroeconomic conditions and a company's
industrial conditions including various financial
indicators and corporate management. The greater
the ROA would be for the company, as it shows that
the total assets used for the company's operations
can provide profits for the company. Return on
assets is a ratio that illustrates the company's ability
to generate profits. This ratio shows profitability in
relation to the rate of return on investment.
Together, this ratio measures the performance of the
company's operations. Return on Assets (ROA) is a
ratio of profitability that compares the company's
operating profit (EBIT) with its total assets (Hery,
2015).Debt to Equity Ratio (DER) is the ratio used
to measure the extent to which the company is
financed by debt. DER is not good if it continues to
increase every year, it indicates that the use of debt
in financing the investment in assets is getting
bigger.Then the next fundamental factor, namely the
current ratio. Basically liquidity ratio analysis is
used to illustrate the company's ability to settle its
short-term liability. This is because the company has
not been able to meetcurrent liabilities with current
assets owned by the company. This ratio can be said
to be good if this ratio is above 1 or above 100%
means that current assets should be far above the
current liabilities.
In addition to fundamental factors affecting
abnormal returns, macroeconomic factors contribute
to the abnormal return, which is inflation. In this
study inflation variable is a control variable that
affects abnormal return. High levels of inflation
candampen people's purchasing power as well as
rising production factor prices. It usually affects the
pessimist assumption about the prospect of a
company that produces goods or services affected by
inflation so that it can affect the stock price offering
of the firm and ultimately result in the movement of
the stock price index on the Indonesia Stock
Exchange.
While research conducted byKalengkongan,
(2011) with the results of the study shows that
partially and simultaneously interest rates and
inflation have an effect on profitability measured by
return on assets. Interest rates have a significant and
positive effect on profitability measured by return on
assets, and Inflation has a significant and negative
effect on profitability measured by return on assets
indicating high inflation leads to the slow movement
of macro assets. Government banks can stabilize
their interest rates and inflation on banking finance
so that firms can increase their profits.Positive
influence of inflation, the company tends to have the
opportunity to profit in accordance with the target in
the business plan. Stable inflationary conditions
make the company inclined to have the opportunity
to allocate some of the profit gains to undertake
business expansion. When the inflation condition is
obtained according to expectation, it will have an
impact on improving the results of a fundamental
factor analysis of a company, one of which is the
profit gaining increase. (Fahmi, 2011).
Differences in research will be done with
previous research, which are variable sizes used and
combined in a period with different research objects.
Independent variables used are fundamental factors
measured by profitability that are proxied by return
on assets, leverage that is proxied with debt to equity
ratio, and liquidity provisional with current ratio.
Inflation variables in this study are used as control
variables. Then the dependent variable used is the
stock abnormal return. In addition, this research was
conducted on service companies listed on the
Indonesia Stock Exchange which are grouped by
several sectors and subsectors such as energy, toll
road, airport, port and building construction,
telecommunications, transportation,and non
buildingconstruction.
The reason the researcher uses a service
company, because the service company is a
developing company at the moment. As an example
of the infrastructure sub-sector, which is the basic
necessity of organizing the structural system
required for public sector and private sector
economic guarantees as necessary services and
facilities with the aim of the economy to function
properly. Therefore, researchers are keen to
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
320

investigate the Influence of Fundamental Factors
and Inflation Against Abnormal Return on Listed
Services Companies in Indonesia Stock Exchange.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Signaling theory is developed in economics and
finance to take into account the fact that insiders
generally have better and faster information relating
to current conditions and company prospects as
compared to outside investors. The emergence of
asymmetric information according to (Zaenal, 2005)
makes it difficult for investors to objectively assess
the quality of the company. The emergence of this
asymmetric information problem makes investors on
average give lower ratings to all company shares.
Thistrend in signaling theory is called pooling
equilibrium, as good quality companies and poor
quality companies are included in the same "Pool"
assessment. Signaling theoriespredict that the
company's highestprofitability and growth, its
performance will be good.
Understanding signalling theory according to
Fahmi (2016) is a theory that discusses the rise and
fall of prices in the market that will affect the
investor's decision. The concept of signaling theory
is very important, as for investors rising and
decreasing stocks in the market will give positive
and negative signals. Whatever the information that
comes from the condition of the stock of a company
is always to give effect to the decision of the
investor as the party who captures the signal. In
addition, Jensen and Meckling say that the signal
theory shows there are three additional elements that
can limit the deviant behaviors performed by agents.
These elements are the management of the labor
market, the capital market and the market elements
of the market for the desire to dominate and
dominate the ownership of the company (Jensen &
Meckling, 1976).
The implications of signalling theory according
to Karim (2015) assume that companies with
supersivosr performance (good companies) are
financial information to transmit signals to market.
This shows that the cost of the signal is higher on the
bad news than good news. In addition, it was found
that bad news companies were not worth replicating
and also sending unreliable signals.
Abnormal returns according to Jogiyanto (2010)
are the advantages of a real return on normal return.
Normal return is the expected return (return
expected by the investor). Therefore, an abnormal
return is the difference between the actual return that
occurs with the expected return. Return is actually a
return that occurs at t-t where the difference in price
is now relative to the previous price, while
expectation return is a return that must be estimated.
Return expectations are the expected benefits of
an investor in the future against the funds he has
placed. Hope describes something that can happen
beyond expectations. For example, an investor
expects to earn a profit of 25%, but it turns out that it
only gets 22%, it can be understood that the profit of
22% can still be said to get a return. Return actual
according is a condition that indicates that investors
have a positive value or greater value than the
expected return. On the contrary, investors have a
negative value or a smaller value than return actual
(Fahmi, 2016)
Fundamental analysis is a securities analysis that
uses fundamental data and external factors related to
business entities. The fundamental data in question
are financial data, market share data, business cycle
and the like. While external factor data relating to
business entities are government policies, interest
rates, inflation and the like. Considering these data,
fundamental analysis results in an analysis of the
assessment of a business entity with the conclusion
whether the company is a stock worth buying or not.
Return On Assets ia a ratio illustrates the
company's ability to generate profits. This ratio
shows profitability in relation to the rate of return on
investment. Together, this ratio measures the
performance of the company's operations.The ratio
of debt to equity ratio is also called debt-to-equity
ratio. This ratio shows how far the company is
financed by debt. The debt to equity ratio is
calculated by dividing the total debt of the firm with
shareholders' equity.Current ratio or current ratio is
also called current assets divided by short-term
liabilities. This ratio is to measure the ability of the
company to meet its immediate short-term debt
obligations using current available assets (Hery,
2015).
Inflation is an event that describes the situation
and condition where the price of the goods increases
and the value of the currencyis weakening, and if
this happens continuously, it will result in worsening
overall economic conditions (Fahmi, 2011). This
definition can be understood that inflation is an
endangering factor for the economy that is capable
of creating a very difficult to overcome effect that
ends in a state that can overthrow a ruling
government.
Research conducted Yanti (2012) by testing
abnormal return before and after the launch of the
Indonesia Sharia Stock Index (ISSI). The result of
The Impact of Fundamental Factors and Inflation on Abnormal Return on Registered Service Company on The Indonesia Stock Exchange
321

this study concludes the abnormal return of the stock
during the observation period 15 days before the
launch of ISSI. While for 10 days and 5 days before
launch and 15 days, 10 days, 5 days after launch
ISSI test one sample t-test showed no abnormal
return. On the test by using paired sample t-test can
be abnormal there is difference of abnormal return at
observation period of 15 days. While for observation
period 10 days and 5 days there was no difference of
abnormal return.
Research conducted Harahap (2012) on the
analysis of the difference in return and abnormal
return of shares before and after the announcement
of the right issue at the financial institutions listed on
the Indonesia Stock Exchange. From the above test
results, the Abnormal Return Shares before the
announcement of the Right Issue was equally
significant with abnormal Return Shares after the
announcement of the Right Issue. The reason is
because, statistically, if the significance of the t
value of 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005, and 2006 is
greater than that. This indicates that there is no
significant difference in abnormal stock returns prior
to announcement after the announcement.
Research Virginia et al., (2012) analyzes the
effect of earnings announcements on Abnormal
Return shares with results of earnings
announcements to market and content of
information. This is indicated by the significant
difference between the average abnormal return on
the 15th day and the average abnormal return during
the period of the event, meaning that the market
reacts to earnings announcements. Meanwhile,
research conducted by N. P. S. Dewi & Putra(2013)
which discusses the influence of right issue
announcement on abnormal return and stock trading
volume. Based on the results of the data analysis it
was found that the right issue announcement did not
have a significant effect on the abnormal return of
companies that did the right issue but significantly
affected the stock trading volume.
Research (F.N., 2013) analyzes the relationship
between economic development and abnormal return
on the Amman stock exchange. The results show
that the consumer price index, the fixed capital
formation and the money in the stock abnormal
return index are statistically significant and there is
no significant industrial production index. And
interest rate index money market and abnormal
return. Researchers emphasize on the economic
variables of fiscal and monetary policy in the
Jordanian economy, which is characterized as rapid
growth and therefore should be a continuous
analysis of market factors and determine the impact
on abnormal returns for firm stocks.
Research Chrisnanti(2015) on the difference in
actual return value, expected return, abnormal
return, trading volume activity and security activity
before and after merger on companies listed on the
Indonesia Stock Exchange. Test results show actual
return, expected return, abnormal return, trading
volume activity and security activity that merger in
the 30-day observation period before the merger
activity is no different than after the merger activity.
Research Randina & Fachrizal(2016) analyzes
the comparison of financial performance, abnormal
return and stock trading volumes between the
periods before and after the Indonesia Sustainability
Reporting Award (ISRA). The results showed that:
(1) There was no significant financial performance
difference between the period before the ISRA
achievement and the period after the achievement
when the proxy used was the net profit margin and
sales growth. However, with earning per share used
as a proxy of financial performance, the difference
between periods already exists. (2) There is no
significant difference in abnormal return between
the period before the achievement of the ISRA and
the period after the achievement. (3) There is a
significant difference in stock trading volumes
between the period before the achievement of the
ISRA and the period after the achievement.
Problem Formulation
Based on the background above which will be the
formulation of the problem in this study are:What is
the effect of fundamental factors and inflation on
abnormal return on service companies listed on the
Indonesia Stock Exchange?
Research Objectives
The purpose of this study is to test and analyze the
effect of fundamental factors and inflation on
abnormal return on service companies listed on
Indonesia Stock Exchange
Hypothesis
Based on the above description, the hypotheses of
this research are fundamental factors measured with
profitability ratio proxied by return on assets, ratio
of leverage is proxied by debt to equity ratio and
liquidity ratio is proxied by current ratio and
inflation as control variable has an effect on
abnormal return.
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
322
3 RESEARCH METHOD
This type of research is a type of quantitative
research. Quantitative research, a study aimed at
explaining causal relationships between independent
variables and dependent variables through
hypothesis testing (Kuncoro, 2013). The object of
this research is a service company listed on the
Indonesia Stock Exchange during the period 2011-
2015.
Independent variables in this study are fundamental
factors that are measured by return on assets (X1),
debt to equity ratio (X2), current ratio (X3), and
(X4) inflation as control variables. Dependent
variable in this research is stock abnormal return
(Y). Analysis techniques used in this study are
double linear regression analysis and classic
assumptions.
Data type used in this research is quantitative
data. Data sources in this study use secondary data.
According to (Kuncoro, 2013), secondary data is a
data usually collected by a data collection board and
published to the data user community. Secondary
data that will be used in this research is the financial
statement data of the service company starting from
2011-2015 which is sourced from www.idx.co.id.
Dependent variable in this study is abnormal
return. According to (Jogiyanto, 2010) an abnormal
return is the return of an investor who does not meet
the expectations. Abnormal return is the difference
between the expected return and the gain it receives.
The difference in return is positive if the gain is
greater than the expected return or calculated return.
Whereas the return will be negative if the returned
gain is less than the expected return or calculated
return. The abnormal return to be used as a
dependent variable in the research is by formula:
(1)
Model estimation used in this test is a market
model, since it is considered that the best guesser to
estimate the return of a security is the return of the
current market index. Calculation of this model,
namely:
1. To calculate the actual price (Rit) used daily stock
price data calculated by
(2)
description:
R
it
= share price of accruals
P
it
= stock price period t
P
i-t
= stock price
2. To calculate the market return in the estimate
period, the daily market price is used by the Joint
Stock Price Index (JCI). Market returns can be
calculated by the formula:
Rmt = (〖IHSG〗 _t- 〖IHSG〗 _ (t-1))
〖IHSG〗_(t-1)
(3)
Description:
Rmt = market return
IHSGt = Joint Stock Price Index period t
IHSGt-1 = Stock Composite Index before
period t
3. To calculate abnormal return (ARIT) will be used
market price method, according to (Jogiyanto,
2014), abnormal return can be calculated by
formula:
AR_it=Rit-Rmt
(4)
Description:
ARit = abnormal return of the 1st security
of the t-period
Rit = return actually happened to the 1st
security t-event period
Rm
t
= expectation return market
Independent variables in this study are
fundamental factors that are measured by financial
ratios consisting of return on assets, debt to equity
ratio, current ratio and inflation.
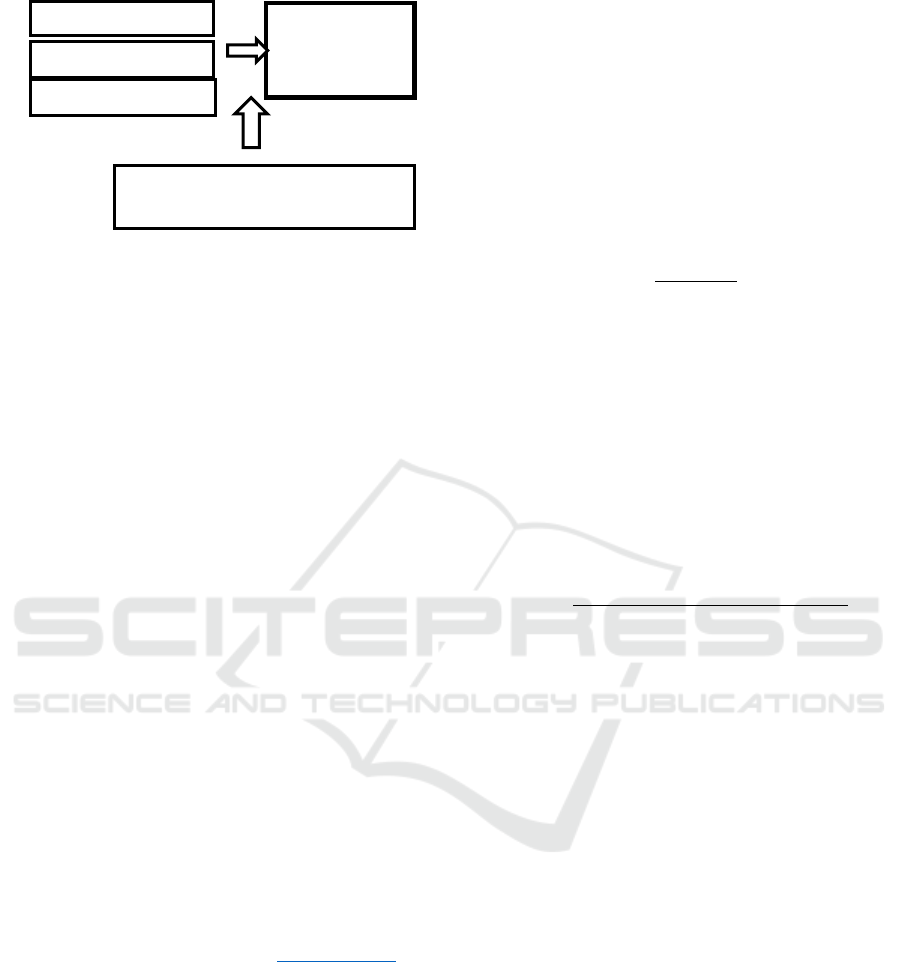
ROA (X
1
)
DER (X
2
)
CR (X
3
)
ABNORMAL
RETURN (Y)
INFLATION
(CONTROL VARIABLE)
Figure 1. Research Model
The Impact of Fundamental Factors and Inflation on Abnormal Return on Registered Service Company on The Indonesia Stock Exchange
323

Return on Assets
Return on assets or return on investment is a form of
profitability ratio to measure the ability of an entity
to generate profits by using the total assets available
and after capital costs (costs used to fund the assets)
are excluded from the entity. (Irfan, 2014). The
ROA indicator in this study is as follows:
ROA = Earning After Tax (EAT)
Total Assets
(5)
Current Ratio
This ratio compares short-term liabilities with short-
term resources available to meet those liabilities
(Horne & Jhon, 2012)
Control Variable
The coefficient variable in this study is inflation rate.
Inflation by Fahmi(2011) is an increase in prices
generally and continuously over a period of time.
The rise in high prices will lead to high inflation,
this condition will have an effect on rising
production costs. High production costs will cause
the price of manufactured goods to rise, and this will
reduce the purchasing power of the people.
Decreasing public purchasing power will lower the
company's profits resulting in decreasing company
performance.
Decrease in corporate performance as the impact
of inflation will be felt by all existing companies. So
no company can avoid the impact of inflation. This
condition will affect the capital market, which
results in high uncertainty in the company's share
price.
Variable Controls or complementary variables to
complement or control their causal relationships to
better obtain a more complete and better empirical
model. These control variables are not the main
variables examined and tested, but rather to other
variables that have the effect of influence
(Jogiyanto, 2010). Indicators used in this study are
to calculate the magnitude of the inflation rate can
be usedThe Price Index, as follows:
IR
x
= (IHK
x
/ IHK
x-1
. 100) – 100
(6)
Analysis Technique
Multiple Linear Regression Analysis
Generally, Y observation data is influenced by free
variables X1, X2, X3, ...... Xn so the general formula
of this multiple linear regression is:
Y = α0 + α
1
X
1it
+ α
2
X
2it
+ α
3
X
3it
+ α
4
X
4it
+ e...
7
Y : Abnormal Return
X1 : Variable Return On Assets
X2 : Variable Debt To Equity Ratio
X3 : Variable Current Ratio
X4 : Inflation Variable
α1 : Regression coefficient
a : Constant
e : Standard Error
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
This study uses a sample of 87 service companies
from various sectors listed on the Indonesia Stock
Exchange (IDX) during the period 2011-2015.
Based on the criteria set out of the population of 149
service companies listed on the IDX during the
period 2011-2015, there were 44 service companies
with IPOs, 7 service companies that compiled their
financial statements with currencies other than the
rupiah and 11 loss service companies during the
2011-2015 period. The total number of listed
companies in this study amounted to 87 companies.
Abnormal Return is the difference between the
actual return that occurs with the expected return.
An abnormal return will be positive if the expected
return is greater than the calculated return. While the
abnormal return will be negative if the gain is less
than expected or calculated return. From stistatic
analysis it is known that the company that gives the
highest abnormal returns between 2011-2015 is PT.
Asuransi Multi Artha Guna (AMAG) is 3,2029
while the lowest abnormal return during the 2011-
2015 period is provided by PT. Reinsurance
Company of Indonesia. Tbk (MREI) of -1,571. From
the table above it can be seen that the average
service firms that became sample in this study gave
a negative abnormal return. This means that the
realized return does not match the expected return.
Return on Assets is a measure of the company's
effectiveness in generating profits by utilizing its
assets. Return on Assets is measured by comparing
net income to assets owned by the company. The
higher the return on asset means a good-looking
company generates profits. Based on the table it can
be seen that the highest value of fundamental return
on asset (ROA) value during 2011-2015 is PT.
Royal Oak Development. Tbk (RODA) with a value
of 1.44838 which occurred in 2015, if viewed from
2011, this company experienced an increase in the
ability to generate profits from its assets ie 0.0056 in
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
324

2011, 0.2925 in 2012, 0.1555 in 2013 and 0.1587 in
2014. While the lowest return on asset during 2011-
2015 is PT Bank Internasional Indonesia with the
value of 0.0050 that occurred in 2014. From 2011 to
2015 there was a fluctuation of the company's ability
in returning profits from its assets of 0.0071 in 2011,
increased to 0.0105 and 0.0112 in 2012 and 2013
and again rising in 2015 to 0.0073.
Debt to equity ratio is a debt to equity ratio. This
ratio measures how far the company financed by
debt, which increasingly indicates this ratio
illustrates the bad phenomenon for the company.
Debt improvement will ultimately affect the size of
the company's profits. This will give a bad signal to
investors. The highest debt to equity ratio during
2011-2015 is PT. Bank Artha Graha Internasional.
Tbk (INPC) with a value of 15,62025 ie in 2011.
This shows that the company has a dependency on
debt in its operational finance. If we see from 2011to
2015, there is a decrease in debt to equity ratio ratio
of 9.61193 in 2012, then decreased in 2013 to
7,12573, in 2014 and 2015 the ratio of DER in the
company at 8%. This suggests that the company
seeks to reduce dependence on debt in its
operational financing. While the lowest debt to
equity ratio during pe 2011 2011-2015 is PT. Bank
Pan Indonesia. Tbk (PNBN) with a value of 0.00643
that occurred in 2014. From 2011 to 2013, there was
a huge debt to equity ratio of 6.88611 in 2011,
7,43124 and 7,21986 in 2012 and 2013. Meanwhile,
in the year of 2015 the company made a loan so the
ratio of debt to equity ratio increased again at 4.94%.
Current ratio shows the company's ability to
meet its short-term liabilities with the company's
current assets. The greater the ratio of current assets
to short-term liabilities, indicating the higher the
company's ability to meet its short-term obligations,
this will likely increase the credibility of the
company in the eyes of investors. The highest
current ratio is PT. Bank Bumi Arta, Tbk (BNBA)
with a value of 12,980 in 2012 and the lowest
current ratio is PT. Bank CIMB Niaga, Tbk is a
magnificent value of 0.0062 in 2012. The value of
the current asset value of the service companies
fluctuates, indicating that there is a change in the
liquidity of the company every year.
Multiple linear analysis is used to find out how
much influence the variables used in this research
are return on assets, debt to equity ratio and current
ratio to abnormal return. processing equation of
multiple regression analysis as follows:
Y=1,860+1,342X1+0.254X2+0.335X3+
0,890X4 +e
(8)
Multicollinearity test
From test result indicates that the tolerance value is
greater than 0.1 and the value of VIF is less than 10
which means that the variable return on assets, debt
to equity ratio, current ratio and inflation to the
abnormal return are multicollinearity. From test
result indicates that the tolerance value is greater
than 0.1 and the value of VIF is less than 10 which
means thatvariable return on assets, debt to equity
ratio, current ratio and inflation to multicollinearity-
free abnormal returns.
Heterokedasticity Test
The heterokedasticity test results show that all
independent variables consisting of return on assets,
debt to equity ratio, current ratio and inflation have
significance value greater than 0.05. Thus the model
made does not contain symptoms of
heterokedastisity, so it is feasible to use to predict.
The model summary the adjusted R
2
is 0.934. This
means that 93.4% of abnormal return variables can
be explained by variable return on assets, debt to
equity ratio and current ratio. While the rest 100% -
93.4% = 6.6% is explained by reasons beyond the
research model.
The first hypothesis of the return value of the
return on asset to abnormal return is significant
because the return on asset value to the abnormal
return has a significant value of 0,000 <0,05 so that
the first hypothesis is accepted. The second
hypothesis of the value of debt to equity ratio to
abnormal return has a significant value of 0,000
<0,05 and the third hypothesis has a value of current
ratio variable to abnormal return of 0,000 <0,05 so
the second and third hypotheses are accepted.
The results shows that covariate variables are not
significant. It is shown by Adjusted R
2
value of
81.4% without covariate to 81.2% with variable
covariate. So, it can be concluded that the model is
good. While the effect of return on sset, debt to
equity ratio and current ratio interaction is not
significant as a result of variable covariate inflation.
Corelational Studies
Correlational study is a study with conditions
involving control variables performed by using
product moment correlation by using partial
correlation method. The higher the control variable,
it can control all independent and dependent
variables. The result shows no correlational between
debt to equity ratio and current ratio to abnormal
return. It is shown that the value of return on assets
The Impact of Fundamental Factors and Inflation on Abnormal Return on Registered Service Company on The Indonesia Stock Exchange
325

has a correlation value of -0,059. Debt to equity ratio
has a correlation value of 0.137 and current ratio has
a correlation value of -0,059.
The Impact of Return On Assets Against
Abnormal Return. Result of t test in multiple
regression analysis in this research is the return on
asset has a significant positive effect on abnormal
return. This is indicated by the value of t
count
> t
table
that is 5,581> 1,98932 significantly smaller than the
confidence level, that is 0,000 <0,05.
The results of this study are in line with the
research conducted Pouraghajan, Emamgholipour,
Niazi, & Samakosh(2012), Zuliarni (2012), Anhar &
Abdullah (2014), Raningsih & Putra (2015) and
Ariyanti(2016) shows that the profitability ratio has
a positive effect on the stock return. Return on assets
reflect how many companies have earned revenue
from financial resources invested in companies.
Profit-producing companies reflect the performance
of a good company so that stock prices and stock
returns increase. Investors will capture the
information and will choose to invest in profit-taking
companies, thereby gaining return on stocks invested
and reducing the risks from such investments.
Influence of Debt to Equity Ratio Against
Abnormal Return. The result of t test in multiple
regression analysis on the influence of Debt to
Equity Ratio on abnormal return is Debt to Equity
Ratio positively affects the abnormal return so the
hypothesis can be accepted. This is indicated by the
value of t
count
> t
table
that is 39,719> 1,98932 and the
significant value is smaller than the confidence
level, that is 0,000 <0,05. Based on the theory that
debt to equity ratio according to Fahmi (2016: 73) is
a measure used in analyzing financial statements to
show the amount of collateral available to creditors.
Debt to equity ratio is preferred because the ideal
firm has a debt to equity ratio = 1 or debt = equity.
The higher the debt to equity ratio, the more debt to
the company than the equity it holds. The results are
in line with the research conducted by Aisyah (2009)
Ullah & Shah (2014), Raningsih & Putra (2015), and
P. E. D. M. Dewi (2016). The result of debt to equity
ratio research has a positive effect on stock return.
The results show that the debt to quity ratio
positively affects the stock return. It reflects the
optimum utilization of the company's debt so there
are benefits earned by using its debt. Companies that
are able to capitalize on debt well and optimally will
provide greater returns and returns than just using
their own capital (Raningsih & Putra, 2015)
The increased use of debt, which is reflected by
the greater debt ratio (ratio of debt to total assets), on
earning the same profit before interest and tax
(EBIT) will result in a larger profit per share. If
earnings per share increases, it will have an impact
on increasing stock prices or stock returns, so
theoretically debt to equity ratio will have a positive
effect on stock returns (Susilowati & Turyanto,
2011). These results indicate that there are different
considerations from some investors in looking at
debt to equity ratio. By some investors debt to equity
ratio is considered the company's responsibility to
third parties ie creditors who lend to the company.
So the greater the value of debt to equity ratio will
increase the company's liabilities. Nevertheless, it
seems that some investors actually view that
growing companies will definitely need debt as
additional funds to meet the funding of a growing
company. The company needs a lot of operational
funds that are unlikely to be met only from the
company's own capital. This condition led to the
possibility of a growing company in the future
which led to an increase in stock returns. This study
uses signal theory as the basic theory. According to
Brigham and Houstan signal theory is an act taken
by a company's management to provide investors
with guidance on how the management assessed the
prospects of the company. Firms with very bright
prospects prefer not to fund through new stock
offerings, while firms with bad prospects are fond of
funding with outside equity. The information
contained in the financial statements is a company
signal to stakeholders who can influence decision
making (Parwati & Sudiartha, 2016).
Influence of Current Ratio on Abnormal Return.
Based on the result of the test, the result of the
current ratio has positive effect on abnormal return.
This is shown by the value of tcount> ttabel of
26,359> 1,98932 and significance value of 0,000
<0,05, which means that the value of significance in
this study is smaller than the specified level of trust.
This research is based on the research conducted by
Aisyah (2009), Amanah, Atamanto, & D(2014),
Parwati & Sudiartha, (2016) and Y.Saputri &
H.Soekotjo(2016) ratio has a significant positive
effect on stock return. The larger the current assets
and the current liabilities the higher the company's
ability to cover its short-term obligations. The higher
the current ratio, it can be said that the company has
a greater ability to meet its short-term financial
obligations. The better the current ratio reflects the
more liquid the company. This is a signal given by
the company to investors, so it will be able to
increase the company's stock return. Current ratio
according to Fahmi (2016) is a commonly used
measure of short-term solvency, the ability of a firm
to meet the needs of debt upon maturity. The
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
326

condition of a company with a good current ratio is
considered to be a good and good company, but if
the current ratio of assets viewed too high is
considered good. On behalf of the company's
manager has a high current ratio considered to be
good, even the creditors view that the company is in
a state of affairs.
5 CONCLUSION
Based on the results of data analysis and discussion,
it can be concluded that the return on assets partially
and togetherly have a significant and positive effect
on the abnormal return. This suggests that the
magnitude of return on assets on the company has an
effect on abnormal return received by investors and
indicates that investors see return on assets have a
role in making investment decisions. The debt to
equity ratio Test partially and togetherly have a
significant and positive effect on abnormal return on
BEI-listed service companies for the period 2011-
2015. These results indicate different considerations
from some investors in view of the debt to equity
ratio. By most debt-to-equity investors, it is seen by
the company's liability to third parties ie creditors
who lend to companies. So the greater the value of
debt to equity ratio will increase the company's
liabilities. Nevertheless, it seems that some investors
actually view that growing companies will definitely
need debt as additional funds to meet the funding of
a growing company. The company needs a lot of
operational funds that are unlikely to be met only
from the company's own capital. This condition led
to the possibility of a growing company in the future
which led to an increase in stock returns. The current
ratio test are partially and togetherly have a
significant and positive effect on the abnormal return
on the BEI-listed service companies for the period
2011-2015. This shows that the small ratio of the
current ratio affects stock return, the increasing
current ratio will give a positive signal to the
investor, thereby increasing the stock price which
will ultimately affect the return that the investor will
receive. This shows that the current ratio can be the
consideration of investors in investing. Test results
together (f Test) variable return on assets, debt to
equity ratio, current ratio and inflation together have
an effect on abnormal return so that the research
model can be used.
For Further Researchers, it is necessary to
conduct a more detailed analysis of the research
sample by combining the financial variables and the
macro and micro variables used so that there is a
clear distinction to further research. For the
Company, investors who will decide on the share
sale and purchase decision should be made based on
the real phenomenon and the latest phenomenon.
Always pay attention to the condition of the capital
market so that it is directly or indirectly clearly the
difference.
REFERENCES
Agustina, L., & Kianto, F. (2012). Pengumuman Informasi
Laba Akuntansi Terhadap Abnormal Return Pada
Perusahaan Yang Tergabung dalam Indeks LQ45.
Jurnal Akuntansi, 4, 135–152.
Aisyah, I. S. (2009). Pengaruh Variabel-Variabel
Keuangan pada Initial Return Saham di Pasar Perdana.
Trikonomika, 8(1), 22–31.
Amanah, R. D., Atamanto, & D, F. A. (2014). Pengaruh
Rasio Likuiditas dan Rasio Profitabilitas Terhadap
Harga Saham (Studi Pada Perusahaan Indeks LQ 45
Periode 2008-2012). Jurnal Administrasi Dan Bisnis,
12(1)
Anhar, P., & Abdullah, H. (2014). Analisis Pengaruh
Return on Asset, Debt to Total Asset dan Debt to
Equity Ratio Terhadap Devidend Payout Ratio Pada
Perusahaan Manufaktur Yang Terdaftar di Bursa Efek
Indonesia Periode 2009-2011. Jurnal Dinamika
Ekonomi, 7(2), 13–31.
Ariani, A. D., Topowijono, & Sulasmiyati, S. (2015).
Analisis Perbedaan Abnormal Return Dan Likuiditas
Saham Sebelum Dan Sesudah Right Issue ( Studi
padaPerusahaan-Perusahaan yang Terdaftar di Bursa
Efek Indonesia Tahun. Jurnal Administrasi Bisnis
(JAB), 33(2), 49–58.
Ariyanti, A. I. (2016). Pengaruh CR, TATO, NPM dan
ROA Terhadap Return Saham. Jurnal Ilmu Dan Riset
Manajemen, 5(4).
Awudu, Y., Sampson, S., & Esumanba, V. (2013).
Determinants of Abnormal Returns on the Ghana
Stock Exchange. Research Journal of Finance and
Accounting, 4(11), 7–17.
Ayu Era Swandewi, Gusti dan Made Mertha, I. (2013).
Abnormal Return Portofolio Winner-Loser Saham
Manufaktur di PT. Bursa Efek Indonesia. Udayana, E-
Jurnal Akuntansi Universitas, 5(1), 85–99.
Chrisnanti, F. (2015). Perbedaan Nilai Actual Return ,
Expected Return , Abnormal Return , Trading Volume
Activity Dan Security Return Variability Sebelum Dan
Sesudah Merjer Pada Perusahaan Yang Terdaftar.
Jurnal Bisnis Dan Akuntansi, 17(1), 1–9.
Dewi, N. P. S., & Putra, I. N. W. A. (2013). Pengaruh
Pengumuman Right Issue Pada Abnormal Return Dan
Volume. E-Journal Akuntansi Universitas Udayana,
3, 163–178.
Dewi, P. E. D. M. (2016). Pengaruh Rasio Likuiditas,
Profitabilitas, Solvabilitas, Aktivitas dan Penilaian
Pasar Terhadap Return Saham. Jurnal Ilmiah
The Impact of Fundamental Factors and Inflation on Abnormal Return on Registered Service Company on The Indonesia Stock Exchange
327

Akuntansi, 1(2), 109–132.
F.N., A.-S. (2013). Analysis of The Relationship Between
Economic Forces And Abnormal Stock Return:
Empirical History of Amman Stock Exchange ( ASE ).
Polish Journal Of Management Studies, 8, 7–15.
Fahmi, I. (2011). Analisis Kinerja Keuangan. Bandung:
Alfabeta.
Fahmi, I. (2016). Pengantar Manajemen Keuangan Teori
dan Soal Jawab. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Harahap, A. (2012). Analisis Perbedaan Return dan
Abnormal Return Saham Sebelum dan Setelah
Pengumuman Right Issue Pada Lembaga Keuangan
Yang Terdaftar Di Bursa Efek Indonesia. Jurnal
Ekonomi, 20(September), 1–12.
Hery. (2015). Analisis Laporan Keuangan (Pendekatan
Rasio Keuangan). Bandung: Kencana.
Horne, J. Van, & Jhon. (2012). Prinsip-Prinsip
Manajemen Keuangan. Jakarta: Salemba Empat.
Irfan, F. (2014). Analisis Laporan Keuangan. Bandung:
Alfabeta.
Jensen, M. C., & Meckling, W. H. (1976). Theory of the
firm: Managerial behavior, agency costs and
ownership structure. Journal of Financial Economics,
3(4), 305–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-
405X(76)90026-X
Jogiyanto, H. M. (2010). Teori Portofolio dan Analisis
Investasi. Yogyakarta: BPFE.
Kalengkongan, G. (2011). Tingkat Suku Bunga dan Inflasi
Pengaruhnya Terhadap Return on Asset (ROA) Pada
Industri Perbankan yang Go Publik di Bursa Efek
Indonesia. Jurnal EMBA, 1(4), 737–747.
Karim, A. (2015). Bank Islam : Analisis Fiqih dan
Keuangan Lainnya. Jakarta: PT. Rajawali Pers.
Kasmir. (2015). Analisis Laporan Keuangan. Jakarta: Raja
Grafindo.
Kuncoro, M. (2013). Metode Riset untuk Ekonomi dan
Bisnis – Bagaimana Meneliti dan Menulis Tesis ? (4th
ed.). Jakarta: Erlanggga.
Agustina, L., & Kianto, F. (2012). Pengumuman Informasi
Laba Akuntansi Terhadap Abnormal Return Pada
Perusahaan Yang Tergabung dalam Indeks LQ45.
Jurnal Akuntansi, 4, 135–152.
Aisyah, I. S. (2009). Pengaruh Variabel-Variabel
Keuangan pada Initial Return Saham di Pasar Perdana.
Trikonomika, 8(1), 22–31.
Amanah, R. D., Atamanto, & D, F. A. (2014). Pengaruh
Rasio Likuiditas dan Rasio Profitabilitas Terhadap
Harga Saham (Studi Pada Perusahaan Indeks LQ 45
Periode 2008-2012). Jurnal Administrasi Dan Bisnis,
12(1)
Anhar, P., & Abdullah, H. (2014). Analisis Pengaruh
Return on Asset, Debt to Total Asset dan Debt to
Equity Ratio Terhadap Devidend Payout Ratio Pada
Perusahaan Manufaktur Yang Terdaftar di Bursa Efek
Indonesia Periode 2009-2011. Jurnal Dinamika
Ekonomi, 7(2), 13–31.
Ariani, A. D., Topowijono, & Sulasmiyati, S. (2015).
Analisis Perbedaan Abnormal Return Dan Likuiditas
Saham Sebelum Dan Sesudah Right Issue ( Studi pada
Perusahaan-Perusahaan yang Terdaftar di Bursa Efek
Indonesia Tahun. Jurnal Administrasi Bisnis (JAB),
33(2), 49–58.
Ariyanti, A. I. (2016). Pengaruh CR, TATO, NPM dan
ROA Terhadap Return Saham. Jurnal Ilmu Dan Riset
Manajemen, 5(4).
Awudu, Y., Sampson, S., & Esumanba, V. (2013).
Determinants of Abnormal Returns on the Ghana
Stock Exchange. Research Journal of Finance and
Accounting, 4(11), 7–17.
Ayu Era Swandewi, Gusti dan Made Mertha, I. (2013).
Abnormal Return Portofolio Winner- Loser Saham
Manufaktur di PT. Bursa Efek Indonesia. Udayana, E-
Jurnal Akuntansi Universitas, 5(1), 85–99.
Chrisnanti, F. (2015). Perbedaan Nilai Actual Return ,
Expected Return , Abnormal Return , Trading Volume
Activity Dan Security Return Variability Sebelum Dan
Sesudah Merjer Pada Perusahaan Yang Terdaftar.
Jurnal Bisnis Dan Akuntansi, 17(1), 1–9.
Darmadji, T. (2006). Pasar Modal Indonesia : Pendekatan
dan Tanya Jawab. Jakarta: PT. Salemba Empat.
Dewi, N. P. S., & Putra, I. N. W. A. (2013). Pengaruh
Pengumuman Right Issue Pada Abnormal Return Dan
Volume. E-Journal Akuntansi Universitas Udayana,
3, 163–178.
Dewi, P. E. D. M. (2016). Pengaruh Rasio Likuiditas,
Profitabilitas, Solvabilitas, Aktivitas dan Penilaian
Pasar Terhadap Return Saham. Jurnal Ilmiah
Akuntansi, 1(2), 109–132.
F.N., A.-S. (2013). Analysis of The Relationship Between
Economic Forces And Abnormal Stock Return:
Empirical History of Amman Stock Exchange ( ASE ).
Polish Journal Of Management Studies, 8, 7–15.
Fahmi, I. (2011). Analisis Kinerja Keuangan. Bandung:
Alfabeta.
Fahmi, I. (2016). Pengantar Manajemen Keuangan Teori
dan Soal Jawab. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Harahap, A. (2012). Analisis Perbedaan Return dan
Abnormal Return Saham Sebelum dan Setelah
Pengumuman Right Issue Pada Lembaga Keuangan
Yang Terdaftar Di Bursa Efek Indonesia. Jurnal
Ekonomi, 20(September), 1–12.
Hery. (2015). Analisis Laporan Keuangan (Pendekatan
Rasio Keuangan). Bandung: Kencana.
Horne, J. Van, & Jhon. (2012). Prinsip-Prinsip
Manajemen Keuangan. Jakarta: Salemba Empat.
Irfan, F. (2014). Analisis Laporan Keuangan. Bandung:
Alfabeta.
Jensen, M. C., & Meckling, W. H. (1976). Theory of the
firm: Managerial behavior, agency costs and
ownership structure. Journal of Financial Economics,
3(4), 305–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-
405X(76)90026-X
Jogiyanto, H. M. (2010). Teori Portofolio dan Analisis
Investasi. Yogyakarta: BPFE.
Kalengkongan, G. (2011). Tingkat Suku Bunga dan Inflasi
Pengaruhnya Terhadap Return on Asset (ROA) Pada
Industri Perbankan yang Go Publik di Bursa Efek
Indonesia. Jurnal EMBA, 1(4), 737–747.
Karim, A. (2015). Bank Islam : Analisis Fiqih dan
Keuangan Lainnya. Jakarta: PT. Rajawali Pers.
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
328

Kasmir. (2015). Analisis Laporan Keuangan. Jakarta: Raja
Grafindo.
Kuncoro, M. (2013). Metode Riset untuk Ekonomi dan
Bisnis – Bagaimana Meneliti dan Menulis Tesis ? (4th
ed.). Jakarta: Erlanggga.
Parwati, R. R. A. D., & Sudiartha, G. M. (2016a).
Pengaruh Profitabilitas, Leverage, Likuiditas dan
Penilaian Pasar Terhadap Return Saham Pada
Perusahaan Manufaktur. E-Jurnal Manajemen Unud,
5(1), 385–413.
Parwati, R. R. A. D., & Sudiartha, G. M. (2016b).
Pengaruh Profitabilitas, Leverage, Likuiditas dan
Penilaian Pasar Terhadap Return Saham Pada
Perusahaan Manufaktur. E-Jurnal Manajemen Unud,
5(1), 385–413.
Permana, H. T., Sutejo, B. S., & Si, M. (2013). Perbedaan
Abnormal Return Pada Sektor Keuangan Sebelum dan
Sesudah Peristiwa Pilkada Gubernur DKI Jakarta 20
September 2012. Jurnal Ilmiah Mahasiswa
Universitas Surabaya, 2(1), 1–9.
Pouraghajan, A., Emamgholipour, M., Niazi, F., &
Samakosh, A. (2012). Information Content of
Earnings and Operating Cash Flows: Evidence from
the Tehran Stock Exchange. International Journal of
Economics and Finance, 4(7), 41–52.
https://doi.org/10.5539/ijef.v4n7p41
Purbawati, T. D., Arifati, R., & Andini, R. (2016).
Pengaruh Pemecahan Saham ( Stock Split ) Terhadap
Trading Volume Activity Dan Average Abnormal
Return Pada Perusahaan Yang Terdaftar Di Bursa
Efek. Journal of Accounting, 2(2), 1–12.
Putra, E. M., Kepramareni, P., & Novitasari, N. L. G.
(2016). Pengaruh Kinerja Keuangan, Inflasi dan
Tingkat Suku Bunga Terhadap Nilai Perusahaan. In
Seminar Nasional 2016. Depasar.
Randina, T. M. M., & Fachrizal. (2016). Analisis
Perbandingan Kinerja Keuangan , Abnormal Return
Dan Volume Perdagangan Saham Antara Periode
Sebelum Dan Sesudah Meraih Indonesia. Jurnal
Ilmiah Mahasiswa Ekonomi Akuntansi (JIMEKA),
1(2), 71–83.
Raningsih, N. K., & Putra, I. M. P. D. (2015). Pengaruh
Rasio-Rasio Keuangan dan Ukuran Perusahaan Pada
Return Saham. E-Jurnal Akuntansi Udayana, 13(2),
582–599.
Sadikin, A. (2011). Analisis Fundamental Return Saham
dan Volume Perdagangan Saham, Sebelum dan
Sesudah Peristiwa Pemecahan Saham (Studi pada
Perusahaan yang Go Publik di Bura Efek Indonesia.
Jurnal Manajemen Dan Akuntansi, 12(April), 25–34.
Susilowati, Y., & Turyanto, T. (2011). Reaksi Signal
Rasio Profitabilitas Dan Rasio Solvabilitas Terhadap
Return Saham Perusahaan. Dinamika Keuangan Dan
Perbankan, 3(1), 17–37.
Tehranizadeh, N. R., & Torabi, R. (2015). The impact of
abnormal returns of shares on slump of one-day shares
price in 50 top companies listed in Tehran Stock
Exchange ( 2003-2013 ). Journal of Scientific
Research and Development, 2(3), 34–37.
Virginia, S., Manurung, E. T., & Muliawati. (2012).
Pengaruh Pengumuman Earnings Terhadap Abnormal
Return Saham. Jurnal Administrasi Bisnis, 8(1), 1–20.
Wei, Y.-C., LU, Y.-C., & LIN, I.-C. (2013). The Impact
Of Financial News and Press Freedom on Abnormal
Returns Around Earnings Announcement Periods in
The Shanghai, Shenzhen and Taiwan Stock Markets.
Romainan Journal of Economic Forecasting, 32(1),
44–45. https://doi.org/10.1002/fut
Wibowo, F. W. (2015). Pengaruh Kinerja Keuangan
Terhadap Return Saham Pada Perusahaan
Manufaktur yang Terdaftar di Bursa Efek Indonesia.
Thesis Universitas Muhammadiyah Surakarta.
Yanti, F. (2012). Pengujian Abnormal Return Saham
Sebelum dan Sesudah Peluncuran Indeks Saham
Syariah Indonesia (ISSI). Jurnal Manajemen,
1(September), 1–7.
Yulita, I. G. . A. A., & Suwarta, I. K. (2014). Pengaruh
Faktor Fundamental dan Ekonomi Makro Pada Return
Saham Perusahaan Consumer Good. E-Jurnal
Akuntansi Universitas Udayana, 8, 353–370.
Zaenal, A. (2005). Teori Keuangan & Pasar Modal.
Yogyakarta: Ekonisia Kampus Fakultas Ekonomi UII.
Zuliarni, S. (2012). Pengaruh Kinerja Keuangan Terhadap
Harga Saham Pada Perusahaan Mining and Mining
Service di Bursa Efek Indonesia. Jurnal Aplikasi
Bisnis, 3(36–48).
The Impact of Fundamental Factors and Inflation on Abnormal Return on Registered Service Company on The Indonesia Stock Exchange
329
