
The Effect of Trading Frequency of Stocks, The Value of Company
and Level of Financial Performance on Stock Return
(Empirical Study on Agribusiness Companies Registered in
Indonesia Stock Exchange)
Firmansyah Arifin, Rifani Akbar Sulbahri, and Padriyansyah
Universitas Negeri Sriwijaya, Palembang, Indonesia
Keywords: Stock of Return, Frequency of Trading, Price Book Value, Return on Assets, Return on Equity, Debt to
Equity, Logistic Regression.
Abstract: The objective of this study was to find out and analyze the impact of financial performance against Stock of
Return on Index Agri companies in Indonesia Stock Exchange period 2015-2017. The data were analyzed
by using logistic regression analysis model. There were five variables in this research. Dependen variabel
was Stock of Return is proxied. Independen variabel in this research was Frequency of trading ,Price Book
Value (PBV) as a proxy of the stock value, Return on Assets (ROA) as a proxy of profitability, Return on
Equity (ROE) as a proxy of profitability and Debt to Equity Ratio (DER) as a proxy capital stucture.These
results of logistic regression showed that the variabels Frequency of trading ,Price Book Value (PBV) as a
proxy of the stock value, Return on Assets (ROA) as a proxy of profitability, Return on Equity (ROE) as a
proxy of profitability and Debt to Equity Ratio (DER) as a proxy capital structure variable has no effect on
stock of return on Index Agri companies in Indonesia Stock Exchange 2015-2017. This research give due
consideration to the company's management to consider the financial governance of the company to
generate earnings and stock of return. For investors can raise the level of profitability as the main indicator
in determining investment decisions to maximize income from dividends on shares held and capital again.
1 INTRODUCTION
Shares are securities that indicate ownership of
the company so that shareholders have the right of
claim over dividends or other distributions made by
the company to its shareholders, including the rights
of claims on the assets of the company, with priority
after the rights of other securities holder claims are
met in the event of liquidity. According to Husnan
(1998), securities is a piece of paper that indicates
the right of the investor (ie ownership the paper) to
obtain a portion of the prospect or wealth of the
organization issuing the securities and the conditions
under which the investor may exercise his right,
while according to tandelilin (2010) stock is a proof
that the ownership of the assets of the company that
issued the shares.
Changes in stock prices is a phenomenon that
always occurs in all stock exchanges in the world,
when stock prices have increased demand by
investors then the stock also experienced an increase
in price of these shares. Increasing demand for a
particular stock will result in an increase to the stock
index where the stock is located. In the increase or
decrease in stock prices caused by the increase and
decrease in demand by investors is fluctuating that
can be quickly or slowly influenced by the
frequency of trading in shares of stock.
The investors are motivated to invest one of them
is to buy the company's stock in the hope of getting a
return on investment in accordance with what has
been invested. According Ang (1997) The concept
of return is the level of benefits enjoyed by investors
on an investment that he did. Return of shares is the
income earned by shareholders as a result of its
investment in certain companies. According
Jogiyanto (2000) Return of stock can be divided into
two types, realized return and expected return.
Return realization is a return that has occurred and
calculated based on historical data. Return
Arifin, F., Akbar Sulbahri, R. and Padriyansyah, .
The Effect of Trading Frequency of Stocks, the Value of Company and Level of Financial Performance on Stock Return (Empirical Study on Agribusiness Companies Registered in Indonesia
Stock Exchange).
DOI: 10.5220/0008439502890299
In Proceedings of the 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference (SEABC 2018), pages 289-299
ISBN: 978-989-758-387-2
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
289

realization can be used as one of the company's
performance measurement and can be used as a
basis for determining future return on risk and
expectation, while expected return is expected return
in the future and still uncertain.
There are several factors that can affect stock
returns. This study will tested several factors.
Frequency of trading shares resulted in stocks traded
to be sensitive, the higher the frequency of trading
stocks resulting in the value of stocks will be more
quickly experienced price changes. The frequency of
stock trading depends heavily on the pattern of
investor behavior in buying and selling stocks on the
capital market, the behavior of stock investors is an
indication of market participants in obtaining retun
shares of capital invested in the capital market.
Return of shares earned by investors in the form of
expected profits can be derived from the dividend
income of the company in the form of dividends
distributed by companies that issue shares as a result
of profit, or can also come from capital again due to
positive difference of stock sale and purchase
transactions.
Investors get stock returns derived from capital
gains due to positive difference in selling and buying
prices, stock trading frequency to the attention of
investors as the capital market actors in determining
the right strategy in investing. The frequency of
stock trading on the Indonesian stock exchanges has
increased in 2016 to 2017, and has increased the
highest in 2016 along the Indonesian stock exchange
which was established in 1992 and is expected in
2017 also experienced better improvement from
2016. Increasing the frequency of stock trading is an
achievement positive by active investors on the
Indonesian stock exchanges.
Based on the Crouch research (1970) produces a
positive correlation between the absolute value of
price changes to daily volume in the stock market as
a whole or in some stock samples. According to
Ariyani Indriastuti Nafiah (2017) which has the
result of positive trading volume but not significant
to stock return, in contrast to the results of Nasir and
Mirza (2011) which have the result of trading
volume have a significant effect on stock returns and
similar results according to Septian, and Bambang
(2017). Based on the above research illustrates that
both directly and indirectly, the frequency of stock
trading affects stock retun. The results of
Kumalasari et al (2017) also argue the more frequent
trading of a stock then it means the stock is more
liquid. Conversely, if the stock is a little trading
frequency means the shares are not liquid or
unattractive in the eyes of investors. According
Sutrisno (2017) shows that there is a positive
relationship between volatility and frequency of
trade and also between volatility and trading
volume. The research results also found that the
trading frequency is better than the volume of trade
in explaining volatility.
From the phenomenon of increasing frequency of
stock trading on the capital market in Indonesia and
some previous research results, researchers feel
interested whether the increase in trading frequency
of shares will significantly affect the stock returns to
be obtained investors.
Corporate value is a very important indicator to
determine the stock return on a company. According
Oktyawati and Agustia (2014) This condition can be
explained that the higher the value of the company
the higher the stock return company. According to
Kurnia and Hasanah (2012) the value of the
company has a significant effect on stock returns,
also according to Sugiarto (2011) the results of his
research firm value significantly influence the stock
return. And the results of the same study also
according to Hardiningsih et all (2017). This
relationship explains that the high value of the firm
can increase the level of market confidence in the
company's prospects so that it becomes the investor's
appeal to share so that the demand for stocks will
increase and the stock price will also rise.
This study measures Company Value by using
Price to Book Value (PBV) proxy. Ginting and
Edward (2013) argue that this ratio is of the ratio
between the stock price and the book value per share
of a company. This may explain that the ratio is a
market size appreciate the value of a company's
stock book. Therefore, the higher this ratio will give
an idea that the higher stock price of the company
shows the better performance of the company, so it
can provide a better rate of return in the future.
Financial performance factor analysis is based on
the company's financial statements that can be
analyzed through the analysis of financial ratios and
other measures such as cash flow to measure the
company's financial performance (Ang, 1997).
Financial ratios are grouped into five types: (1)
liquidity ratio; (2) activity ratio; (3) profitability
ratio; (4) solvency ratio (leverage); and (5) market
ratios.
In this study, the researchers using Profitability
and Solvency ratios because these two indicators
are often used by investors to see the condition of
company performance. Where Profitability Ratio
consists of Return on Assets, Return On Equity, and
Solvency Ratio Debt to Equity Ratio. According to
Sugiarto (2013) Debt to Equity Ratio. Have a
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
290

neggative effect to the value of the company. In
contrast to the research of Susilowati and Turyanto
(2011) which concluded the results of Debt to
Equity Ratio. Have a positive effect to the value of
the company. The results of differences in previous
research findings researchers became interested to
examine the Debt to Equity Ratio as one indicator of
the ratio of financial performance.
Return On Asset is one of the financial indicator
with another Return On Investment which is often
used in assessing company performance. The greater
the ROA, the better of the company's performance,
because the rate of return the greater. Return On
Asset used in assessing the company's financial
performance by looking at how the company utilize
assets to generate net income. According to
Hardiningsih et all (2017) Return On Asset do have
positif effect on stock return. While different from
the results of research by Susilowati and Turyanto
(2011) which states Return On Asset does not have a
significant effect on stock returns. From the results
of differences in previous research findings
researchers became interested to examine Return On
Assets as one of the indicators of financial
performance ratios.
Return On Equity or ROE, is the proportion of
profit earned after tax, with the average equity used
to measure the return on investment shareholders.
According to Susilowati and Turyanto (2011) ROE
(Return On Equity) has no significant effect on stock
return, similar research results according to Sutomo
and Ardini (2017), while the researcher has ROE
hypothesis (Return On Equity), have significant
effect on firm return.
Profit become the main focus for shareholders, as
shareholders who invest their funds into a company
will have the expectation of getting the return from
investments made by investors, so that researchers
feel interested to make ROA, ROE and DER as an
indicator of company performance.
Based on the existing phenomena and the lack of
consistency of previous research results then the
authors will conduct research with the title The the
effect of trading frequency of stocks, the value of the
company and the level of financial performance on
stock return (Empirical Study on Agribusiness
Companies listed in Indonesia Stock Exchange).
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Definition of Stock Returns
According to Mamduh M. Hanafi and Abdul
Halim, the Stock Return also referred as stock
income and change in the value of the period t share
price with t-ı. And that means that the higher the
stock price change, the higher the stock return will
be generated.
Components of Stock Returns
According to Abdul Halim Stock Return consists
of two main components, namely:
a. Gain is an advantage for investor which is
obtained from the excess selling price above the
purchase price which both occurs in the secondary
market.
b. Yield is income or cash flow that is received
periodically. As the form of dividends or interest.
Factors that influence stock returns
Based on Sudiyatno and Irsad (2011) stated that
many factors influence the stock returns, including
fundamental and technical information. The use of
models is very important to assess stock prices and
help investors to plan and decide their investments
effectively.
Calculation of Stock Returns
a) Realization return (actual return)
Realization return is the return that has occurred.
Actual return is used in analyzing data is the result
obtained from investment by calculating the
difference in the price of individual shares in the
current period with the previous period by ignoring
dividends, can be written in the formula:
Pi, t - Pi, t-1
Ri, t = Pi, t-1
Which:
Ri, t = Stock Return i at time t
Pi, t = Share Price i in period t
Pit-1 = Share Price for the period t-1
bro, Stock Returns
b) Expectations returns (Expected return)
Expectations return are returns that are expected
to be obtained by investors in the future. According
to Brown and Waren the calculation of Expected
return namely:
E (Rit) = Rmt
Information:
The Effect of Trading Frequency of Stocks, the Value of Company and Level of Financial Performance on Stock Return (Empirical Study on
Agribusiness Companies Registered in Indonesia Stock Exchange)
291

E (Rit) = The level of profit of the stock
expected on day t
Rmt = Level of market profit in period t
2.2 Efficient Market Theory
One of the important in the development of
corporate financial theory is that the Efficient
Market Hypothesis. According to Fama (1969) who
first put forward and popularized it, efficient market
theory is a market that can be efficient if no one,
both individual investors and investors in the form
of business entities, will be able to obtain abnormal
returns, after adjusting for risk, using existing
trading strategies. The point is that the stock price
and the frequency of stock trading formed in the
capital market which is a description of the
information available.
Frequency of Stock Trade
The frequency of trading shares is how many
times the sale and purchase transaction occurs in the
shares concerned at a certain time (Rohana et al,
2003). In the activities of the stock exchange or the
capital market, trading frequency activity is one of
the elements that one of the ingredients to see the
market reaction to an information entering the
capital market. The development of stock prices and
frequency trading activities in the capital market are
important indications to study market behavior as a
reference for the capital market in determining
transactions in the capital market.
The Value of The Company
Company value is the main goal of company
management. The higher the value of a company,
the more prosperous the stakeholders will be.
According to Hasnawati (2005) in Hardinigsih
(2009) the value of the company can be reflected in
the price of a stock. In addition, the stock price is a
reflection of the ability of business units to generate
profits that have used company resources efficiently.
Price Book Value (PBV)
The value of the company in this study uses the
Price Book Value proxy. Price Book Value (PBV) is
a comparison between stock prices and Book Value
per Share (BVS). The ratio is used to assess whether
a stock is undervalued or overvalued. A stock is
called undervalued if the stock price is below the
book value of the company concerned, it should be
said to be overvalued if the stock price exceeds the
book value (Siamat, 2004: 226).
Return on Assets (ROA)
Return On Assets (ROA) is often also referred to
as Return On Investment (ROI) which is used to
measure the effectiveness of a company in
generating profits by utilizing its assets. This ratio is
the most important ratio among other profitability /
profitability ratios. ROA or ROI is obtained by
comparing the net income after tax (NIAT) to
average total assets. NIAT is a net income after tax,
but if there is a benefit minority rights must be taken
into account. Average total assets represent the
average total assets at the beginning of the year and
the end of the year. The greater ROA / ROI shows
better performance, because the rate of stock returns
is getting bigger.
According to Hanafi and Halim (1996), the
return on assets (ROA) can be measured by the
following formula:
ROE (Return On Equity)
ROE (Return On Equity), is a comparison of
profits obtained after tax for a certain period, with
the average equity that exists. This calculation is
used to measure management's ability to manage
existing assets to make a profit. Return on Equity
can be calculated with the following formula:
Debt to Equity Ratio (DER)
Debt to Equity Ratio (DER) is used to measure
the level of leverage to the total shareholders' equity
owned by the company (Ang, 1997). Debt to equity
ratio (DER) can be used as a proxy for the solvency
ratio (Natarsyah, 2000). DER describes the
comparison between total debt and total equity of
the company that is used as a source of business
funding. Ang (1997) states that DER can be
calculated with the following formula:
Hypothesis
The hypothesis in this study is as follows:
H1 = The frequency of trading has a positive
effect on stock returns
H2 = Firm value has a positive effect on stock
returns
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
292

H3 = Return on Assets (ROA) has a positive
effect on stock returns
H4 = Return on Equity (ROE) has a positive
effect on stock returns
H5 = Capital Structure (DER) has a positive
effect on stock returns
3 METHODOLOGY
This research is conducted at manufacturing
company which still valid until now which is listed
in Indonesia Stock Exchange period 2015-2017.
Data retrieval in this research will be executed
through website of Indonesia Stock Exchange (BEI)
that is www.idx.co.id.
This study uses statistical data approach, such as
research sample (N), mean (average), maximum
value, minimum value and standard deviation for
each research variable. This data analysis is used for
data presentation and data analysis to clarify the
situation or characteristics of the data concerned.
Population
The population in this study are all agribusiness
companies listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange
during the period 2015-2017 which amounted to 22
companies that have the following criteria.
1. Agribusiness companies listed on the Indonesia
Stock Exchange (BEI) in the period 2015-2017.
2. The Company publishes the audited financial
statements for the period ended 31 December.
3. Companies that issue audited financial statements
with monetary units of rupiah.
4. Companies that do not have consecutive stock
returns or no stock returns change.
The period of observation in this study is
between 2015 and 2017. As well as, 2014 will be a
benchmark for changes in dividend payments to be
made in the following year.
Sample
According Sugiyono (2007: 116) Sample is part
of the number and characteristics possessed by the
population. The number of samples that meet the
criteria of 17 companies with the sample
determination method in this study is a sample of
census or saturated sampling, which is a sample
determination technique in which all members of the
population who meet the criteria are used as a
sample.
Data Analysis Model
Logistic Regression Analysis
Data analysis in this research is done by using
logistic regression because the dependent variable is
stock return change using dummy variable (Ghozali,
2013). The independent variable in this research is
Stock Return, while the dependent variable in this
research is Frequency of Stock Trading, Company
Value (Price Book Value) and Company Financial
Performance consisting of Return on Assets (ROA),
Return on Equity (ROE) and Debt to Equity Ratio
(DER).
Based on the above, the research model can be
written with the following equation:
Ln = +
1
∆FPS+
2
PBV +
3
ROA+
4
ROE +
5
DER + ɛ
Where:
∆DDPS : Dummy Change of Stock Return
1= Increased; 0 = Decreased.
FPS : Frequency of Stock Tranding
1= Increased; 0 = Decreased.
PBV : Price Book Value as a proxy for Company
Value variables.
ROA : Return on Assets as a proxy of profitability.
ROE : Return on Equity as a proxy profitability
variables.
DER : Debt to Equity Ratio as a proxy solvency
variables.
: Costants
1
-
5
: Independent variable coffecient
ɛ : Error term
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Logistic regression analysis in this research is
used to test the hypotheses that have been proposed
before. Logistic regression test result is used to
know the effect of Frequency of Stock Trading
(Freq), Company Value (PBV), capital structure
(DER), profitability (ROA) and profitability (ROE)
on Stock Return.
Testing the Regression Model Eligibility
The feasibility of the regression model was
assessed using the Hosmer and
Lemeshow'sGoodness of Fit Test. The Hosmer and
Lemeshow's Goodness of Fit Test tests the null
hypothesis (H0) that empirical data match or match
The Effect of Trading Frequency of Stocks, the Value of Company and Level of Financial Performance on Stock Return (Empirical Study on
Agribusiness Companies Registered in Indonesia Stock Exchange)
293
the model (not the difference between the model and
the data so that the model is fit). The test results
showed Chi-square value of 7.932 significance of
0.440 whose value is greater than 0.05. Based on
this it is concluded that the model is able to predict
the value of the observation or model has been
sufficient to explain the data.
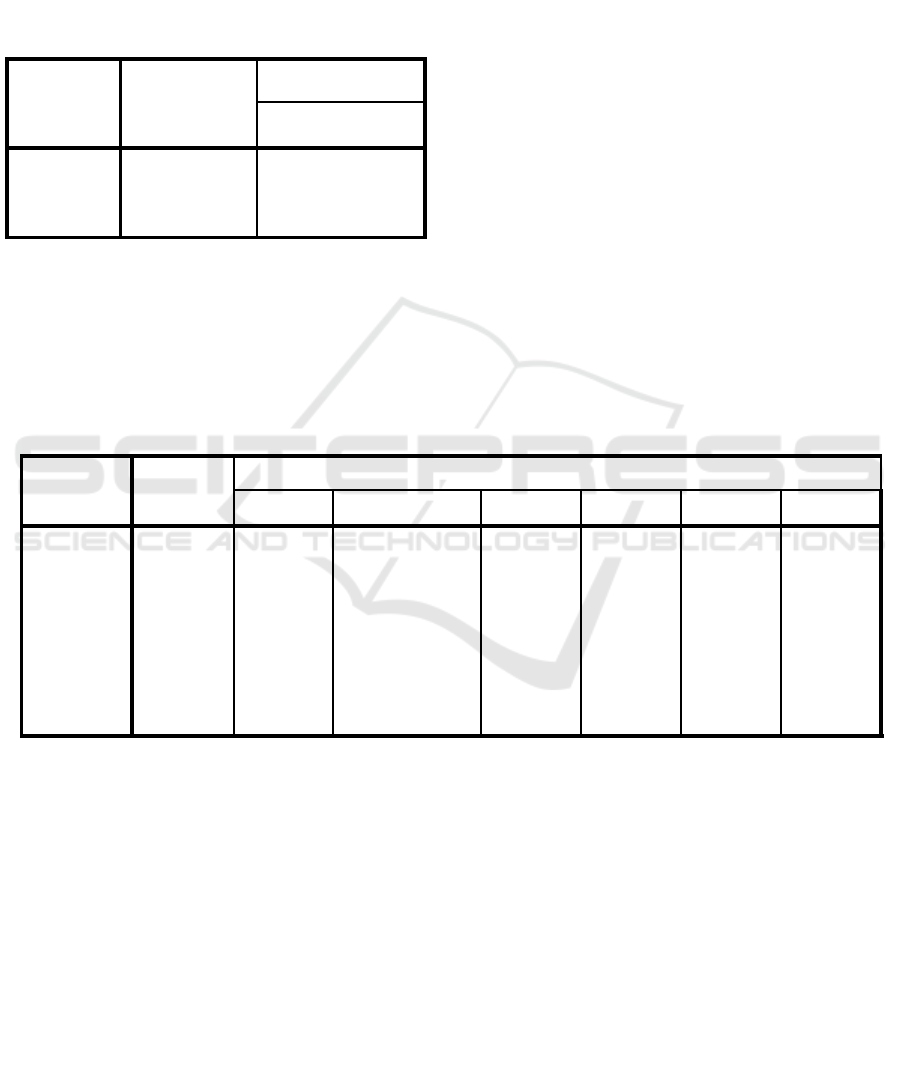
Table 1: Nilai -2 Log Likelihood in the Start.
Iteration
-2 Log
likelihood
Coefficients
Constant
St
ep
0
1
71,779
-,154
2
71,779
-,154
Source: Secondary Data Processed 2018
Overall Model Fit Test
This test is performed to assess the model that
has been hypothesized to be fit or not with the data.
Test results can be seen in Table 1 below:
Table 1 show the likelihood at start -2log value of
71,779 and after the fourth independent variable is
entered, the value of -2log likelihood in Table 2
decreases to 65.828. The decrease in the likelihood -
2log value after adding this independent variable
indicates a good regression model or in other words
the modulated mode is fit to fit the data.
Assessing the fit model can also be seen from the
statistical without value -2LogL just constant only
for 71.779 after the inserted four new variables then
the value -2LogL down to 65.828 or a decrease of
5.951. This decrease is significant or incomparable
with table c2 with df (difference df with constants
only and df with 4 independent variables), df1 = 52
and df2 = 52-5 = 47 so the difference df = 52-47 = 5.
By 5.951 greater than the value in table c2 it can be
concluded that the decrease -2LogL difference is
statistically significant. Thus the addition of
Frequency (Freq), Price Book Value (PBV), Debt to
Equity Ratio (DER), Return on Assets (ROA), and
Return on Equity (ROE) variables model fit.
Table 2: Nilai -2 Log Likelihood at End.
Iteration
-2 Log
likelihood
Coefficients
Constant
X1
X2
X3_1
X3_2
X3_3
Step 1
1
66,429
-1,444
,365
,136
,263
-,093
,462
2
65,937
-1,704
,375
,148
,309
-,111
,617
3
65,834
-1,845
,374
,148
,331
-,120
,712
4
65,828
-1,890
,375
,147
,338
-,122
,743
5
65,828
-1,893
,375
,146
,338
-,122
,745
6
65,828
-1,893
,375
,146
,338
-,122
,745
Source: Secondary Data Processed 2018
Coefficient of Determination (Nagelkerke R
Square)
The coefficient of determination aims to
determine the variability of the dependent variable
which can be explained by the independent variable.
The large value of the coefficient of determination
on the logistic regression model can be indicated by
the value of Nagelkerke R Square.
Based on the results of the test that the value of
Nagelkerke R Square is equal to 0.144, which means
dependent variables that can be explained by
independent variables is 14.4 percent, while the
remaining 85.6 percent explained by variables
outside the research model.
Table Classification
This study uses a classification table to show
the predictive strength of the regression model to
predict the likelihood of the occurrence of the
dependent variable. Based on the results of data
analysis conducted it can be seen from Table 5 that:
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
294
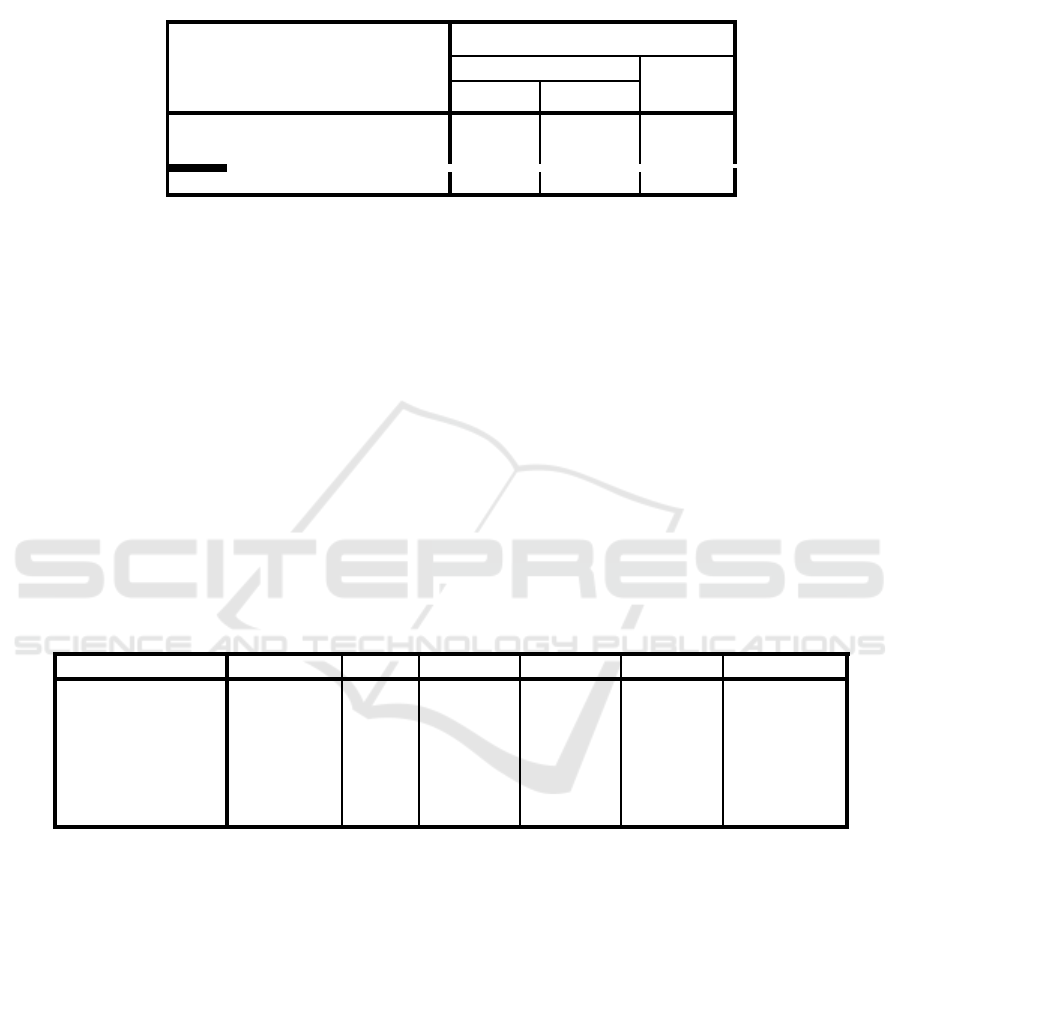
Table 3 : Classification Table.
Classification Table
a,b
Observed
Predicted
Stock Return
Percentage
Correct
Incerased
Decreased
Step
0
Stcok Return
Increased
28
0
100,0
Decreased
24
0
,0
Overall Percentage
53,8
Source: Secondary Data Processed, 2018
Table 3 shows the company's prediction that its
stock return decreased by 28, while the observation
result is only 0 so the accuracy of classification. So
the classification accuracy of this model for the
event of a declining stock return is 28/28 or 100%.
Meanwhile, the prediction of the incidence of stock
return increased by 24, while the observation result
showed 24 so the accuracy of classification. Thus,
the precision of the model to predict the stock return
event increases is 24/24 or 100%.
Based on Table 3 it can also be seen that the
logistic regression equation formed can make a
classification in the assessment of the dependent
variable that is stock return with the proportion of
stock return that is equal to 53.8%. That is, this
logistic regression equation model can predict the
occurrence of the decrease of stock return and the
increase of stock return accurately with the accuracy
of 53.8%.
Multicollinearity test
Multicollinearity test in this study to
determine the situation where the linear relationship
is perfect or near perfect between independent
variables in a regression model. Multicollinearity
test results in logistic regression analysis using
correlation matrix between independent variables.
Based on Table 4 it can be seen that:
Tabel 4: Corralation Matrix
Constant
X1
X2
X3_1
X3_2
X3_3
Step 1
Constant
1,000
-,341
-,196
-,717
,663
-,790
X1
-,341
1,000
-,036
,195
-,163
,045
X2
-,196
-,036
1,000
-,319
,284
-,152
X3_1
-,717
,195
-,319
1,000
-,965
,793
X3_2
,663
-,163
,284
-,965
1,000
-,809
X3_3
-,790
,045
-,152
,793
-,809
1,000
Source: Secondary Data Processed, 2018
Table 4 above shows the correlation between the
independent variables. The correlation matrix table shows
that there is no indication of multicollinearity symptoms
among the independent variables. It can be seen that the
values contained in Table 4 are not more than 0.90.
Meanwhile, these negative correlations indicate that there
is a negative relationship between the independent
variables.
The Effect of Financial Performance on
Cash Dividend Policy in Manufacturing
Companies in Indonesia Stock Exchange.
Based on the results of the hypothesis test, the results
of this study can be explained in Table 5 below:
The Effect of Trading Frequency of Stocks, the Value of Company and Level of Financial Performance on Stock Return (Empirical Study on
Agribusiness Companies Registered in Indonesia Stock Exchange)
295

Table 5: Regression Coefficients and Significance.
No
Nama Variabel
Kooefisien
Regresi (Beta)
Sig.
Exp (B)
Keterangan
1
Trading frequency (Freq)
,375
,547
1,455
Not Significant
2
Firm value (PBV)
,146
,621
1,158
Not Significant
3
Probitability (ROA)
,338
,168
1,403
Not Significant
4
5
Probitability (ROE)
Capital Stucture (DER)
-,122
,745
,167
,132
,885
2,106
Not Significant
Not Significant
Source: Secondary Data Processed, 2018
Table 5 gives the result that all independent
variables ie trading frequency, firm value; ROA,
ROE and capital structure do not have a significant
influence on stock returns in the company's agri-
index on the Indonesia Stock Exchange. Here is a
description of the explanation of each variable.
The Effect of Trade Frequency On The
Stock Return Of The Company On The
Agri Index In Indonesia Stock Exchange.
Based on the results of data analysis has been
done statistically it can be stated that the frequency
of trading has no effect on stock return in this case
relates to changes in the company's stock price on
the index agri in Indonesia Stock Exchange period
2015-2017.
This study gives an indication that the frequency
of trade is an indicator that is not considered by
investors in determining the investment of company
shares in the index agri in Indonesia Stock
Exchange. Although the frequency of trading is a
measure or indicator that is often used to determine
investment decisions to get stocks that have future
earnings prospects, but the results of this study is not
in line with the statement by Kumalasari et al (2017)
that the more the frequency of trading a share then
means shares are increasingly liquid. Conversely, if
the stock is a little trading frequency means the
shares are not liquid or unattractive in the eyes of
investors.
The condition that explains the frequency of the
stock trades does not affect significantly with the
positive coefficient marks on the above statistical
tests with an indication that the higher frequency of
stock trading yields a small probability for investors'
decision to buy increased stocks is a statement
which, according to Crouch (1970) have a positive
correlation between absolute value price changes to
daily volumes in the stock market as a whole as well
as on some stock samples. And, investors should
also consider in depth changes in stock returns that
will be done, it is because a change in stock return
decline will impact on new investors will buy shares.
Although in reality the frequency of stock
trading is almost always associated with the increase
and decrease in stock prices. In addition, the decline
in the frequency of stock trading is considered bad
news because it is considered unattractive by some
investors, where the Return of stock as a reflection
of the optimistic attitude of the market if the stock
returns rise. However, this is not necessarily the
cause is the decline in stock returns. This condition
in line with the research According to Ariyani
Indriastuti Nafiah (2017) which has the results of the
study of positive but not significant volume of
trading on stock returns. Thus, this causes the
fraction of the stock trades to have no effect on stock
returns in terms of increases and decreases in stock
returns.
Meanwhile, the results of this study is different
from the results of Nasir and Mirza (2011) which
have the result of trading volume have a significant
effect on stock returns and similar research results
according to Septian, and Bambang (2017). Thus,
the trading frequency has a positive and significant
influence on return stock.
The Effect of Corporate Value on Stock
Return of Companies on Agri Index at
Indonesia Stock Exchange
Based on the results of data analysis has been
done statistically it can be stated that the value of the
company has no effect on stock return in this case
relates to changes in the company's stock price on
the Indonesian Stock Exchange index of the period
2015-2017.
This study gives an indication that the value of
the company is an indicator that is not considered by
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
296

the investor in determining the company's
investment in the Agri index at the Indonesia Stock
Exchange. Although the value of the company is a
measure or indicator that is often used to determine
investment decisions to get stocks of high firm value
can increase the level of market confidence in the
prospect of the company so that the appeal of
investors to share so that the demand for stocks
increases and then the stock price increases, but the
results of this study are not in line with the statement
according to Kurnia and Hasanah (2012) the value
of the company have a significant effect on stock
returns, also according to Sugiarto (2011) the results
of his research firm value significantly influence the
stock return .
Conditions that explain that value of the firm
does not affect significantly with a positive
coefficient sign on the above statistical test with an
indication that the higher the value of the firm
produces a small probability for the tendency of
investors increasingly discussing the decision is a
statement according to Ginting and Edward (2013)
states that this ratio is the ratio of between the stock
price and the book value per share of a company.
This may explain that the ratio is a market size
appreciating the value of a company's stock book.
Therefore, the higher this ratio will give an idea that
the higher stock price of the company shows the
better performance of the company, so as to provide
a better rate of return in the future. Although in fact
the value of the company is almost always
associated with the increase and decrease stock
price.
Effect of Profitability (ROA) on the Return
of Company Shares on Agri Index in
Indonesia Stock Exchange.
The third hypothesis that states profitability
(ROA) has a positive and significant effect on stock
returns. The test results using logistic regression
analysis that the significant level of profitability
proxied return on assets has a higher significance
level of error rate () 0.05 and has a direction of
positive coefficient on stock returns. This means that
the high ability of a company to earn a profit cannot
cause the probability of a decision of investors in
buying shares to become larger
The results of this study do not match the signal
theory that the increase in profitability is a signal to
investors that management can predict the existence
of an income that will be better in the future. Based
on the theory shows that high income through
owned reflected from the ability to generate profit
showed a positive influence on stock return. The
same is also conveyed by Hardiningsih et al (2017)
Return on Asset have a positive effect on stock
return. While different from the results of research
by Susilowati and Turyanto (2011) which states
Return on Asset does not have a significant effect on
stock return.
The Effect of Profitability (ROE) on the
Return of Company Shares on Agri Index in
Indonesia Stock Exchange.
The fourth hypothesis which states profitability
(ROE) has a positive and significant effect on stock
returns. The test results using logistic regression
analysis that the significant level of profitability
proxyed return on equity has a level of significance
higher than the error rate () 0.05 and has a negative
coefficient toward stock return. This means that the
high ability of a company to earn a profit cannot
cause the probability of a decision of investors in
buying shares become larger.
The results of this study do not match the signal
theory that the increase in profitability is a signal to
investors that management can predict the existence
of an income that will be better in the future. Based
on the theory shows that high income through equity
owned reflected by the ability to generate profits
show a positive influence on stock returns.The same
thing is also conveyed by Susilowati and Turyanto
(2011) ROE (Return on Equity) no significant effect
on stock return, similar research results according to
Sutomo and Ardini (2017), while the researcher has
a hypothesis ROE (Return on Equity), significant
effect on return company.
The Influence of Capital Structure against
the Return of Company Shares On Agri
Index at Indonesia Stock Exchange.
The results of hypothesis testing states that the
capital structure has positive and insignificant effect
on stock return by the company on the index Agri in
Indonesia Stock Exchange period 2015-2017. It can
be understood that the condition of capital structure
that has high or low liabilities of a company does not
affect the decision of investors to buy shares.
Analysis of statistical data shows that the level of a
company's financial leverage proxied with debt to
equity ratio not a consideration of priority in taking
investors to increase or decrease interest in buying
shares. Based on this, the condition of the company
that has a high and low level of liability to external
parties is not a factor to be considered in
The Effect of Trading Frequency of Stocks, the Value of Company and Level of Financial Performance on Stock Return (Empirical Study on
Agribusiness Companies Registered in Indonesia Stock Exchange)
297

determining the decision to buy or sell shares by
investors.
Although the results of hypothesis testing of this
study did not significantly influence, when looking
at the regression coefficient of capital structure
positive in accordance with has been hypothesized
on the research, it can be seen that the direction of
the influence of capital structure to stock return has a
positive influence with the indication that the lower
capital structure produces probability of a small
trend for investors' decision to buy shares.The
statistical analysis states that the capital structure
that influences stock returns is consistent with the
results of research conducted by Susilowati and
Turyanto (2011) which concludes the results of Debt
to Equity Ratios. The positive influence on the firm's
value
Research conducted by Sugiarto (2013) different
results with hypothesis testing in this study that the
capital structure has a negative influence and
significance of stock returns. Explanation of the
results of this study it can be seen that the existence
of the level of capital structure into a priority
consideration for investors in buying and selling
shares.
5 CONCLUSION AND
SUGGESTION
Here are some conclusions from the results of
research: (1) Frequency of stock trading on stock
return shows positive and insignificant effect, this is
proved by obtaining value of regression coefficient
(beta) 0,375 with significance equal to 0,547. (2)
The value of the firm to stock return shows a
positive and insignificant effect. It is proved by
obtaining regression coefficient value (beta) 0,146
with significance equal to 0,621. (3) The level of
financial performance (Profitability ROA) on stock
return shows a positive and insignificant effect. (4)
The level of financial performance (Profitability
ROE) on stock return shows a negative effect and
not significant. (5) The level of financial
performance (Capital Structure) on stock return
shows a positive and insignificant effect on the stock
return by the company on the index Agri in
Indonesia Stock Exchange period 2015-2017.
The suggestions of this research are: (1)
Investors are expected to pay attention to variables
of Trade Frequency, Corporate Value, and Financial
Performance Level (ROA, ROE, and DER) which
have an insignificant effect on Stock Return before
taking the decision to invest in the capital market.
(2) For the next researcher needs to do research on
the factors of Frequency of Stock Trading,
Corporate Value, and Financial Performance Level
(ROA, ROE, DER) that potentially contribute to
Stock Return, for example trading day, dividend
policy, profit, leverage, and other factors.
REFERENCES
Arthur, Keown J., Martin D John., Petty William J &
Scott F David. 2011. Managmen Keuangan. Edisi
Kesepuluh. Jakarta:PT.Indeks
Ang, Robbert Ang.1997.Buku Pintar: Pasar Modal
Indonesia. Jakarta: Mediasoft Indonesia.
Ariyani, Indriastuti & Zumrotun Nafiah, 2017.’Pengaruh
Volume Perdagangan, Kurs dan Risiko Pasar
Terhadap Return Saham’. Jurnal STIE Semarang,
Volume 9 Nomor 1 Februari 2017.
Brigham and Houston. 2011. Dasar-Dasar Managmen
Keuangan. Penerjemah Ali Akbar Yulianto. Edisi
Kesebelas. Buku II.Jakarta:Salemba Empat.
Cheng F Lee, Gong Meng Chen and Oliver M Rui, 2001,
“Stock Return And Volatility On China’s Stock
Market, The Journal of Finance, Vol. 24 p. 523 – 543
Chordia, Tarun dan Bhaskaran Swaminathan, 2000,
Trading Volume and Cross-Autocorrelations in Stock
Returns, The Journal of Finance, Vol. LV, No. 2, p.
913 – 935
Christiawan, Yulius Jogi & Josua
Tarigan.2007.’Kepemilikan Manajerial: Kebijakan
Hutang, Kinerja,dan Nilai Perusahaan’, Jurnal
Akuntansi dan Keuangan, Volume 9, Nomor 1 Mei
2007.
Crouch, RL. 1970. The Volume of Transaction and Prices
Change on The New York Stock Exchange. America
Economic Review 60, pp. 199-202
Fahmi, Irham. 2014. Analisis Laporan Keuangan.
Bandung: Penerbit Alfabeta.
Fama,E.F.,L. Fisher, M. C. Jensen and R.Roll.1969. ‘The
Adjustment of Stock Pricesato New Information’.
International Economic Review.Volume 10, pp.1-21.
Ghozali, Imam. 2013. Analisis Multivariate dengan
Program IBM SPSS 21. Semarang: Badan Penerbit
Universitas Diponegoro.
Ginting, Suriani & Edward., 2013.’Analisis Faktor-Faltor
yang MempengaruhiReturn Saham pada Perusahaan
Manufaktur yang Terdaftar di Bursa Efek Indonesia’,
Jurnal Wira Ekonomi Mikroskil, Volume 3, Nomor 1
April 2013, hal 31-39.
Hardiningsih, Pancawati., 2009.’Determinan Nilai
Perusahaan’, JAI, Volume 5, Nomor 2 Juli 2009,
hal.231-250.
Hanafi, Mamduh M & Halim, Abdul. 1996,.Analisis
Laporan Keuangan. Yogyakarta: UPPAMP YKPN.
Husnan, Suad., 1998. Manajemen Keuangan. Yogyakarta:
BPFE
Jogiyanto. 2000. Teori Portofolio dan Investasi. Edisi
Pertama. Yogyakarta: BPFE UGM.
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
298

Kumalasari, Carissa., Agus Wahyudi Salasa Gama &I
Wayan Suarjana, 2017. Pengaruh Internet Financial
Reporting dan Tingkat Pengungkapan Informasi
Website Terhadap Frekuensi Perdagangan Saham
Perusahaan. Jurnal ilmu Manajemen Fakultas
Ekonomi Universitas Mahasaraswati Denpasar,
Volume 7, Nomor 7 .
Natarsyah, Syahib. 2000.’Analisis Pengaruh Beberapa
Faktor Fundamental dan Resiko Sistematis terhadap
Harga Saham’, Jurnal Ekonomi dan BisnisIndonesia,
Volume 15, Nomor 3, hal. 294-312.
Oktyawati, Dianila & Dian Agustia., 2014.’Pengaruh
Profitabilitas, Leverage, dan Nilai Perusahaanterhadap
Income Smoothing dan Return Saham pada
Perusahaan Manufaktur yang Terdaftar di Bursa Efek
Indonesia (BEI), Jurnal Akuntansi & Auditing,
Volume 10, Nomor 2 Mei 201 , hal.195 – 214.
Robinson, R. Thomas., Greuning Van Hennie., Henry
Elaine.,& Broihahn A. Michael. 2008. International
Finance Statement Analysis. USA:Willey-John Willey
& Sons,Inc.
Sudiyatno, Bambang dan Moch.Irsad.2011.’Menguji
Model Tiga Faktor Fama DanFrench Dalam
Mempengaruhi ReturnSaham Studi Pada Saham Lq45
Di BursaEfek Indonesia, Jurnal Bisnis dan Ekonomi,
Vol. 18 No. 2.
Sutrisno, Bambang, 2017.’Hubungan Volatilitas dan
Volume Perdegangan Dibursa Efek Indonesia’.Jurnal
Bisnis dan Manajemen, Volume 7, Nomor 1, April
2017, hal. 15-26
Tandelilin, Eduardus. 2010. Teori Portofolio dan Analisis
Investasi.Yogyakarta: Penerbit Kanisius.
Yadav et al, 1999.’Non-linear Dependence in Stock
Returns: Does Trading Frequency Matter’, Journal of
Business Finance and Accounting, Volume 26,
Number 5, pp. 651 – 679.
The Effect of Trading Frequency of Stocks, the Value of Company and Level of Financial Performance on Stock Return (Empirical Study on
Agribusiness Companies Registered in Indonesia Stock Exchange)
299
