
Leverage of Number of Population, GDRP, HDI
and Unemployment on Poverty Level in Six District in South
Sumatera
Erawati Agustini
Master Program of Economics, Faculty of Economics, Universitas Sriwijaya
Keywords: Number of Population, Gross Domestic Regional Product, Human Development Index , Unemployment
Rate, Poverty
Abstract: The level of poverty in South Sumatra Province is still a development issue that requires lot of focus of
attention to be resolved. The purpose of this study is to know the leverage of population, PDRB, HDI, and
unemployment on poverty level in six urban districts in South Sumatra in 2011-2016. Data analysis using
panel data regression techniques with the help of Software Eviews Version 8.1. The results showed that
both simultaneously and partially independent variables significantly influence the dependent variable.
1 INTRODUCTION
Poverty is an inequality of opportunity to
formulate the basis of social power, which includes
assets (land, housing, equipment, health), financial
resources (adequate income and credit),
socio-political organizations that can be used to
achieve common interests, goods or services,
adequate knowledge and skills, and useful
information. Therefore, the government's program to
handle poverty is primarily to reduce the number of
poor people. But in reality the number of poor
people from year to year is not getting decreased,
but even more and more.
Differences between districts and cities in some
aspects can affect the number of poor people. In this
case the problem of poverty in the district is more
complex, because of the wide poverty range.
Nevertheless, the existing public facilities in the
district are still inferior to the existing public
facilities in the city, other than that for people living
in remote villages will find it difficult to access these
services. The wide area of the district is also an
obstacle to the spread of infrastructure evenly,
because it requires more funds than infrastructure
development in cities that tend to be more narrow
than the district.
The existence of regional expansion discourse
that continues to grow in the community especially
the community in the region behind the government
and Regional Representative Council (DPD)
Republic Indonesia (RI) to formulate a grand
strategy or grand design on the arrangement of
autonomous regions in Indonesia to be used until the
year 2025. From the grand design is the reference
for the number of provinces and the ideal districts in
Indonesia that gave birth to the division of
pemekaran, one of which is the Province of South
Sumatra, which is rumored to be divided into 2
(two) with the possibility of the province to be
formed is the Province of South-West
Sumatera(Sumselbar) or with the possibility of other
names namely Musi Raya Province developed as
part of the Great Design of the Regions (Desartada)
RI 2025. Sumselbar or Musi Raya Province is
planned to be 6 (six) districts / cities, namely Lubuk
Linggau City, Empat Lawang Regency, Musi Rawas
Regency, North Musi Rawas Regency (Muratara) ,
Musi Banyuasin Regency (Muba), and Banyuasin
Regency.
The districts and municipalities belonging to the
Musi Raya area, especially in Musi Rawas and Musi
Banyuasin districts, are based on data having higher
numbers and percentage of poor people than the
number and percentage of poor people in South
Sumatera Province.
Based on the data in the last 4 (four) years can be
seen that in terms of poverty rate and the level and
number of poverty in the region of Musi Raya every
year experienced changes in the increase and
184
Agustini, E.
Leverage of Number of Population, GDRP, HDI, and Unemployment on Poverty Level in Six District In South Sumatera.
DOI: 10.5220/0008438201840188
In Proceedings of the 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference (SEABC 2018), pages 184-188
ISBN: 978-989-758-387-2
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
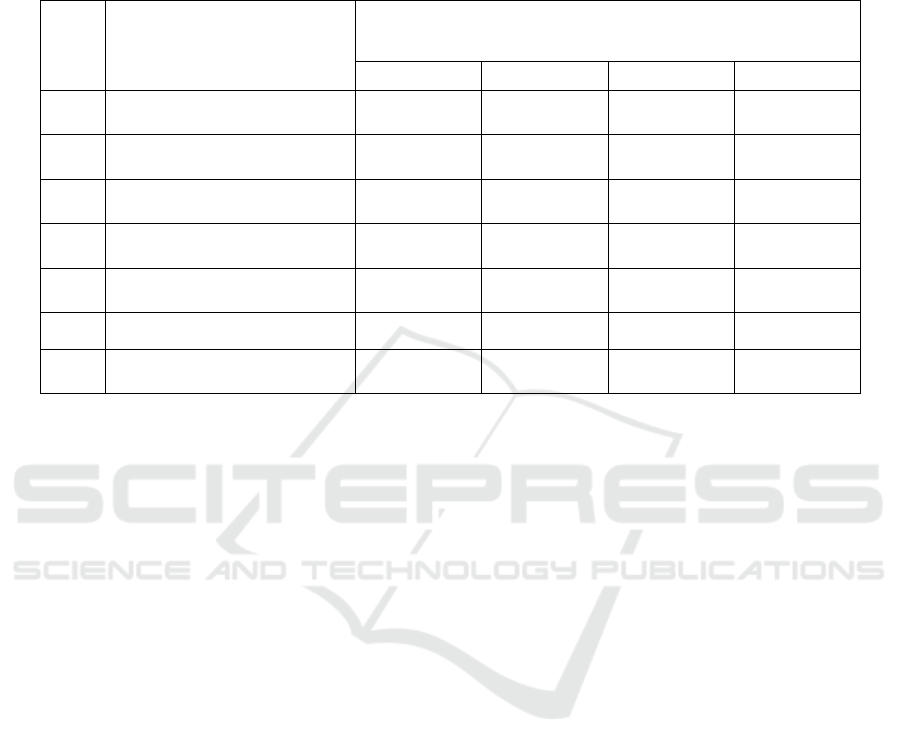
decrease. However, the order of regencies /
municipalities did not change, as follows: Musi
Banyuasin Regency, Musi Rawas, Lubuk Linggau,
Four Lawang, and last Banyuasin Regency.
Tabel 1: Number And Percentage of Poor People In the Regency / City Region Musi Raya Province of South Sumatera (In
Thousands Heads)
NO
KABUPATEN/KOTA
JUMLAH/
% PENDUDUK MISKIN
2011
2012
2013
2014
1
Musi Rawas
97,99
18,25
96,39
17,67
98,79
17,85
97,01
17,28
2
Musi Banyuasin
108,84
18,99
107,03
18,29
107,17
18,02
105,08
17,38
3
Banyuasin
89,35
11,66
87,87
11,27
97,14
12,28
95,38
11,88
4
Empat Lawang
31,32
13,82
30,64
13,37
30,47
13,10
30,38
12,89
5
Lubuk Linggau
29,69
14,43
29,22
13,89
30,73
14,37
30,18
13,90
6
Musi Rawas Utara
Prov. Sumsel
1,105,00
14,80
1,043,62
13,48
1,104,57
14,06
1,085,80
13,62
Source : BPS Publication of 2018, Community Welfare Indicator South Sumatera Province
Seeing the condition of areas that still have high
poverty rates, the authors are interested to conduct
research on poverty issues with the title "analysis of
the leverage of number of population, grdp, hdi, and
unemployment on poverty level in six district in
south sumatera".
The amount of poverty can be influenced by
various factors, especially the population, GRDP,
human development index, and unemployment.
Therefore, in this study formulated the problem on
how and how big the variable of the number of
population affect the level of poverty?
2 RESEARCH VARIABLE
This study uses poverty level as dependent
variable, while the independent variables in this
study are population, GRDP, HDI, and
unemployment rate in six regencies / cities in South
Sumatera Province Year 2011-2017.
Definisi Operasional
2.1 Poverty Level
the poverty rate data is used, the percentage of
poverty, which is the comparative data between the
number of poor and total population in 6 (Six)
districts cities in South Sumatra Province in 2011
until 2017.
2.2 Total population
The population is the number of population in 6
(Six) districts / municipalities in South Sumatra
Province in 2011 until 2017 in units of soul which
then dilog to obtain percentage number for the unit
becomes equivalent to other variables.
2.3 Gross Regional Domestic Product
(GRDP)
GRDP is the net value of goods and services
produced by various economic activities in an area
within a period. Data used in this research is GRDP
data at 6 (Six) Regency / City in South Sumatera
Province in 2011 until 2017.
2.4 Human Development Index (HDI)
HDI is a single composite indicator used to
measure the achievement of human development
that has been done in a region. Data used in this
research is data of HDI at 6 (Six) Regency / City in
South Sumatera Province year 2011 until 2017.
2.5 Unemployment Rate
Unemployment is a person who enters the
Leverage of Number of Population, GDRP, HDI, and Unemployment on Poverty Level in Six District In South Sumatera
185

workforce (15 years and above) who is looking for a
job, preparing a business, who is not looking for a
job. Data used to see unemployment is the ratio of
open unemployment to population in 6 (Six)
Districts / Cities in South Sumatra Province in 2011
to 2017 (in percentage units).
2.6 Data Source
Sources of data used in this study are secondary
data, ie data obtained in the form that has been or
has been collected from other sources and obtained
from other parties such as literature books, notes or
sources related to the problems studied. The data
taken is the data of all six districts / cities in South
Sumatra.
Research model
The research model in this research is using
econometric model of regression of data panel. This
equation model will be estimated based on the
theory and hypothesis that the poverty rate is
influenced by population variables, unemployment
rate, GRDP, and HDI.
Y
K
= f (X
JK
, X
TPT
, X
PDRB
, X
IPM
)
K = a + b
1
JK
it
+ b
2
TPT
it
+ b
3
PDRB
it
+ b
4
IPM
it
+ e
K = Poverty rate
A = constants/intercept
b
1
, b
2
,
b
3
, b
4
= variable coefficient number
JK = total population
TPT = unemployment rate
GRDP = Gross Regional Domestic
Product
HDI = Human Depelopement Index
I =Regional Zone (City Lubuk
Linggau, Empat Lawang District, Musi Rawas
District, North Musi Rawas Regency(Muratara),
Musi Banyuasin District (Muba), and Banyuasin
Regency.
T = years of observation
(2011-2017)
e = error/(s)
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
ANALYSIS
3.1 Analysis of Classical Assumption
Detection With Eviews
Prior to the interpretation of the regression
results of the model used, then first tested the
classical assumption, to determine whether the
model is considered relevant or not. In this study
after testing classical assumption that includes data
normality test, heterokesdastisitas test,
multicolinearity test, and autocorrelation test then
based on the results if the data is declared free of
assumption test.
3.2 Panel Data Regression Analysis
Panel data regression analysis is used to
determine the effect of Population, GRDP, HDI and
unemployment rate to poverty level in six districts /
cities in South Sumatra in 2011-2015. Based on
calculations conducted using Program Eviews then
obtained the following results:
1. The constant values is 12.8408000088, meaning if
the population, GRDP, HDI, and unemployment rate
is 0, then the values of K is 12.840800001003.
When adjusted for population data, GRDP, HDI, and
existing unemployment rate, each increase of 0 then
the poverty rate will be constants at 12.8408000088
in the next year.
2. The regression coefficient of the population
variable is -3.605227, meaning that any increase in
population of 1 unit will decrease K by -3.605227.
3. The regression coefficient of GRDP is -8.251528,
meaning that any increase of GRDP by 1 unit will
reduce poverty by 8.251528.
4. The coefficient of variable regression of HDI is
-5.217020, meaning that every increase of HDI of 1
unit will decrease poverty of 5.217020.
5. Regression coefficient of variable unemployment
rate equal to 8.189897, meaning every increase of
unemployment rate equal to 1 unit will increase
poverty equal to 8,189897.
4 CONCLUSION
This study analyzes how the influence of
population variable, GRDP, HDI, and
unemployment to poverty level in six districts /
cities in South Sumatra in 2011-2015. Based on the
description that has been done in the previous
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
186

chapters, it can be concluded as follows:
1. Variable of population has positive and significant
sign of poverty level. In accordance with the
hypothesis, the positive sign indicates that the higher
the population, the higher the level of poverty. In
addition, the rapid population growth will cause new
problems both in social and economic terms.
2. Gross Regional Domestic Product (GRDP)
variable has negative and significant sign of poverty
level. In accordance with the hypothesis, the
negative sign indicates that the higher the GRDP, the
lower the poverty level.
3. Variable of Human Development Index (HDI) has
a negative sign and significant to poverty level. In
accordance with the hypothesis, the negative sign
indicates that the higher the HDI, it will reduce the
level of poverty. The value of HDI in its calculation
includes education, health, and expenditure
indicators per capita, so that it can be used as one of
the indicators of poverty of a region.
4. The unemployment variable has a negative and
insignificant sign to the poverty level. The results
are not in accordance with the hypothesis and the
previous theories and research that became the
theoretical basis of this study. Because as the
population is open unemployed there are some kinds
of unemployed, those looking for work, those
preparing for the business, those who are not looking
for a job because they feel unlikely to get a job and
the last one who already has a job but has not started
work.
5 SUGGESTION
1. Further research is expected to examine other
variables besides the variables in this study in order
to obtain a varied outcome of anything that affects
poverty.
2. Subsequent research can take samples in the
narrower scope of the City / District for more
accurate research results.
3. The object of research should be more focused in
order to really know the variables that affect the
level of poverty.
4. Required solutions of large population from year
to year, for example with population-oriented
development, population-oriented development
contains two meanings that are development that is
adjusted to the potential and condition of the
existing population. Population should be a central
point in the development process, the population
must be subject and object in development,
development is by residents and for the population.
This means that development is more emphasis on
improving the quality of human resources than
infrastructure development alone.
5. From the result of the research, it is found that
GRDP have negative effect to poverty level, so that
in the future the improvement of GRDP can be
balanced with equitable distribution of income
oriented equity and equitable distribution of
economic results to all community groups, and
efforts to increase economic growth in each region
by relying on its own potential.
6. Indicators of HDI that describe the human life
cycle consisting of educational measures, life
expectancy and adjusted per-capita expenditure are
crucial to the decline of the poor in the study area,
the government needs to design a sustainable
program in order to spur up the HDI value by
facilitating access education and health especially
for the poor.
7. Unemployment based on the results of the study
has a negative and significant effect on poverty, with
the result is expected more districts / cities to expand
the employment opportunities and promote the
development of the informal sector, such as home
industry.
8. The need for longer time series data usage to
know how the influence of government policy in
efforts to reduce the poverty level of research areas
in particular and South Sumatra in particular.
REFERENCES :
Amartya, Sen. 2001. Poverty and Femines : An Essay on
Entittlement and Deprivation. Terjemahan, Google
Books
Arsyad, Lincolin. 2010. Ekonomi Pembangunan.
Yogyakarta: UPP STIM YKPN.
BPS Prov. Sumsel.2018. Data Series Sumatera Selatan
(Sumatera Selatan in Data Series)
BPS. 2018. Produk Domestik Regional Bruto Provinsi
Sumatera Selatan Menurut Kabupaten/Kota
2010-2016, Gross Domestic Regional Product of
South Sumatera Province by Regency/Municipality
2010-2016
BPS. 2018. Provinsi Sumatera Selatan Dalam Angka,
Sumatera Selatan Province in Figures 2017
BPS. Prov Sumsel. 2017. Indikator Kesejahteraan Rakyat
Sumatera Selatan 2016
BPS. Prov Sumsel. 2017. Kumpulan Berita Resmi Statistik
Provinsi Sumatera Selatan 2016
BPS. Prov Sumsel. 2018. Indikator Pembangunan
Sumatera Selatan. Katalog BPS
Djojohadikusumo, Sumitro. 1995 Perkembangan
Pemikiran Ekonomi Dasar Teori Pertumbuhan dan
Ekonomi Pembangunan, Jakarta. LPES
Dumairy MA. 1996. Perekonomian Indonesia. Penerbit
Leverage of Number of Population, GDRP, HDI, and Unemployment on Poverty Level in Six District In South Sumatera
187

Erlangga. Jakarta.
Gujarati, Damodar. 2003. Ekonometrika Dasar.
Erlangga. Jakarta
Hoover, Gary A. dan Geoffrey L. Wallace.. Examining the
Relationship between the Poverty Rate and Economic
Conditions: A Comparison of the 1980s-1990". The
University of Alabama.Economic, Finance and Legal
Working Paper Series.Oktober 2003.
Kuncoro , Mudrajad. 2006. Metode Kuantitatif. Penerbit
UPP AMP YKPN,
Mankiw. N. G. 2000. Teori Makroekonomi. Penerjemah
Iman Nurmawan , Edisi ke-4. Erlanga, Jakarta
Nasikun, 2001. Isu dan Kebijakan Penanggulangan
Kemiskinan. Diktat MataKuliah. Magister
Administrasi Publik. Universitas Gadjah Mada.
Yogyakarta.
Nasution, S. 2007. Metode Research (Penelitian Ilmiah).
Jakarta : Bumi Aksara
Rustiono, Deddy. 2008. Analisis Pengaruh Investasi,
Tenaga Kerja, dan Pengeluaran Pemerintah Terhadap
Pertumbuhan Ekonomi di Provinsi Jawa Tengah..
Said, Abidin. 2012. Kebijakan Publik. Jakarta. Salemba
Humanika
Simatupang, Pantjar & Saktyanu K. Dermoredjo. 2003.
Produksi Domestik Bruto, Harga, dan
Kemiskinan.Media Ekonomi dan Keuangan Indonesia,
Hal. 191 - 324, Vol. 51, No. 3
Sukirno Sadono. (2010) Makro Ekonomi Modern
Perkembangan Pemikiran Klasik Hingga Keynesian
Baru. Penerbit PT Raja Grafindo Persada : Jakarta.
Sumitro, Djojohadikusumo. 1995. Perkembangan
Pemikiran Ekonomi Dasar Teori Pertumbuhan dan
Ekonomi Pembangunan. Jakarta: LP3ES
Sunyoto, Danang. 2012. Model Analisis Jalur untuk Riset
Ekonomi. Jakarta: Yrama Widya
Suyanto, dkk. 2005.Metode Penelitian Sosial. Jakarta :
Kencana
Todaro, MP dan Stephen C. Smith. 2006. Pembangunan
Ekonomi di Dunia Ketiga 1. Edisi ke Delapan, Jakarta:
Erlangga.
UU RI No. 32 Tahun 2004 Tentang Pemerintahan Daerah
(yang diganti dengan UU RI No. 23 Tahun 2014
Tentang Pemerintahan Daerah
Windawati, Helmi. 2015. Analisis Pengaruh Belanja
Modal Daerah, Investasi, dan IPM terhadap
Kemiskinan di Indonesia Tahun 2009-2013
World Bank. 2006. Making The News Indonesia , Work
for The Foor
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
188
