
Aggregator Business as an Intermediary in Agriculture: A Literature
Review
Janita Sembiring Meliala, Musa Hubeis, Siti Jahroh and Agus Maulana
Bogor Agricultural University, Jalan Pajajaran, Bogor, Indonesia
Keywords: Aggregators, Business Models, Disruption Era, ICT, Intermediaries
Abstract: This paper reviews the literature on the basic concepts of aggregator business in Indonesia’s agricultural
sector. An aggregator business is essentially an intermediary that utilises information communication
technology (ICT). Intermediaries in the Indonesian agricultural sector are known as Tengkulak, Pengepul, and
Bandar all of which carry a negative image. The length of the supply chain associated with intermediaries
results in a decrease in farmers‘ profits. This research reviews the relevant publications, including articles
published in referenced books and journals, along with definitions of intermediary and business aggregators
in business disruption. The phenomenon of disruption initiated the birth of a new business intermediary
model, namely the business aggregator.This research was conducted in 12 business aggregators based in
Indonesia using in-depth interviews with their owners and with a deputy assistant team from the coordinating
ministry for the economy to get an alternative business aggregator model as an intermediary.There are six
alternative aggregator business models comprising information sources (clearinghouses), connector (spark-
plug), communities (village-preneur), food hubs, and upstream efficiency. This aggregator business will cut
the supply chain and increase farmers‘ profits.
1 INTRODUCTION
The term‘intermediary’ is used commonly in
business sectors including agriculture and has both
positive or negative connotations (Monieson, 2010).
Judging from the scale of farming in Indonesia, most
farmers in Indonesia are small-scale farmers suchthat
intermediaries have a positive role because the
majority of farmers in Indonesia are fragmented. If
they distribute their agricultural productsdirectly to
consumers, it will cause prices to vary,and costs
distribution will be more expensive due to irregular
quantities (Fixing, 2013; Mejía& García-Díaz, 2018).
Mejía and García-Díaz (2018) revealed that in the
long-run, intermediaries could reduce the profitability
of producers/farmers. Intermediaries are often
considered to reduce the efficiency of distributing
agricultural products by lowering prices at the level
of farmers (Ranjan, 2017; Tapsavi, 2009).
Intermediaries only increase personal profits without
increasing the added value of these products by
utilising the limitations of market information of
farmers as producers (Shankar, Singh, &Dwiwedi,
2017).
Various efforts have sought to improve the
farmers’ welfare such as government intervention by
providing extension programmes, assistance, and
regulations. One such regulation is to develop farmer
group institutions as stipulated in Law No. 16 of 2006
with the aim that such groups would increase their
bargaining power (Ranjan, 2017). However, the
institution that was formed has not provided optimal
benefits for farmers whofarmers still face the same
problem (Hanggana, 2018).
The role of farmer institutions is currently limited
to distribution assistance from the government, such
that the process of marketing agricultural products is
still overseen by intermediaries (Hanggana, 2018).
Intermediaries, when viewed positively, provide
many benefits tofarmers.The majority of farmers in
Indonesia do not have marketing knowledge in selling
their products. Both consumers and farmers gain
immensely from the roles of intermediaries, who
ensure that there is a seamless flow of farmers'sgoods
in the market by matching supply and demand.Rapid
technological advancements could improve the
marketing system. Technological advances,
especially information technology, have been proven
to improve the welfare of farmers in various
56
Sembiring Meliala, J., Hubeis, M., Jahroh, S. and Maulana, A.
Aggregator Business as an Intermediary in Agriculture: A Literature Review.
DOI: 10.5220/0008436800560064
In Proceedings of the 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference (SEABC 2018), pages 56-64
ISBN: 978-989-758-387-2
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

developing countries (Knoche, 2010). Information
Communication Technology (ICT) services can be
used for distance learning, financial services, market
information, marketing networks, and various other
information needs (Ranjan, 2017).ICT can be applied
by intermediaries to connect farmers with consumers
and reduce the marketing chain.
2 INTERMEDIARIES
Some of the intermediary terms used in the
agricultural sector in Indonesia include middlemen,
dealers, brokers, and collectors, among others.
“Pengepul are steaming people. Brokers are
intermediary traders who connect traders with
one another in terms of buying and selling or
between sellers and buyers (Example: stocks and
so on); While Tengkulak are intermediary traders
(who buy agricultural products and so on from
farmers or first owners); Bandar is a person who
have fund for transaction “(KBBI Online)
The terms Tengkulak, Pengepul, and Bandar, are
mostly interpreted negatively by farmers because
they have negative impacts. Middlemen strive to
make a profit by reducing the prices of farmers as low
as possible (Shankar, Singh, &Dwiwedi, 2017;
Ranjan, 2017; Simon, Benghozi, & Salvador, 2015).
Farmers sometimes have no other choice because
agricultural products rot easily and are bulky, so it is
better for farmers to sell them to middlemen (Fixing,
2013). Farmers also face problems in terms of access
tofunding which is aggravated bycomplicated
regulations forapplying for credit frombanks. This is
where the Bandar enters as a middleman who not
only buy the farmers’ products but also invest in their
harvest giving farmers no choice but to sell to
theBandar at prices that are usually below the market
price.
2.1 Marketing Channels for
Agricultural Products
The agricultural sector has an important role in
economic development in Indonesia. Nevertheless,
there are many obstacles to developing agricultural
products such as marketing. Large demand for
agricultural commodities createsa long distribution
network starting from the level of farmers/producers,
intermediary traders, to mobile traders/retailers who
sell directly to end consumers. On the other hand,
agricultural products have perishable characteristics
that necessitate their special handling, and short
marketing channels areneeded so that the distribution
processes arequick and the products reach the
consumers in a timely fashion. A long marketing
chain causes a decline in quality, losing weight due to
damage to a commodity resulting in a loss (food loss)
resulting in high distributioncosts.
Farmers do not have other alternatives to
markettheir products because based on the BPS
Agricultural Order (2013), the average area of land
controlled by agricultural enterprises in 2013 was
0.89 ha. Agricultural products in Indonesia are
scattered in various regions,and the quantity spread is
also small (Sudiyono, 2004). Therefore, farmer
institutions play importantroles incollecting products
from farmers and distributing them to consumers.
Annotation:
Farmers
Middleman
Wholesaler
Retailer
Consumer
Figure 1: Marketing Channels of agricultural products (Sudiyono, 2004)
Aggregator Business as an Intermediary in Agriculture: A Literature Review
57
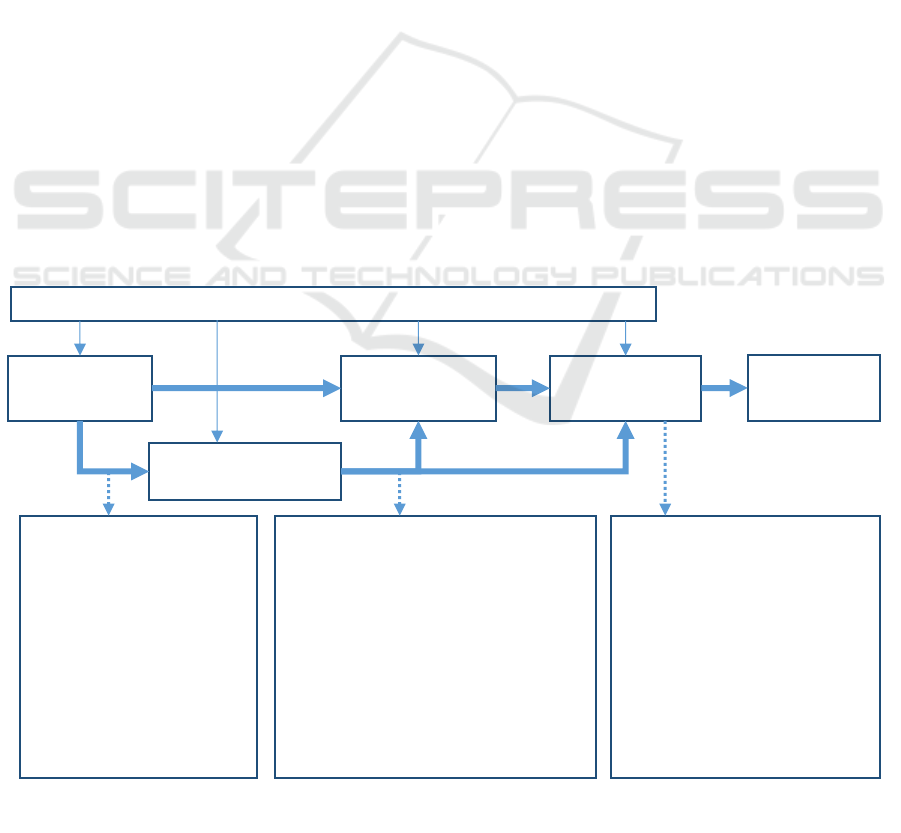
Figure 1 illustrates the marketing characteristics of
agricultural products.
2.2 Aggregator Business Concept
The distribution of agricultural products in
Indonesia is still weak as seen from the long-chained
marketing channels. Ikhsan et al. (2015) found high
prices at the consumer level due to production and
productivity problems, while high prices at the level
of wholesalers and retailers can occur due to the long
chain and high logistics costs. Several developing
countries are currently undergoing a period of
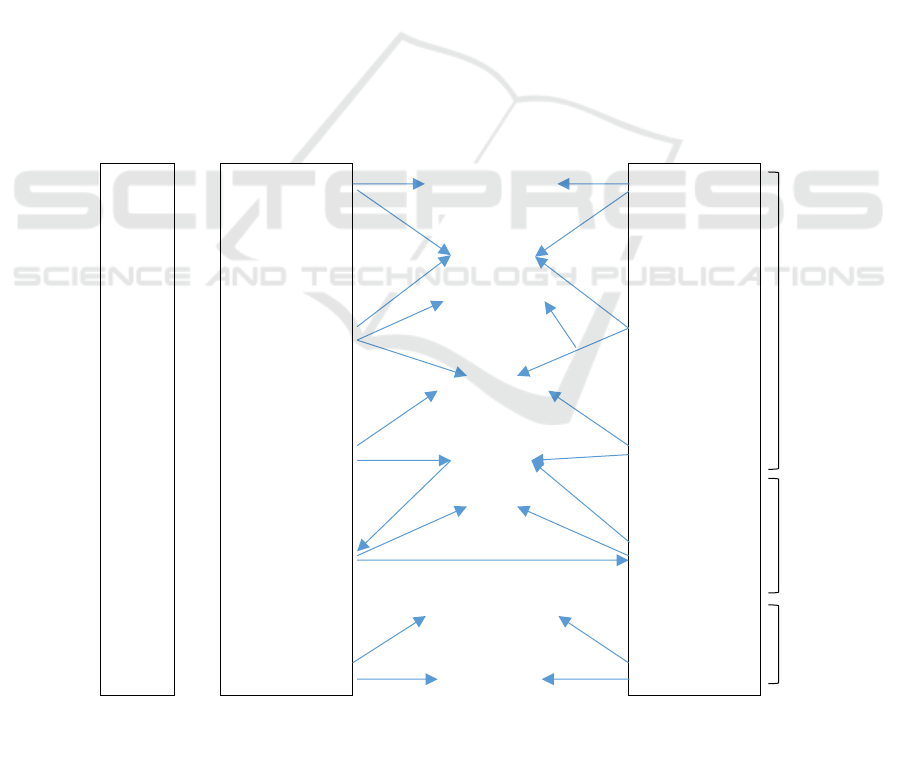
disintermediation of the value chain (Figure 2).
Indonesia as a developing country does not yet know
whether it has implemented a value chain
disintermediation. According to Laudon & Traver
(2017), disintermediation is the loss of the function of
market intermediaries (distributors and wholesalers).
Reardon &Timmer (2012) revealed that the role
of intermediaries had been reduced due to the use of
ICT so that producers can reduce interaction with
intermediaries and can distribute directly. This shows
that ICT plays a role in addressing the problem of
inefficiency in marketing agricultural products.
2.2.1 Alternative Markets
The marketing process for horticultural
commodities has been through long marketing
channels such that producers have low bargaining
power and are the recipients of prices (Figure 1).
Advancements in ICT opens up alternative markets
for producers so that they are more efficient by
sellingBusiness-to-Business (B2B) or Business-to-
Consumer (B2C). Farmers can do B2B by selling
directly to restaurants, institutions/agencies, and
wholesale markets. Also, farmers can increase their
bargaining power,and the buyer (company/agency)
can maintain the price, quality, and quantity of
products purchased by providing advice and
responses directly to farmers. Likewise,inthe B2C
mechanism, small farmers can have high bargaining
power.
However, ICT adoption in Indonesia is still
minimal, because the majority of farmers in Indonesia
arenot tertiary educated and access to ICT is still
difficult due to infrastructure that is not evenly
distributed. The following factors limit the use of ICT
at the farm level, namely the lack of ability to use
ICT, lack of awareness about the benefits of ICT, too
difficult to use, lack of technological infrastructure,
high technological costs, low levels of trust in ICT
systems, lack of ICT application training, system
integration and low availability of software (Taragola
and Gelb 2005). Therefore, there is a need for actors
who play a role in channelling ICT knowledge so that
adoption of ICT can continue to grow at the level of
farmers and consumers in Indonesia.
Value- creation, Value Addition, Value-from trading
Farmers Wholesalers
Retail/
Supermarket
Consumer
Food Modern
Company
The role of intermediaries
has been reduced because
of the reduced interaction
between farmers and
middlemen, improvement of
roads to the market and use
of cellular telephones
(Reardon, & Timmer, 2012)
The emergence of "modern actors",
including:
1. Modern Wholesalers carry out
activities of value added: collecting,
selecting, evaluating, packaging,
processing and delivering.
2. Modern logistics companies do
wholesaling, warehousing,
integrated information technology
and packaging.
(Reardon, & Timmer, 2012)
Supermarkets replace
traditional markets, although
poor traditional market
infrastructure is a major problem
and not because of the
emergence of supermarkets.
(Suryadharmaet al.,2010)
Figure 2: Value chain disintermediation in developing countries (Ikhsan et al., 2015)
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
58

2.2.2 Aggregator Business in the Disruption
Era
Aggregate means the total obtained by adding
shared items. Aggregation can also be defined as
uniting in a coherent collection of different
information sources (Moghaddam and Moballegh
2007).
Lembong (2016) refers toaggregator as a
company or service provider that helps accommodate
a variety of products from sellers and makes the
product available in a place that is easily found by
potential customers.
Aggregator in the context of this paper relates to
‘actors’ who play a role in the process of
accommodating various types of agricultural
products from various sources (farmers) and suppliers
of agricultural products to end consumers in
aggregate. Aggregators arecollectors and
intermediaries (Tapsavi, 2009). However, the concept
that should be developed is how an intermediary
business model plays a role in creating profits for
farmers and remains actively connected with this
marketing intermediary. This can be done by
developing the right business model by packaging
products and services that can be provided by an
aggregator (Tapsavi, 2009).
Brokers who are currently developing can help
farmers to reduce transaction costs, but with the
digital era, ICT-based services need to be explored as
a solution to existing problems (Tapsavi, 2009;
Ranjan, 2017).
Digitalisation is the result of technological
evolution (especially information) that changes
almost all disruptions. This era of disruption is a
phenomenon when people shift activities that were
originally carried out in the real world, into
cyberspace. This phenomenon is developing in the
changing pattern of the business world. The onslaught
on various disruptive fields and the siege of
technology, ranging from the Internet of Things
(IoT), big data, automation, robotics, cloud
computing, to artificial intelligence (artificial
intelligence) managed to carve .a big mark in history:
number 4.0 behind the industrial revolution. Efforts
to improve the competitiveness of agricultural
commodities in the era of disruption or industrial
revolution 4.0 concernbusiness actors who need to
improve their ability to understand technology
specifically ICT so that they can utilise and integrate
internet / ICT capabilities within the business
processes such as e-commerce.
12 business aggregators in Indonesia who have
developed online applications for businesses in
agriculture that are objects in this paper can be seen
in the following table.
Table 1: Aggregator Business in Agriculture
No
Business
Aggregator
Website
1
Sayurbox
www.sayurbox.com
2
Keranjangsayur
www.keranjangsayur.com
3
PT Mandala
AgroPersada
Nusantara
www.sayours.co.id
4
IGrow
www.iGrow.asia
5
PT
LimakiloMajub
ersamaPetani
www.limakilo.co.id
6
Kecipir
www.kecipir.com
7
Sikumis
www.sikumis.com
8
KORPRI Jawa
Tengah
www.regopantes.com
9
Etanee
www.etanee.co.id
10
Brambang
www.brambang.com
11
Tanihub
www.tanihub.com
12
KedaiSayur
www.kedaisayur.com
This aggregators provide information on
production supply agriculture, production processes
in agriculture, and the process of marketing
agricultural products (e-commerce).
2.2.3 Objectives and Functions of Business
Aggregators
The depth interviews with the deputy assistant
team of the coordinating ministry for the economy
resulted in obtaining the objectives and functions of
the aggregator business, which are as follows:
(1) Improve the efficiency of agricultural product
trading systems;
(2) Maintaining the availability of agricultural
products;
(3) Maintain stable prices of agricultural products;
(4) Improve the welfare of farmers.
Business aggregator functions are:
(1) Serving several distribution nodes at a regional
scale;
(2) Providing local supplies that are easily affordable
and always ready at all times;
(3) A broader and more selective offer that is more
diverse to the source of branded commodities and
local products;
Aggregator Business as an Intermediary in Agriculture: A Literature Review
59
(4) Develop the supply of local products through
training and mentoring activities to increase the
number of producers;
(5) Take advantage of available infrastructure to
support cross-regional marketing;
(6) Creating economic growth in general;
(7) Reducing the cost of the trading system which has
been considered a waste
2.2.4 Aggregator Business Models
According to Hubeis (2011), business is an
economic activity that involves community members
in the resources of production factors into goods /
services that can meet consumer needs and generate
profits for the producers on an ongoing basis through
production activities (transformation technology),
distribution (potential), and sales (consumption
technology). The aggregator business model in
agriculture was developed by the (Africa, Wo, Group,
& Note, 2015) which revealed that the aggregation
model benefits are as follows:
a. Logistic support: aggregation reduces logistical
costs from smallholder farmers. It may also be a
tool for improving quality, as producer
organisations can add value to crops through
sorting, drying, storing and other functions,
depending on their capacity.
b. Marketing and distribution of services:
aggregation can reduce marketing, distribution,
money-lending and servicing costs for companies
selling inputs or financial
services to smallholders.
c. Provision of training: training groups to increase
productivity are generally more cost-efficient than
working with farmers on a one-on-one basis.
d. Information dissemination: aggregation reduces
the cost of collecting and disseminating
information for companies seeking certified
crops, by reducing auditing
costs for example.
e. Bargaining power: collective action gives farmers
bargaining power to secure better prices.
Corporate Databases
Provided
info
Find
Customer
Provided
info
Fulfill Order
Support
Identify
Need
Find Source
Evaluate
Purchase
Support
Phone, Fax, E-mail
send info
request info
Website
Newsgroup
Net
Communities
Website
EDI
Website, Phone,
Fax, E-mail
Emailing list
Web surfing
Data sheets,
catalogs,
demos, etc.
web searches,
web ads
w
demos,
reviews
credit cards,
digital cash
deliver soft goods electronically
Information
sharing
ordering
payment
fulfillment
service &
support
SELLER
BUYER
Figure 3: Business Process in the framework of e-commerce system (David Kosiur in Indrajit (2001)
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
60

In this paper, based on the reviewed literature and
interviews with business people and experts from the
ministry of coordinators of the Indonesian economy,
we classify business models as follows:
(1) Based on e-commerce
The advancement of information and internet
technology over the past few decades has had a
significant impact on economic change. Increased
internet diffusion and has made e-business a great
potential in developing countries (Mishra, 2010).
Because of the rapid advances in ICT, technology
adoption is considered one of the main determinants
for the survival of the company (Lip-Sam, T., &
Hock-Eam, 2011).
The use of e-commerce is dominated by
marketing and purchasing and procurement activities
(Rahayu and Day, 2017). Indrajit (2001) revealed that
e-commerce has characteristics including
transactions between two parties; the exchange of
goods, services or information; the main media in the
trade process is the internet. Laudon & Traver (2017)
revealed that the type of e-commerce that is most
often discussed is business-to-consumer (B2C) e-
commerce, where online businesses are trying to
reach individual consumers in this case, which has
been widely developed for downstream products. The
business process in e-commerce can be seen in Figure
3.
Figure 3 shows that the company or group of
people can offer their products and services through
the internet. From the consumer side, the internet
offers broad access to company information. After the
information exchange, the next step is the process of
ordering products or services electronically. In this
business process,four streams mustbe managed well,
namely the flow of goods, the flow of information,
the flow of money, and the flow of documents.
One of the concepts of this aggregator business
can be online by building e-commerce. The
Indonesian trade minister revealed that all farmers
would be connected virtually through e-commerce.
Farmers who are members of the aggregator
mechanism with e-commerce models can deal
directly or sell their products directly to consumers.
(2) Information sources (clearinghouses)
The internet is instant in conveying all forms of
information and can be used to deal with the problem
of information asymmetry experienced by producers
and consumers regarding availability, price, and
product quality (Laudon & Traver, 2017). Therefore,
the aggregator business is not just selling
farmers’products but can play a role in providing the
information needed by each region.
Given that agricultural products are mostly
seasonal, with the presence of ICT, information
related to planting schedules and harvest schedules
that are not simultaneous in each region can be
handled by the existence of the aggregator. Singh
(2009) revealed that farmers need to review their crop
patterns to ensure which cropping patterns are most
beneficial for farmers.
The advancement of technology infrastructure
can improve internet access both in rural and urban
areas so that farmers can access information about
crops, weather, input and set prices, and also improve
their abilities related to agricultural science (Singh,
2009). Proper information management can help
farmers in making business decisions (Abreu, 2009).
(3) Connectors (spark-plug)
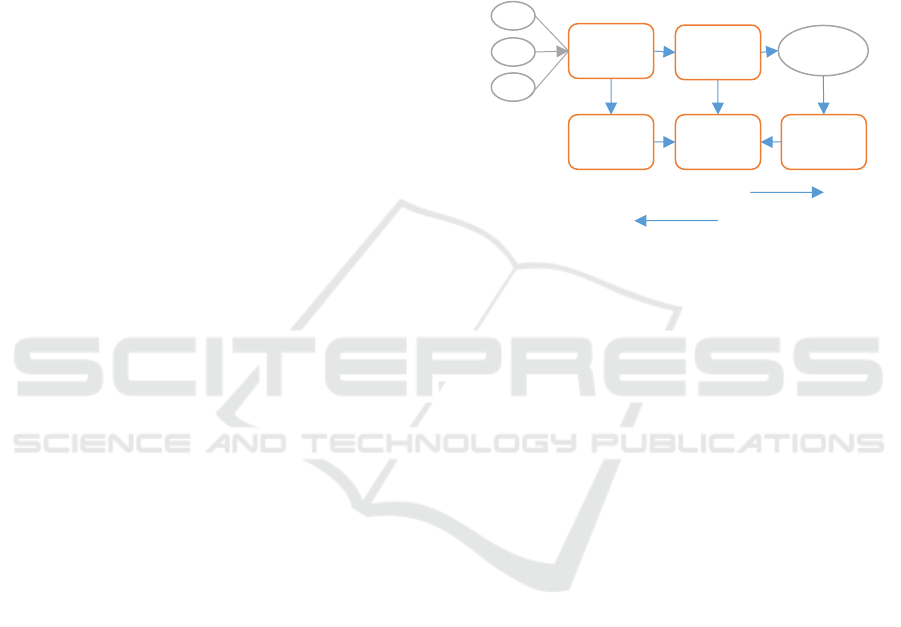
Aggregators can also be referred to as spark-plugs
or connectors (Lembong, 2016). Aggregators can
reduce inefficiencies in the process of distributing
agricultural products (the availability of a strong sales
information system that producers can dynamically
set the price of their products to reflect actual demand
or can play a role in the perfectly competitive market
(Lambert, 2012).
The mechanism will form a producer selling price
system where the roles of distributors and wholesalers
are intermediaries between producers and consumers
where they demand payment and raise costs but add
little value will be lost (Laudon & Traver, 2017).
Connectors can also play a role in determining
product standardisation in accordance with the
characteristics of the product desired by consumers so
that farmers can do their sorting and grading
processes whichwill certainly increase the selling
value of their products (Asokan, 2009; Revathy,
2015; Abreu, 2009).
(4) Community (village-preneur)
The aggregator business model can also be a
farmer community in each region. This farming
community will be very much needed as a gathering
place for farmers. The government has made an
effortto build farmer communities in each region to
be more competitive by forming farmer groups (Law
No. 16 of 2006).
In addition to the farmer groups, cooperatives can
also move to run the aggregator business function by
prioritising the interests of their members. In
countries that have a developed and developing the
cooperative system, this model is also progressing
rapidly because cooperatives work for the interests of
Aggregator Business as an Intermediary in Agriculture: A Literature Review
61
members. Cooperatives or farmer groups can build
bazaars or farm markets in each region to create a
platform where farmers can sell their products
directly to consumers without the intervention of
intermediaries (Dey, 2012).
Increasing the capacity of rural resources in the
context of village-preneur will improve the village
economy and the development of the industrial and
service sectors.
(5) Food Hub
Hub defined as “a centre of activity”. Harrington
(2018) defines food hubs as physical or virtual
entities that help various players in the movement of
food from farmers to consumers. Meanwhile, Barham
et al. (2012) define food hubs as businesses or
organisations that actively manage aggregation,
distribution, and marketing of food products
identified by sources, especially from local and
regional producers to strengthen their ability to meet
wholesale, retail and individual demands.
Hamilton (2015) revealed the role of food hubs in
the marketing value chain of agricultural products
includes 1) food hubs (aggregating) which play a role
in combining products from various sources,
including small and medium producers to
institutional consumers; 2) Food hubs play a role in
distributing products from farmers to buyers that can
be done alone or in collaboration with third parties
(examples of expedition services); 3) Food hubs as a
broker is considered more efficient than farmers
marketing their products privately; and 4) food hubs
as processing by carrying out activities that can add
value to the product.
(6) Upstream Efficiency
Literally “efficiency” is defined as the accuracy of
the way (effort, work) in carrying out something (by
not wasting time, effort, cost (KBBI Online).
Economists as a whole describe that economic
efficiency will occur when individuals in society
maximise their utility, remembering available
resources (Productivity Commission, 2013).
The agribusiness sub-system includes upstream,
cultivation, and downstream agricultural sub-systems
(Saragih 2004). Upstream agricultural sub-systems
include hatchery/plant/animal nursery industries,
industries that produce facilities and infrastructure
used in the process of agricultural cultivation.
Several previous aggregator business models
explain the efficiency of forwarding linkage from
sub-cultivation systems to marketing agricultural
products. Activities related to backward linkage are
how farmers can obtain precise, timely and
appropriate production inputs.
The majority of farmers in Indonesia are small-
scale, so the aggregator can act as a provider of
production facilities and infrastructure, including as a
facilitator of services to farmers to meet the needs of
production facilities including fertilisers, certified
seeds, pesticides, agricultural machinery, and farming
capital (Singh, 2009).
Figure 4: The aggregator mechanism as a spark plug
(Asokan, 2009)
3 CONCLUSIONS
People often have negative perceptions of
intermediaries or middleman in the agricultural sector
which are often called Tengkulak, Pengepul, and
Bandar. Middleman tries to make a profit by lowering
the prices of farmers as low as possible. The large
demand for agricultural commodities createsa long
distribution network in agricultural products starting
from the level of farmers/producers, intermediary
traders, to mobile traders/retailers who sell directly to
end consumers. This causes expensive distribution
costs and low-quality agricultural products. An
aggregator is a strategic solution for solving these
problems. An aggregator is amodern actor in
disruption era who plays a role in distributing
agricultural products to consumers directly by
utilising the advancement of information technology
and also the role of the aggregatorto improve both the
welfare of farmers and consumer satisfaction.
There were six alternative aggregator business
models namely e-commerce based, information
sources (clearinghouses), a connector(spark-plug),
communities (village-preneur), food hubs, and
upstream efficiency. The six alternative aggregator
business model share similarities with the function of
an aggregator business that already exists in Africa.
Member of
Farmer’s
Association
Aggregator
Consumer
Delivery
Center
Settlement Payment
Sortation and grading
process
Goods Delivery
Cash Payment
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
62

The aggregator business will cut the supply chain and
increase farmers’ profits.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Iwould like to thank LPDP (Indonesia Endowment
Fund for Education), Ministry of Finance, Republic
Indonesia for taking part in providing me with the
financial support to finish this paper.
REFERENCES
Abreu. 2009. Uttarakhand state cooperative federation: can
it help the horticulture farmers?: Case Analysis 4. The
Journal of Business Perspective. 13(2l): 68
Africa, G., Wo, S., Group, R., & Note, S. (2015). How
do off-takers and smallholder farmers use
aggregation models to grow their business?,
(October), 1–7.
Asokan. 2009. Uttarakhand state cooperative federation:
can it help the horticulture farmers?: Case Analysis 2.
The Journal of Business Perspective. 13(2l): 64-66.
Barham, J., Tropp, D., Enterline, K., Farbman, J., Fisk, J.,
& Kiraly, S. (2012). Regional Food Hub Resource
Guide. Retrieved from Washington, DC:
Dey, S. (2012). Rythu Bazaar: A Study of the Supply Chain
of the Farmers’ Markets of Andhra Pradesh, IUP
Journal of Operations Management, 11(3), pp. 43–66.
Available at:
https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&d
b=bth&AN=79827835&site=ehost-live.
Fixing supply chain in agriculture. (2013, May 14). The
Financial Express. Retrieved from
https://search.proquest.com/docview/1350265680?acc
ountid=32819
Hamilton, J. M. and Goldman, A. L. (2015). Food Hub
Decision-Making and Development A thesis submitted
by, (May).
Hanggana, S. (2018) ‘Regulations Weakness Analysis of
Farmers Group, Gapoktan, UPJA, and LKM-A in Order
to Enhance Farmers’ Income’, Jurnal Analisis
Kebijakan Pertanian, 15(2), pp. 137–149.
Harrington, H.F. (2018). A study of food hub buyers in
Vermont: Motivation, Marketing, and Strategy,
[Thesis]. The University of Vermont.
Hubeis M. (2011). Prospek Usaha Kecil dalam Wadah
Inkubator Bisnis. Bogor: Ghalia Indonesia
Ikhsan, M., Alatas, V., Wihardja, M., and Taufik. 2015.
Apa yang salah dengankebijakanperberasankita?.
Retrieved from:
(http://www.perhepi.org/wpcontent/uploads/2015/03/
Apa-yang-salah- dengan- kebijakan-
perberasannew.pdfdiakses 20 Maret 2018)
Indrajit, R. E. (2001). E-commerce: kiat dan strategi bisnis
di duniamaya. Indonesia: PT Elex Media Komputindo
Knoche, H. (2010). Voices in the field: A mobile phone
based application to improve marginal farmers
livelihoods. Human Factors.
Lambert, Q. (2012). Business models for an aggregator.
Information Management & Computer Security.
Laudon, K. C. and Traver, C. G. (2017) E-Commerce 2017-
Business.Technology. Society.
Lembong T. (2016). Konsep dasar agregator. [article]. Info
Perdagangan Dalam Negeri.
Lip-Sam, T., & Hock-Eam, L. (2011) ‘Estimating the
Determinants of B2B E-Commerce Adoption Among
Small & Medium Enterprises’, International Journal of
Business and Society, 12(1), pp. 15–30
Mejía, G. and García-Díaz, C. (2018) ‘Market-level effects
of firm-level adaptation and intermediation in
networked markets of fresh foods: A case study in
Colombia’, Agricultural Systems, 160(October 2015),
pp. 132–142. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2017.06.00
Moghaddam, G. and Moballeghi, M. (2007) ‘The
importance of aggregators for libraries in the digital
era’, Interlending & Document Supply, 35(4), pp. 222–
225. doi: 10.1108/02641610710837536.
Monieson, D. D. (2010) ‘Explorations & insights a
historical survey concerning marketing middlemen as
producers of value’, Journal of Historical Research in
Marketing, 2(2), pp. 218–226. doi:
10.1108/17557501011042560.
Rahayu, R. and Day, J. (2017) ‘E-commerce adoption by
SMEs in developing countries: evidence from
Indonesia’, Eurasian Business Review. Springer
International Publishing, 7(1), pp. 25–41. doi:
10.1007/s40821-016-0044-6.
Reardon, T., Timmer, C.P. (2012). The Economics of the
Food System Revolution, The Annual Review of
Resource Economics. 4(14), 1–40.
Productivity Commission. (2013). On efficiency and
effectiveness: some definitions. Staff Research Note:
Canberra.
Ranjan, R. (2017). Challenges to farm produce marketing:
A model of bargaining between farmers and middlemen
under risk, Journal of Agricultural and Resource
Economics, 42(3), pp. 386–405.
Revathy, L. N. (2015, Jul 16). Bypassing middlemen to
boost farmers’ income, the masakkal way. Businessline
Retrieved from
https://search.proquest.com/docview/1696787483?acc
ountid=32819
Saragih, B. (2004). Pembangunan
PertaniandenganParadigma Sistem dan Usaha
Agrbisnis. [Online]. Available at:
https://pse.litbang.pertanian.go.id /ind/pdffiles/An
jak_2004_VI_01.pdf
Shankar, T., Singh, K. M. and Dwiwedi, S. (2017). An
Analysis on Problems of Vegetables Marketing in
Farmers ‘ Market of Jharkhand: A Case Study in Ranchi
District, 62(1), pp. 175–183. doi: 10.5958/2230-
7311.2017.00054.X.
Simon, J. P., Benghozi, P. J. and Salvador, E. (2015). The
new middlemen of the digital age: The case of cinema,
Info, 17(6), pp. 97–115. doi: 10.1108/info-04-2015-
Aggregator Business as an Intermediary in Agriculture: A Literature Review
63

0023.
Singh. 2009. Uttarakhand state cooperative federation: can
it help the horticulture farmers?: Case Analysis 3. The
Journal of Business Perspective. 13(2l): 66-68
Sudiyono, A. (2004). PemasaranPertanian. 2nd Edition.
Malang: UMM Press
Suryadarma, D. et al. (2010) ‘Traditional food traders in
developing countries and competition from
supermarkets: Evidence from Indonesia’, Food Policy.
Elsevier Ltd, 35(1), pp. 79–86. doi:
10.1016/j.foodpol.2009.11.002
Tapsavi S.K. 2009. Uttarakhand state cooperative
federation: can it help the horticulture farmers?: Case
Analysis 1. The Journal of Business Perspective. 13(2l):
63-64
Taragola N., Gelb E. (2005). Information and
Communication Technology (ICT) adoption in
horticulture: a comparison to the EFITA Baseline.
Proceedings of the EFITA/WCCA 2005 Joint
Conference Vila Real, Portugal (PT): Universidade De
Tras-os-Montes e Alt.
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
64
