
Strengthening Model of Character Through Citizenship Education
Based on Lesson Study in Malang
Suparlan Al Hakim, Sri Untari, Desinta Dwi Rapita, Muhammad Mujtaba Habibi
Universitas Negeri Malang, Malang, Indonesia.
Keywords: Character, Citizenship Education, Lesson study
Abstract: This article draws on the strengthening model of character trough citizenship education based on lesson study.
The approach used is a research and development design with Classroom Action Research. Data were
collected through interviews, observations, document studies and questionnaires on several Junior High
Schools in Malang District. Data analysis techniques implemented by (1) quantitative data, to answer the
effectiveness of strengthening model of character trough citizenship education based on lesson study subjects
was analysed by paired T-Test; (2) implementation of character strengthening prototypes on learning process
was analysed by case study. The result, (1) prototype of strengthening model of character trough citizenship
education process developed by analysis of content / material; culture analysis; analysis process, organizing
value learning with the 5 W + 1H paradigm, supported by the selection of the main values of the characters;
(2) implementation principle: planning; implementation and reflection; (3). The prototype of strengthening
model of character trough citizenship education based on lesson study in Malang is effective, quantitatively
able to improve the behaviour of mutual cooperation of junior high school students.
1 INTRODUCTION
At this point, character education has been an
increasing issue in schools, and it is slowly but surely
beginning to show its importance in the curriculum,
this is due to the number of adverse factors in the
education system including behavioral issues,
disrespect, and bullying. The case of maltreatment of
teachers by students causing deaths that occurred in
Madura became one of bad behavior and many more
cases far from the mirror of noble behavior according
to the personality of the nation.
Building the nation's character to strengthen the
values of national identity has become the
commitment of all country in the world. The cross-
country comparison study, on character education in
Malaysia, the United States and Indonesia, proves
some examples of the truth of the commitment of
states to the urgency of character education for
generations. Nevertheless, in the context of
Indonesia, Pancasila Culture and the Strengthening of
Character Education (PPK) in Indonesia are facing a
major problem calling all components of the nation
responsible for intelligent and contextual solving. In
2010, the Government launched the National
Movement of Character education intensively
(Kemendikbud, 2017), but this movement has not
been felt by all education units in Indonesia. Praxis of
Pancasila as the moral of the nation, the personality
of the nation and the view of life of the Indonesian
people still many problems that need to be addressed
seriously by the entire nation of Indonesia.
Today, the national concern inherent in the
Indonesian nation is the lack of expression and
commitment to its character. The performance of the
nation emphasizes more on the quantitative and
mechanical dimensions of life, while the qualitative
dimensions of life are often ignored (Al Hakim,
2010). The gap between idealized characters, realities
and instruments to develop is a separate problem in
character education. (Guidry, 2008; Untari, 2017)
Other disrespectful, irresponsible, and weak character
traits that students have, seeing the behavior of people
around them, from political leaders, corrupt
government officials, and teachers and parents
(Untari, 2017; Perles, 2018)
One effort to address the problem is the
government issued Presidential Regulation of the
Republic of Indonesia Number 87 the Year 2017
About Strengthening Character education. especially
Article 1 Paragraph (1) says "Strengthening character
education is an educational movement under
Al-Hakim, S., Untari, S., Rapita, D. and Habibi, M.
Strengthening Model of Character Through Citizenship Education Based on Lesson Study in Malang.
DOI: 10.5220/0008409301590170
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Learning Innovation (ICLI 2018), pages 159-170
ISBN: 978-989-758-391-9
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
159

educational units to strengthen the character of
learners through harmonization of the heart, taste,
thought and sport with the involvement and
cooperation between education units, family, and
society as part of the National Movement of the
Mental Revolution (GNRM) ". In the National
Character Grand Design Manuscript (2010), there are
some fundamental reasons underlying the importance
of national character building, from philosophical,
ideological, normative historical and sociocultural
perspective. Philosophically, building the character
of the nation is a fundamental need in the process of
nationhood because only a nation that has a strong
character and identity that will exist.
Ideologically, character building is an effort to
embody the ideology of Pancasila in the life of nation
and state of Indonesia. Normatively, the development
of the nation's character is a manifestation of the step
of achieving the state's goal of protecting the whole
nation and the entire blood of Indonesia, promoting
the general welfare, the intellectual life of the nation
and joining the independence of the world, eternal
peace and social justice. Historically, the
development of the nation's character is the dynamics
and journey of the national process that occurred non-
stop in the period of history both in colonial times and
in the era of independence. While sociocultural, the
development of national character is a practice of
habituation of the potential sociocultural values
multicultural.
Character Education Strengthening is important to
implement in the classroom by integrating with all
subjects. In the 2013 curriculum, the subjects of
Citizenship Education and Religious Education
expect core competencies 1 and 2 that include
spiritual attitudes and social attitudes, generating
great responsibilities for schools, principal teachers of
Citizenship Education and Religious education,
parents and communities. Character Education
integrated with learning is expected to strengthen the
morale of learners. The psychological character of
character education includes the moral dimensions of
reasoning, moral feeling, and moral behavior
(Lickona, 1991). Therefore, it is necessary to develop
a model for integrating Character Education properly
to achieve the expected goals of good and intelligent
citizens (Untari, 2016; Perles, 2018). As noted
(Hakam, 2017) that the process of internalization of
the character is essentially carried out by stages:
Moral information level, Moral belief level, Moral
Attitude level, Moral value level, Moral
character/personality level, and Moral dignity level.
(2017).
2 METHOD
This method used Classroom Action Research
approach. Strengthening model of character was
conducted by researchers, four students and teachers
in one junior high school as a model school for one
year, from August 2017 to July 2018. SMP Negeri 1
Sumberpucung, established in 1985 and located in
Malang Regency. It has more than 867 students and
consists of 27 classes. This school became a partner
school of Lesson Study program based on the local
wisdom which conducted by Faculty of Social
Sciences. At 2016, the principal developed LS on all
subjects not just Social Studies and Citizenship
Education. Since the implementation of the 2013
curriculum, the school has begun to strengthen
character education, to build the 21st century
generation.
The stages of classroom action research that have
been used refer to the opinions of Kemmis and Mc.
Taggart: (1) planning, (2) implementation, (3)
observation, (4) reflection. The models and
explanations for each stage are as follows.
The following are detailed activities carried out by
researchers at each step.
2.1 Pre-Research Activities
In the pre-research stage initial observations were
made which included the implementation of the
learning process of citizenship education that
integrated the character values and observed frequent
problems, the availability of facilities and
infrastructure in learning through interviews with
teachers and students.
2.2 Research Implementation
The study was conducted over two cycles to
determine the religious value, mutual cooperation in
student behavior. If in the first cycle there is no
religious and mutual cooperation behavior, then a
second cycle is needed. In the second cycle, learning
is done on the same basic competencies but the
indicators are different.
ICLI 2018 - 2nd International Conference on Learning Innovation
160
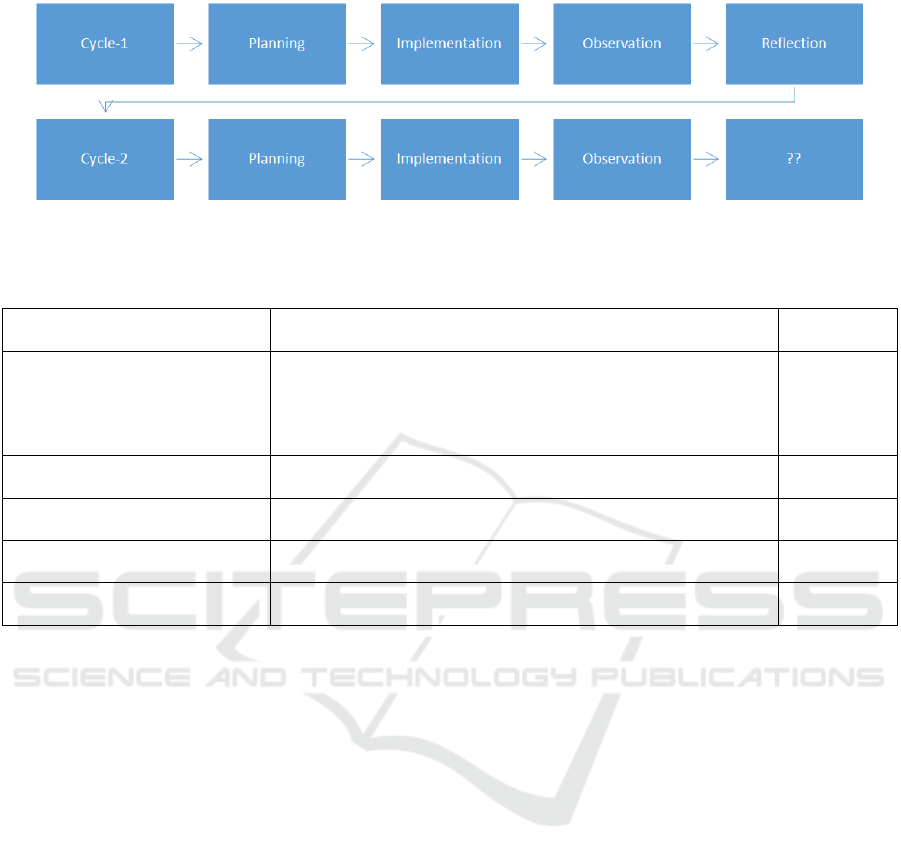
Figure 1: The stages of classroom action research.
Table 1: Steps for problem based learning models.
Phase
Activity
Time
Allocation
Orientation
Student orientation on problems
The teacher explains the learning objectives, explains the materials
needed
The teacher motivates students to be actively involved in solving
selected problems
5’
Organizing
Students are helped to define and organize learning tasks related to
problems
10’
Individual and group
investigations
Encourage students to gather appropriate information
Carry out experiments to get explanation and problem solving
40’
Development and presentation of
performance results
Students are given the opportunity to plan and prepare works in the
form of reports and various assignments with friends
10’
Analysis and evaluation of
problem solving processes
Evaluate learning outcomes about material
Student groups present performance results
40’
2.2.1 Cycle-I
Teaching and learning activities carried out in this
cycle are as follows:
Action Planning
The action planning includes:
a) Develop plans for implementing learning by
using problem based learning model learning
b) Make an observation instrument to find out the
implementation of learning done by teachers
and students and religious behavior and mutual
cooperation.
Actions and Observations
The action taken at this stage is the
implementation of learning by applying the PBL
model. Each cycle consists of 3 meetings. The first
cycle discusses the association of regional
characteristics within the framework of the Unitary
Republic of Indonesia. Knowledge tests or
assessments are carried out at the end of each cycle.
In this learning students sit classically and in groups.
In this activity the researcher acted as a colleague
from the teaching teacher and carried out learning
activities in accordance with the learning
implementation plan that had been prepared together
previously using the PBL model with its syntax, as
shown in Table 1.
When implementing the action, the researcher acts as
a teacher's colleague, class VII PPKn teaching acts as
an observer who records specific events during the
learning process and observes the teacher's activities
assisted by another researcher. The observed teacher
activity is the suitability of the teacher's activities
with the drafted RPP. In addition, what is observed is
activity when implementing PBL learning. This
observation was carried out in conjunction with the
implementation of learning. This is intended so that
observers can find out the activities carried out by the
teacher and students when implementing learning.
Observations were made to determine the religious
behavior and mutual cooperation of students. After
the implementation of cycle one, the attitude is given
to students to find out the observed behavior, namely
the religious and mutual cooperation of students. In
addition, researchers also conducted interviews with
students and observers to find out how the PBL
learning model was implemented.
Strengthening Model of Character Through Citizenship Education Based on Lesson Study in Malang
161
Reflection
Reflection is an activity to analyze actions that have
been carried out with observers. Reflection aims to
examine what has been done and not done, what has
been achieved, what problems can be solved and
which have not been solved, if a problem is found
then a solution will be sought and determine the next
action in order to improve the process and results of
learning outcomes at the next meeting . Furthermore,
there are corrective measures implemented that will
be implemented in the next cycle. The indicators of
achievement of the actions used in the first cycle and
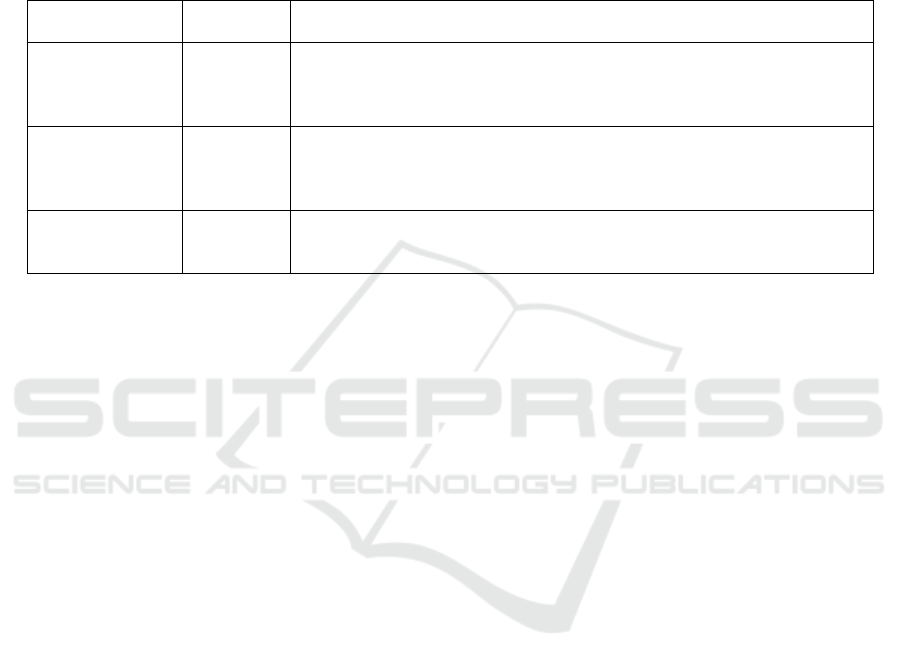
so on are shown in Table 2.
Table 2: Indicator of achievement of cycle actions.
Indicator
Target of
each cycle
Measurement
The
implementation of
PBL model
Very good
(≥ 81)
Observed when students carry out the PBL model stages using the learning
implementation observation sheet. Calculated from the number of
achievement stages divided by all stages of the learning model.
Religious
behavior appears
Appear (≥
81)
Measured from the results of the religious attitude scale filled by students
after following PBL learning. Calculated from the number of acquisition
scores divided by the total score of the attitude scale.
Mutual
cooperation
Appear (≥
81)
Calculated from the scale of mutual cooperation attitude of students and
calculated from the number of students who obtained a score of ≥ 75 divided
by all students
2.2.2 Cycle-II
After studying the overall results of reflection in cycle
I, the results of reflection on cycle I are used to plan
cycle II actions. The action steps of cycle II are the
same as the stages in cycle I. In this cycle, it is done
to overcome the obstacles in cycle I, what has not
been achieved in cycle I, so that in cycle II it is
expected that the results will be more significant and
better meet the criteria of results predetermined. the
implementation of the second cycle is an
improvement and refinement of the first cycle so as
to be able to achieve the objectives expected in this
study.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
3.1 The Prototype of strengthening
model of character trough
citizenship education based on
lesson study
Strengthening model of character trough citizenship
education based on lesson study concept, essentially
is how to sort and choose the main character values
that are (1) religious, (2) nationalist, (3) independent;
(4) gotong-royong (cooperative coordination) and (5)
integrity. The five main values of these characters are
included in the Syllabus and Learning Program Plan
(RPP). The integration of character education in
Lesson Study-based is focused on achieving core
competencies and basic competencies that include
knowledge, good attitude, spiritual attitudes, and
social and skills attitudes. Thus integrating the core
values of characters in learning Citizenship
Education, students are expected to have good
cognition, psychosocial and skills. As stated by
(Lickona, 1991) which states that the character of
character education psychologically includes the
moral dimensions of reasoning, moral feeling, and
moral behaviour (1991). They are also expected to
develop life skills in understanding themselves,
others and nation and country. A learner as the next
generation is a human resource that must be built both
soul and body. Developing human resources is the
foundation of nation-building. Character education is
expected to deliver students to the Golden Generation
2045 with 21st-century skills, namely Character
Quality, Basic Literacy, and 4C (Critical thinking;
Communicative; Collaborative; Creative)
Competencies.
This study is carried out by considering the
following principles: (1) cantered on the learner; (2)
learners are facilitated for active, physical,
intellectual, social, mental and spiritual; (3)
interactive dialogue is preferred, so that awaken each
other tackle, care and love between teacher-learners,
learners-learners; (4) encouraging learners to adapt
themselves to a dynamic environment; (5) learners
are able to apply basic skills in everyday life; (7)
ICLI 2018 - 2nd International Conference on Learning Innovation
162

learners can solve complex problems. (8) The noble
values of Pancasila are practised in life.
The development of an integrated character
education model in lesson study-based basically
begins with the findings of the problems that
challenge the immediate implementation of character
education integrated into learning. Challenges found
in the field as follows: (1). Not optimal harmonization
of potential development of learners between the liver
(ethics), thinking (literate), taste (aesthetic), and
sports (kinaesthetic) . The reality of the field shows
learning Citizenship Education, until now still
emphasizes the aspects of thinking; (2). School
facilities, means of transportation, the distance
between students' houses to schools is very limited,
still not able to be a supporting factor in character
education integrated with learning; (3) the limitations
of teacher competence in understanding the
importance of integrating character education into
learning in its class; (4) not yet optimal teacher skills
in conducting KI / KD analysis and selection of
character values developed; (5) not yet optimal
understanding and skill of teachers in conducting
evaluation on implementation of character education
integrate in learning; (6). The negative influence of
information and communication technology on the
lifestyle of learners in adolescence, as well as the
faded values of religiosity and wisdom local nation.
Another problem from teacher's point of view
shows that many teachers do not yet have an
understanding of how strategic Citizenship Education
subjects are as a vehicle for character education. They
are still confused because there is a change of term in
character education. Various terminologies are used
such as character education of the nation, character
education, and further strengthening character
education. The apparent tendency of teachers to
integrate Pancasila values as accessories in the
Lesson Plan, character values are also without an
analysis process and careful selection. The practice of
learning is already innovative, but the character's
values are taught, not the habit.
The strengthening model of character trough
citizenship education based on lesson study as a basis
is developed using a scientific learning approach as
used in the 2013 curriculum. With the steps: (a)
observing; (b). ask; (c). collect information / try; (d).
Reasoning / associating; and (e). Communicate.
Execution strategy p there are several scientific
approaches, recommended by the Ministry of
Education and Culture, among others, contextual
learning with learning model is a form of learning that
has the names, characteristics, syntax, arrangement,
and culture, as follows: discovery learning, project-
based learning, problem-based learning, inquiry
learning. The 2013 curriculum has focused the
character education in all subjects, as an effort to
build the character of good learners. Of course,
through the process as proposed (Lickona, 2012) that
components of good characters include: Moral
Knowing: Moral awareness, Knowing moral values,
Perspective taking, Moral reasoning, Decision
making, Self-knowledge. Moral Feeling: Conscience,
Self-esteem, and empathy, loving the good, Self-
control, Humility and Moral Action: Competence,
Will, Habit.
The integration of the main values of the
characters in learning is not merely a mere "moral
speaker," but begins the process, understands the
value, commitment to values and is willing to carry
out in life, it is more important for the learner to be
one of the means to make the value of character
education open just learning value (Al Hakim, 2011;
Chowdhury, 2016)
3.1.1 Formulate learning objectives
The essence of learning objectives is as a further
elaboration of the indicators of achievement of basic
competencies possessed by students to achieve basic
competencies. The formulation of goals must be
based on ethics or principles, among others, must be
operational, describe the competence or
crystallization of student behaviour, both related to
knowledge, skills and attitudes. Therefore, in order
for the teacher to formulate the learning objectives
properly, it is necessary to pay attention to the
following:
Learning objectives must be a form of student
behaviour that can be observed and measured;
Learning objectives must be learning
outcomes, and not refer to student learning
processes;
Each learning goal only points to one type of
behaviour from skills, skill or attitude as a
result of student learning;
Each learning goal must be clearly stated and
straightforward. Therefore, in formulating
learning objectives must use operational words
(unambiguous, can be evaluated and realistic
with students' abilities);
Learning objectives should mention the
conditions for achieving student behaviours;
Each learning goal must contain complete
components, which include: Goals (A =
Audience); Behaviour (B = Behaviour);
Conditions (C = Condition) and Criteria (D =
Degree).
Strengthening Model of Character Through Citizenship Education Based on Lesson Study in Malang
163

The contents of the learning objectives should
be of good quality or quality. Learning
objectives must contain appropriate and
meaningful competencies (abilities) for
students. In this regard the teacher can use
criteria, for example what was stated by
Benyamin S. Bloom, known as "Bloom
Taxonomy", which includes three domains,
namely cognitive, affective and psychomotor.
Using a taxonomy, shows that the teacher
emphasizes one aspect that is the ability of his
students.
3.1.2 Analysis of the Main Character Values
This component is an activity to identify the value of
Strengthening Character Education (PPK) that is
intended to be developed in students so that it
becomes visible behaviour. In accordance with the
main values contained in the guidelines for
strengthening character education from the Ministry
of Education and Culture (2010) as shown in Table 3.
Table 3: The main value table developed in the prototype.
No.
Main value
Sub value
1
religious
Peaceful love, tolerance, respect
for different religions and beliefs,
firm conviction, confidence,
cooperation between followers of
religion and belief, antibuli and
violence,
Friendship sincerity not imposes
the will, love the environment,
and protect the small and
marginalized.
2
Mutual
cooperation
respect, cooperation,
inclusive, commitment to
decision
together, consensus, help,
solidarity,
empathy, anti-discrimination,
anti-violence, attitude of
volunteerism
3.1.3 Content analysis
Content analysis is an activity focused on the process
of identifying; selecting and
determining learning materials, can be taken in the
following ways:
Using signs of learning material in the
Syllabus;
Establish essential learning material;
Determine the scope or scope of the scope of
the learning material;
Arrange the sequence (sequence) of learning
material.
3.1.4 Background analysis
This activity was developed using cultural
approaches and life cycles , which contained two
concepts, namely the concept of region or
environment (local, regional, national and global);
and the concept of human activity that covers all
aspects of life (ipoleksosbuhankam). In addition, the
background analysis also considers the cultural
values that grow and develop and are upheld by a
community and the possible benefits for students'
lives. In this connection, background analysis is
closely related to the principles that must be
developed in teaching values and morals, namely the
principle: from a narrow / close environment to a
broader environment.
3.1.5 Organizing Material
Organizing the material (content organizing) and
mapping of materials (content mapping) learning,
can be done with due regard to the principle of "4 W
and 1 H", namely: What (what), Why (why),
When (when), Where (where) and how (how).
In the design of learning, the five principles must
be colour by the characteristics of learning
with Problem Based Learning in the direction
of experience of moral values and critical thinking in
the effort to achieve the concept ( concept
attainment ) and the development of concepts
( concept development ). All of this is done by
empowering learning methods that enable students
to foster religious and mutual cooperation.
3.1.6 Determination of Learning Strategies
and Methods
The choice of strategies and learning methods
is expected to function in achieving learning goals,
namely changes in behaviour that exist in students
both cognitive, psychomotor and affective and
conative (willingness to do). Strategies and methods
must be explicitly mentioned in the Learning Plan, as
a sign of the teacher's "transactional decision" to do it
in the learning process in order to save and achieve
the learning objectives.
In civic education learning, the choice with the
PBL model should be harmonized with the
characteristics of this subject which is not merely
interpreted as a memorization lesson (cognition). The
material is full of values and attitudes which play a
ICLI 2018 - 2nd International Conference on Learning Innovation
164

role as the formation of national awareness, which is
an integral part in strengthening character education.
3.1.7 Selection and Determination of
Learning Media
Media which is used in accordance with the
characteristics of the material and learning objectives
must be revealed in the Learning Design. Thus, the
selection and determination of learning media is not
arbitrary, but must be carefully chosen in accordance
with the characteristics of the material and functional
value in achieving learning objectives. In other
words, as a tool and at the same time as a messenger
and messenger, the learning media also contributes to
the experience and behaviour of the subject of
learning.
Analogous to its function, in the framework of
formulating learning design using
a scientific approach with the PBL model,
the selection, designation or use and use of media are
expected to colour a conducive, dialogical,
democratic and empathic learning environment.
3.2 Implementation of Strengthening
Model of Character Trough
Citizenship Education Based on
Lesson Study
The implementation of strengthening model of
character trough citizenship education based on
lesson study uses the following procedures: (1)
Planning; (2) Implementation; (3) observation and
reflection
3.3 Citizenship Education Learning
Planning That Integrates Gotong
Royong (Cooperative Coordination)
Values
The lesson planning in this study basically meets the
requirements recommended by Briggs as to which is
referred to by (Untari, 2010) essentially (1)
systematically designed planning, in accordance with
the planning principles contained in the guidelines for
the implementation of the 2013 curriculum; (2) in
planning has described the observable and measured
learning outcomes; (3) planning is based on system
theory; (4) planning should be arranged flexibly.
Learning planning that integrates the value of
Cooperative Coordination, by teacher model is made
with the following stages:
3.3.1 Map KI / KD and Indicators
In learning this Citizenship Education essence
"Understanding the norms prevailing in the life of
society and nation". The main value of the characters
developed is the character cooperative coordination.
Achievement indicator of competence includes: (1)
Grateful for the norms prevailing in society can create
conditions ma s yar a kat orderly for the grace Tyme.
(2) Appreciate the behaviour according to the
prevailing norms around it. (3) have the attitude of
giving the benefit of the environment, (4) having the
attitude of giving benefit, (5) being the role and
contribute, (6) being sacrificial and cooperation, (7).
Wear school uniforms as a form of appreciation of the
prevailing norms in the surrounding environment. (8).
Explain the importance of norms for the life of
society, nation and state (9) conduct a survey of the
implementation of rules, rules and regulations that
apply in interaction with peer groups and surrounding
communities. (10) make a report and present the
survey results of the implementation of the provisions
or norms applicable in the surrounding environment.
3.3.2 Formulate learning objectives
Based on the indicators of achievement of
competencies as defined above, the following
objectives are defined:
Through habituation students are able to be
grateful for the prevailing norms in society can
create an orderly society condition on religious
grace.
Through exemplary teachers, students are able
to appreciate the behaviour according to
prevailing norms in the vicinity.
Through the students' diligence and habituation
having an environmental caring attitude,
Through teacher training and modelling
students have an attitude of giving benefit,
Through the motivation and modelling of
teachers students are able to play a role and
contribute,
Through the direction and example of students
able to be sacrificial and cooperation,
Through habituation, students wear school
uniforms as a form of appreciation of the
prevailing norms in the surrounding
environment.
Through reading the textbook students are able
to explain the importance of norms for the life
of society, nation and state.
Through a survey of the enforcement of rules,
rules and regulations applicable in interactions
with peer groups and local communities.
Strengthening Model of Character Through Citizenship Education Based on Lesson Study in Malang
165

The report and presented the results of a survey
of the implementation of the provisions or the
applicable norms surrounding environment.
3.3.3 Organizing Learning materials
The material that will be planned by the teacher
model is as follows:
Meaning of the importance of norm for the life
of society, nation and state
Obey the rules, rules and regulations applicable
in interactions with peer groups and local
communities.
Complying with prevailing regulations or norms
surrounding the environment due to the violation of
norms/rules including corrupt acts.
The function of norms in society.
The importance of obeying to the norms
prevailing in society
Various norms prevailing in society.
Sanctions imposed for violators of applicable
norms
Observations/survey reports on the
implementation of existing regulations in the
vicinity
3.3.4 Approach, Strategy and Learning
Method
The approach used by the model teacher as defined
by the 2013 curriculum is a scientific approach, with
cooperative learning strategy with problem-based
learning model with discussion and group work
method, and social action. Strategies and methods are
explicitly mentioned in the lesson plan as an indicator
of a teacher's "learning contract" to be implemented
in the learning to achieve the goal. This is the view of
(Al Hakim, 2010) which states that the choice of
strategy and method should be aligned with the
characteristics of Citizenship Education subjects who
want to internationalize the values and attitudes that
contribute to the nation's awareness-raising vehicle
which is an integral part in the nation's character
building.
3.3.5 Selection and Determination of
learning media
In accordance with the characteristics of learning
materials and objectives, the selection and
determination of instructional media by teacher
model as follows:
Media: Images of students crossing the street
through zebra cross; Images of traffic
congestion, Community drawings are being
deliberated; Picture of friendliness behaviour
Tools and materials: LCD; Computer; Wall
Magazine Board/media information
The selection of media by the model teacher
has been sufficient, as stated by (Al Hakim,
2010) that learning media should be able to be
a helpful tool and simultaneously bearer and
transmitter messages, learning media must also
contribute in providing experience and
behaviour of study subjects.
3.3.6 Assessment of Learning Assessment
a. assessment technique
Assessment of attitude with observation
technique, that is using observation guidance
which contains a number of the observed
behavioural indicator. Instruments used in the
form of observation guidelines using
checklists.
Assessment of knowledge by written test
technique essay form/essay
Assessment of skills with presentation
techniques, using a presentation assessment
guide containing a number of observed skill
indicators and assessment of social cooperative
coordination practices in schools.
b. assessment instruments
Generally, the instrument developed teacher
model as demanded by the curriculum and assessment
standards apply. Specifically related to the main value
of the character, Instrument Assessment using
Journal. Hint: This sheet is filled by teachers to assess
the social attitudes of learners in the learning process.
Score 1-4 on the behaviour indicator column
displayed by the learner during the learning process,
with the following criteria: 4 = Very Good; 3 = Good;
2 = Enough; 1 = less.
ICLI 2018 - 2nd International Conference on Learning Innovation
166
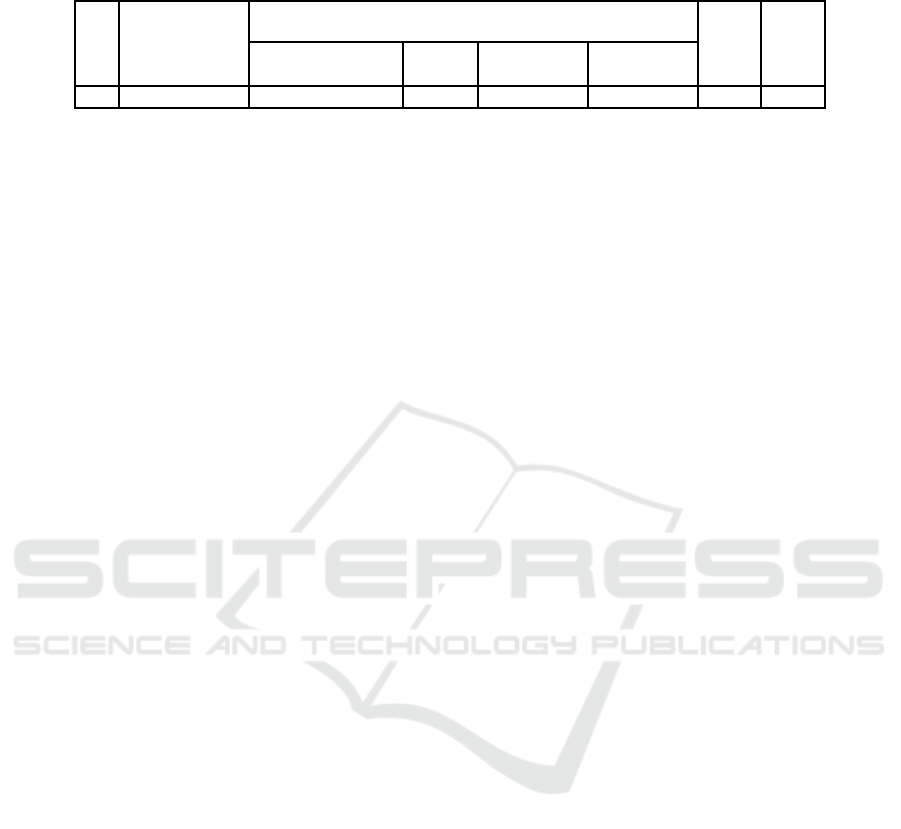
Table 4: Assessment of Gotong Royong's (cooperative coordination) attitude and behaviour.
No
Student's name
Behaviour indicators
Score
Value
Environment Care
Give
Benefit
Roles and
contribution
Cooperation
Learning planning by teacher model, theoretically
has fulfilled requirement that is (1) oriented to
certain competence; (2) between one component with
another is synchronized; (3) be flexible, according to
conditions, situations and needs; (4) effective and
efficient; (5) contains the principle of depth, breadth;
continuity and contrasting principles. (Al Hakim,
2010; Hamalik, 2017).
3.4 Implementation of Character
Education Learning that Integrate
Gotong Royong (Cooperative
Coordination)
3.4.1 Initial activity
Master begins learning with greetings and asks the
students, then proceeds to read the poem "Social
Norms". One of the students was asked to read a poem
that the teacher deliberately omitted the title. This
activity is intended to build the first perception while
creating a pleasant atmosphere. Furthermore, the
teacher prompts students to ask questions. Some ask
what is the title of the poem, some ask who the author
is. Teachers encourage other students to answer this
process of finding the concept, then the teacher asks
students to define by using words in the poem, this is
the process of developing the concept. Learning
activities beginning with this fun atmosphere have
motivated students to learn.
3.4.2 Core activities
The core activity of the teacher conveys the subject
matter according to the one made in the RPP.
Teachers continue to strive to motivate students to
participate actively in the learning process. In this
open class teacher model integrates one of the main
values of the character that is gotong-royong
(cooperative coordination) in learning. the
atmosphere of learning is quite the main rule of
learning. And go according to purpose. In the learning
process that integrates character into citizenship
education based on lesson study turns out to invite
many activities of students to be active in the learning
process, in addition to showing the improved
behaviour of mutual assistance, both implemented in
the classroom and implemented outside the
classroom. This is because teachers also always
encourage students to take an active role and give
exemplary in their daily life, so that can be an
example by their students.
3.4.3 Closing Activity
The concluding activities were done by praying and
greeting, then with the students, the teacher makes a
summary of the learning materials, the teacher
reflects to evaluate the whole set of learning activities
and the results obtained to further jointly discover the
direct and indirect benefits of the learning outcomes
that have taken place; provide feedback on the
learning process and outcomes; conduct follow-up
activities in the form of assignment, both individual
and group tasks; For example: Individually students
are asked to find exemplary behaviors from leaders to
compliance with prevailing norms; inform the lesson
plan for the next meeting.
The results reflect the existence of strengths and
strengths in learning that integrate character values,
inculcate the value of characters that have been
contracted in the RPP (plan for the learning process),
not just "moral speakers," but also expressed in
teacher-student behavior, so that value-investing is
not indoctrination, but the result (Al Hakim, 2011)
But in learning teachers often forget to miss this
mutual aid mission, as a result of learning goes like
there is no difference between learning that integrates
character value with learning which has been going
on. This is expressed by the principal who gave the
results of his observations on the appearance of
teachers in learning activities.
From the input given by the principal, and
observer observation it is known that the teacher is
still not enough to understand how to make learning
as a vehicle for strengthening the values of important
characters. Therefore training and mentoring of
teachers for the next program is still needed. In
reflection activity, the observer give high
appreciation to the model teacher in this learning, on
the contrary the model teacher also give appreciation
and gratitude to the principals who become observers
Strengthening Model of Character Through Citizenship Education Based on Lesson Study in Malang
167
who have sharply, carefully in observing the course
of learning, and provide constructive input in
improving learning the teacher concerned in the
school on the next lesson.
3.4.4 Reflection
At this stage the following stages are performed:
reflecting all that has been done in the form of
discussion led by a moderator with the following
procedures: (a) the moderator opens the discussion
with greetings, and congratulations on the model
teacher on the open class process being undertaken;
(b). Provide opportunities for model teachers to
convey their teaching experience, whether satisfied or
dissatisfied; (c) allowing observers to take turns
communicating observations during the lesson; (d)
allowing the model teacher to respond to all observer
submissions; (e) the moderator invites the notary to
convey the results of reflection; (f) the author reads
the prepared note; (g) the moderator closes the
discussion with greetings and thanks to all the
discussion participants.
Based on the above explanation shows that the
implementation of learning Citizenship Education
with Lesson Study has been integrating the main
values of the characters ranging from planning,
implementation and assessment, so that not only able
to build students' cognitive abilities, but psychomotor
and affection of the students. In accordance with the
food of Al-Hakim that the achievement of student
competence cannot be separated from the
collaborative atmosphere, openness, honesty,
democracy, mutual empowering, mutual civilization
and taking care of values agreed by the common
character (2018: 174). Implementation of the
strengthening model prototype of character trough
citizenship education based on lesson study with a
plan, do, see make the quality of internalization of
character values higher, so as to grow student
behaviour attitude in accordance with the value of
character implanted,
3.5 The Effectiveness of Strengthening
Model Prototype of Character
Trough Citizenship Education
Based On Lesson Study
The strengthening model prototype of character
trough citizenship education based on lesson study as
mentioned in the research method that is by using pre-
test and post-test. Based on field trial to grade VII
students of SMP Negeri Sumberpucung Malang
Regency showed after the experimental strengthening
model of character trough citizenship education based
on lesson study got average data in experiment class
equal to 84, mean control class mean (citizenship
education learning model without character
education) amounting to 79.75. From the previously
obtained data tested normality and homogeneity as a
prerequisite for using the t-test. Based on the
normality test conducted showed that both groups
came from the normally distributed population as
Shown in Table 5.
Then homogeneity test was done so that the result of
both groups had homogeneous variance ( F arithmetic
= 0, 0547 <2.0879 = F table ). The result of the
normality and homogeneity test on the basis of the t-
test for normal and homogenous distribution data.
The calculation result t-test with significance level of
0.05 obtained 7.0573 while t 0, 05; 40 = 1.6838, t
table obtained DK = DK. Therefore, H 0 rejected so
that it can be concluded that the integrated
strengthening model of character trough citizenship
education based on lesson study can improve the
attitude and behavior of mutual assistance to students
rather than character education strengthening that
does not integrate into citizenship education with
Lesson study or direct learning model of character
education.
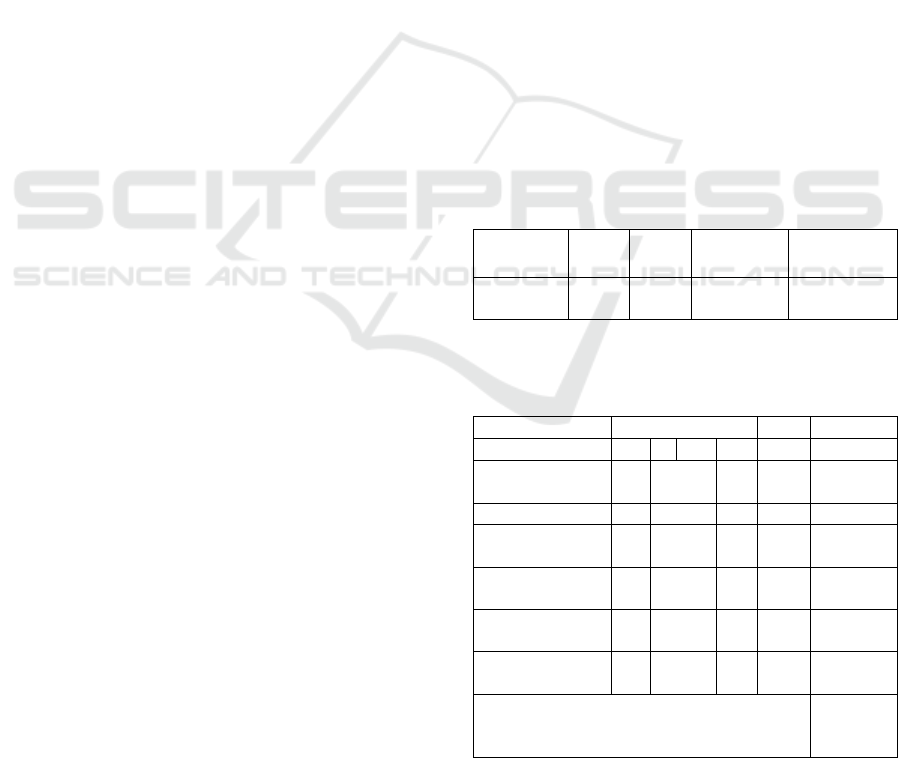
Table 5: Normality test of student achievement test.
Class
Lobs
Label
Decision
Distributed
data
Experiment
0.1647
0.1730
H 0 is
accepted
Normal
Control 0, 1862 0, 2060 H
0
received Normal
Table 6: Results affective learning attitude and behavior
gotong-royong (cooperative coordination).
Indicator
Meeting
%
Category
I.
III
VI
Environmental
care
90
95
98
8.89
Rising
Give us benefit
58
77
80
37.9
Rising
Contribute and
contribute
70
75
84
20.0
Rising
Sacrifice and
cooperation
51
70
73
43.1
Rising
Group
collaboration
73
80
86
17.8
1
Rising
Average
68
4
79
4
84
2
23.1
1
Rising
Information
Effective
ICLI 2018 - 2nd International Conference on Learning Innovation
168

That process is effective if the attitude and
behavior of gotong-royong (cooperative
coordination) seem to be done by the students in daily
life. Affective learning outcomes include student
learning outcomes about the attitude and behavior of
mutual cooperation during the learning process and in
behaving at school. To get the result of effective
learning done by observation 3 times at Research
based on Class cycle 1, and cycle 2 quantitatively
obtained the result as table 6.
Based on the above table it can be seen that the
score of affective learning result that is the attitude
and behaviour of gotong-royong (cooperative
coordination) shows improvement in all indicators at
each meeting. In the first session I obtained the
average score of student learning involvement of
68.4, then at the third meeting obtained an average
score of 79.4, and on cycle II at the meeting, VI
obtained the average score of 84.2. The overall
increase percentage is taken at meeting I and meeting
VI of 23.11%. Based on the effectiveness criteria
used is the model of integrating the main values of
characters in learning is said to be effective if there is
an increase in attitude and behaviour of mutual
cooperation, then the model of integrating
strengthening model of character trough citizenship
education based on lesson study said to be effective.
4 CONCLUSION
Development of strengthening model prototype of
character trough citizenship education based on
lesson study performance can be done with five core
procedures namely first, content/material analysis
that is (1). Analyzing Core Competence (KI) and
Basic Competence (KD); (2). arrange the table as a
map of linkage analysis between KI / KD with
selected values and indicators to determine the value
to be developed Second, culture analysis. Third,
process analysis. Fourth, organizing Lesson study-
based learning is intended in a character education
learning design that integrates into citizenship
education with the 5W + 1H paradigm: What, Where,
Who, When and Why and How should guide the
internal values of the main characters in learning and
the five strengthening model prototype of character
trough citizenship education based on lesson study in
Junior High School.
The application of this model prototype is done by
classroom action research, with lesson study strategy
through the following stages: planning,
implementation and reflection: a) Character
Education Learning Planning That Integrates Value-
Gotong Royong. Learning planning that integrates
gotong-royong (cooperative coordination) value, by
the model teacher was made with the following
stages: (1 ) Map KI / KD and Indicator, (2) Formulate
learning objectives; (3). Organizing Learning
materials; (4) Determination of Approach, Strategy
and Method of Learning; (5) Selection and
Stipulation of instructional media; (6). Assessment
of Learning Assessment; b) Implementation of
Character Education Learning which Integrates
Value-Gotong Royong. (1) Initial activity, Master
begins learning with greetings and asks her students
news, apperception while creating a pleasant
atmosphere. then the process of finding the concept,
the process of developing the concept, (2) Core
activities, The core activity of the teacher conveys the
subject matter according to the one made in the lesson
plan, the learning atmosphere is in line eith the main
rule of the study enough. And go according to
purpose. In the learning process that integrates
Character Education Strengthening into citizenship
education learning based on LS turns out to invite
many activities of students to be active in the learning
process, in addition to showing the improved
behaviour of mutual cooperation. (3) Closing
Activity, Closing activities are done by praying and
greeting, reflection to evaluate the whole set of
learning activities and the results obtained in this
lesson, (4) Reflection, At this stage, the following
stages are carried out: reflecting all that has been done
in the form of a discussion led by a moderator, with
the aim of finding weaknesses and strengths in the
implementation of learning to be input in any
subsequent learning.
Based on the results of research and data analysis
shows improvement of affective learning outcomes in
the form of improvement of attitude and behavior of
gotong-royong that is environmental care attitude,
giving attitude benefit, attitude and contribution,
sacrificial attitude and student cooperation 23,11%
from initial average value equal to 68 , 4 then
increased to 84.2. that of the four indicators and
criteria used, Strengthening model prototype of
character trough citizenship education based on
lesson study learning is able to meet all the criteria
that exist. Thus, the prototype model of inquiry is
effective in improving the attitude and behaviour of
the student's gotong-royong.
Strengthening Model of Character Through Citizenship Education Based on Lesson Study in Malang
169

REFERENCES
Chowdhury, M. (2016) ‘Emphasizing Morals, Values,
Ethics, and Character Education in Science Education
and Science Teaching’, Malaysian Online Journal of
Educational Sciences, 4(2), pp. 1–16.
Guidry, A. O. (2008) ‘Character education through a
reflective moral inquiry: A revised model that answers
old questions’, Journal of Curriculum and Instruction,
2(1), pp. 21–37.
Hakam, K. (2017) Strategi Gerakan Penumbuhan Budi
Pekerti. Jakarta.
Al Hakim, S. (2010) Strategi Belajar Mengajar Berbasis
Nilai-Nilai Pancasila. Malang: Universitas Negeri
Malang.
Al Hakim, S. (2011) Media Pembelajaran PPKn Berbasi
Nilai-nilai Pancasila. Malang: Universitas Negeri
Malang, Press.
Hamalik, O. (2017) Proses Belajar Mengajar. Jakarta:
Bumi Aksara.
Lickona, T. (1991) Educating for Character: How Our
School Can Teach Respect and Responsibility. New
York: Bantam Books.
Lickona, T. (2012) Educating for Character: How Our
Schools Can Teach Respect and Responsibility,. New
York.
Perles, K. (2018) Character Education: Good Hearts Lead
to Good Grades, Education.com LLC All Rights
Reserved. Available at:
https://www.education.com/download-
pdf/article/85158/.
Untari, S. (2010) Model Pembelajaran Inovatif Berbasis
Nilai-Nilai Pancasila. Malang: Universitas Negeri
Malang, Press.
Untari, S. (2016) Implementasi Gerakan Penumbuhan Budi
Pekerti di kelas. Jakarta.
Untari, S. (2017) Pengintegrasian Penguatan Pendidikan
karakter dalam Pembelajaran SMA berdasarkan
Kurikulum 2013., Makalah disampaikan dalam
Pertemuan MGMP Sejarah SMA. Malang.
ICLI 2018 - 2nd International Conference on Learning Innovation
170
