
Head Nurses’ Supervision and Its Correlation with Patient Safety
in Aceh Hospital Setting, Indonesia
Yuswardi
1
, Delvina Julita
2
, Ardia Putra
1
, Budi Satria
3
, Hajjul Kamil
1
1
Department of Nursing Management, Faculty of Nursing, Syiah Kuala University, Banda Aceh, Indonesia
2
Undergraduate Programme of Nursing Science, Faculty of Nursing Syiah Kuala University, Aceh, Indonesia
Department of Community Health Nursing, Faculty of Nursing, Syiah Kuala University, Banda Aceh, Indonesia
hajjul.kamil@unsyiah.ac.id
Keywords: Supervision, Head nurse, Patient safety
Abstract: The application of patient safety in hospital requires an active role from the head nurse in the form of
guidance or supervision. The Application of an adequate supervision of the head nurse will have an impact
on the application of optimal patient safety. This study aims to determine the relationship of head nurses’
supervision and the implementation of patient safety in hospital ward. This correlative study utilised cross
sectional design. It involved 124 nurses who work in the ward of public hospital in Banda Aceh by single
random sampling. Data was collected by a self-report questionnaires. The study shows that there was a
relationship of the head nurses’ supervision and the implementation of patient safety (p-value = 0,000). The
correlation was significant when viewed based on sub variables of 1) implementer (p-value = 0,000); 2)
target (p-value = 0,000); 3) goal (p-value = 0,000). However, the correlation was insignificant viewed based
on other sub-variables of frequency (p-value = 0,131); 2) and techniques (p-value = 0,164). The researchers
suggest that the hospital should conduct the training for the head nurses to increase the knowledge of
supervision and improve the application of patient safety in the hospital ward.
1 INTRODUCTION
Globally, healthcare systems have improved
significantly in many aspects resulting in better
patient outcomes. However, there is also a growing
recognition that patients do not always receive a
consistent and high quality of healthcare. Healthcare
services in hospitals provide hundreds of different
types of drugs, tests, many high-tech devices and
various health professions that are ready to provide
services to patients. However, the diversity of health
services might lead to ‘adverse events’ in patient
safety if not managed properly. The report from the
Institute of Medicine (IOM) in 2000 “To Err Is
Human, Building a Safer Health System” showed
that hospitals in Utah and Colorado found adverse
event in patient safety about 2.90%, which 6.60% of
them died. Adverse events in New York was 3.70%
with a 13.60% mortality rate in the hospital. The
mortality rate of adverse events in hospitalized
patients across the United States, reach to 33.60
million per year ranges from 44,000 - 98,000 per
year (IOM, 2004).
In Indonesia, patient safety is a new issue applied
in hospitals as standard for quality of delivery of
care. There are few studies regarding patient safety
focusing on the prevalence of adverse events. The
incidence of patient safety is still high. Hospital
Patient Safety Committee reported that patient safety
incidents from September 2006 to December 2007
contained 145 cases. Since 2008 - 2011 the number of
patient safety incidents is still high. In 2008 there
were 61 cases and increased to 114 cases in 2009. In
2010 decreased to 103 cases and January - April
2011 fell to 34 cases. In addition, Banten Province
found to have the highest number of patient safety
incidents in 2011 where 23.67% among the 3 other
provinces in Indonesia namely DKI Jakarta 5.15%,
Lampung 3.90%, and East Java 1.30% (Hospital
Patient Safety Committee of Indonesian, 2011).
The number of incidence during hospitalization
reflects the implication of patient safety. The
Ministry of Health of the Republic of Indonesia has
issued regulation about patient safety during
hospitalization. Based on these regulations, every
hospital is required to pursue the fulfillment of
Yuswardi, ., Julita, D., Putra, A., Satria, B. and Kamil, H.
Head Nurses’ Supervision and Its Correlation with Patient Safety in Aceh Hospital Setting, Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0008395401290135
In Proceedings of the Aceh International Nursing Conference (AINC 2018), pages 129-135
ISBN: 978-989-758-413-8
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
129

patient safety goals (Minister Health of Republic of
Indonesia, 2011). The same thing is also stated by
the Commission on Accreditation of Hospitals that
the goal of patient safety is one of the conditions that
must be applied in all accredited hospitals
(Accreditation of Hospital Committee, 2012).
The Joint Commission International (2011) has
established six areas of patient safety goals that can
be used to assess head nurses’ management towards
patient safety. These include (a) identifying patients
correctly, (b) improving effective communication,
(c) maintaining the safety of high alert medications,
(d) ensuring correct procedure (e) reducing the risk
of health care associated infections, and (f) reducing
the risk of patient harm resulting from falls.
Furthermore, head nurses must have the competency
to design, communicate, and apply these patient
safety goals to all nurses and other healthcare
providers under their supervision (IOM, 2004).
Head nurses are at the middle level of nursing
management system. They are working closely with
the staff nurses as well as perform day-to-day
managerial tasks (Marquis & Huston, 2015). Head
nurses perform a hierarchy of management functions
beginning with planning, organizing, staffing,
directing, and controlling. The implementation of
patient safety goals in hospital ward to all nurses
required head nurses’ supervision (Huber, 2006 in
Sugiharto, Keliat, & Tutik, 2012). According to
Mudayana (2015) explained that the implementation
of patient safety at Muhammadiyah Hospital in
Yogyakarta in the hospital ward indicated that
nurses had not been implemented the patient safety
properly (50.8%) and the collaboration between
work units was still inapropriately implemented
(65.1%).
Head nurses’ supervision considered enable to
increase patient safety goals. A study by Nur, Noor
and Irwandy (2013) in Hasanuddin University
Hospital showed that the implementation of good
supervision (59,40%) by head nurses will increase
the motivation of nurse (70,60%) increases nurse
performance in applying patient safety (73,70%).
Furthermore, according to Yuswardi, Boonyoung,
and Thiangchanya (2015) note that 14 hospitals in
Aceh against 123 head nurses stated that high head
management of patients regarding patient safety
could improve the quality of health services in order
to reduce the adverse events in patient safety, errors
and deaths in patients. With this reason, it is
challenging for the head nurses to manage their unit
to be a safety ward. To date, there is unknown study
regarding this matter. Therefore, it is substantial to
explore head nurses’ supervision and its relation
with patient safety in Aceh province.
2 METHOD
A descriptive study was conducted to examine the
head nurses’ supervision and its relation with patient
safety of Aceh province, Indonesia from Mei to July
2017. The subjects were nurses who had been
working in hospital wards who have met the
following criteria: (a) being a nurse for at least one
year and (b) holding at least diploma degree in
nursing. There were 124 nurses participated in this
study.
The instruments used for data collection was the
questionnaire designed by the reserchers. It
consisted of three parts which is the demographic
data to collect personal and work-related data
including age, gender, level of education, the
duration of working experience in current area. The
second part was the head nurses’ supervision
regarding patient safety questionnaire. The third part
was the applying patient safety. It is a 38 - item
questionnaires which consisted five dimensions
elaborating supervision of patient safety. Each
statement was rated on a three-point Likert scale,
ranging from 1 (do not perform as the item stated) to
3 (perform exactly as the item stated). The total
scores and the dimension scores were calculated and
presented as the average scores. The high scores
indicate the high level of head nurses’ supervision
regarding patient safety. This newly developed
questionnaires was content validated by experts.
Internal consistency reliability was tested, yielding
the satisfactory coefficient of .89 for the entire scale,
and .87 to .92 for the dimension scales.
3 FINDINGS
Table 1 shows that the demographic data consisted
of 124 nurses. More than half participants were at 26
- 35 years (77.42%). Most of them (79.04%) were
women, more than half head nurses (56.45%) were
had a diploma degree in nursing and most of them
(61.30%) had worked as a nurse for two to ten years.
AINC 2018 - Aceh International Nursing Conference
130
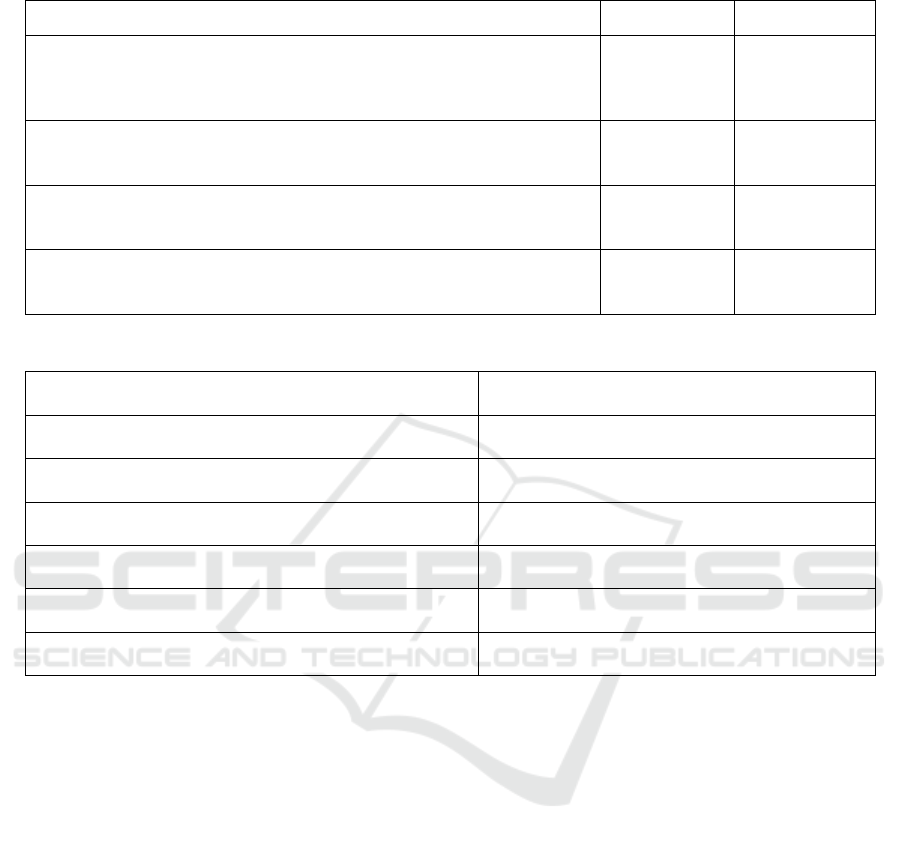
Table 1: Demographic Characteristics (n = 124).
Demographic Data
f
%
Age
17-25 year
26-35 year
36-45 year
24
96
4
19,35
77,42
3,23
Gender
Male
Female
26
98
20,96
79,04
Education
Diploma
Ners
70
54
56,45
43,55
Working Time
Establishment stage (< 2 years)
Advancement stage (2-10 years)
48
76
38,70
61,30
Table 2 Application of Patient Safety (n=124).
Variable
p-value
Supervision
0,000
Implementer
0,000
Target
0,000
Frequency
0,131
Aim
0,000
Technique
0,164
Table 2 shows that relationship of head nurses’
supervision and the application of patient safety. A
chi-square analysis was conducted to test whether
there is any significant association of head nurses
supervision and applying the patient safety. The
result revealed that in general the implementation of
head nurses supervision has the relationship (p-value
= 0,000) with the application of patient safety. In
detail it can be seen that the sub variable of
implementer (p-value = 0,000), target (p-value =
0.000) and target (p-value = 0.000). Conversely, the
result of frequency (p-value = 0.131) and technique
(p-value = 0.164) have no relationship with the
application of patient safety.
4 DISCUSSION
The result of this study are described sequentially.
The finding of the study using statistical chi-square
test (= 0.05) indicated that in general the
implementation of head nurses’ supervision has a
relationship (p-value = 0.000) with the application of
patient safety. The result of this study are supported
by Rasdini, Wedri and Mega (2014) showed that
there was a relationship (p-value = 0.000) of
application of patient safety and supervision of
nursing service in inpatient ward Sanglah Denpasar.
This study indicated that the nurses have good
interaction in supervision to improve nurse
professionalism and provide safe service for patient
through active communication between nurses,
supervisors and patients.
A good relationship of the supervisor and the
nurses will improve the achievement of service
standards. Therefore, the nurses’ guidance in
providing quality of care for patient safety could
raise their awareness of supervisors to enhance the
role and responsibility of the nurses. Similarly,
Sugiharto, Keliat and Tutik (2012) mentioned that
supervision as a formal and professional process
undertaken by the supervisors or leaders to support,
guide, direct, evaluate, and develop the nurse
Head Nurses’ Supervision and Its Correlation with Patient Safety in Aceh Hospital Setting, Indonesia
131

knowledge and competence to complete the task
with full responsibility for achieving hospital and
patient safety goals.
Head nurses perform high level in management
regarding patient safety as their role of nursing
manager in managing staff, financial and any
resources to ensure safety and quality of care for
patients. The good harmony of work relationship
will grow the work environment. According to
Kerfoot (2009) that head nurses were obligated to
provide safety work environment.
The work environment has a role in improving
nurses’ performance. Conversely, less attentive work
environment will have a negative impact and reduce
nurses’ performance. This study is similar to the
research conducted by Oktariani and Murharyati
(2015) which suggests that nurses who have a poor
working environment have a risk of applying good
patient safety 2.9 times greater than those who have
a good work environment. The creation of a pleasant
work environment and meeting the needs of nurses
will provide satisfaction and increase their morale
especially in providing services that prioritize
patient safety.
Thus head nurses may realize that the
supervision of the head nurses will influenced the
application of patient safety. Supervision is carried
out to ensure the work is carried out in accordance
with the patient safety. Thus, the maximum service
could be given to the patients. A good relationship
between the head nurses and the nurses will create a
harmonious work environment that enable leading to
improve service according to work standards.
Furthermore, the common reason for the head
nurses perform the implementer has a relationship
with the application of patient safety (p-value
0,000). The result of this research is supported by
Rumampuk, Budu and Nontji (2013) which shows
that there is a relationship (p-value = 0.04) of the
role of head nurses to supervise the application of
patient safety at Gunung Maria Tomohon General
Hospital. This study shows that the head nurses in
the hospital is guiding, directing and assisting the
nurses.
A supervisor provides a way out of the problems
faced related to health services. According to
Sugiharto, Keliat and Tutik (2012) pointed out that
the supervision is not only to supervise the
performance of the nurses in accordance with the
instruction or the provisions but also to provide
solutions for things that have not been successfully
implemented. A supervisor has the advantages in the
organization because the function of supervision is
considered to be the managers’ job. But for the
success of supervision, the more priority is the
advantage in terms of knowledge and skills (Suarli
& Bahtiar, 2009).
Head nurses as the supervisor in hospital ward is
required to be able to run the supervision properly to
the nurses. Therefore, to increase the supervision
competency of the head nurse is through supervision
training. This result similar to the results of
Widiyanto, Hariyati and Handiyani (2013) showed
that the quality of supervision after the training
better than before. This result suggests that
supervision training becomes an important part of
improving the quality of the head nurses to be a
good supervisor.
The result of statistical test from the sub variable
of target is found that p-value 0,013 <0.05 meaning
there is correlation of target of supervision and
applying the patient safety. The study is similar to
Mua, Hariyati and Afifah (2011) noted that the head
nurses’ supervision significantly improves the
performance of nurses in the hospital ward in Palu;
since the head nurses of space instills a sense of
responsibility and compliance of nurse implementers
to the standard of care which has been set.
The nurses who perform their duties well and full
of responsibility certainly has a high work
discipline. According to Langingi, Kandou and
Umboh (2015) noted that the discipline of work will
affect the performance of nurses. A disciplined nurse
will follow and adhere to the application of patient
safety to the maximum and the rules set by the
organization. High discipline should always be
maintained and enhanced so that if there are nurses
who are not disciplined then the head of space can
give sanctions for him.
The result of statistical test in terms of
supervision frequency is found that p-value 0.131>
0.05, there is no correlation of supervision frequency
with applying the patient safety. This is similar to
Rozani (2009) mentioned that there is no correlation
(p-value = 0.102) of frequency factor with work
motivation of nurse executor in the hospital ward of
Dr. Zainoel Abidin Banda Aceh. The study shows
that often the head nurses to supervise when the
problem is found only and usually only conducted
on young nurses who do not have a long experience.
Thus, the nurses who have long working period in
the ward no longer need supervision since it is
considered already understood, although the fact is
the science of nursing always growing.
The researcher argued that there are no certain
guidelines regarding the number of times
supervision should be conducted. It has an impact on
some nurses who do not get supervision. In addition,
AINC 2018 - Aceh International Nursing Conference
132

the excessive workload factors will also reduce
nurses’ performance productivity. According
Astriana, Noor and Sidin (2014) explained that high
workload decreases nurses’ performance in the
implementation of patient safety programs in the
hospital ward of Haji Makassar Hospital.
In contrast, Sarwili (2015) explains that the
longer working period of a nurse, the more
experience gained in his work. Therefore, they could
reduce the caution in work. Therefore, supervision
which is not scheduled properly will have an impact
on the inability to improve the performance of
nurses in the midst of an ever-evolving environment
that will affect the implementation of patient safety.
Supervision is conducted in order to enable the
nurses always follow the development of science in
health services that prioritize patient safety. Suarli
and Bahtiar (2009) suggested that supervision
should be conducted at regular intervals. If
supervision is only conducted once, it is said as not
good supervision. This is happened since the
organization and environment is always developing.
This indicates that there are no definited guidelines
regarding the duration of the supervision should be
performed. Thus, some nurses are not supervised by
their supervisors.
The result of the aim of supervision has the
correlation (p-value 0,000) with applying patient
safety. According to Hadisah (2015) noted that there
was a relationship (p-value = 0.002) of the
supervision’s purpose and the implementation of
nursing care in the hospita; wards of Dr. Zainoel
Abidin Banda Aceh. This study shows that the
supervision performed by the head nurses to
improve the performance of nurses in providing
nursing care in order to decrease mistakes made by
the nurses.
Supervision from the head nurses could provide
continuous learning opportunities in providing
health care services to ensure patient safety at the
hospital. This is consistent with that proposed by
Arikunto (2004) mention that the implementation of
supervision is not to find fault but it contains more
coaching elements so that the work done can be
known for its shortcomings in order to be informed
of the parts that need to be improved.
Furthermore, techniques of supervision has no
correlation with applying the patient safety (p-value
= 0.164). In contrast, the study of Helendina,
Sitanggang and Rustika (2014) at Premier Jatinegara
Hospital showing a relationship (p-value = 0.015) of
supervision performed by head nurse and the
behavior of the nurses. The study shows that the
supervision has an important role in shaping the
behavior of nurses, particularly in terms of
documentation.
Several factors might be contributed to
insignificant techniques of supervision with applying
the patient safety. The supervision techniques that
include direct and indirect supervision techniques
performed by the head nurses did not affect the
application of patient safety. The knowledge of
nurses could influence in applying the patient safety.
According to Wahyuningsih, Sidin, and Noor (2014)
that there is a relationship (p-value = 0,02) of
knowledge and performance of nurses in
implementing work safety in the hospital ward of
Syekh Yusuf Hospital. Motivation is one of an
important role in the application of patient safety.
Motivation is the energy that encourages a person to
perform the job tasks to achieve the established
goals. This is inherent with the results of Nivalinda,
Hartini and Santoso (2013) research which
suggested the higher the motivation, the better the
application of patient safety culture.
5 CONCLUSION
This study has shown that there was a relationship of
supervision of the head nurses and the
implementation of patient safety. The form of sub
variables based on sub variable of implementer,
target and goal. But the correlation was insignificant
when viewed based on other sub-variables of
frequency and techniques.
ETHICS APPROVAL
This study had the ethical approved from Ethics
Committee of Faculty of Nursing, Syiah Kuala
University in Banda Aceh, Indonesia.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors state that they have no conflict of
interests.
AUTHORS’ CONTRIBUTIONS
Y and DJ conceptualizing and designing the study.
DJ conducted data collection and Y analysed the
data also prepared for the article’s first draft. All
Head Nurses’ Supervision and Its Correlation with Patient Safety in Aceh Hospital Setting, Indonesia
133

authors commented on the first draft and contributed
to the revisions of the manuscript. All authors read
and approved the final manuscript.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank all nurses who have
participated in the study and the head nurses also the
stakeholders in the study setting for enabling this
research to be conducted.
REFERENCES
Accreditation of Hospital Committee. 2012. Accreditation
instrument of standard hospital accreditation
version of 2012 edition 1. Jakarta
Arikunto, S. 2004. Basics of supervision. Jakarta: Rineka
Cipta.
Astriana, Noer Bahry Noor, dan Andy Indahwaty Sidin.
2014. Factor instrinsik motivasi perawat terhadap
pelaksanaan asuhan keperawata. Semarang.
Hadisah, N. (2015). The relationship of supervision to the
implementation of nursing care in the inpatient wards
of the Regional General Hospital Dr. Zainoel Abidin
Banda Aceh. Retrieved from Underdraduate Thesis.
Banda Aceh: Faculty of Nursing, Syiah Kuala
University. Publication.
Helendina, S., Sitanggang, L & Rustika. 2015.
Relationship of head room supervision with the
behavior of nurses in documenting nursing care
inpatient room of Premier Jatinegara Hospital East
Jakarta. Retrieved from http://ejournal.stik-
sintcarolus.ac.id/
Hospital Patient Safety Committee. 2011. Patient safety
incident report. Retrieved from
http://www.inapatsafety.persi. or.id.
IOM. (2004). Keeping patients safe: transforming the
work environment of nurses. Washington, DC:
National Academies Press.
Joint Commission International. 2011. International
patient safety goals: Accreditation standards for
hospitals. Illinois, USA: Joint Commission
International.
Kerfoot, Karlene M. 2009. The CNO's Role in
professional transformation at the point of care. Nurse
Leader. 7 (5): 35 - 38.
Karlene M. 2009. The CNO's Role in professional
transformation at the point of care. Nurse Leader. 7
(5): 35-38.
Langingi, A.R.C., Kandou, G.D & Umboh, J.M.L. 2015.
Relationship of internal and external factors with the
performance of nurses in the installation of inpatient
wards RSUP Prof. Dr. R. Kandou Manado. Journal
of Paradigm, 1 (2). Retrieved from
http://jkesmasfkm.unsrat.ac.id/
Marquis, B. L., & Huston, C. J. 2015. Leadership Roles
and Management Functions in Nursing. United States:
Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Minister Health of Republic Of Indonesia. 2011. Decree of
health minister of republic of indonesia number 1691 /
MENKES / SK / VIII / 2011 about patient
safety at hospital. Jakarta.
Ministry of health of Indonesia. 2008. National patient
safety guidelines (patient safety) hospital. Ministry of
Health of the Republic of Indonesia, Jakarta.
Mua, E., Hariyati, T., & Afifah, E. 2011. Increased
satisfaction and performance of nurses through the
supervision of the head of the room. Journal of
Nursing Indonesia.14 (3). Retrieved from
http://jki.ui.ac.id/
Mudayana. 2015. Pelaksanaan patient safety oleh perawat
di RS PKU Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta. Retrieved
from http://ejournal.stikesyogyakarta.ac.id
Nivalinda, D., Hartini, M.C.I., & Santoso, A. 2013.
Influence of nurse motivation and leadership style of
head to the application of patient safety culture by
nurse executor at government hospital in Semarang.
Journal of Nursing Management. 1 (2). Retrieved
from http://jurnal.unimus.ac.id/
Nur,Q.M., Noor, H.N.B., & Irwandy. 2013. Relationship
of motivation and supervision on the performance of
nurse implementing in applying patient safety at
Hasanuddin University Hospital in 2013. Retrieved
fom http://repository.unhas.ac.id/
Oktariani, M., & Murharyati, A. 2015. Relationship
between Work Environment and Individual
Awareness with Application of Patient Safety at
Sukoharjo District Hospital. Kusuma Husada Health:
Jakarta
Putra, B.P., Hamid,D., & Ruhana,I. 2015. Comparative
analysis of work performance of contract employees
with permanent employees. Journal of
Business Administration. 26 (1). Retrieved from
http://administrasibisnis. studentjournal.ub.ac.id/
Rasdini, I., Wedri,N & Mega, I. 2014. Hubungan antara
penerapan budaya keselamatan pasien dengan
supervisi pelayanan keperawatan oleh perawat
pelaksana. Retrieved from http://poltekkes-
denpasar.ac.id/
Rozani, M. 2009. Hubungan supervisi dengan motivasi
kerja perawat pelaksana di ruang rawat inap Rumah
Sakit Umum Daerah dr. zainoel Abidin Banda Aceh.
Retrieved from Underdraduate Thesis. Banda Aceh:
Faculty of Nursing, Syiah Kuala University.
Publication.
Rumampuk, M., Budu, & Nontiji, W. 2013. Peran kepala
ruangan melakukan supervisi dengan penerapan
patient safety di ruang rawat inap rumah sakit.
Retrieved from http://pasca.unhas.ac.id/
Sugiharto, A., Keliat, B & Tutik 2012. Manajemen
Keperawatan : Aplikasi MPKP di Rumah Sakit.
Jakarta: EGC
Suarli & Bahtiar. (2009). Manajemen Keperawatan.
Jakarta: Erlangga Medical Series
AINC 2018 - Aceh International Nursing Conference
134

Sugiharto, A., Keliat, B & Tutik 2012. Manajemen
Keperawatan : Aplikasi MPKP di Rumah Sakit.
Jakarta: EGC.
Widiyanto, Puguh., Hariyati, Rr Tutik Sri., Handiyani,
Hanny. (2013). Pengaruh Pelatihan Supervisi
Terhadap Penerapan Supervisi Klinik Kepala ruang
dan Peningkatan Kualitas Tindakan Perawatan Luka
Di RS PKU Muhammadiyah Temanggung. Prosiding
Konferensi Nasional PPNI Jawa Tengah .
Wahyuningsih, R.N; Sidin, A.I& Noor, N.B. (2014).
Hubungan pengetahuan, motivasi dan beban kerja
terhadap kinerja keselamatan pasien RSUD Syekh
yusuf gowa. Universitas Hassanudin Makasar.
Yuswardi, Boonyoung., N, dan Thiangchanya., P. (2015).
Head nurses’ management regarding patient safety in
public hospitals Aceh Province. Idea Nursing Journal.
5 (3).
Head Nurses’ Supervision and Its Correlation with Patient Safety in Aceh Hospital Setting, Indonesia
135
