
The Influence of Health Coaching on the Self Efficacy of Women of
Childbearing Age in the Prevention of Cervical Cancer with Visual
Inspection Acetic Acidate (IVA)
Khairun Nisa’
1
, Budi Santoso
2
and Esti Yunitasari
1
1
Faculty of Nursing Universitas Airlangga, Kampus C Mulyorejo, Surabaya, Indonesia
2
Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: Health Coaching, Self-efficacy, Woman of Childbearing Age, Cervical Cancer Prevention.
Abstract: Introductions: Cervical cancer is the second leading cause of death in women after breast cancer, Mortality
and morbidity rates increase continously, this phenomenon occurs because IVA examination is rarely found
in women of childbearing age. in women Low self-efficacy, lowers the commitment of society to prevent
cervical cancer With Visual Inspection Acetic Acidate. Method: This research was a quasi-experiment study
using pre and post control group design. A total of 70 responden from Puskesmas panaguan pamekasan
divided into 35 for the treatment group and 35 for the control group. The sampling method used was cluster
sampling based on the area. The dependent variable was self-efficacy and health coaching was the
independent variable. Data were taken with questionnaire and analysed by Wilcoxon signed rank test and
Mann Whitney U test with significance level 0.05. Result: The results showed the value of pre-test and post
test both in the health coaching group and the control group there is a significant difference this can be seen
from the known value of Asymp.Sig. (2-tailed) for the health coaching group of 0,000 and the control group
0.001. but when compared to post test between both groups it is known that the average difference is 49.14
for health coaching group and 21.86 for control group where there is difference of difference of mean value
equal to 27,28 points. By looking at the value of Asymp.Sig. of 0,000, where the value of Asymp.Sig. 0.000
<0.05, then there is a significant difference in self efficacy value between the health coaching group and the
control group. Conclusion: It can be concluded that health coaching is effective in improving women of
childbearing age (WUS)’s self-efficacy in the prevention of cervical cance
1 BACKGROUND
Cervical cancer is the second leading cause of death
in women after breast cancer, especially in
developing countries. (Denny and Prendiville, 2015)
states that cervical cancer is the second leading
cause of death in women after breast cancer.
Mortality and morbidity rates increase continously,
cases of cervical cancer are found to be more
advanced and cause death in women (WHO, 2007).
This phenomenon occurs because IVA examination
is rarely found in women of childbearing age. They
already came to health services in a state of illness
so late to be treated, consequently the mortality and
morbidity caused by cervical cancer increase
continously.
(Kolutek, Avci and Sevig, 2016) states that
women come to health services already in a state of
illness and in advanced stage so that the mortality
and morbidity caused by cervical cancer continues
cancer increase continously in the community.
Dealing with it, it is necessary to prevent cervical
cancer by performing IVA tests. According to the
study (Rogers et al., 2008) that the mortality rate in
women due to cervical cancer decreased
significantly after screening. IVA examination in
Indonesia is less than five percent (2.45%,) WHO
(2007). Estimated number of cervical cancer patients
in Indonesia in 2013 known East Java Province has
the largest cancer patients that is 98,692 cases
(Riskesda, 2013). Based on preliminary study in
Panaguwen Puskesmas work area, health promotion
about cervical cancer and IVA test have been done,
only few women come to do IVA test, carrying the
examination of IVA in 2017 as many as 5 from 341
women of childbearing age, and all found albuse
fluoride and recommended therapy according to
738
Nisa’, K., Santoso, B. and Yunitasari, E.
The Influence of Health Coaching on the Self Efficacy of Women of Childbearing Age in the Prevention of Cervical Cancer with Visual Inspection Acetic Acidate (IVA).
DOI: 10.5220/0008332007380742
In Proceedings of the 9th International Nursing Conference (INC 2018), pages 738-742
ISBN: 978-989-758-336-0
Copyright
c
2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

doctor's instructions. In the previous year nobody
did an IVA test. According to the study (Saleh et al.,
2013) stated that from 200 participants After the
IVA examination was found positive in 24/200
(12%) patients and Pap smears found 8 (4%). This
means that IVA examination is more sensitive to
early detection of cervical cancer and easier and
more affordable.
Highly effective IVA screening contributes to
lower mortality & morbidity associated with
malignancy of cervical cancer. In some large clinical
studies, IVA screening has shown clinical sensitivity
ranging from 41% - 92%, nearing the standard of
colposcopy. When compared with Pap-smear
examination, IVA increases detection by up to 30%.
Provision of health coaching in women of
childbearing age (WUS) is one method of education
not only providing cognitive aspects but also
psychomotoric and psychological aspects. Before
Health Coaching respondents do not understand how
to manage the disease, but after doing Health
coaching patients understand how to manage in
order to avoid recurrence (Crittenden, at al., 2017).
Health coaching is centered on the patient, where
the selection of activity objectives is determined by
the patient so that the patient is more involved, and
there is a learning process which can influence the
self efficacy that has a role in shaping the
commitment and behavior of cervical cancer
prevention. (Hermens et al., 2014) health coaching
Personal Health coaching Systems is a great way to
develop and maintain healthier behaviors. After
educating cervical cancer and health awareness all
respondents experienced increased knowledge of
cervical cancer screening and willing to participate
in screening (Lor., Al., 2014). Health promotion
provides support in relation to healthy behaviors,
and this leads to disease reduction and reduction of
unhealthy behaviors such as smoking, drinking
alcohol, fatigue, depression (West-Leuer, 2014). The
visual inspection of cervical cancer with visual
inspection acetate (IVA) in puskesmas panaguan
pamekasan.
2 METHOD
This research was a quasi-experiment study using
pre and post control group design. A total of 70
responden from Puskesmas panaguan pamekasan
divided into 35 for the treatment group and 35 for
the control group. The sampling method used was
cluster sampling based on the area. The dependent
variable was self-efficacy and health coaching was
the independent variable. Data were taken with
questionnaire and analysed by Wilcoxon signed rank
test and Mann Whitney U test with significance
level 0.05. The research design used in this research
is the type of quantitative research with Quasi
experimental design, that is the research that gives
treatment or intervention on the research subject
then the effect of the treatment is measured and
analyzed. The research templates used were pre-test
and post-test with control group desaign. This design
was used to compare the results of health coaching
interventions on women of childbearing age in the
group measured before and after intervention. In the
implementation of the research the treatment group
was given a health coaching on cervical cancer
prevention behavior with IVA method, while the
control group only followed the standard of
Puskesmas.
3 RESULT
The population in this study are women of
reproductive age who are married and who are in the
working area of Panaguwen Puskesmas.
Based on the above "Test Statistics" output, it is
known Asymp.Sig. (2-tailed) is worth 0,000. Since
the 0.000 value is less than <0.05, it can be
concluded that "Ha is accepted". This means that
there is a difference in self efficacy before the
Health Coaching action is given after being given
Health Coaching action on the treatment group. so it
can be concluded also that "there is influence Health
Coaching on self efficacy in treatment group. In
addition to knowing the magnitude of the
improvement of health coacing intervention results
Table 1: Different test before and after action of
Health Coacing on treatment group
Post test - Pre test Self-efficacy
group Health Coacing
Z
-4.927
b
Asymp. Sig. (2-
tailed)
.000
a. Wilcoxon Signed Ranks Test
b. Based on negative ranks.
The Influence of Health Coaching on the Self Efficacy of Women of Childbearing Age in the Prevention of Cervical Cancer with Visual
Inspection Acetic Acidate (IVA)
739
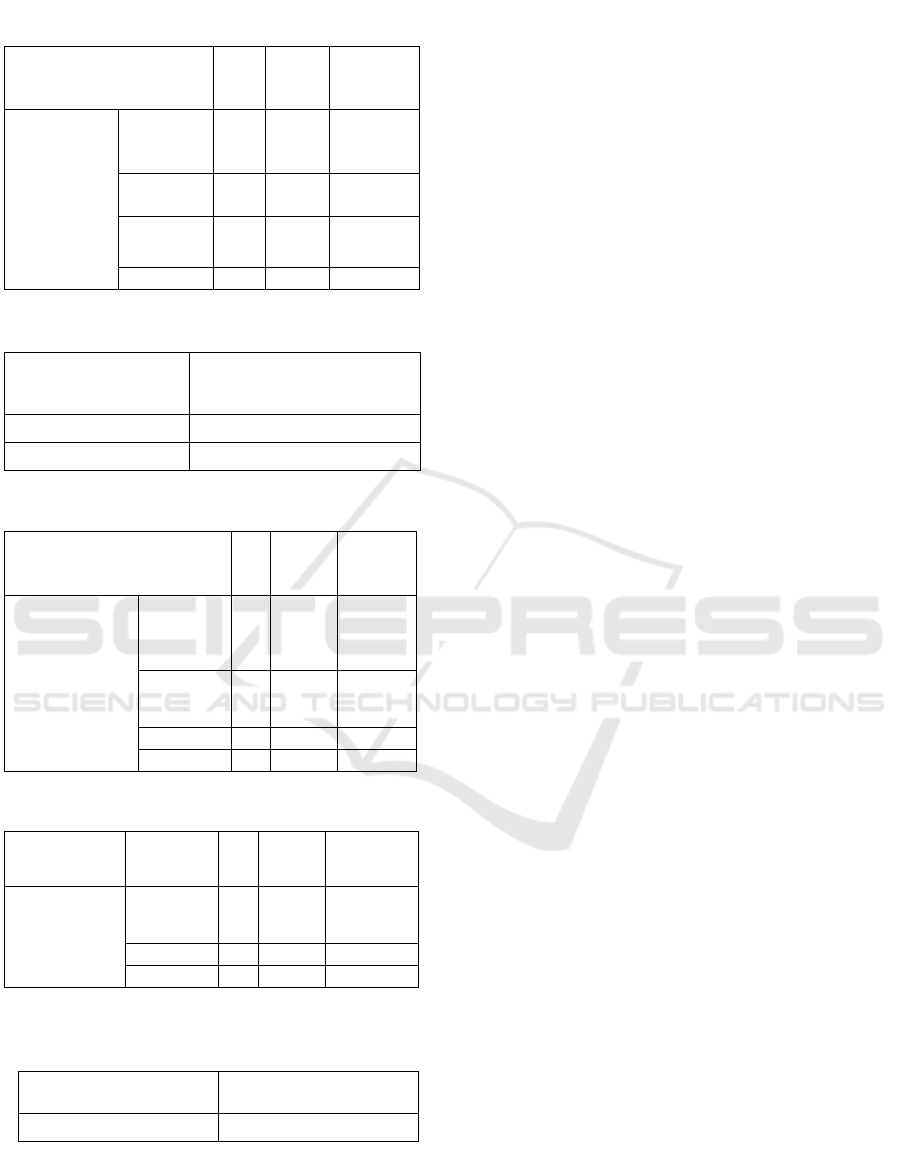
can be seen from the ftable 2.
Based on the value of Positive Ranks Pre Test
and Post Test of respondents experienced
improvement of self efficacy from Pre Test to Post
Test value, with the average increase is 16.0.
Based on the table 3 "Test Statistics" output, it is
known Asymp.Sig. (2-tailed) is worth 0,000. Since
the value of 0.001 is less than <0.05, it can be
concluded that "Ha is accepted". This means that
there are differences in self efficacy in the control
group.
In addition to knowing the magnitude of
effusions of pre and post results in the control group
can be seen from the table 4.
Based on the value of Positive Ranks Pre Test
and Post Test of respondents experienced
improvement of self efficacy from Pre Test to Post
Test value, with the average increase is 6.50.
Based on Mean Rank value post self efficacy test
in helath coacing group with control group table 5
known average difference of 49.14 for health
coaching group and 21.86 for control group which
happened difference difference of mean value equal
to 27,28, while to know whether the difference is
significant or not seen from nilia P (Asymp Sig. (2-
tailed) in the table 6:
Based on the above table, the value of
Asymp.Sig is known. of 0,000, due to the value of
Asymp.Sig. 0.000 <0,05, hence there is significant
difference of self efficacy value between treatment
group and control group. So it can be concluded that
there is influence Health Coacing on self efficacy in
women of childbearing age in doing cervical cancer
prevention with Visual Acetate Inspection method
(IVA).
4 DISCUSSION
Based on the result, the difference of self-efficacy
level of treatment group on pretest and posttest
through Wilcoxon test showed p value <0.05, beside
that in Mann Whitney test to see difference of
posttest result between treatment group and control
group got p value <0,05 which mean H1 accepted
that there is influence of health coaching to increase
self-efficacy of woman of child-bearing age in
prevention of cervical cancer in work area of
Puskesmas panaguan the 35 respondents in the
intervention group, there were 19 respondents who
did IVA examination, and the result of IVA
examination found that 6 respondents positive IVA
and 1 respondent found lumps on the uterine wall of
large and small size, 1 respondent whitish with
infection, and 4 respondents found regular whiteness
without the presence of infection, the rest is 7
respondents stated normal, for respondents who have
Table 2: Self efficacy of treatment group
N
Mean
Rank
Sum of
Ranks
Post test- Pre
test Self-
efficacy
group Health
Coacing
Negative
Ranks
0
a
.00
.00
Positive
Ranks
31
b
16.00
496.00
Ties
4
c
Total
35
Table 3: Statistic result of treatment group
Post Tests - Pre-test Self-
efficacy Control Group
Z
-3.464
b
Asymp. Sig. (2-tailed)
.001
Table 4: Pre and Post test on control group
N
Mean
Rank
Sum of
Ranks
Post Tests Self-
efficacy Control
Group
Pre-test Self-
efficacy Control
Group
Negative
Ranks
0
a
.00
.00
Positive
Ranks
12
b
6.50
78.00
Ties
23
c
Total
35
Table 5: Statistic test of treatment and control group
Group
N
Mean
Rank
Sum of
Ranks
Post self-
efficacy
Health
Coacing
35
49.14
1720.00
Control
35
21.86
765.00
Total
70
Table 6: Mann-whitney test of treatment dan control
group
post self efficacy
Mann-Whitney U
135.000
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
740

problems on IVA examination directly followed up
by a specialist obstetric disease (Obgen), while 16
respondents who did not do IVA examination, 6 of
them were not allowed by her husbands, 5 of them at
the time of examination before the IVA test,
respondents was declared menstruation so they did
not do IVA test, and 5 others resigned at the time of
IVA examination, for fear of known their illness
Based on the Pender theory there are 2 basic
assumptions underlying health coaching: first the
health worker as part of the environment will affect
the person and the second is that each individual will
actively regulate his own behavior (Alligood, 2014).
The principle of health coaching is to help the
respondent self-regulate to change his behavior
where according to the Pender theory by changing
the affective status of a person will increase the self-
efficacy of the person (Gale, 2012). health coaching
contributes to care, patient planning and physician
activation as well as leadership development
(National Health Service, 2014). Individuals take
active and anticipatory action to eliminate or
mitigate harm by placing themselves directly on
existing circumstances and taking action in
accordance with what has been done by people who
have experienced before (Yunitasari, 2016)
Based on data analysis, the result of self-efficacy
is increasing. This is in accordance with the opinion
of Gale (2012) which states the goal of health
coaching is to improve self-efficacy. Mechanism of
the increase of self-efficacy during health coaching
begins with the determination of goals together with
researchers and respondents in implementing the
prevention of cervical cancer with IVA action
method.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Health coaching effectively improves self-efficacy
in the prevention of cervical cancer by IVA method
with realistic goal selection mechanisms as well as
lowering HIT and increasing HET which is a form
of affective response that determines the level of
one's self-efficacy.
Respondents are advised to always conduct a
clean and healthy lifestyle by routinely performing
the correct vulva hygiene and immediately replace
the pads at the time of menstruation and perform
IVA tests for early detection of cervical cancer.
Health coaching to momodify healthy lifestyles,
study results show that patient participation in health
management is necessary (Crittenden, Seibenhener
and Hamilton). Health Coaching is designed to
promote a healthy lifestyle and prevent T2DM,
whereby Health Coaching is provided with a Via
Cell Phone method provided to adolescents to
reduce the risk of T2DM, via via telephone health
coaching is given as a healthy lifestyle change
(Jefferson et al., 2011). Nurses are advised to use
health coaching as an alternative method in
implementing health promotion programs in the
prevention of cervical cancer as well as other cases.
The researcher is then expected to conduct research
with health coaching as well as to examine other
aspects of behavioral and affective behavioral
cognition domains which include benefit of action,
barrier, action, activity related affect, interpersonal
influence, and situational influence.
REFERENCES
A., N. et al. (2011) ‘Effect of health promotion model
(HPM) based education on physical activity in diabetic
women’, Iranian Journal of Endocrinology and
Metabolism. Diabetes India, 13(4), pp. 6–11. doi:
10.1016/j.dsx.2017.08.013
Alligood, M R. (2014). Nursing Theorist and their work.
8th Edition, ST. Louis
Bott, R. (2014) ‘Data dan Informasi Kesehatan Situasi
Penyakit KankerDeteksi Dini Kanker Leher Rahim
dan Kanker Payudara di Indonesia 2007-2014 Mugi
Wahidin, SKM, M.Epid Sub Direktorat Pengendalian
Penyakit Kanker, Direktorat Pengendalian Penyakit
Tidak Menular’, Igarss 2014, (1), pp. 1–5. doi:
10.1007/s13398-014-0173-7.2
Crittenden, D., Seibenhener, S. and Hamilton, B. (no date)
‘of Hypertension’, TJNP: The Journal for Nurse
Practitioners. Elsevier, Inc, 13(5), pp. e237–e239. doi:
10.1016/j.nurpra.2017.02.010.
Denny, L. and Prendiville, W. (2015) ‘Cancer of the
cervix: Early detection and cost-effective solutions’,
International Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics.
Elsevier B.V., 131, pp. S28–S32. doi:
10.1016/j.ijgo.2015.02.009.
Gale, J. (2012). A Practical Guide to Health Behaviour
Change using the HCA approach. Australia: HCA.
Hermens, H. et al. (2014) ‘Personalized Coaching Systems
to support healthy behavior in people with chronic
conditions’, Journal of Electromyography and
Kinesiology. Elsevier Ltd, 24(6), pp. 815–826. doi:
10.1016/j.jelekin.2014.10.003.
Jefferson, V. et al. (2011) ‘Coping Skills Training in a
Telephone Health Coaching Program for Youth at
Risk for Type 2 Diabetes’, Journal of Pediatric Health
Care. Elsevier Ltd, 25(3), pp. 153–161. doi:
10.1016/j.pedhc.2009.12.003.
The Influence of Health Coaching on the Self Efficacy of Women of Childbearing Age in the Prevention of Cervical Cancer with Visual
Inspection Acetic Acidate (IVA)
741

Kementerian Kesehatan RI. (2013). Riset Kesehatan Dasar
(RISKESDAS). Jakarta: Badan Litbang Kemenkes RI
Kolutek, R., Avci, I. A., & Sevig, U. (2016). Effect of
Planned Follow-up on Married Women’s Health
Beliefs and Behaviors Concerning Breast and Cervical
Cancer Screenings. Journal of Cancer Education.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s13187-016-1114-2
Prevention : APJCP, 12(1), 199–202. Retrieved from
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21517257
Lor, M. and Bowers, B. (2014) ‘Evaluating teaching
techniques in the hmong breast and cervical cancer
health awareness project’, Journal of Cancer
Education, 29(2), pp. 358–365. doi: 10.1007/s13187-
014-0615-0.
Macadam, C., (2014). Health Coaching A Powerfull
Approach to Support Self-Care, 1-5.
Martinez, N. and Adelita, R. Æ. (2009) ‘The Nurse ’ s
Role in the Prevention of Cervical Cancer Among
Underserved and Minority Populations’, pp. 135–143.
doi: 10.1007/s10900-008-9134-4.
Manuaba,I Gede. 2004. Ilmu Kebidanan, Penyakit Dalam
Dan Keluarga
Berencana. Jakarata: YBP- SP.
National Health Service., 2014, Does health coaching
work, 23 oktober 2016, eoeleadership.hee.nhs.uk.
UCHF, Center for excellence in primary care., 2014,
“Health coaching in primary care intervention
protocol” , University of California
Santoso, Satmoko. (2009). Buku Pintar Kanker.
Yogyakarta: Power Books
Saleh, H. S. (2014) ‘Can visual inspection with acetic acid
be used as an alternative to Pap smear in screening
cervical cancer?’, Middle East Fertility Society
Journal. Middle East Fertility Society, 19(3), pp. 187–
191. doi: 10.1016/j.mefs.2013.10.003.
Sherifali, D. et al. (2016) ‘Evaluating the Effect of a
Diabetes Health Coach in Individuals with Type 2
Diabetes’, Canadian Journal of Diabetes. Elsevier Inc.,
40(1), pp. 84–94. doi: 10.1016/j.jcjd.2015.10.006.
West-Leuer, B. (2014) ‘Health Coaching for Medical
Doctors–Bringing Owls to Athens?’, Procedia - Social
and Behavioral Sciences. Elsevier B.V., 140, pp. 353–
360. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.04.434.
World Health Organization. (2007). Prevention. cancer
control: knowledge into action: WHO guide for
effective programmes: module 2). Geneva: World
Health Organization
Yunitasari, E. (2016) THE DEVELOPMENT OF
COPING-ROY’S ADAPTATION NURSING CARE
MODEL TO INCREASE THE RESILIENCY OF
POST RADIKAL HYSTERECTOMY + BSO
CERVICAL CANCER PATIENTS WHO
RECEIVED CHEMOTHERAPY. Universitas
Airlangga
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
742
