
The Relationship between Sensory Neuropathy and Self-efficacy and
the Degree of Diabetic Foot Injuries in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Patients
Kusnanto, Nurul Aini and Ferry Efendi
Faculty of Nursing Universitas Airlangga, Kampus C Mulyorejo, Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: Neuropathy, Self-Efficacy, Diabetic Foot Injury.
Abstract: Introduction: Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is a hyperglycemia condition caused by inadequate insulin, insulin
action, or both. Clients experience foot injuries that have serious complications and affect the lower
extremities. The purpose of this study was to identify the relationship between sensory neuropathy and self-
efficacy with the level of diabetic foot wounds. Method: This research design is cross sectional and data are
collected using a cluster sampling technique. The population of the study were 63 diabetic patients who
suffered diabetic foot injuries. Data analysis was conducted using the Spearman rho statistical test with a
significance level p <0.05. Results: the result was p = 0.027, which means there is a correlation between
sensory neuropathy and self-efficacy with levels of diabetic foot wound at p = 0.000 with r = -0.681, which
means there is a strong correlation of negative direction or crosses. Conclusions: Most respondents had
positive sensory neuropathy, the self-efficacy of respondents was moderate, and the level of diabetic foot
injuries was the highest at level 1. The support from a patient’s family was beneficial in improving self-
efficacy and was instrumental in increasing the patient's confidence in controlling behavior and adapting to
the conditions experienced.
1 BACKGROUND
Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is a chronic condition that
occurs when the body cannot produce enough insulin
or cannot use insulin and has increased blood glucose
levels. High levels of glucose in the blood
(hyperglycemia) cause damage to many body tissues,
leading to the development of life-threatening
complications (International Diabetes Foundation,
2017). DM is also one of the leading causes of health
problems and appears in almost every country
(Bakker, van Houtum, and Riley, 2005; Fujiwara et
al., 2011). Around 15% of all diabetics have foot
ulcers that cause serious complication and have
impact on lower extremity amputations (Apelqvist et
al., 2008). Diabetic foot injuries are one of the most
important chronic complications of DM in the world
of health and also of social aspects; these
complications have a significant effect on the quality
of life of the patient and are associated with higher
health care costs (Tresierra-Ayala & García Rojas,
2017). The rate of ulcers on the feet may occur over a
five-year time span of 70% (Bharat Kotru, Kotru and
Joshi, 2015).
During the preliminary study, interviews were
conducted with research nurses of the Poly General
Taliwang Health Center in the West Sumbawa
district. As many as 659 people were diagnosed with
DM between January and September 2017, and data
from the ER reported that 10.77% or 71 people were
diagnosed with diabetic ulcers. Interviews with six
clients determined that no checks were done to detect
the risk of diabetic foot injuries; the only test
conducted was controlled blood glucose screening at
least once a month or according to complaints from
clients. Some clients who had been diagnosed with
diabetic injuries said they could not avoid the
occurrence of diabetic foot injuries due to their
inability to control blood sugar due to inability to
avoid injury in an activity as well as a lack of
knowledge regarding the risks of diabetic foot
wounds.
The International Diabetes Federation (IDF)
states that Indonesia is the seventh most prevalent
country in the world for diabetes with as many as 10
Kusnanto, ., Aini, N. and Efendi, F.
The Relationship between Sensory Neuropathy and Self-efficacy and the Degree of Diabetic Foot Injuries in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patient.
DOI: 10.5220/0008330006310638
In Proceedings of the 9th International Nursing Conference (INC 2018), pages 631-638
ISBN: 978-989-758-336-0
Copyright
c
2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
631

million people. The estimation of people suffering
from DM in 2040 in Indonesia is 16.2 million
(International Diabetes Foundation, 2017). Riskesdas
(2013) adds that the increase occurred in accordance
with age, but from the age of ≥65 years it tends to
decline, is higher in women than in men, and higher
in urban than in rural areas. The IDF states that this
incidence indirectly increases the prevalence of
diabetic injury in 1%–4% of DM patients (Amin &
Doupis, 2016).
The results of the study of diabetic foot injury in
Semarang in 2015 indicate that 85.7% of people with
neuropathy have a high risk of foot injuries. People
with DM, who suffer diabetic injuries, are at risk of
amputation. In Indonesia, diabetic ulcers are the most
common cause of amputation relating to a non-
traumatic event (Lazzarini et al., 2015).
One of the measures used in accordance with the
recommendations of the American Diabetes
Association (2016) are interdisciplinary
multidisciplinary team services, involving several
fields of science, including nursing (Aalaa et al.,
2017). In general, there are four main purposes in the
provision of services such as health promotion,
disease prevention, patient care, and patient needs
(Aalaa et al., 2017). Therefore, the role of health
practitioners, especially nurses, in the early detection
of diabetic foot wound risk are important. (Aalaa et
al., 2012). Nurses should be more active in providing
treatment and prevention in diabetic neuropathy.
One form of prevention is to perform neuropathy
detection. This examination is very important to
prevent the worsening incidence of neuropathy that
impacts on diabetic wounds. Early detection of high-
risk foot is very important to reduce mortality and
morbidity. An interprofessional approach (i.e.
doctors, nurses, and foot care specialists) is often
needed to meet the patient's needs (Alavi et al., no
date; Alavi et al., 2014).
The purpose of this research is to understand the
relationship of sensory neuropathy and self-efficacy
with the level of diabetic foot wounds in patients with
Type 2 diabetes. The study will conduct sensory
neuropathy screening and assess DM patients’
confidence and self-ability levels in reducing the risk
of injured diabetic feet.
2 METHODS
The design of this study is a description of correlation
with a cross sectional approach with the independent
variables: sensory neuropathy and self-efficacy, and
the dependent variable: the level of diabetic foot
wounds. The population in this research were all
passien DM from the area of health office of kab,
West Sumbawa with a total sample of 75 respondents
chosen according to inclusion criteria using an
accidental/convenience sampling technique. Data
were collected by conducting sensory neuropathy and
kuisoner examination, which were then analyzed
using a Spearman rho statistical test and a significant
level (p) = 0.000 <0.05, which means H1 was
accepted.
3 RESULTS
The table of respondent characteristics in this study
shows that most (32) respondents (50.8%) are aged
50–59 years, 20 respondents (31.7%) are aged 40–49
years, and 11 respondents are aged 60–69 years
17.5%. There were 52 female respondents (82.5%),
which was more than the male population of 11
(17%). Regarding the length of time suffering with
DM, the largest number of respondents (31) were in
the range of 6–10 years (49.2%), 26 respondents
(41.3%) had suffered <5 years, and 6 respondents
(9.5%) had suffered with DM for more than 10 years.
Smoking history was dominated by male respondents
(11 people or 17.5%.) On examination of blood sugar,
the result of 200–400 mgdl applied to 44 respondents
(69.8%). There were 35 respondents (55.6%) with a
presence of comorbidities (hypertension). Forty-eight
respondents (76.2%) had never experienced diabetic
foot injuries and 15 respondents (23.8%) had suffered
diabetic foot injuries. Most of the respondents had
never experienced amputation (57 people or 90.5%).
There were six (9.5%) respondents who had
experienced amputation.
Based on the Table 2 54 respondents or 85.7%
showed positive neuropathy, while nine respondents
(14.3%) showed negative results regarding
neuropathy. The respondent's distribution for self-
efficacy was mostly 43 respondents (68.3%),
followed by low self-efficacy as much as 18
respondents (28.6%) and only 3.2% or 2 respondents
who had high self-efficacy.
Based on the Table 3, the level of diabetic foot
injury showed that 23 people (36.5%) (most
respondents) had suffered Level 1 (superficial ulcer
limited to skin) followed by 14 respondents (22.2%)
who had suffered at Level 3, 13 respondents (20.6%)
who had suffered at Level 2, seven respondents
(11.1%) who had suffered at Level 4 and six
respondents (9.5%) had not suffered foot injuries at
Level 0.
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
632
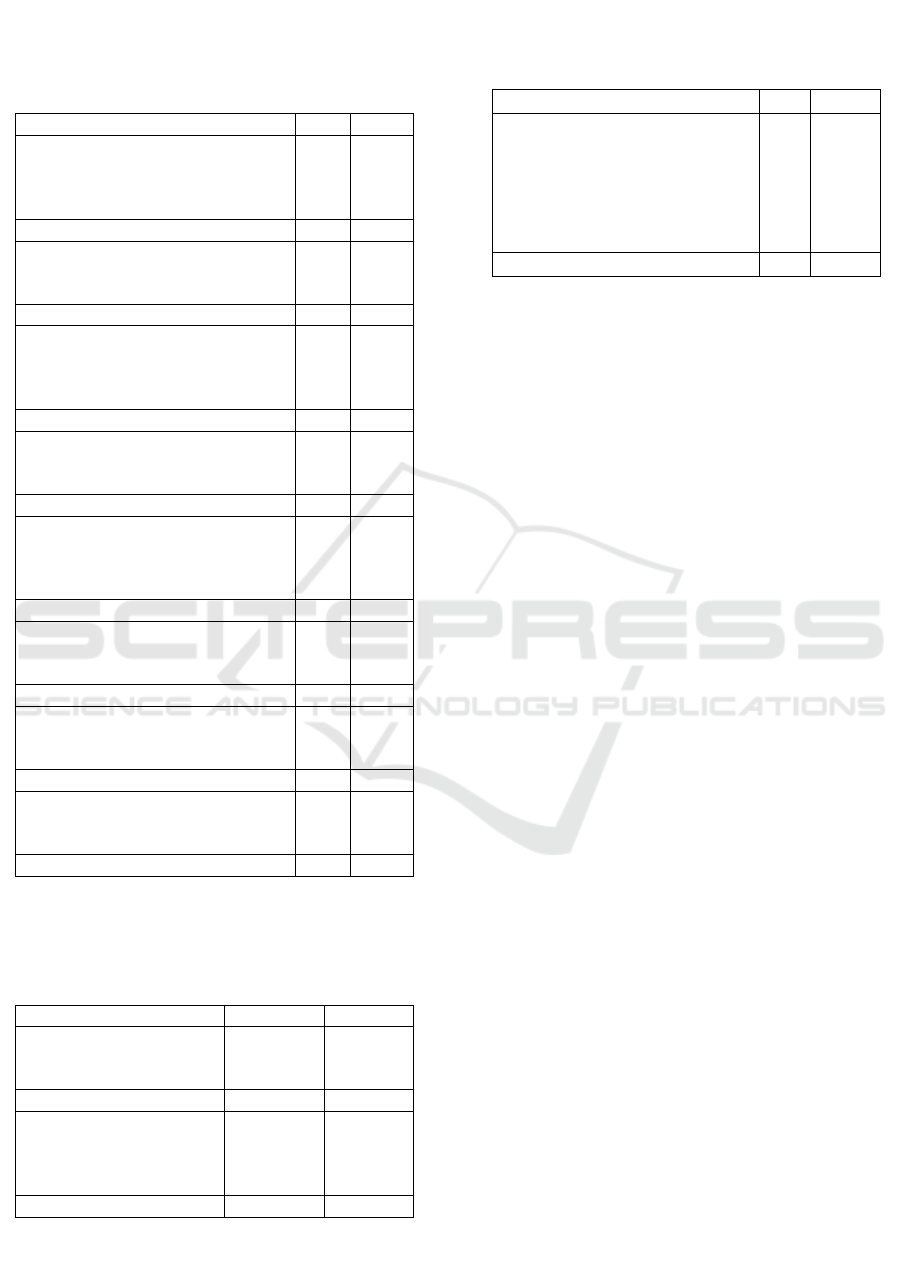
Based on the relationship of sensory neuropathy
with the level of diabetic foot wounds in the area of
the district health office, West Sumbawa, results were
obtained. Fifteen (23.8%) respondents had
experienced positive neuropathy at Level 1, 14
respondents (22.2%) had experienced Level 3, 12
respondents (19%) had experienced Level 2, seven
respondents (11.1%) had experienced Level 4, and six
respondents (12.7%) indicated Level 0. Regarding the
negative results of neuropathy, 8 respondents (12.7%)
indicated Level 1, one respondent (1.6%) indicated
Level 2. The total number of respondents who
indicated positive neuropathy was 54 (85.nine
respondents (14.3%) indicated negative neuropathy
The results of the statistical test using the
Spearman rho test obtained a significant level equal
to p = 0.027 with set significant level α≤ 0.05, which
suggests that there is a relationship between sensory
neuropathy and the level of diabetic foot wounds. In
the correlation coefficient we achieve the result r = -
.279, which indicates that the variables of sensory
neuropathy and the level of diabetic foot wounds have
low correlation (0.2– 0.399) with a negative or
directional correlation.
Based on the table referring to the relationship
between self-efficacy and the level of diabetic foot
wounds it is evident that obtained the results of self-
efficacy level in the medium category, there are at 1st
level as much as 20 respondents or 31.7%, then level
2 as many as 12 respondents (19%) and at levels 0 are
6 respondents or 9.5%. Then followed by low level of
self-efficacy is found in level 3 as many as 9
respondents (14%) and level 4 are 7 respondents
(11.1%). High self-efficacy level found in respondent
with level 1 in which consist of 2 respondent (3.2%).
Total respondents with self-efficacy were 43
respondents or 68.3%, then the low self-efficacy were
18 respondents (28.6%) and only 2 respondents
(3.2%) who had high self-efficacy (Table 2).
The results of the Spearman rho statistics test
showed significant level of p = 0.000 with significant
level of α≤ 0.05, indicating that there is correlation
Table 1: Distribution of DM type 2 respondents’
relationship between sensory neuropathy and self-
efficacy with the level of diabetic foot injury
within the district health office.
Characteristic of respondents
n
%
Age
40–49 years
50–59 years
60–69 years
20
32
11
31.7
50.8
17.5
Total
63
100
Gender
Male
Female
11
52
17.5
82.5
Total
63
100
Length of time with DM
1–5 tahun
6–10 tahun
>10 tahun
26
31
6
41.3
49.2
9.5
Total
63
100
Smoking
Yes
No
11
52
17.5
82.5
Total
63
100
Blood glucose result
< 200 mg/dl
200-400 mg/dl
>400 mg/dl
9
44
10
14.3
69.8
15.9
Total
63
100
Hypertension
Yes
No
35
28
55.6
44.4
Total
63
100
Diabetic foot ulcer history
Yes
No
15
48
23.8
76.2
Total
63
100
Amputation history
Yes
No
6
57
9.5
90.5
Total
63
100
Table 2: Distribution of independent variables
(sensory neuropathy and self-efficacy) in DM type
2 patients in the work area of the district health
office West Sumbawa.
Characteristic
n
%
Neuropathy sensory
Positive
Negative
54
9
85.7
14.3
Total
63
100
Self efficacy
Low
Moderate
High
18
43
2
28.6
68.3
3.2
Total
63
100
Table 3: Distribution dependent variable of level of
diabetic foot injury in DM type 2 patient in the work
area of the district health office. West Sumbawa.
Characteristic
N
%
Level of diabetic foot ulcer
Level 0
Level 1
Level 2
Level 3
Level 4
6
23
13
14
7
9.5
36.5
20.6
22.2
11.1
Total
63
100
The Relationship between Sensory Neuropathy and Self-efficacy and the Degree of Diabetic Foot Injuries in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Patient
633

between self-efficacy and the level diabetic foot
wound. The correlation coefficient obtained r = -
0.681 which means the correlation was strong (0.6–
799) but the correlation direction was negative or in
the opposite direction, which means that higher self-
efficacy was evident in patients with lower levels of
diabetic foot injury.
4 DISCUSSION
The neuropathy sensory identification found that
most respondents had a positive result. This
assessment used Semmes-Weinstein’s monofilament
10g (Martinez-Hervás et al., 2017). The results
indicated that most respondents who experienced
sensory neuropathy were from the age group 50–59
years. These results support the study by Aalaa et al.,
2012; Hutapea, Kembuan and P.S., 2016 who report
that the percentage was between 72.3% and 91.4%.
This percentage is supported by Solomon et al. (2016)
who states that the event arises at the age of >38. This
is due to changes in the blood vessel walls where there
is thickening of the intima layer. These changes cause
stiffness of the blood vessels so that the transport of
oxygen and nutrients to the tissue decreases resulting
in ischemia, then, over a long period, neuropathy will
occur. Neuropathy is more common in people with
diabetes who have GDS above 200 mg/dl.
Hyperglycemia can make the blood flow so small that
it can damage the nerves in the soles of the feet,
reduce sensitivity in the legs. Results of research
conducted by Ardiansyah Muhammad (2012)
indicate that higher levels of GDS raise the risk of
neuropathy. The statement was supported by Suri,
Haddani, and Sinulingga, (2015) who state that
people with hyperglycemia GDS above 200 mg/dL
and people with diabetes are at greater risk of fibular
damage, especially in the distal nerves. Most
respondents results from the blood glucose
examination in this study, were 200–400 mg/dl, but
the results of blood glucose at this time cannot be
interpreted because the blood glucose check and the
examination were not taken at the same time. The
examination was done randomly during the morning,
day and night at the time of data retrieval.
For self-efficacy, it was identified that most
respondents, predominantly women, were in the
moderate category, followed by low category and
there are two respondents with high self-efficacy
level. The self-efficacy assessment combined three
aspects: magnitude, generality, and strength. Self-
efficacy was found more in women than men. These
results also support research conducted by Wendling
and Beadle (2015) and Bandura (1997) who said that
women have a higher level of self-efficacy than men
and women are more efficacious in managing their
roles. Housewives and career women have higher
self-efficacy than an employed man.
Suffering long periods of diabetes may affect
patients’ self-efficacy; respondents who have
suffered for a long time recognize the symptoms and
can be more confident in overcoming the encountered
problems. Bandura’s theory states that success is
strongly influenced by the function of affection to
which self-belief will give individuals the ability to
cope and overcome stress and depression experienced
in difficult and pressing situations. It will also affect
the level of individual motivation. Most respondents
were unable to regulate their diet when feeling
stressed and could not implement the diet treatment.
Respondents felt they were able to control blood
glucose, but on each examination, respondents’ blood
glucose was high.
Respondents who have high self-confidence in
controlling stress, anxiety, having better glycemic
control, and some psychosocial factors such as self-
confidence related to health, social support, problem-
solving strategies, and personality strongly influence
their quality of life, either directly or through their
ability to deal with the negative effects of diabetes
(Porojan, Poantă & Fodor, 2009). Most respondents
in this study are still unable to improve aspects of
magnitude, strength, and generality. Lack of
respondents' self-confidence influenced the results
and assessment in this study.
Respondents diabetic ulcer identification was
mostly within Level 1 (superficial ulcer is limited to
the skin), followed by Level 3 then Level 2. Most
female respondents suffered diabetic foot wounds.
The duration of diabetes occurs over a range of >5
years, and more blood glucose screening results at
200–400 mg/dl. The results determined that most
respondents that have levels of diabetic foot wounds
are aged 50–59 years. These results are in line with
Whittemore, Melkus and Grey (2005) who
determined that the average age of respondents who
experienced diabetic ulcers were 57.6 years old. In
another study, around 6% of individuals were aged
45–64 years and 11% were over 65 years (Donna,
Ignatavicius and Workman, 2018). Also, in this study,
it was determined that most respondents who suffered
diabetic injuries were women which similar with
Huang et al., (2014) research, in which 364 people
suffered with DM Type 2 and most were women. It
can be concluded that diabetic mellitus Type 2 is
more common in women than in men. This opinion is
in line with the results of research conducted by Ortiz
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
634

et al., 2010 who explain that men are more likely to
do physical exercise regularly. Regular exercise can
stimulate the sensitivity of cells to insulin and reduce
central fat and muscle tissue development (Kriska,
2000).
The research found that some respondents, at the
time of activity, have not been able to check and
maintain that no injuries have occurred. This is
because respondents cannot feel pain, so only severe
injuries are felt. The presence of neuropathy causes a
loss of sensation in the leg that results in an
unrecognizable trauma, especially in areas of
repeated pressure. This results in many traumatic
injuries that the patient are not aware of. This
situation further exacerbates the development of
ulceration. Neuropathy develops due to the
accumulation of glucose products resulting in
increased activation of aldose reductase and sorbitol
dehydrogenase enzymes. This causes the conversion
of glucose into sorbitol and fructose. In addition,
there is an increase in oxidative stress in nerve cells
and increased vasoconstrictors, which result in nerve
cell ischemia.
The results of injury level identification was
determined by respondents’ assessment, directly
based on the Wagner scale accompanied by family
and researchers. It was found that most of the
respondents had previous diabetic scars so the
assessment was based on the wound conditions that
occurred during the study.
The correlation of sensory neuropathy with
diabetic foot ulcer levels has largely been positive and
mostly occurs at Level 1 (superficial ulcers confined
to the skin). The occurrence of this in female
respondents is higher than with males. It was found
that the longer diabetes was suffered, the more
neuropathy occurred, in which the longest survivor
was within a range of 5–10 years. This is in
accordance with research conducted by Hutapea,
Kembuan, and P.S. (2016) who said that most
neuropathy occurs in respondents who suffer from
DM within a period of 1–10 years. This is because the
longer DM is suffered, greater the chances of chronic
hyperglycemia. Chronic hyperglycemia can lead to
complications of DM, i.e. retinopathy, nephropathy,
coronary heart disease, and diabetic ulcers. Research
conducted by Vincent et al., (2004) says that the
severity of neuropathy may increase with the duration
of DM.
Another finding was that smoking history had no
relation to the occurrence of neuropathy. It is in
contrast to Keith R’s (2016) finding that smoking can
cause the risk of diabetic foot wounds. The results are
diverse due to the more woman respondents with no
smoking history while than male respondents which
only one-third of the total respondents.
The results of Criqui and Aboyans, (2015) show
that PAD (peripheral arterial disease) is associated
with the incidence of diabetic ulcers. PAD is one
factor that causes diabetic ulcers. Ischemia that
occurs causes red and dry feet often coincides with
neuropathy, causing an increased risk of diabetic
ulcers. The non-fluid blood flow in the leg causes the
wound to heal and causes the risk for greater
amputation. In addition, there is less oxygenation to
the affected area, meaning it is difficult for antibiotics
to distribute causing bacteria to breed rapidly. The
study found that history of comorbidities, such as
hypertension, has no relationship with the incidence
of neuropathy. This is because most respondents have
never had complete checks such as blood pressure
measurements. Respondents only attended blood
glucose checks, so the results of this study cannot
describe the relationship between the history of
accompanying diseases with diabetic wounds.
It was also determined that age was not the main
causal factor of neuropathy and diabetic injury. Some
respondents in this study, aged 60–65 years, were still
able to control blood sugar and perform foot care
independently so the incident of diabetic foot ulcer
was minimized.
The statistical analysis showed that neuropathy
detection had a low correlation with the level of
diabetic foot wounds within negative correlation.
This is because the examination of sensory
neuropathy found some respondents with diabetic
foot wounds can still feel the sensation of the
instrument used by researchers. So, the results of this
sensory neuropathy examination affected the
outcome between sensory neuropathy and diabetic
foot wounds.
The statistical test for correlation result regarding
self-efficacy towards diabetic foot ulcer levels shows
that the higher the self-efficacy of respondents, the
lower the level of diabetic injuries experienced. Low
confidence of respondents was due to severe ulcers
needing amputation. The wound-healing process is
felt for so long that respondents feel desperate and
stressed because of the pain. This is in line with the
theory of Bandura, who discusses self-ability, which
is one of the factors that affects self-efficacy.
Individuals will have a high self-efficacy if they feel
they are making positive progress, while individuals
with low self-efficacy experience negative self-
progress. Most of the respondents have moderate self-
efficacy because their actions are correct according to
their diabetic treatment. After the investigation it was
The Relationship between Sensory Neuropathy and Self-efficacy and the Degree of Diabetic Foot Injuries in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Patient
635

found that it appertained with their confidence in self
treatment
Respondents with high self-efficacy experienced
support and motivation of their spouses and family to
control blood sugar, regular exercise, and regulatory
diet to ensure they are highly prepared, even though
they had a history of diabetic wounds (Level 3) and
took several months to recover. This is also in line
with the theory of Bandura, who states that high self-
efficacy is often formed from events that have been
experienced directly, promoting higher confidence
levels. A person who has gained mastery experience
(experience of success) will demonstrate increased
self-efficacy, while failure reduces self-efficacy. If
the success of a person is due to outside factors, this
will usually not affect self-efficacy levels. However,
if the success of carrying out a task and outcome
expectations (a belief that the behavior applied will
be in accordance with the wish or the initial goal), and
both will affect the balance of one's behavior
(Bandura, 1997)
Most participants in this study were women who
worked as housewives and had moderate self-
efficacy. These respondents were unable to do any
activity due to foot ulcers and this delayed the healing
process. Cognitive theory explains that when
individuals feel helpless regarding stressful
challenges, anxiety rises when considering the next
challenge (Bandura in Nevid, Rathus, & Greene,
2011). Conversely, if individuals can cope better, the
haunted anxiety will be gone, and the challenges can
be solved.
Quality of life is a concept that relates to the
welfare of patients, in terms of physical,
psychological, social, and environmental aspects. The
quality of life of diabetics is the primary goal of care;
a quality of life that is as good as possible should be
maintained in diabetics, because a poor quality of life
and psychological problems can aggravate metabolic
disorders, either directly through hormonal stress or
indirectly through complications (Mandagi, 2010).
The quality of life of diabetic patients can be
improved by improving glycemic control, therefore a
strong belief that the patient will be able to self-
manage is required so their quality of life can be
maintained and improved (Ariani, Sitorus, Gayatri,
2012). An important aspect that affects patients’
psychological factors is self-efficacy (Lange et al.,
2010).
The increase in blood sugar can trigger the
occurrence of diabetic foot wounds. This increase
illustrates that most respondents are less adherent to
self-care activities such as dieting, daily activities,
exercise, lifestyle activities such as smoking, taking
diabetes drugs, and insulin use, and stress experience
(Smeltzer and Bare, 2001).
Lack of respondents’ belief in facing diabetic
wounds causes difficulties in controlling behavior
and adapting to conditions. This level of difficulty
(magnitude) is strongly influenced by the
psychological factors of respondents. The inability to
behave and the limitation of activity prevents the
respondent maintaining and increasing self-
management regarding the disease.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Most of the respondents in this study were tested
positive regarding sensory neuropathy. Most
respondents’ self-efficacy level was in the medium
category. The level of diabetic foot injuries found in
respondents were within Level 1 (superficial ulcers
confined to the skin). Sensory neuropathy with
degrees of diabetic foot wounds is associated with a
low correlation coefficient. For self-efficacy, there is
a strong relationship with the direction of negative
correlation, which means the greater the value of one
variable, the smaller the value of another.
It is hoped that an overall neuropathic
examination can be formed, not only for sensory
neuropathy but also for motor and autonomic
neuropathy. Nurses can provide support for patients’
self-sufficiency in managing and modifying lifestyles
by involving the families’ active role in patient care;
family support and people close to them play a
significant role in improving patients' self-efficacy
and prevent the onset of depressive symptoms in
patients with Type 2 DM.
REFERENCES
Aalaa, M. et al. (2012) ‘Nurses’ role in diabetic foot
prevention and care; a review’, Journal of Diabetes &
Metabolic Disorders. BioMed Central, 11(1), p. 24.
doi: 10.1186/2251-6581-11-24.
Aalaa, M. et al. (2017) ‘Diabetic foot workshop: Improving
technical and educational skills for nurses.’, Medical
journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran. Iran University
of Medical Sciences, 31, p. 8. doi: 10.18869/mjiri.31.8.
Alavi, A. et al. (2014) ‘Diabetic foot ulcers’, Journal of the
American Academy of Dermatology, 70(1), p. 21.e1-
21.e24. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2013.07.048.
Alavi, A. et al. (no date) ‘C ONTINUING Diabetic foot
ulcers Part I . Pathophysiology and prevention’, Journal
of American Dermatology. Elsevier Inc, 70(1), p. 1.e1-
1.e18. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2013.06.055.
Amin, N. and Doupis, J. (2016) ‘Diabetic foot disease:
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
636

From the evaluation of the "foot at risk" to
the novel diabetic ulcer treatment modalities.’, World
journal of diabetes. Baishideng Publishing Group Inc,
7(7), pp. 153–64. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v7.i7.153.
Apelqvist, J. et al. (2008) ‘The development of global
consensus guidelines on the management of the diabetic
foot’, Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews,
24(S1), pp. S116–S118. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.832.
Ardiansyah Muhammad (2012) Medikal Bedah untuk
Mahasiswa - Oleh: Muhammad Ardiansyah. 1st edn.
Jakarta: Diva Press. Available at:
https://www.bukupedia.com/id/book/id-47-
60709/kesehatan-gaya-hidup/medikal-bedah-untuk-
mahasiswa.html (Accessed: 18 May 2018).
Ariani, Y., Sitorus, R. and Gayatri, D. (2012) ‘Motivasi dan
Efikasi Diri Pasien Diabetes Melitus Tipe 2 Dalam
Asuhan Keperawatan’, Jurnal Keperawatan Indonesia,
15(1), pp. 29–38. doi: 10.7454/JKI.V15I1.44.
Bakker, K., van Houtum, W. H. and Riley, P. C. (2005)
‘2005: The International Diabetes Federation focuses
on the diabetic foot.’, Current diabetes reports, 5(6),
pp. 436–40. Available at:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16316594
(Accessed: 18 May 2018).
Bandura, A. (1997) Self-efficacy in changing societies.
Available at:
http://www.cambridge.org/id/academic/subjects/psych
ology/social-psychology/self-efficacy-changing-
societies?format=PB&isbn=9780521586962#eY756Jh
VvUVUygu5.97 (Accessed: 18 May 2018).
Bharat Kotru, S. K., Kotru, B. and Joshi, K. (2015)
‘Intervention of Diabetes Foot Care Practices on the
Prevention of New Diabetic Foot Ulcers in Patients
with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus’, Journal of Diabetes &
Metabolism. OMICS International, 6(2). doi:
10.4172/2155-6156.1000494.
Criqui, M. H. and Aboyans, V. (2015) ‘Epidemiology of
Peripheral Artery Disease’, Circulation Research,
116(9), pp. 1509–1526. doi:
10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.303849.
Donna, D., Ignatavicius and Workman, L. M. (2018)
Medical-Surgical Nursing, 9th Edition. 9th edn.
Saunders. Available at:
https://evolve.elsevier.com/cs/product/9780323444194
?role=student (Accessed: 18 May 2018).
Fujiwara, Y. et al. (2011) ‘Beneficial effects of foot care
nursing for people with diabetes mellitus: an
uncontrolled before and after intervention study’,
Journal of Advanced Nursing, 67(9), pp. 1952–1962.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2011.05640.x.
Huang, E. S. et al. (2014) ‘Rates of Complications and
Mortality in Older Patients With Diabetes Mellitus’,
JAMA Internal Medicine, 174(2), p. 251. doi:
10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.12956.
Hutapea, F. S., Kembuan, M. A. H. N. and P.S., J. M.
(2016) ‘Gambaran klinis neuropati pada pasien diabetes
melitus di Poliklinik Neurologi RSUP Prof. Dr. R. D.
Kandou periode Juli 2014 – Juni 2015’, e-CliniC, 4(1).
Available at:
https://ejournal.unsrat.ac.id/index.php/eclinic/article/vi
ew/12115 (Accessed: 18 May 2018).
International Diabetes Foundation (2017) ‘IDF Diabetes
Atlas 8th Edition’, Diabetes Atlas 8th Edition. 8th edn.
International Diabetes Federation. doi:
https://www.idf.org/component/attachments/attachme
nts.html?id=813&task...
Kriska, A. (2000) ‘Physical activity and the prevention of
type 2 diabetes mellitus: how much for how long?’,
Sports medicine (Auckland, N.Z.), 29(3), pp. 147–51.
Available at:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10739265
(Accessed: 18 May 2018).
Lange, S. et al. (2010) ‘Effects of treatment in women with
gestational diabetes mellitus: systematic review and
meta-analysis.’, BMJ (Clinical research ed.), 340, p.
c1395. Available at:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20360215
(Accessed: 18 May 2018).
Lazzarini, P. A. et al. (2015) ‘Reduced Incidence of Foot-
Related Hospitalisation and Amputation amongst
Persons with Diabetes in Queensland, Australia.’, PloS
one. Public Library of Science, 10(6), p. e0130609. doi:
10.1371/journal.pone.0130609.
Mandagi, A. M. (2010) ‘FAKTOR YANG
BERHUBUNGAN DENGAN STATUS KUALITAS
HIDUP PENDERITA DIABETES MELLITUS (Studi
di Puskesmas Pakis Kecamatan Sawahan Kota
Surabaya)’. Available at:
http://repository.unair.ac.id/21954/ (Accessed: 18 May
2018).
Martinez-Hervás, S. et al. (2017) ‘Altered Semmes-
Weinstein monofilament test results are associated with
oxidative stress markers in type 2 diabetic subjects.’,
Journal of translational medicine. BioMed Central,
15(1), p. 187. doi: 10.1186/s12967-017-1291-8.
Nevid, J. S., Rathus, S. A. and Greene, B. (2011) Abnormal
Psychology in a Changing World | Pearson. 8th edn.
Pearson. Available at:
https://www.pearson.com/us/higher-
education/product/Nevid-Abnormal-Psychology-in-a-
Changing-World-8th-Edition/9780205773404.html
(Accessed: 18 May 2018).
Porojan, M., Poantă, L. and Fodor, D. (2009) ‘Health-
related quality of life of diabetic patients.’, Romanian
journal of internal medicine = Revue roumaine de
medecine interne, 47(4), pp. 409–13. Available at:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21179925
(Accessed: 18 May 2018).
Smeltzer, S. c. and Bare, brenda g. (2001) BUKU AJAR
KEPERAWATAN MEDIKAL-BEDAH brunner &
suddarth Vol. 3 ed.8. buku kedokteran EGC. Available
at: http://onesearch.id/Record/IOS3145.slims-4523
(Accessed: 18 May 2018).
Suri, M. H., Haddani, H. and Sinulingga, S. (2015)
‘Hubungan Karakteristik, Hiperglikemi, dan Kerusakan
Saraf Pasien Neuropati Diabetik di RSMH Palembang
Periode 1 Januari 2013 Sampai dengan 30 November
2014’, Jurnal Kedokteran dan Kesehatan. Sriwijaya
University, 2(3), pp. 305–310. Available at:
https://www.neliti.com/id/publications/181703/hubung
The Relationship between Sensory Neuropathy and Self-efficacy and the Degree of Diabetic Foot Injuries in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Patient
637

an-karakteristik-hiperglikemi-dan-kerusakan-saraf-
pasien-neuropati-diabeti (Accessed: 18 May 2018).
Tresierra-Ayala, M. Á. and García Rojas, A. (2017)
‘Association between peripheral arterial disease and
diabetic foot ulcers in patients with diabetes mellitus
type 2’, Medicina Universitaria. No longer published
by Elsevier, 19(76), pp. 123–126. doi:
10.1016/J.RMU.2017.07.002.
Vincent, A. M. et al. (2004) ‘Oxidative Stress in the
Pathogenesis of Diabetic Neuropathy’, Endocrine
Reviews, 25(4), pp. 612–628. doi: 10.1210/er.2003-
0019.
Wendling, S. and Beadle, V. (2015) ‘Journal of Clinical &
Translational Endocrinology The relationship between
self-ef fi cacy and diabetic foot self-care’. The Authors,
2, pp. 37–41. doi: 10.1016/j.jcte.2015.01.001.
Whittemore, R., Melkus, G. D. and Grey, M. (2005)
‘Metabolic control, self-management and psychosocial
adjustment in women with type 2 diabetes’, Journal of
Clinical Nursing, 14(2), pp. 195–203. doi:
10.1111/j.1365-2702.2004.00937.x.
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
638
