
Early Warning Score System (EWSS) and Length of Stay Patients
with Dengue Hemmoragic Fever
Dwi Priyantini, Imroatul Farida and Herfina Setianingsih
STIKES Hang Tuah Surabaya
Keywords: Dengue Hemorragic Patient, Early Warning Score System, Length of Stay.
Abstract: Dengue hemorrhagic fever is a disease from dengue virus accompanied by bleeding and shock. Early Warning
Score System may help nurses to predict that risk of critical condition based on vital’s sign result. This study
was analize the relationshipbetween EWSS Agregate value and the length of stay in DHF patients. This study
used observational design with retrospective cohort approach. The population in this study were DHF patients.
The sample were 100 DHF’s patients, used probability sampling technique with simple random sampling
approach. The instrument on this study used observational paper of EWSS form, analized by Spearman rho
test. The result shows the most EWSS aggregate value is low risk (91,9%) whereas the length of stay is in
category medium stay (73%). Spearman rho test showed that there was relationship between early warning
score aggregate value with length of stay in DHF patient with ρ = 0.002 (ρ≤α = 0.05) and the correlation
coefficient 0,590 (r≤ 0,1000). Implications of the results shows that the EWSS Agregate value have a
relationship with length of stay in DHF patient. Moreover this study can predict the length of stay DHF
patients when they are got an EWSS aggregate value to improve Quality of care in hospital.
1 BACKGROUND
Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (DHF) is an infectious
disease that occurs in tropical area frequently. It cause
by dengue viruses spread out by Aedes Aegypti
mosquitoes, and its accompanied by bleeding
manifestations which is tends to cause shock and
death (Misnidiarly 2009; Hikmah and Moroni 2015).
Treatment and nursing care of DHF patients will
takes time and intensively care. It refers with
increases of vascular’s permeability membrane,
leading to decreased platelets and plasma leakage.
The risk of bleeding or shock, regarding with
decreased of platelet’s level will impact on the
worsening the condition itself. Furthermore, Early
Warning Score System (EWSS) is an appropriate
observation tool to identify the risk of critical
condition in patients or patients at risk of death in
hospital (Burch et al. 2008). More higher the score it
will reflected the condition getting worse or critical.
Critical condition of patients, will impact on the
length of their stay in the hospital in order to get
treatment instensively. Some studies were carried out
on the benefit of Early Warning score system in order
to detect the critical condition. However, the
agregate’s score of EWSS related with the lenght of
DHF’s patients stay is still underutilized.
The World Health Organization (WHO) describes
cases of dengue fever in worldwide around 50-100
million annually, with 250,000-500,000 cases and
24,000 deaths per year. Ministry of Health of
Republic Indonesia stated until 28 August 2014 the
number of DHF patients is 48,905 cases with 376
deaths. (Astuti 2016). Meanwhile, in Dr. Ramelan
Hospital, one of the biggest hospital in East Java
Indonesia, the number of dengue patients in 2016
around 257 patients with the average length of the day
hospitalization in range 3-14 days.
In the study conducted by (Siregar 2010) reported
that the average length of treatment of DHF patients
is a minimum of two days while the longest is 9 days
based on platelet count. Previous study reported that
Early Warning Score over 4 in the first assessment
then the patient would get longer treatment than
patients who in the initial assessment received a 0-3
EWS score that only took 48 hours of treatment.
Positive results on better clinical outcomes were
obtained after introduction of EWS charts in patients
with acute conditions (Alam 2014). This suggests that
EWS can help accelerate the improvement of the
patient's condition by observing through the resulting
Priyantini, D., Farida, I. and Setianingsih, H.
Early Warning Score System (EWSS) and Length of Stay Patients with Dengue Hemmoragic Fever.
DOI: 10.5220/0008328805710575
In Proceedings of the 9th International Nursing Conference (INC 2018), pages 571-575
ISBN: 978-989-758-336-0
Copyright
c
2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
571

EWS score and reducing the length of patient's day in
hospital, through recognizing signs of worsening
condition.
By Identification of abnormal clinical signs as
well as patient health history, and appropriate
diagnostic test were tends to predict the risk of
adverse outcomes objectively (Burch et al. 2008).
However, the deterioration of these clinical signs is
often unclear and may occur unnoticed. Furthermore,
the development and availability of tools that can
described the evidence of clinical deterioration are
essential. Ultimately, this can prevent adverse events
and improve the patient's condition (Alam 2014).
Early warning score (EWS) is a scoring system
used to help detect early deterioration of the patient's
condition and reduce unexpected events in the clinical
ward associated with the patient's condition (Smith
2012). EWS will help the health worker to identify
the emergency situation in the patients which can then
be handled from the beginning, so the hospitalization
time will be much faster because the patient gets the
treatment well and can help improve the hospital
service quality. This socialization needs to be done in
order to improve the implementation of early warning
score on inpatient patients especially in patients with
critical condition so that the achievement of patient
satisfaction and staff who do the maintenance.
Researchers want to analyze the relationship of
early warning score system with length of stay
dengue hemorrhagic patients in inpatient wards of the
disease based on the above background. Dengue
Hemorrhagic Fever (DHF) is an infectious disease
that occurs in tropical area frequently. It cause by
dengue viruses spread out by Aedes Aegypti
mosquitoes, and its accompanied by bleeding
manifestations which is tends to cause shock and
death(Misnidiarly 2009; Hikmah and Moroni 2015).
Treatment and nursing care of DHF patients will
takes time and intensively care. It refers with
increases of vascular’s permeability membrane,
leading to decreased platelets and plasma leakage.
The risk of bleeding or shock, regarding with
decreased of platelet’s level will impact on the
worsening the condition itself. Furthermore, Early
Warning Score System (EWSS) is an appropriate
observation tool to identify the risk of critical
condition in patients or patients at risk of death in
hospital(Burch et al. 2008). Critical condition of
patients, will impact on the length of their stay in the
hospital in order to get treatment instensively. Some
studies were carried out on the benefit of Early
Warning score system in order to detect the critical
condition. However, the agregate’s score of EWSS
related with the lenght of DHF’s patients stay is still
underutilized.
The World Health Organization (WHO) describes
cases of dengue fever in worldwide around 50-100
million annually, with 250,000-500,000 cases and
24,000 deaths per year. Ministry of Health of
Republic Indonesia stated until 28 August 2014 the
number of DHF patients is 48,905 cases with 376
deaths. (Astuti 2016). Meanwhile, in Dr. Ramelan
hospital, one of the biggest hospital in East Java
Indonesia, the number of dengue patients in 2016
around 257 patients with the average length of the day
hospitalization in range 3-14 days.
In the study conducted by (Siregar 2010) reported
that the average length of treatment of DHF patients
is a minimum of two days while the longest is 9 days
based on platelet count. Previous study reported that
Early Warning Score over 4 in the first assessment
then the patient would get longer treatment than
patients who in the initial assessment received a 0-3
EWS score that only took 48 hours of treatment.
Positive results on better clinical outcomes were
obtained after introduction of EWS charts in patients
with acute conditions (Alam 2014). This suggests that
EWS can help accelerate the improvement of the
patient's condition by observing through the resulting
EWS score and reducing the length of patient's day in
hospital, through recognizing signs of worsening
condition.
By Identification of abnormal clinical signs as
well as patient health history, and appropriate
diagnostic test were tends to predict the risk of
adverse outcomes objectively (Burch et al. 2008).
However, the deterioration of these clinical signs is
often unclear and may occur unnoticed. Furthermore,
the development and availability of tools that can
described the evidence of clinical deterioration are
essential. Ultimately, this can prevent adverse events
and improve the patient's condition (Alam 2014).
Early warning score (EWS) is a scoring system
used to help detect early deterioration of the patient's
condition and reduce unexpected events in the clinical
ward associated with the patient's condition (Smith
2012). EWS will help the health worker to identify
the emergency situation in the patients which is
determine the treament and nursing care. Turn over
Interval (TOI) of hospital bed will influnced by the
lenght of stay each patients, so the lenght of
hospitalization can be minimize if patients get the
treatment efficiently. This socialization needs to be
done in order to improve the implementation of early
warning score on inpatient patients especially in
patients with critical condition so that the
achievement of patient satisfaction and the staff itself.
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
572
Researchers want to analyze the relationship of early
warning score system with length of stay dengue
hemorrhagic patients in inpatient wards Dr. Ramelan
Hospital Surabaya.
2 METHODS
This study uses obeservational design with a
retrospective cohort approach. The sample in this
study were DHF patients in in-patient wards of Dr.
Ramelan Surabaya, which amounted to 100 patients
using probability sampling technique with simple
random sampling approach. The independent variable
is the aggregate value of early warning scored and the
dependent variable is the length of patient care of
DHF. In demographic data the instrument used is an
observation sheet filled by researchers consisting of
gender, age, Occupation, date of admissin, date of
discharge, and EWS score. Meanwhile, the
observations sheet of EWS aggregate scores and
observation of length of day care using day. The data
used secondary data in the medical record of the EWS
score.Data analysis techniques is Spearman rho test
showed that there was relationship between early
warning score aggregate value with length of stay in
DHF patient with
ρ = 0.002 (ρ≤α = 0.05) and the
correlation coefficient 0,590 (r
≤
0,1000).) The length
of their stay, based on the day the patient first entered
the treatment room until return home. The hypothesis
in this study is that there is an association Early
Warning Score with the length of day treatment of
DHF patients in the Inpatient Room Dr.Ramelan
Surabaya.
3 RESULTS
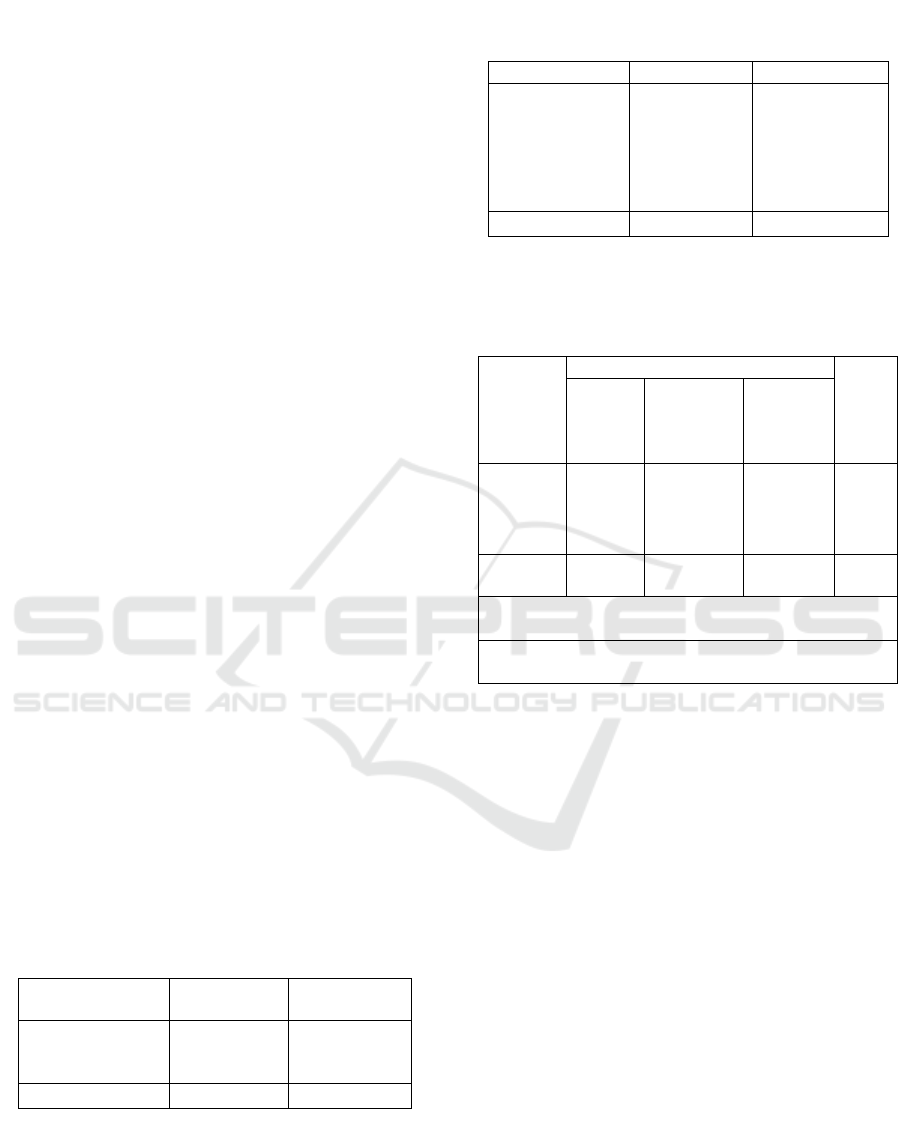
Based on table 1, 100 respondents had aggregate
value of EWSS with a low score (92%), and moderate
score (8%). Table 2 showed that from 100
respondents, there were 16 respondents (16%) short
stay, 73 respondents (73%) médium stay, and 11%
respondents were long stay.
In this study, the amount of respondents with
EWSS aggregate value and the length of stay of DHF
patients in Dr.Ramelan Surabaya, there were low
EWSS value and short stay (16%),
medium stay
(73%), and long stay (3%) respondents. Whereas 8%
respondents with EWSS médium value (8%) have
long stay care. According to Spearman statistic test
results obtained ρ less than α,ρ=0,002 < α = 0,05,
which means that there is a statistically relationship
between the EWSS agregate value with the length of
stay patient with DBD in Dr. Ramelan Surabaya.
Then from the results of Correlation Coefficient
showed the results of 0.590 which refers to the
closeness of the relationship between the aggregate
value of EWSS with the length of stayin a medium
context.
Table 1: Aggregate Value of Early Warning Score
System DHF patients in inpatient Ward Dr.Ramelan
Surabaya (n=100).
EWSS aggregate
value
Frekuency
(f)
Percentage
(%)
Low
Medium
High
92
8
0
92%
8%
0%
Total 100 100%
Table 2: Lenght of stay DHF patients in inpatient Ward
Dr.Ramelan Surabaya (n=100).
Len
g
ht of Sta
y
Frekuenc
y
(
f
)
Percenta
g
e
(
%
)
Short Stay (≤ 3
days)
Medium Stay (4-
11 days)
Long Stay (≥ 12
days)
16
73
11
16 %
73%
11 %
Total 100 100%
Table 3: Spearman’s rho test of The relationship
between EWSS agregate value and the lenght of stay
DHF patientsin Inpatient ward Dr. Ramelan Surabaya
(n = 100).
Agregate
value
EWSS
Lenght of Stay
Total
Short
stay
(1-3
days)
Medium
stay
(4-11
days)
Long
stay
(≥12
da
y
s
)
Low
(0, 1-4)
Medium
(5-6)
16
16%
0
0%
73
73%
0
0%
3
3%
8
8%
92
92%
8
8%
Total
16
16%
73
73%
11
11%
100
100%
Spearman Rho test
ρ = 0.002
Correlation Coefficient = 0,590
Early Warning Score System (EWSS) and Length of Stay Patients with Dengue Hemmoragic Fever
573

4 DISCUSSION
4.1 Aggregate Value Early Warning
Score System DHF Patients in
Inpatient Room Dr. Ramelan
Surabaya
Results of this research, reported that in general DHF
patients in inpatient Ward, generally have low
aggregate EWSS value as much as 92 respondents
(92%). Low EWSS values can be affected by several
factors including the age, the severity of the disease,
and gender. Majority DHF’s patients were in range
17-25 years. In this period, one's body is able to
compensate well in ill condition. It assumed the value
obtained influenced by the patient's clinical condition
which is showed by the increases of body
temperature, the pulse and the presence of the
respondent using the additional oxygen therapy (nasal
canule). Any change in the EWSS component can be
an indicator of physiological changes due to the
degree of DHF condition. Increased body temperature
is a mechanism of the dengue virus inflammation in
patients with DHF. Patients may develop to shock
dengue fever if the score are increased such as pulse
and blood pressure, acral (tip) cold extremities,
accompanied by skin congestion. These changes
show symptoms of circulatory disorders, as a result of
mild or severity of plasma infiltration (Nopianto
2012). Furthermore, the score will add with 2 point if
the patients supported by oxygen therapy (Physicians
Royal College 2012)
.
4.2 Lenght of Stay DHF Patient in
Inpatient Ward Dr. Ramelan
Surabaya
The results obtained that 73% have a medium stay (4-
11 days). It means, DHF cases were in moderate
treatment, varies depend on their clinical
manifestations and the role of healh care personnel
during the treatment. Patients with DHF is highly
potential for bleeding due to changes in homeostasis
in the body caused by Dengue virus (Soedarto 2012).
We assumed that the length of the day of care related
with health’s history of patients and their physical
condition to adapt and recover. Vital’s sign data
obtained in average, their respiration rate is 20 times
per minute, pulse rate 92 time per minute and 37
degree celcius for the body temperature.
Surprisingly, there were 3 (three) female respondents
on long stay (>12 days). It was argue that it was
related with the anatomy of capillary permeability in
female patients. Kasper DL et al (2009)
cited(Nopianto 2012)mention that in female, the
clinical manifestation dengue fever is more severe
rather tan in men. It related with the capillary walls in
women tend to increase rather than in men
anatomically.
4.3 Relationship Between Aggregate
Value Early Warning Score System
and Length of Stay Dengue
Hemmoragic Patients in Dr.
Ramelan Surabaya
In this research, it was found that there was
significantly relationship between EWSS aggregate
value and the length of stay patient with DHF and also
the closeness relation both variable was in moderate
relationship. It was appropriate with the theories that
more higher the aggregate value will impact the
worsening condition. The treatment and nursing care
will depend on the necessity of body requirements
focused on the leakage of plasma into extravascular
space. It was a risk for severe bleeding such as
petechia, epistaxis, bleeding in gums as well as
hemoptisis.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The EWSS aggregate value of DHF patients have
relationship with their lenght of stay during
hospitalization. It was recomended to measure the
EWSS aggregate value in the first and continued
assesment in order to identify the condition of
patients as well as to identify the appropriate
treatment and the quality of nursing care.
REFERENCES
Alam, 2014. The impact of the use of the Early Warning
Score (EWS) on patientoutcomes: A systematic
review.
Astuti, M.D., 2016. Upaya pencegahan Risiko Perdarahan
Pasien Demam Berdarah Dengue di RSUD dr.
Soehadi Prijonegoro. Fakultas Ilmu Kesehatan
Universitas Muhammadiyah Surakarta.
Burch, Tarr & Moroni, 2008. Modified early warning score
predicts the need for hospital admission and
inhospital mortality. England: Elsevier.
Hikmah & Moroni, 2015. Faktor yang Berhubungan
Dengan Kejadian Kematian Akibat Demam
Berdarah Dengue. Unnes Journal of Public Health.
Misnidiarly, 2009. Demam Berdarah Dengue (DBD):
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
574

Ekstrak Daun Jambu Biji Bisa untuk DBD, Jakarta:
Pustaka Populer Obor.
Nopianto, H., 2012. Faktor-Faktor yang Berpengaruh
terhadap Lama Hari Rawat pada Pasien Demam
Berdarah Dengue di RSUP Dr. Kariadi Semarang.
Physicians Royal College, 2012. National. Early Warning
Score (NEWS): Standardising the assessment of
acute illness severity in the NHS. Report of a
workingparty. London: RCP.
Siregar, N., 2010. Hubungan Hasil Pemeriksaan Jumlah
Trombosit Dengan Lama Rawat Inap Pada Pasien
Demam Berdarah Dengue di Rumah Sakit Umum
Pusat Haji Adam Malik Medan. Fakultas
Kedokteran Universitas Sumatera Utara.
Smith, 2012. The ability of the National Early Warning
Score (NEWS) to discriminate patients at risk of
early cardiac arrest, unanticipated intensive care unit
admission, and death.
Soedarto, 2012. Demam Berdarah Dengue, Jakarta: Sagung
Seto.
Early Warning Score System (EWSS) and Length of Stay Patients with Dengue Hemmoragic Fever
575
