
Factors Affecting the Feeding Pattern of Under-Five Children with
Stunting in Indonesia
Praba Diyan Rachmawati, Retnayu Pradanie and Robeta Lintang Dwiwardani
Faculty of Nursing Universitas Airlangga, Kampus C Mulyorejo, Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: Stunting, Feeding Pattern, Under-Five Children.
Abstract: Under-five children with stunting are still commonly found in Indonesia, this issue is related to the culture.
However, research on stunting children in terms of cultural aspects is still limited. The aim of this research
was to identify the factors related to feeding patterns for stunting children based on transcultural nursing. This
research used a cross-sectional approach, with 139 mothers of under-five stunting children as a sample. The
variables were education, economy, regulation and policy, cultural values and lifestyle, religiosity and
philosophy, social support and family, technology, and feeding patterns. The data was collected using
questionnaires and tested with Spearman’s rho. The results show the relationship between feeding patterns
and economics (p= 0,013; r = 0,210), regulation and policy (p = 0,040, r = 0,174), cultural values and lifestyle
(p = 0,000; r = 0,502), social support and family (p = 0,000, r = 0,337), religiosity and philosophy (p = 0,000,
r = 0,371), and technology (p = 0,017; r = 0,203), the feeding pattern was not related with education (p =
0,732). Cultural values and lifestyle are the dominant factors. The findings suggest that the factors based on
a cultural approach can be used as a basis for preventing a stunting incident.
1 BACKGROUND
Adequacy of nutrition in under-five children is very
important to support their growth and development
(Jackson, 2015). However, currently there are still
high rates of stunting incidents in under-five children.
Stunting has become a problem worldwide (Black et
al., 2008). There are approximately 171 million
under-five children affected by stunting and 167
million from developing countries (de Onis, Blössner
and Borghi, 2012). Around 3 in 4 of the world's
stunting children are in Sub-Saharan Africa at 40%,
and 39% are in South Asia. Indonesia is included in
the 14 countries with the largest number of stunting
under-five children and ranked fifth after India,
Nigeria, Pakistan and China (Kementerian Kesehatan
- Ministry of Health/Indonesia, 2016).
Stunting in Indonesia in 2010 is included in the
high prevalence category. Stunting events reach more
than 30% (Henry, 2015). The results of the Riskesdas
report (2013) show that the national stunting
incidence increased to 37.2% with 19.2% of short
children and 18% very short. Based on data from the
Health Department of Sumenep Regency (2012) the
Sumenep area is included in the list of regional groups
that have high stunting toddler problems that is <32%.
Based on the preliminary data collection at the
Sumenep District Health Office in October 2017, the
stunting problem in children increased to 32.6% in
2016.
Stunting is a condition that occurs due to chronic
malnutrition caused by poverty and inappropriate
feeding patterns (Black et al., 2008; Kementrian
Kesehatan - Ministry of Health/Indonesia, 2015). The
feeding patterns of parents will affect the growth and
development of children (Kudlova and Schneidrova,
2012). The pattern includes the type, amount, and
schedule (Ministry of Health RI 2014). The pattern of
feeding at each age varies. A study conducted by
Subarkah (2016) shows that for the pattern of proper
feeding in toddlers, most toddlers have normal
nutritional status. Mothers who have a good feeding
pattern, indicate that the mother has given the right
food according to the age of the child and meets the
nutritional needs of children (Kumala and Warsiti,
2013).
Behavioral factors associated with malnourished
children in Indonesia are associated with habits and
culture (Ramli et al., 2009). Feeding problems in
children that appear in culturally related communities
include the types of foods given to children not being
age appropriate and less attention to nutritional
Rachmawati, P., Pradanie, R. and Dwiwardani, R.
Factors Affecting The Feeding Pattern of Under-Five Children with Stunting in Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0008323102290235
In Proceedings of the 9th International Nursing Conference (INC 2018), pages 229-235
ISBN: 978-989-758-336-0
Copyright
c
2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
229
content in food. Based on a preliminary study
obtained from 20 mothers, all mothers give early
feeding for children aged less than 6 months; they say
that it is a tradition. Duration of breastfeeding less
than 6 months is one of the causes of stunting in
children (Jiang et al., 2015). Lack of mother's
knowledge about the fulfillment of children's
nutritional needs is one of the factors causing stunting
(Nkurunziza et al., 2017).
The impact of stunting in the short term includes
the disruption of brain development and intelligence,
impaired physical growth, and metabolic disorders of
the body (Ministry of Health, 2016; Lestari et al.,
2018). The prolonged implications of stunting are
poor health, increased risk of non-communicable
diseases, and poor cognitive and educational
attainment achieved in childhood (The Ministry of
National Development Planning (Bappenas) and the
United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), 2017).
There is a high risk of illness and disability in old age,
as well as the uncompetitive quality of work resulting
in low economic productivity (Ministry of Health of
the Republic of Indonesia, 2016).
One of the National Medium-Term Development
Plans in Indonesia in 2015-2019 is addressing the
problem of under-five children with stunting
(Kementerian Kesehatan - Ministry of Health/
Indonesia, 2015). However, the efforts have not been
able to solve the problem of stunting in under-five
children. The aims of this study are to analyze the
factors related to the feeding pattern of stunting
toddlers based on the transcultural nursing approach.
2 METHODS
This research design uses a cross-sectional approach.
The population in this study were under-five children
with stunting, amounting to 213 children and their
mothers. The total sample in this study was as many
as 139 children and their mothers. The sampling
technique used in this research is cluster sampling.
The independent variables in this study are
educational, economic, regulatory and policy factors,
cultural values and lifestyle, social and family
support, religiosity and philosophy, and technology.
The dependent variable in this research is feeding
pattern. Instruments in this study are questionnaires
and the WHO standard for stunting measurement.
This research was conducted in 15 villages in the
Dasuk Health Care Centre (Puskesmas) work area.
The study was conducted in November 2017. Each
data will be measured using a Spearman's rho (rs)
statistic test if the significance value of α ≤ 0.05 is
determined. This study has passed the ethics review
of the Health Research Ethics Commission of Faculty
of Nursing Airlangga University with number: 579-
KEPK.
3 RESULTS
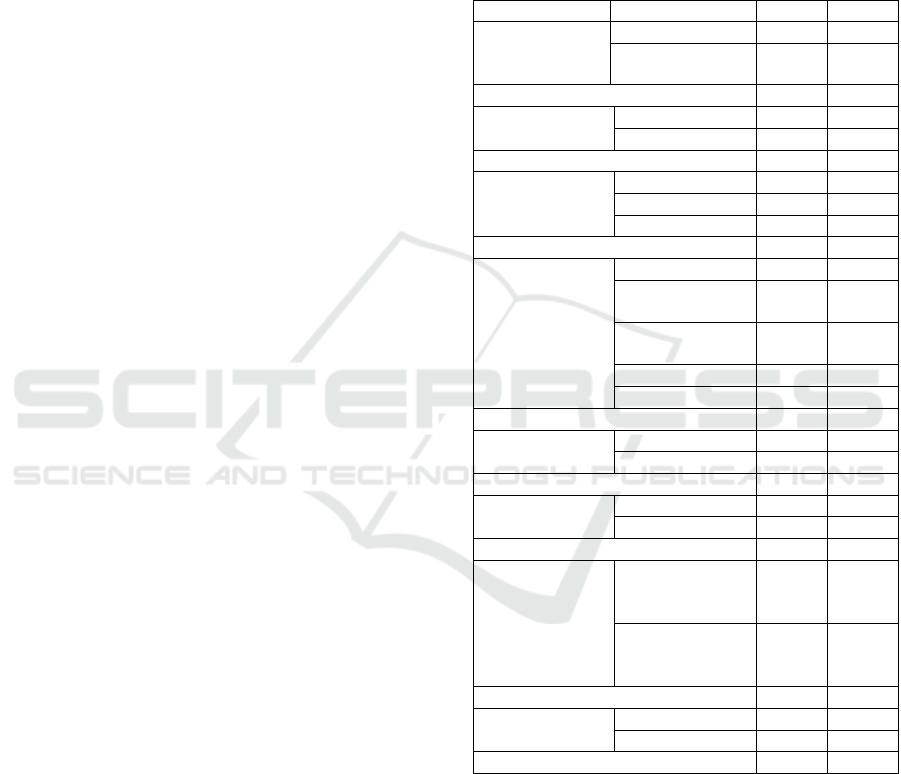
Table 1: Characteristics of respondents.
Characteristics
Category
f
%
Age of the
child
(months)
12-24
70
50.4
>24
69
49.6
Total
139
100
Gender
Boys
71
51.1
Girl
68
48.9
Total
139
100
Mother’s Age
(years old)
< 20
7
5
20-35
112
80.6
>35
20
14.4
Total
139
100
Occupation
Housewife
87
62.6
Government
employees
2
1.4
Private
employees
5
3.6
Entrepreneur
4
2.9
Farmers
41
29.5
Total
139
100
Number of
Children
≤ 2
110
79.1
>2
29
20.9
Total
139
100
Family number
≤ 5
67
48.2
>5
72
51.8
Total
139
100
Family income
Under the
average
minimum wage
109
78.4
Over the
minimum
average wage
30
21.6
Total
139
100
Attendance at
POSYANDU
Active
125
89.9
Rarely
14
10.1
Total
139
100
Based on Table 1 the characteristics of
respondents indicated that most of the stunting age
children were 12-24 months i.e. 70 (50.4%). The
majority of respondents were male gender – 71
(51.1%) of the children. Most mothers were aged 20-
35 years – 112 (80.6%) of respondents. Most of the
respondents were housewives – 87 (62.6%) of
respondents. Most of the respondents had fewer than
two children – 110 (79.1%) of respondents and 72
(51.8%) of the respondents had more than five family
members. The income of respondent families per
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
230
month is mostly less than the average minimum wage
– 109 (78.4%) respondents. Most of the active
respondents attended the Posyandu – 125 (89.9%)
respondents.
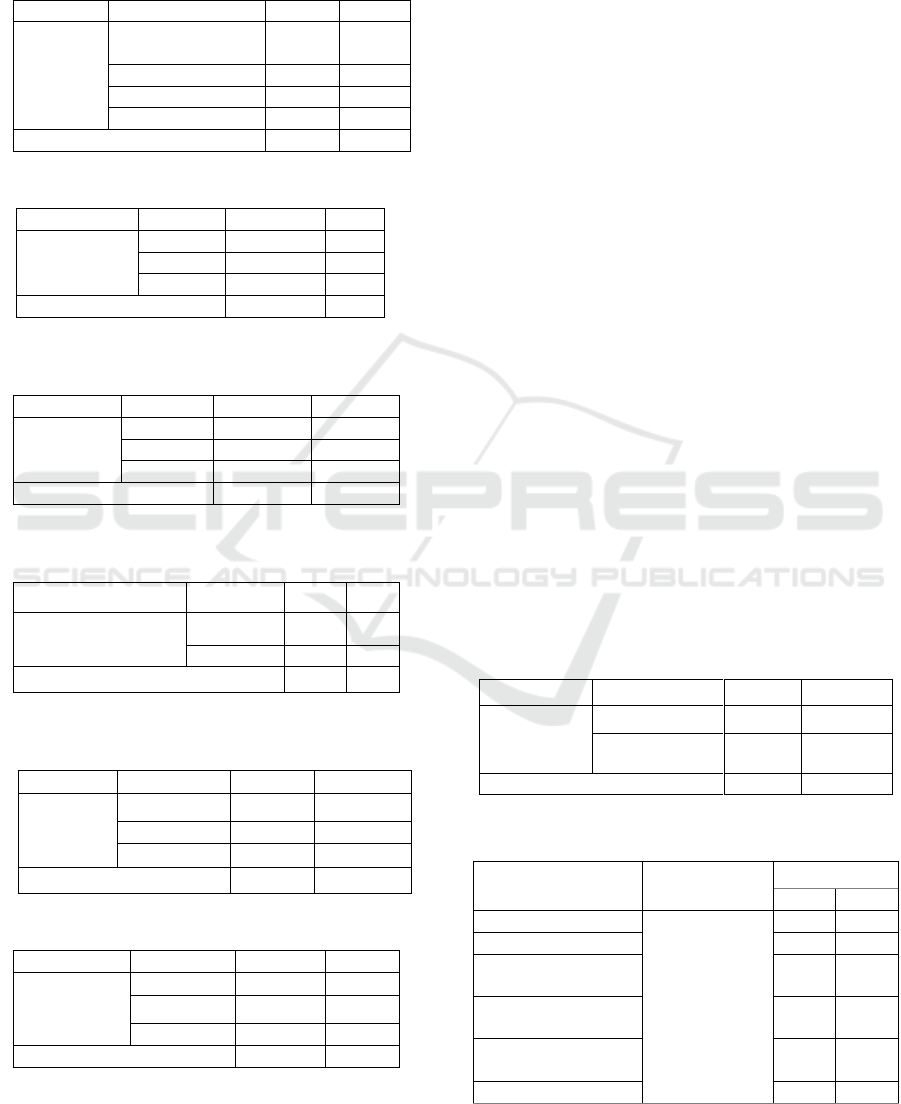
Table 2: Distribution of respondents by mother's education.
Variable
Category
f
%
Education
No school/ no
primary school
8
5.8
Basic education
99
71.2
Middle education
23
16.5
Higher education
9
6.5
Total
139
100
Table 3: Distribution of respondents by maternal economy.
Variable
Category
f
%
Economy
level
Good
89
64
Enough
37
26.6
Less
13
9.4
Total
139
100
Table 4: Distribution of respondents based on regulations
and policies.
Variable
Category
f
%
Regulations
and
Policies
Good
102
73.4
Enough
24
17.3
Less
13
9.4
Total
139
100
Table 5: Distribution of respondents by cultural values and
lifestyle.
Variable
Category
f
%
Cultural Values and
Lifestyle
Positive
74
53.2
Negative
65
46.8
Total
139
100
Table 6: Distribution of respondents by social and family
support.
Variable
Category
f
%
Social and
Family
Support
Good
66
47.5
Enough
73
52.5
Less
0
0
Total
139
100
Table 7: Distribution of respondents by technology.
Variable
Category
f
%
Technology
Good
31
22.3
Enough
67
48.2
Less
41
29.5
Total
139
100
Table 2 shows most of the respondents have a
basic education – 99 (71.2%) of respondents. Middle
education 23 (16.5%), higher education 9 (6.5%) and
no school shows 8 (5.8%).
Based on Table 3, the economic variables indicate
that most respondents have sufficient economic status
to meet the needs of feeding an under-five child with
stunting – 89 (64%) respondents.
Table 4 shows that the most respondents had good
regulations and policies – 102 (73.4%). Enough
category 24 (17.3%) respondents and Less category
shows 13 (9.4%) respondent. Table 5 shows that most
respondents had positive scores on cultural values and
lifestyle – 74 (53.2%) and 65 (46.8%) showed
negative values.
Table 5 shows most respondents have a positive
score for cultural values and lifestyle in feeding on
stunting, as many as 74 (53.2%) respondents.
However, it still found the factors of cultural values
and lifestyle in the negative category (46.7%).
Table 6 shows that most of the respondents had
sufficient social and family support in feeding
toddlers as many as 73 (52.5%) respondents, 66
(47.5%) were in the good category. Based on Table 7
the majority of respondents used technology in
feeding stunting children – 67 (48.2%) of
respondents, while 31 (22.3%) were in the good
category and 41 (29.5%) were in the low category.
Table 8 shows that most respondents are right in
the feeding pattern of under-five children as many as
137 (98.6%) of respondents and 2 (1.4%) have
inappropriate feeding patterns.
Table 8: Distribution of respondents by feeding patterns in
under-five children with stunting.
Variable
Category
f
%
Feeding
Patterns
Right
137
98.6
Not exactly
2
1.4
Total
139
100
Table 9: Analysis of the relationship between feeding
pattern factors in stunting children.
Independent
variable
Dependent
variable
Analysis
p
r
Education
Feeding
Pattern
0.732
0.029
Economy
0.013
0.210
Regulations and
policies
0.040
0.174
Cultural values and
lifestyle
0.000
0.502
Social and family
support
0.000
0.337
Technology
0.017
0.203
Factors Affecting The Feeding Pattern of Under-Five Children with Stunting in Indonesia
231

The educational factor has no relationship with
the mother’s feeding pattern p = 0.732. Economic and
regulatory factors, cultural and lifestyle values, social
and family support, and technological factors have a
relationship with the feeding pattern of stunting
children with a significance value α <0.05. Factors of
cultural values and lifestyle became the dominant
factor associated with the pattern of feeding with the
result of correlation r = 0.502.
4 DISCUSSION
4.1 Maternal Education Factor in
Feeding Pattern on Under-Five
Children with Stunting
The results showed that there was no statistically
significant relationship between maternal education
factors and the feeding pattern. It can be seen that
most mothers have elementary education that is
graduated from elementary school/junior high school,
while the pattern of feeding on toddler stunting is
appropriate.
According to transcultural nursing theory by
Leininger (2002), the higher the client's education the
more likely the client's conviction is usually
supported by rational scientific evidence and the
individual can learn to adapt to a culture appropriate
to their health condition. The results of Nkurunziza et
al. (2017) suggest that maternal education is a
determinant of nutritional status of children with most
studies showing low maternal education is a major
determinant of malnutrition. The results of this study
indicate that maternal education is not related to the
pattern of feeding in children. However, according to
the research by Casale, Espi and Norris (2018) the
maternal education factor indirectly has an effect on
the occurrence of stunting in a child and the study by
Subarkah, Nursalam and Rachmawati (2017) states
that mothers who have a proper diet are influenced by
maternal education and good knowledge about child
feeding.
The results of this study are in accordance with
research by Sholikah, Rustiana and Yuniastuti
(2017), which states that there is no significant
relationship between maternal education and
nutritional status of children. It can be influenced by
the knowledge about nutrition and health that can be
obtained by visiting Posyandu. Children with
stunting need special attention and intervention.
Health workers at Posyandu and health volunteers
play an active role in providing health education such
as counseling about appropriate feeding patterns for
stunting children. The mother's knowledge increases
and they apply it properly.
4.2 The Economic Factors in Feeding
Pattern on Under-Five Children
with Stunting
Economics is a human effort to meet the material
needs of a limited source. Family income is a factor
affecting the pattern of feeding in toddlers. Revenue
and prices of food products also affect the level of
food consumption. The transcultural nursing theory
explains that factors affecting one's economic value
are income in the family, other income sources, health
insurance, and the impact of income on health
(Andrews and Boyle, 2012).
Research by Subarkah, Nursalam and
Rachmawati (2017) states that high income will
determine good purchasing power. Conversely, low
income will lower purchasing power. This study
shows that most respondents use income received to
meet basic needs so that mothers can provide the right
foods for children. The results of this study contradict
Fauziah's (2009) study which states that a person's
income level will affect the type and amount of food
they consume. The higher the income the better the
quality of food consumed by buying food that is better
quality and more expensive. In this study, although
the majority of families earn less than the average
minimum wage in Sumenep Regency, the mother
divides the money so that the child's nutritional needs
are fulfilled, and also most of the fathers have jobs as
farmers so that the source of the food is readily
available without buying it. Most mothers when they
get extra money also spend it to meet the needs of
children first such as on milk or fruit. This study is in
line with Hagos et al. (2017) showing that the family
income incurred to improve the nutritional status of
children, by spending to buy quality food, can protect
children from malnutrition.
4.3 The Regulatory and Policy Factors
in Feeding Patterns in Under-Fives
Mothers with appropriate feeding patterns for
children is closely related to general education
received by mothers who visit Posyandu, which can
increase knowledge about nutrition and health
(Masithah, Soekirman, and Martianto, 2005).
Posyandu is one form of policy as an effort for
Community-Based Health (UKBM) managed to
provide convenience to the community in obtaining
basic health services, especially for under-five
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
232

children. Posyandu provides a routine once a month
service; the children are weighed, have health checks,
supplementary feeding, and nutrition counseling.
Children are measured by height and age, and if
known to have stunting it is recorded by a Posyandu
health volunteer, then a health worker reports to the
nutritionist in Puskesmas so that respondents can
consult with a nutritionist and receive supplementary
food.
According to research by Welasasih et al. (2012)
the emergence of stunting in nutritional status is not
only because of the lack of food but also because of
disease. The implementation of immunization is to
prevent the occurrence of infectious diseases. In this
study, most mothers have provided complete basic
immunization for infants. According to Ulfani et al.
(2011) the utilization of Posyandu and complete
immunization is a factor related to the occurrence of
underweight, stunting and wasting.
4.4 Cultural Value and Lifestyle
Factors in Feeding Pattern of
Under-Five Children with Stunting
Culture is the norm or action of group members who
are studied and divided, and it gives instructions for
thinking, acting, and making decisions (Leininger,
2002). The choice of food is influenced by the
lifestyle and culture in which a person is located, and
the feeding of children will also be influenced by
cultural factors (Meier-Ploeger, 2003). Cultures
influence the pattern of feeding in children (Culhane-
Pera et al., 2002) in terms of beliefs, values, and
behaviors associated with different foods (Erika,
2016). Some studies suggest that cultural values and
negative lifestyle will cause the pattern of feeding in
children to be inappropriate, whereas the values of
culture and positive lifestyle will enable the pattern of
proper feeding in children.
In this study, most of the respondents had positive
cultural values and did not believe in dietary
restrictions such as eggs, fish and chicken were not
good for the growth of children, and believed that
nutritious food was good for child growth. This is
supported by the willingness of mothers to come to
Posyandu, so that mothers gain knowledge in the
right feeding pattern to improve nutritional status,
especially for stunting children. This research is in
line with that of Isnatri, (2016) which states that there
is a relationship between cultural values and lifestyle
and the pattern of feeding in children with
malnutrition status. This is because most respondents
have cultural values and negative lifestyle that causes
the pattern of feeding for children to be inappropriate.
In this study, respondents who had a negative
cultural and lifestyle score of 46.8%, among others,
have a history of giving early breast-milk in the form
of young coconut water or ro'-moro to give a smooth
banana crushed with rice or lotek when newborn with
the intention that the babies are healthy and strong.
They are convinced that giving more rice than the side
dishes and vegetables is good for health, and they
believe that their child is stunting due to the offspring
of the parents. Thus, it is necessary to provide
continuous health counseling about feeding infants
and children to increase mothers’ knowledge so as to
improve the inappropriate behavior to improve the
nutritional status of children.
4.5 Social and Family Support Factors
in Feeding Pattern of Under-Five
Children with Stunting
Social and family factors function as a support system
for its members and are shown to improve health and
adaptation processes (Leininger 2002). Each family
member has several roles such as motivator, educator,
and facilitator. The head of the family or husband
plays an important role including providing
motivation, education, and facilitating the wife when
giving food to the child (Efendi and Makhfudli,
2009).
Most husbands provide support in the form of
giving time to monitor child growth and knowing the
appropriate pattern of feeding for children. A father’s
involvement is necessary and determines the
nutritional status and diet of the child (Vollmer et al.,
2015). In addition, based on demographic data most
mothers have only 1-2 children, and the number of
family members in a house is mostly more than 5
people because of living with grandparents. Other
family also took care of under-five children with
stunting.
In this study, the social and family support is
valuable in supporting and facilitating the mother in
performing activities related to feeding patterns for
under-five children with stunting. This study is
consistent with Rumaseuw's et al. (2018) study which
states that social factors and good family attachment
improve proper maternal behavior.
This research is in contrast to Isnatri's (2016)
study, which states that social and family support
factors are not related to the pattern of feeding in
under-fives with and without malnutrition. This is
because most respondents have adequate social and
family support, but the feeding pattern is not
appropriate.
Factors Affecting The Feeding Pattern of Under-Five Children with Stunting in Indonesia
233

4.6 Technological Factors in Feeding
Pattern of Under-Five Children
with Stunting
Technological factors are one of the factors that
influence a person's behavior based on culture
(Leininger, 2002). Health technology is a means of
infrastructure that allows individuals to choose or
obtain services that solve problems in health (Giger,
2013).
Nutrition in children involves adequate access to
care and feeding for children (Kim et al., 2017). In
this research most of the mothers simply use
technology that utilizes existing health service
facilities and most of the active mothers come to
Posyandu every month. Most mothers use electronic
media to get information about the appropriate
feeding patterns of toddlers according to their age.
Utilization of adequate technology in this study
caused the respondents to utilize electronic media to
identify the proper feeding patterns in toddlers.
Respondents find it easy to utilize healthcare facilities
such as attending Posyandu to monitor the growth of
children under five and it is easy to consult with
health officers at the Public Health Center. However,
based on the results obtained the lowest score is for
using print media (books, magazines, etc.). Most
respondents said they rarely get information from
books or magazines. Thus, the need is for printed
media (leaflets, booklets, etc.) in health counseling
about proper feeding for toddlers so as to support the
pattern of technology utilization to improve the
nutritional status of children. The results of this study
are also in accordance with the results of research by
Dwi Astuti, Fardhiasih; Sulistyowati (2013) shows
that the current technological developments can
easily access information from various media about
feeding patterns for stunting children, so that mothers
can improve knowledge.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the Transcultural Nursing theory approach,
the feeding pattern provided by mothers for under-
five children with stunting is influenced by economic
level, regulatory and policy factors, cultural values
and lifestyle, social and family support, and
technological factors. Factors of cultural values and
lifestyle are the most dominant factors associated
with the pattern of feeding in under-five children with
stunting.
REFERENCES
’The Ministry of National Development Planning
(Bappenas) and the United Nations Children’s Fund
(UNICEF)’ (2017) Laporan Baseline SDG tentang
Anak-Anak di Indonesia. Jakarta: BAPPENAS dan
UNICEF.
Andrews, M. M. dan Boyle, J. (2012) Transcultural
Concepts in Nursing Care. 6th edn. China: Wolters
Kluwer Health.
Black, R. E. et al. (2008) ‘Maternal and child
undernutrition: global and regional exposures and
health consequences’, The Lancet, 371(9608), pp. 243–
260. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61690-0.
Casale, D., Espi, G. and Norris, S. A. (2018) ‘Estimating
the pathways through which maternal education affects
stunting: evidence from an urban cohort in South
Africa’, Public Health Nutrition, pp. 1–9. doi:
10.1017/S1368980018000125.
Culhane-Pera, K. A. et al. (2002) ‘Cultural feeding
practices and child-raising philosophy contribute to
iron-deficiency anemia in refugee Hmong children’,
12(2), pp. 199–205. Available at:
https://www.scopus.com (Accessed: 17 May 2018).
Dwi Astuti, Fardhiasih; Sulistyowati, T. F. (2013)
‘Hubungan Tingkat Pendidikan Ibu Dan Tingkat
Pendapatan Keluarga Dengan Status Gizi Anak
Prasekolah Dan Sekolah Dasar Di Kecamatan Godean’,
Jurnal KesMas, 7(1). doi: 10.12928/kesmas.v7i1.1048.
Erika, K. A. (2016) ‘The Effect of Transcultural Nursing,
Child Healthcare Model and Transtheoretical Model
Approaches to Knowledge and Culture of Family’,
Jurnal NERS, 9(2), p. 262. doi:
10.20473/jn.V9I22014.262-269.
Fauziah, D. (2009) Pola Konsumsi Pangan dan Status Gizi
Anak Balita ang Tinggal di Daerah Rawan Pangan di
Kabupaten Banjarnegara, Jawa Tengah. Bogor
Agricultural Institute.
Giger, J. dan D. (2013) Transcultural Nursing:
Assesmentand Intervention. Canada: Mosby.
Henry, christiani J. (2015) ‘Dietary Intake Research in
Asian Children: Significance and Challenges’, Journal
of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology. Center for
Academic Publications Japan, 61(Supplement), pp.
S189–S191. doi: 10.3177/jnsv.61.S189.
Isnatri, F. (2016) ‘Analisis Faktor yang Berhubungan
dengan Pola Pemberian Makanan pada Balita Gizi
Kurang dan Gizi Buruk Berdasarkan Teori
Transcultural Nursing’. Fakultas Keperawatan
Universitas Airlangga.
Jackson, A. A. (2015) ‘Feeding the normal infant, child and
adolescent’, Medicine. Elsevier, 43(2), pp. 127–131.
doi: 10.1016/J.MPMED.2014.11.005.
Jiang, Y. et al. (2015) ‘Prevalence and risk factors for
stunting and severe stunting among children under three
years old in mid-western rural areas of China’, Child:
Care, Health and Development, 41(1), pp. 45–51. doi:
10.1111/cch.12148.
Kementerian Kesehatan - Ministry of Health/Indonesia
(2015) Rencana Strategis Kementrian Kesehatan
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
234

Republik Indonesia tahun 2015-2019, Kementerian
Kesehatan RI. Jakarta. Available at:
http://www.depkes.go.id (Accessed: 12 March 2018).
Kementerian Kesehatan - Ministry of Health/Indonesia
(2016) Situasi Balita Pendek. Jakarta. Available at:
http://www.depkes.go.id/resources/download/pusdatin
/infodatin/situasi-balita-pendek-2016.pdf (Accessed:
12 March 2018).
Kim, R. et al. (2017) ‘Relative importance of 13 correlates
of child stunting in South Asia: Insights from nationally
representative data from Afghanistan, Bangladesh,
India, Nepal, and Pakistan’, Social Science & Medicine.
Pergamon, 187, pp. 144–154. doi:
10.1016/J.SOCSCIMED.2017.06.017.
Kudlova, E. and Schneidrova, D. (2012) ‘Dietary patterns
and their changes in early childhood.’, Central
European journal of public health, 20(2), pp. 126–134.
Kumala, M. and Warsiti, W. (2013) ‘Hubungan Pola
Pemberian Makan Anak Usia Toddler (1-3 Tahun) di
Posyandu Kelurahan Sidomulyo Godean Sleman’.
Available at: http://digilib.unisayogya.ac.id/623/
(Accessed: 6 March 2018).
Lestari, S. et al. (2018) ‘The prevalence and risk factors of
stunting among primary school children in North
Sumatera, Indonesia’, IOP Conference Series: Earth
and Environmental Science, 125, p. 12219. doi:
10.1088/1755-1315/125/1/012219.
Masithah, T., Soekirman and Martianto, D. (2005)
‘Hubungan Pola Asuh Makan dan Kesehatan dengan
Status Gizi Anak Balita di Desa Mulya Harja’, Media
Gizi dan Keluarga , 29(2), pp. 29–39. Available at:
http://repository.ipb.ac.id/handle/123456789/41876
(Accessed: 6 March 2018).
Meier-Ploeger, A. (2003) ‘Motivation zur gesunden
ernährung - Genuss mit verantwortung’, pp. 215–221.
Available at: https://www.scopus.com (Accessed: 17
May 2018).
Ministry Of Health (2016) Situasi Balita Pendek. Jakarta.
Nkurunziza, S. et al. (2017) ‘Determinants of stunting and
severe stunting among Burundian children aged 6-23
months: evidence from a national cross-sectional
household survey, 2014’, BMC Pediatrics. BioMed
Central Ltd., 17(1), p. 176. doi: 10.1186/s12887-017-
0929-2.
de Onis, M., Blössner, M. and Borghi, E. (2012)
‘Prevalence and trends of stunting among pre-school
children, 1990–2020’, Public Health Nutrition.
Cambridge University Press, 15(1), pp. 142–148. doi:
10.1017/S1368980011001315.
Ramli et al. (2009) ‘Prevalence and risk factors for stunting
and severe stunting among under-fives in North Maluku
province of Indonesia’, BMC Pediatrics, 9(1), p. 64.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2431-9-64.
Rumaseuw, R. et al. (2018) ‘Factors Affecting Husband
Participation in Antenatal Care Attendance and
Delivery’, IOP Conference Series: Earth and
Environmental Science, 116, p. 12012. doi:
10.1088/1755-1315/116/1/012012.
Subarkah, T., Nursalam, N. and Rachmawati, P. D. (2017)
‘Feeding pattern toward the increasing of nutritional
status in children aged 1-3 years’, INDONESIAN
NURSING JOURNAL OF EDUCATION AND CLINIC
(INJEC), 1(2), p. 146. doi: 10.24990/injec.v1i2.120.
Vollmer, R. L. et al. (2015) ‘Association of fathers’ feeding
practices and feeding style on preschool age children’s
diet quality, eating behavior and body mass index’,
Appetite. Academic Press, 89, pp. 274–281. doi:
10.1016/J.APPET.2015.02.021.
Welasasih, B. D. et al. (2012) ‘Beberapa Faktor yang
Berhubungan dengan Status Gizi Balita Stunting’, The
Indonesian Journal of Public Health, 8(2), pp. 99–104.
Available at: http://journal.unair.ac.id/download-
fullpapers-2. Beberapa Faktor yang Berhubungan
dengan.pdf (Accessed: 6 March 2018).
Factors Affecting The Feeding Pattern of Under-Five Children with Stunting in Indonesia
235
