
Dental Caries Based on Age Under Five Years Old Children
Ristya Widi Endah Yani
Dental Public Health Department, Faculty of Dentistry, University of Jember
Jalan Kalimantan No. 37, Kampus Tegalboto, Sumbersari, Jember, Sumbersari, Kabupaten Jember, Jawa Timur 68121
Keywords: Dental Caries, Age, Under Five Years Old Children.
Abstract: Children under 5 years old has the most risk in having dental caries and its percentage reaches 40-70%. It
happens because they do not show positive attitude towards their own dental hygiene. The objective of this
study is to analyze the correlation between the children’s dental caries and their age. Analytic observational
research and cross-sectional approach was done in January 2018. This study involved under five years old
children in Glingseran Village, Bondowoso Indonesia. The purposive sampling was done and 56 sample
were examined ( 33 boys and 23 girls). The variable was dental caries and the children ages. The
measurement is dental diagnosis code which consists of , PI (pulp irritation), PH (pulp hiperemia), PG
(pulp gangrene) and RG (radix gangrene). The data was drawn in frequency distribution table and figure,
and Spearman correlation was done for analyzing the relationship between dental caries and the children
ages. It was found there is correlation between dental caries to the under five years old children (p>0,05). In
other words, the higher age of children, the more dental caries they will have. In conclusion, there is a
correlation between dental caries to the under five years old children.
1 BACKGROUND
It is reported that there are 90% of rampant caries
prevalence. Moreover, the most untreated caries are
belong to children. Some sources reported that there
is 29% rampant caries prevalence of the five years
old children in Denmark, 39% in Norwegia, 40% for
England 43% Greece, and 55% in Scotland (Leroy,
2011). On the other hand, ECC prevalence in
England, Finland, USA, Indonesia, Western China,
Hong Kong, and Taiwan are reported 4%, 6%,
20.2%, 48%, 20.2%, 31.5% and 56% (Tang et al.,
2012).
The highest prevalence of Oral and Dental
problem is dental caries. It has the high percentage
that shows 40%-75% which are belonging to the
children within 3-5 years old. Seven out of ten
children under 5 years old have caries on their baby
teeth. In addition, the most common dental caries on
their baby teeth is rampant caries. This kind of caries
mostly found to the children within the age of 1-5
years. (Maharani dan Rahardjo, 2012). Furthermore,
Data Riskesdas (2013) states that the percentage of
people who has oral and dental problem is
increasing from 2007 until 2013 and the percentage
is showing 23,2% to 25,9%. Dental caries to the
children under five years old also shows
improvement, which reaches 10,4% (Riskesdas
2013).
Rampant caries prevalence has the highest
position in all around the World. Indonesia is
reported having the oral and dental problem for the
baby teeth dealing with the untreated rampant caries.
It becomes such a serious problem regarding to the
children’s oral and dental health. The fact found that
there were many children under five years old who
have rampant caries. Thus, this study is intended to
know the condition of the dental and oral health of
children under five years old. Thus, it will help to
achieve the goal in putting the effort of concerning
the dental and oral health for children under five
years old (Winda dkk, 2015).
Children under five years old belong to the most
highly risk for having dental and oral health
problem. It happens because they have bad habit that
is causing oral and dental problem (Worotitjan dkk.,
2013). Further, those who have this serious problem
come from the family which has the low level in
economy and education. However, the parents take
the important roles for their children especially in
having dental and oral health problem. They decide
whether or not they will take their own children to
Yani, R.
Dental Caries Based on Age (Under Five Years Old Children).
DOI: 10.5220/0008320500610066
In Proceedings of the 9th International Nursing Conference (INC 2018), pages 61-66
ISBN: 978-989-758-336-0
Copyright
c
2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
61
see the dentist treat the children’s caries. (Leghari,
2012).
Untreated caries can cause ache, loosing tooth,
infection, and other consequential causes which tend
to increase year by year. Dental caries which
belongs to enamel (pulp irritation) usually having no
treatment until it becomes pulp gangrene even, radix
gangrene, when the children feel the ache, at the
same time, the parents will look for the medicine
(Yani, 2016). Based on the explanation above, the
researcher is interested in conducting a research
entitled, “Dental Caries Based on Under Five Years
Old Children”
2 METHODS
Analytic observational research with cross-sectional
approach was conducted. This research was
conducted in Glingseran village, Wringin district,
Bondowoso Indonesia in February 2017. The
population involved is under five years old children
who live at Glingseran village and there are 44
sample through purposive sampling. Meanwhile, the
variables are dental caries and age. Dental caries is
measured by dental diagnosis code based on
International Classification of Diseases to Dentisry
and Stomatology that consists of pulp irritation, pulp
hyperemia, pulp gangrene and radix gangrene, while
the age variable is using the measurement data from
health mom and children book. The data will be
drawn through the frequency distribution table and
figure. Then, it is being analyzed by spearman
correlation for analyzing the relationship between
dental caries and the children ages.
3 RESULTS
The research to the five years old children in
Glingseran village, Wringin district, Bondowoso
Indonesia with the data of 44 samples showed as
follows.
To know the distribution of the children’s age
with pulp irritation diagnose can be seen this
following Table.
The distribution of the children ages with the
pulp hyperemia diagnose can be seen in Table 3.
The following table, Table 4, refers to the
distribution of the Children Ages with the gangrene
pulp Diagnose
The Distribution of the Children’s Age with
radix gangrene diagnose can be seen in Table 5.
To know the relationship of dental caries and the
children’s ages, correlation spearman test is
conducted through this following table.
Table 1: Respondents’ distribution characteristic
based on ages (under five years old children).
Age (month)
Total
%
1-12
20
35.71
13-24
7
12.50
25-36
10
17.86
37-48
5
8.93
49-60
14
25.00
Table 2: The distributions of the children’s age with
pulp irritation diagnose.
Age (Month)
Pulp Irritation
%
1-12
0
0
13-24
0
0
25-36
4
7.14
37-48
2
3.57
49-60
0
0
Figure 1: Diagram of the distribution of the children’s
age with pulp irritation diagnose.
Tabel 3: The distribution of the children ages with the
pulp hyperemia diagnose.
Age (month)
Pulp Hypermia
%
1-12
0
0
13-24
0
0
25-36
0
0
37-48
0
0
49-60
0
0
0 0
4
2
0
0
1
2
3
4
5
Total of Children
Pulp
Irritation
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
62

4 DISCUSSION
Table 1 shows there are 20 respondents (35.71%)
who belong to the children within the age of 1-12
month. There are 7 respondents (12.50%) who
belong to the children within the age of 13-24
month. There are 10 respondents (17.86%) who
belong to the children within the age of 25-36
month. There are 5 respondents (8.93%) who belong
to the children within the age of 37-48 month, and
14 respondents (25.00%) who are children within
the age of 49-60 month. The highest total of the
Figure 2: Diagram of the distribution of the children’s
age with pulp hyperemia diagnose.
Table 4: The distribution of the children’s ages with
pulp gangrene diagnoses.
Age (month)
Pulp Gangrene
%
1-12
0
0
13-24
1
1.79
25-36
6
10.71
37-48
1
1.79
49-60
2
3.57
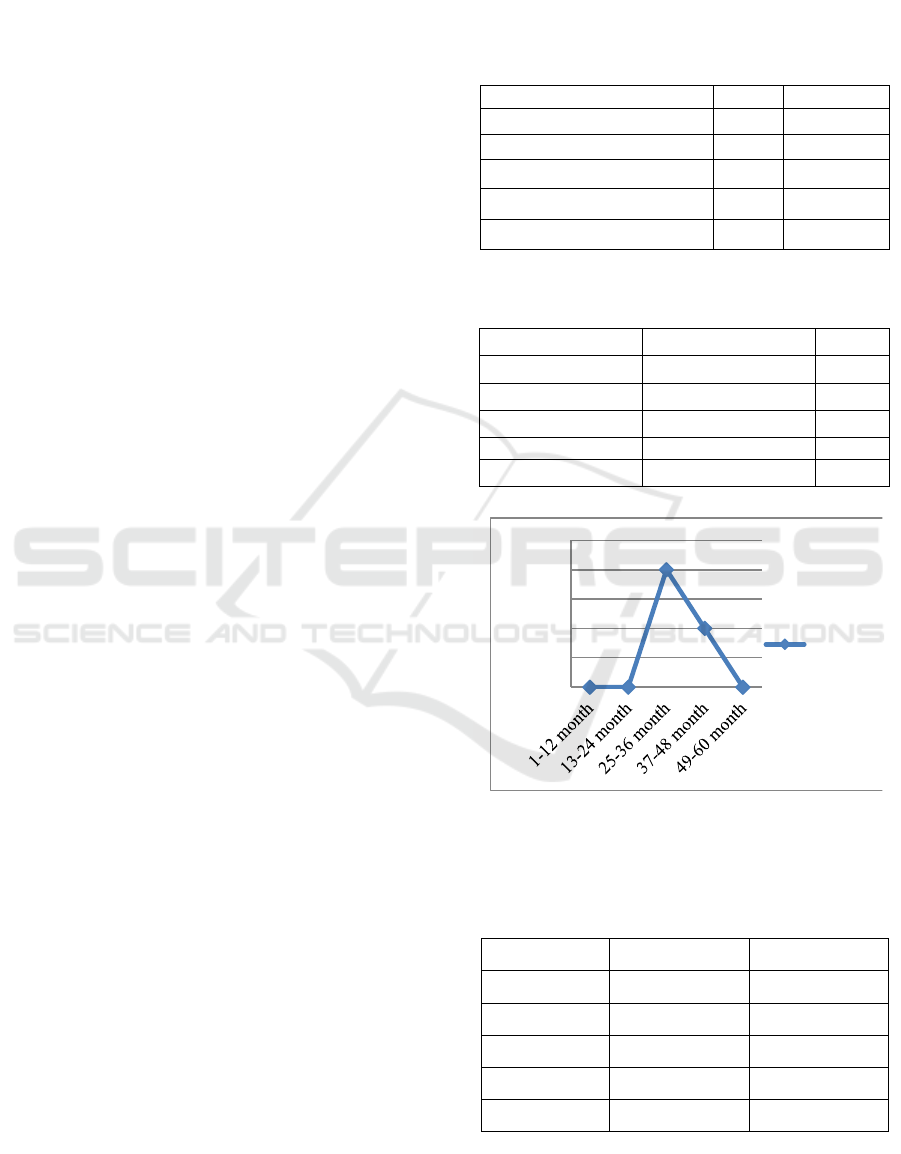
Figure 3: Diagram of the distribution of the children’s
age with pulp gangrene diagnose.
0
1
2
3
4
5
Total of The Children
HP
0
1
6
1
2
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1-12
month
13-24
month
25-36
month
37-48
month
49-60
month
Total of The Children
Pul
p
G…
Table 5: The distributions of the children’s age with
radix gangrene diagnose.
Age (month)
Radix Gangrene
%
1-12
0
0
13-24
0
0
25-36
0
0
37-48
0
0
49-60
1
1.79
Figure 4: Diagram of the distribution of the children’s
age with radix gangrene diagnose.
Table 6: Correlation spearman test for dental caries
and children’s ages.
Variable
p-value
Result
Dental caries-
Children’s Ages
0,000
There is a
relationship
0
1
2
3
4
5
1-12
month
13-24
month
25-36
month
37-48
month
49-60
month
Total of The Children
Radix
Gangr
ene
Dental Caries Based on Age (Under Five Years Old Children)
63

respondents belong to the children within the age of
0-12 month.
Table 2 and figure 2 shows there is no children
within the age of 1-24 month who have pulp
irritation. There are 4 children within the age of 25-
36 month who have pulp irritation. There are 2
children within the age of 37-48 month who have
pulp irritation, while for those who are 49-60 month
old have no pulp irritation. It can be said that mostly,
the children within the age of 25-36 month have the
pulp irritation.
The highest percentage of children within the age
of 25-36 month who have dental caries of pulp
irritation can happen because of some factors. The
first is their baby teeth have growth perfectly so they
start to eat cariogenic, while its condition is so
highly risk because the enamel and the dentin are so
thin, pulp cavity is and the pulp horn is tall so it
causes the dental caries for the baby teeth easily.
The enamel of the baby teeth has less in
mineralization so the mineral of its enamel is less
than permanent teeth (Baginska, 2014).
Table 3 and figure 3 show that children within
the age of 1-60 month have no pulp hyperemia.
Enamel and dentin of the baby teeth are thinner than
the permanent ones. There is no pulp hyperemia
found because the process if dental caries is done
quickly and it can be related to the baby teeth
morphology which has wide pulp cavity also the thin
enamel and dentin range. Moreover, when the pulp
irritation has no treatment, dental caries will get
worse quickly becoming pulp hyperemia and it takes
less time to be pulp irritation. Some of parents do
not care and understand dealing with oral and dental
health. Commonly, they do not realize about dental
caries to their children and tend to ignore it. It
makes pulp hyperemia growths quickly to the worse
condition (Baginska, 2014). It causes that there is no
found of pulp hyperemia.
Table 6 shows that there is a relationship of the
dental caries with the children’s age (p>0,05). The
elder of children, the more dental caries will found.
The higher age of the children, the more dental
caries they will have. Under five years old children
who have the less dental caries are those within the
age of 0-12 month. One of the factors to avoid dental
caries is through giving breast milk exclusively
because it contains non-cariogenic. Giving breast
milk more than 40 days will obstruct the growth of
bacteria which causes caries, Streptococcus mutants.
Caries index is improving to the non-breast milk
(common milk) that contains lots of sugar. Breast
milk must be given for those who are 0-24 month,
and they consume breast milk mostly than others, so
they have less risk in having dental caries.
The habitual of consuming sticky and sweet
foods, also having milk before going to sleep,
adding some sugar to children’s food, giving fiber
foods, and some snack make the increasing causes of
dental caries. Some foods which contain liquid
texture will be easier to be cleaned up and it will
avoid the dental caries (Ramayanti dan Purnakarya,
2013). Widayati (2014), states that there are 88,4%
children within the age of 3-6 years old who likely
to consume sweet and sticky food and contains
carbohydrate. On the other hand, various kinds of
foods that they consume make less of them have no
dental caries. As it has been stated before, dental
caries belong to the multifactorial disease that comes
from host, time, substrate, and bacteria. That is why,
the consuming food of the children within the age of
3-5 years old is various and it gives influence of the
substrate to their dental surface, and the most highly
risk is baby teeth. Moreover, the total host which
belongs to the growth of substrate and bacteria also
the certain time are needed to create dental caries.
Children still have bad attitude and habitual
dealing with their oral and dental problem. Their less
attention of looking after their teeth can be caused of
their parents’ knowledge regarding to oral and dental
health. Notoatmodjo states that attitudes and
knowledge comes second after practices, and it is
well known as K-A-P (knowledge-attitude-practice)
(Notoatmodjo, 2007). This case shows that mothers’
practices and attitude in treating their oral and dental
health is influenced by their knowledge. Commonly,
the mothers think that the baby teeth are not
important so, even it becomes decay, it brings no
problem as long as permanent ones will change it.
Nevertheless, it must be stressed that the function of
baby teeth is to help the process of chewing and as
the guidelines of the growth of permanent ones.
Table 4 shows the children within the age of 1-
12 month have no pulp gangrene. There is 1 child
within the age of 13-24 month who has pulp
gangrene. There are 6 children within the age of 25-
36 month who have pulp gangrene. There is 1 child
within the age of 37-48 month who has pulp
gangrene. Meanwhile, there are 2 children within the
age of 49-60 month who have pulp gangrene. It can
be said that the most children who have pulp
gangrene are those who are 25-36 month old. It is in
line with a research that was conducted by Sari
(2017), that showed that there are two third out of all
the children above 3 years old have dental caries.
The dental caries happen is influencing of four main
factors, host (teeth surface), microorganism (bacteria
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
64

of causing dental caries), substrate (fermentation
carbohydrate) and time. (Yulita, 2013).
Besides those factors, the important one is the
under five years old children are not able yet to look
after their teeth. The parents also assume that the
baby teeth are not that too important because they
will be changed with permanent ones. This thought
drives the parents tend to ignore their children’s oral
and dental health problem so it increases the risk of
dental caries (Suarniti, 2014). The parents are likely
to give no treatment for their children’s dental caries
until becoming worse. The first stage of caries which
coming through pulp irritation is usually does not
bring pain and then it grows becoming pulp
gangrene. If the stage reaches pulp gangrene, the
children will feel the pain and the parents will bring
the children to see the dentist (Yani dkk, 2015).
Besides, the highest case of pulp gangrene also
happens because the children tends to eat many
various food. Widayati (2014) says that there are
88.4% of the children within the age of 1-6 years old
who likes to consume sweet food, sticky food and
containing carbohydrate. Besides, Public Health
England/PHE (2017) also states that the increase of
dental caries risk to the children happens when they
start eating every food and drink except milk and
breast milk, yet still need some food and drink that
contains sugar(PHE, 2017). The kind of food that is
sweet and stick also carbohydrate, that have been
stated by Widayati, belong to cariogenic food and it
is easy to stick on the teeth. It causes the increasing
of high risk dental caries.
Table 5 shows that there is no child within the
age of 1-36 months who has radix gangrene. There
is one child found for each within the age of 1-36
month and 49-60 month who have radix gangrene.
Some developing country such as Indonesia is
causing decay tooth with the percentage reaches 80-
90% to the under five years old children (Winda,
2015). Survey Public Health England 2015 in PHE
(2017) said that 25% of children under five years old
in England have dental caries. Further, they have 3-4
teeth for each and most of them do not have any
treatment for the caries. Besides that, the appearing
dental caries also take time. Casamassimo dkk
(2013) states that dental caries can happen because
of some factors, such as host (tooth and saliva),
microorganism, substrate, and time. This statement
make the researcher assume that to reach the radix
gangrene stage, dental caries do take time. This
research proves it by looking at the radix gangrene
case which appears to those who are 4 and 5 years
old.
Parents’ knowledge dealing with oral and dental
problem also give influence for the radix gangrene
case. They likely pay no attention of their children’s
dental caries because there is no complain of any
aches of the children’s teeth. Moreover, they tend
thinking that the baby teeth are not worth it because
it will be changed to the permanent ones. That is
why, it causes the growth of dental caries becomes
worst to the radix gangrene level (Nugroho, 2014;
Sibarani, 2016). Children within the age above five
years old belong to the transition age when they start
consuming some food which they commonly like the
most, such as sweet and sticky food and they often
eat those foods so it increases the causing of dental
caries. (Leghari, 2012; Winda, 2015). The highly
risk of dental caries causes of how long the time will
take for the teeth to be in oral cavity with high
frequency and exposing cariogenic.
5 CONCLUSIONS
There is relationship between dental caries and the
age of children. The higher age of the children, the
more dental caries they will have .
REFERENCES
Baginska J, Rodakowska E, Milewski R, Kierklo A. 2014.
Dental Caries In Primary And Permanent Molars In
7-8-Year-Old Schoolchildren Evaluated With Caries
Assessment Spectrum And Treatment (CAST) Index.
BMC Oral Health. 14:74
Bernadetha B Sibarani., 2016. Pola Makan dan Profil
Status Gizi Anak Balita di Posyandu Jakarta Utara
[Skripsi]. Bogor : Institut Pertania Bogor.
Casamassimo, P.S., Fields, H.W., McTigue, D.J., Nowak,
A.J. 2013. Pediatric Dentistry: Infancy Through
Adolescence 5
th
Edition. Missouri: Elsevier. 178:183 p.
Handayeni, Ratih, 2015. Hubungan Riwayat ASI Eksklusif
dan Tingkat Pendidikan Ibu dengan Kejadian Karies
Gigi Balita di Posyandu Ambarsari, Damping I,
Sleman. Stikes AISIYAH: Yogyakarta
Leghari MA, Tanwir F, Ali H. 2012. Dental Caries
Prevalence And Risk Factors Among Schoolchildren
Age12-15 Years In Malir, Karachi. Pakistan Oral &
Dental Journal. 32 (3): 484-488.
Leroy R, Bogaerts K, Martens L, Declerck D. 2010. Risk
Factors for Caries Incidence in a Cohort of Flemish
Preschool Children. Clinical Oral Investigations. Vol.
12. No. 4
Maharani, D.A., Rahardjo, Anton. 2012. Mother’s Dental
Health Behaviors and Mother-Child’s Dental Caries
Experiences : Study of A Suburb Area in Indonesia.
Makara Kesehatan, 16 (2) : 72-76.
Dental Caries Based on Age (Under Five Years Old Children)
65

Notoatmodjo, S., 2007. Metodologi Penelitian Kesehatan.
Jakarta: PT Rineka Cipta.
Nugroho, Christianto. Hubungan Pengetahuan Dengan
Sikap Ibu Dalam Perawtan Gigi Anak Usia Pra
Sekolah. Jurnal AKP. Januari-Juni 2014; 5(1).
Public Health England. Guidance, Health Matters: Child
Dental Health. Juni 2017.
Ramayanti, S. dan Purnakarya. 2013. Peran Makanan
Terhadap Kejadian Karies Gigi. Jurnal Kesehatan
Masyarakat. 7(2):1-5.
Riskesdas. 2013. Laporan Hasil Riset Kesehatan Dasar,
Departemen Kesehatan RI. Jakarta. 118-119
Sari, Endah Purwani. 2017. Hubungan Pemberian Susu
Formula dengan Karies Gigi pada Anak Prasekolah di
TK Dayyinah Kids.Akademi Kebidanan Dharma
Husada. Pekanbaru
Suarniti, Luh putu. 2014. Pencabutan dini gigi sulung
akibat karies gigi dapat menyebabkan gigi crowding.
Jurnal kesehatan gigi Vol 2. No.2
Tang Ru-Shing, Meng-Chuan Huang, Shun-Te Huang.
2012. Relationship between dental caries status and
anemia in children with severe early childhood caries.
Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences; xx, pp. 1-7
Widayati, N. 2014. Factors Associated with Dental Caries
in Children Aged 4-6 Years Old. Jurnal Berkala
Epidemiologi. 2(2): 196–205.
Winda, S. U., Paulina, G., Dinar. A. 2015. Gambaran
Karies Rampan Pada Siswa Pendidikan Anak Usia
Dini Di Desa Pineleng Ii Indah. Jurnal e-GiGi (eG).
3(1): 1-7.
Worotitjan Indry, Mintjelungan N. Christy, Gunawan
Paulina. Pengalaman karies gigi serta pola makan dan
minum pada anak sekolah dasr di desa kiawa
kecamatan kawangkoan utara. Jurnal e-GiGi (eG);
2013 mar:1(1):60-8.
Yani, R.W.E., Hadnyanawati, H., Kiswaluyo, Meilawaty,
Z. Gambaran Tingkat Keparahan Karies Gigi Anak
Sekolah Dasar di 10 Kecamatan Kabupaten Jember.
Bagian Ilmu Kesehatan Mayarakat Fakultas
Kedokteran Gigi Universitas Jember. Jurnal
Stomatognatic K. G. Unej. Desember 2015; 12(2): 42-
45.
Yulita, Ita, dkk. 2013. Air Susu Ibu dan Karies Gigi
Sulung. Poltekkes Kemenkes. Jakarta.
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
66
