
Empirical Antibiotics Study on Pneumonia in Intensive Care Unit
Yeni Farida, Katarina Puspita and Zahra Yusvida
Department of Pharmacy, Faculty of Mathematics and Science, Universitas Sebelas Maret, Ir.Sutami Street No. 36A
Kentingan, Surakarta, Central Java, Indonesia
Keywords: Bacterial culture, Empiric antibiotics, Intensive care unit, Pneumonia
Abstract: Microorganisms and inflammatory cells are present in the air sacs of the lungs in most pneumonia patients,
preventing their lungs from functioning normally. The main treatment for pneumonia is antibiotics
supported by physiotherapy. This study aimed to determine the pattern of empirical antibiotic use and
bacterial etiology (sputum culture test) of ICU patients at a government hospital in Madiun, West Java. This
descriptive research used retrospective data collected from January to December 2016. The samples were
purposively selected based on specific inclusion criteria (i.e., patients diagnosed with pneumonia who
received antibiotic therapy and had information on their bacterial culture data). The study examined the
medical records of 77 subjects who were mostly aged 0-5 years old (67.5%). Acinetobacter baumannii was
the most commonly isolated organism (42.1%), followed by Klebsiella pneumonia and Pseudomonas
aeruginosa (15.79%). Meropenem was mostly used as a single antibiotic in pediatrics (24%), while
ceftriaxone was most common in adult (16.22%). The most widely used combinations of antibiotics were
ampicillin and gentamycin for pediatrics ICU patient (20%) and meropenem and metronidazole for adult
patients (13.51%). Acinetobacter baumannii was completely resistant to Ampicillin-sulbactam and partially
resistant to other beta-lactam antibiotics. Both Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Klebsiella pneumonia were
completely resistant to Ampicillin and Ampicillin-sulbactam.
1 INTRODUCTION
Pneumonia is one of the common infections that
require hospitalization and is considered one of the top
causes of death, especially in developing countries.
Basic health research in Indonesia claims that
pneumonia is the second leading cause of death after
diarrhea (Indonesian Health Ministry, 2013). The
mortality rate of hospitalized pneumonia patient is
15.5-24.8 % (Firmansyah et al., 2015). Furthermore,
the mortality rate for intensive care unit (ICU) patients
with pneumonia remains high, approximately 15-50 %
(Li et al., 2016). Ventilator-associated pneumonia
(VAP) is the most frequent infection in patients
admitted to ICU (Chawla, 2008). Most deaths in
pneumonia are attributable to VAP.
Empiric antibiotic therapy is highly recommended
to begin soon after the diagnosis, which is within 6
hours, to reduce the mortality and morbidity rate
(Harris et al., 2017). Ideally, antibiotic therapy can
cure pneumonia patients without causing
complications or contributing to the development of
antibiotic resistance (Stralin, 2008). IT requires proper
antibiotic choice based on sputum bacterial sensitivity
culture test. The bacterial etiology pattern of
pneumonia differs from one region to another. The
selection of antibiotics has to be based on the profile of
the local bacterial etiology and antibiotic susceptibility
(Hsueh et al., 2011).
In this study, we determined the pattern of
empirical antibiotic use and bacterial etiology based on
sputum culture test.
2 MATERIALS AND METHOD
2.1 Study Design
The retrospective study was designed by collecting
data from patients’ medical record. The data included
patient characteristics, empirical antibiotics use,
bacterial culture information, and antibiotics
susceptibility test data.
48
Farida, Y., Puspita, K. and Yusvida, Z.
Empirical Antibiotics Study on Pneumonia in Intensive Care Unit.
DOI: 10.5220/0008239200480053
In Proceedings of the 1st Muhammadiyah International Conference on Health and Pharmaceutical Development (MICH-PhD 2018), pages 48-53
ISBN: 978-989-758-349-0
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
2.2 Patient and Setting
This study focused on ICU patients at a government
hospital in Madiun, West Java starting from January
until December 2016. Patients admitted to ICU during
this period, who recieved antibiotic therapy for at least
three days, and had bacterial culture data were eligible
as samples in this study.
2.3 Data Analysis
The patient profile was analyzed descriptively by
calculating the percentage of sex, age, length of stay
(LOS), and the type of antibiotics use. The antibiotics
use was grouped into two, namely single-use and
combination. The percentage of each type of
antibiotics use was calculated. Bacterial etiology and
the pattern of antibiotics resistance were identified
from the bacterial culture data.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Patient Characteristic
This study involved 77 patients, including neonates,
infants, toddlers, adults, and geriatrics. The age range
of the patients was from 1 day old to 72 years old. No
patients from the age range of child and adolescent
were identified in this study. The distribution of
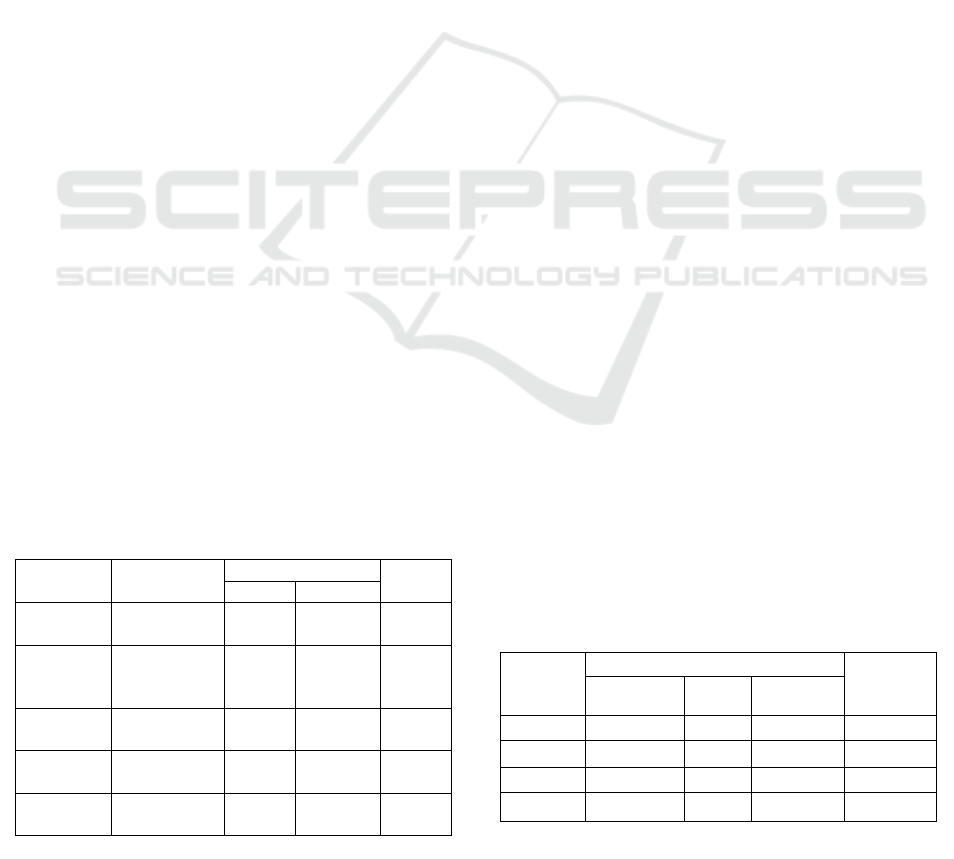
patient age and gender is presented in Table 1.
The highest frequency of pneumonia cases was
found in the age range of <5 years old. Other studies
state that the incidence of pneumonia is dominant in
population aged younger than 5 years old and older
than 65 years old (Eida et al., 2015; Rozenbaum et al.,
2015). However, in this study, the proportion of
geriatric patients admitted to ICU is relatively small.
The results of this study are in line with a study in the
Philipines, a neighboring country of Indonesia, which
claims that the majority of pneumonia episodes occurs
in children aged < 2 years old (Kosai et al., 2015).
Table 1 also shows that the incidence of
pneumonia is similar in male and female patients. In
adult or geriatric patients, the incidence of pneumonia
in both sexes is nearly similar. While many studies
believe that gender contributed contributes to the risk
factor of pneumonia differently (Falagas et al., 2007;
Rozenbaum et al., 2015), another study reveals that
mortality rate among pneumonia patients doesn not
differ in gender (Gannon et al., 2004). On the contrary,
this study affirmed that either male or female had the
same chance of contracting pneumonia. Nevertheless,
compared with the other studies, this research had a
limited number of samples.
There are any risk factors related to pneumonia.
Besides age and sex, the other factors that contribute to
the incidence of pneumonia are chronic comorbidities,
exposure to cigarette smoke, alcohol abuse,
malnutrition, conditions that promote pulmonary
aspiration or inhibit coughing, and exposure to
contaminated respiratory equipment. Unfortunately,
this study could not evaluate these factors due to the
lack of retrospective data.
The length of stay of the patients in the ICU ranged
from 1 to 26 days. shows that most of the patients are
hospitalized in the ICU for 0-7 days. The average
lenght of stay is 8.5 days in pediatric patients and 9.5
days in adult and geriatric patients. It is substantially
shorter than the result of a study in the Netherlands
(i.e., 15.2 days) (Rozenbaum et al., 2015).
3.2 The Bacterial Etiology and Antibiotic
Susceptibility Test
The obstacles in this study lie in the limited bacterial
culture data due to financial problem. Bacterial culture
was not performed in all patients (19 out of 77
patients). Gram-negative bacteria were the dominant
pathogen that caused pneumonia in this study. Gram-
positive usually cause community-acquired pneumonia
(CAP), while gram-negative bacteria are behind
Table 1: The characteristics of the patients observed in this
study
Patient
(N= 77)
Age
Gende
r
(%)
Male Female
Neonates
0 – 1 month
(
n=17
)
7 10 22.08
Infants
1 month –
2years
(
n=33
)
17 16 42.96
Todlers
2–5 years
(n=2)
2 - 2.60
Adults
18–64 years
(n=18)
12 13 32.57
Geriatrics
≥ 65 years
(
n=7
)
4 3 9.09
Table 2: The length of stay in the intensive care unit (ICU)
Length
of Stay
(days)
Frequency (N=77)
Total
Pediatric Adult Geriatric
0 – 7 29 4 4 37
8 – 14 16 8 3 27
15 – 21 4 3 - 7
≥ 21 3 3 - 6
Empirical Antibiotics Study on Pneumonia in Intensive Care Unit
49
hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) (Cukic and
Hadzic, 2016). Based on the microbiological
observation results, the most bacterial etiologic agents
in ICU patients were Acinetobacter baumannii
(42.11%), followed by Klebsiella pneumonia and
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (15.79%). This result is in
line with a study in Thailand and India (Chawla,
2008). A study in the United States also confirms that
Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Klebsiella pneumonia
are two of the three major microorganisms that cause
HAP. The etiological bacteria in the observed patients
are listed in Table 3.
Acinetobacter baumannii has high survivability
and can form colonies outside the human body
(Uwingabiye, 2017). It is discovered as the main
nosocomial pathogen, that causes severe infections in
patients treated in (ICUs) (Sileem et al., 2017). A
study in Poland reveals that Acinetobacter baumannii
is the most frequent pathogen of VAP (53.3%)
(Duszynska et al., 2018).
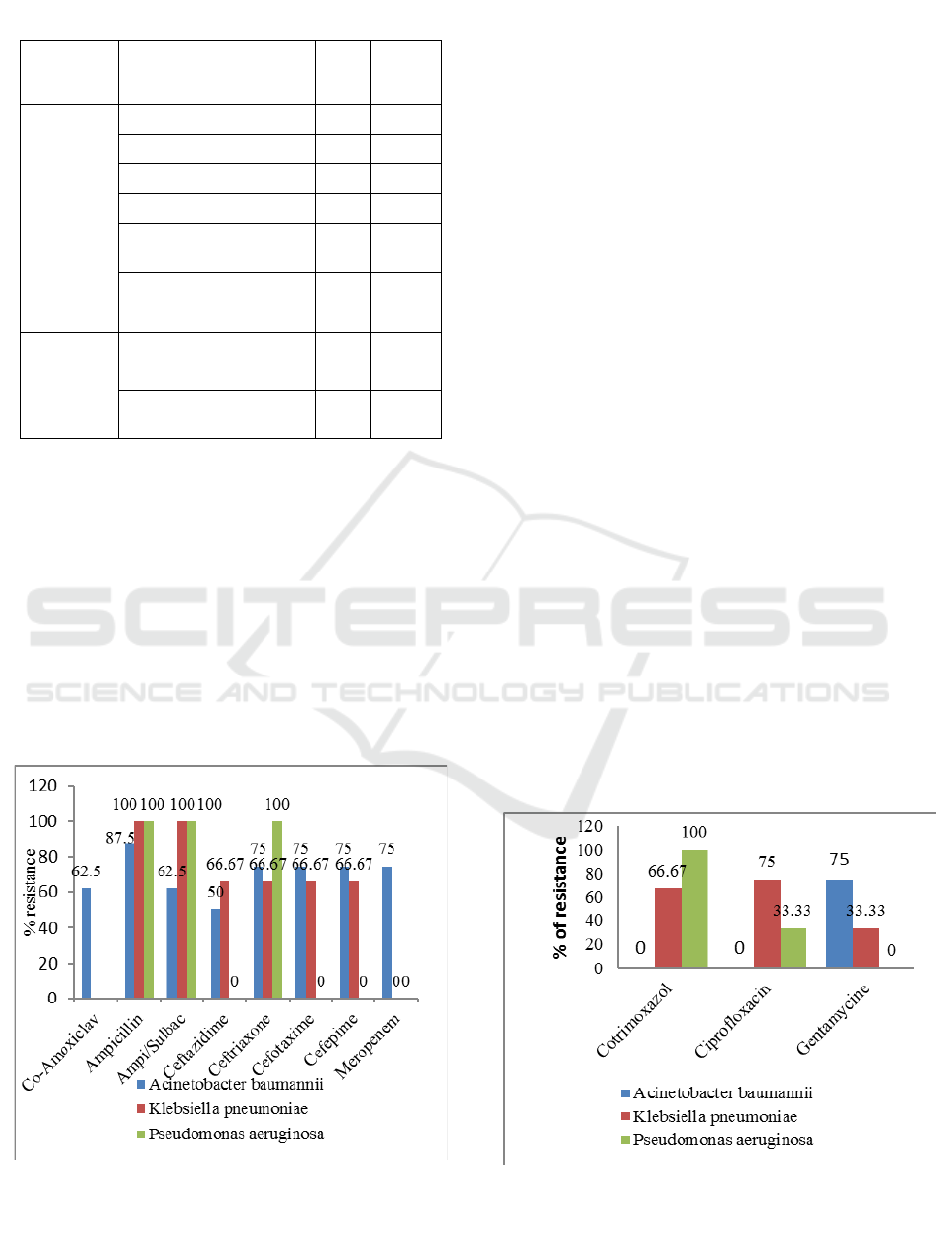
Based on Figure 1, the isolated bacteria in ICU
patients are resistanr to nearly all beta-lactam
antibiotics. This study found that Acinetobacter
baumannii was completely resistant to Ampicillin-
sulbactam and partially resistant to other beta-lactam
antibiotics. Both Pseudomonas aeruginosa and
Klebsiella pneumonia were completely resistant to
Ampicillin and Ampicillin-sulbactam. However,
several cephalosporine antibiotics were not effective
for treating the infections caused by Pseudomonas
aeruginosa and Klebsiella pneumonia.
Aside from being resistance to beta-lactam
antibiotics, the pathogens had developed the ability to
adapt to Cotrimoxazole and Ciprofloxacin, except for
Acinetobacter baumannii. Because Pseudomonas
aeruginosa and Klebsiella pneumonia are highly
resistant to gentamycin, this antibiotic is not preferable
for treating their infections.
Multiple drug-resistant pathogens have increased in
hospitalized pneumonia, especially in the ICU
(Cilloniz et al., 2016). The bacteria that causes HAP
are more difficult to overcome due to its high
resistance level to several antibiotics.
Table 3: The bacterial etiology in ICU
Bacterial
type
Bacterial species
freq.
%
Gram-
negative
(N = 17)
Acinetobacter baumannii 8 42.11
Klebsiella pneumonia 3 15.79
Pseudomonas aeruginosa 3 15.79
Pasteurella pneumotropic 1 5.26
Pseudomonas
oryzibabitans
1 5.26
Stenotrophomonas
maltophilia
1 5.26
Gram-
positive
(N = 2)
Staphylococcus aureus
(MRSA)
1 5.26
Staphylococcus aureus 1 5.26
Figure 2: The pattern of bacterial resistance to other
antibiotics
Figure 1: The pattern of bacterial resistance to beta-lactam
antibiotics
MICH-PhD 2018 - 1st Muhammadiyah International Conference on Health and Pharmaceutical Development
50
3.3 Empirical Antibiotics Use
Antibiotics are the major therapy in infection cases
like pneumonia. The selection of appropriate
antibiotics can increase the success rate of therapy and
reduce the risk of death. A quick and precise
administration of empirical antibiotics can
immediately fix common symptoms of pneumonia,
such as fever and rapid breathing or tachypnea (Hazir
et al., 2013).
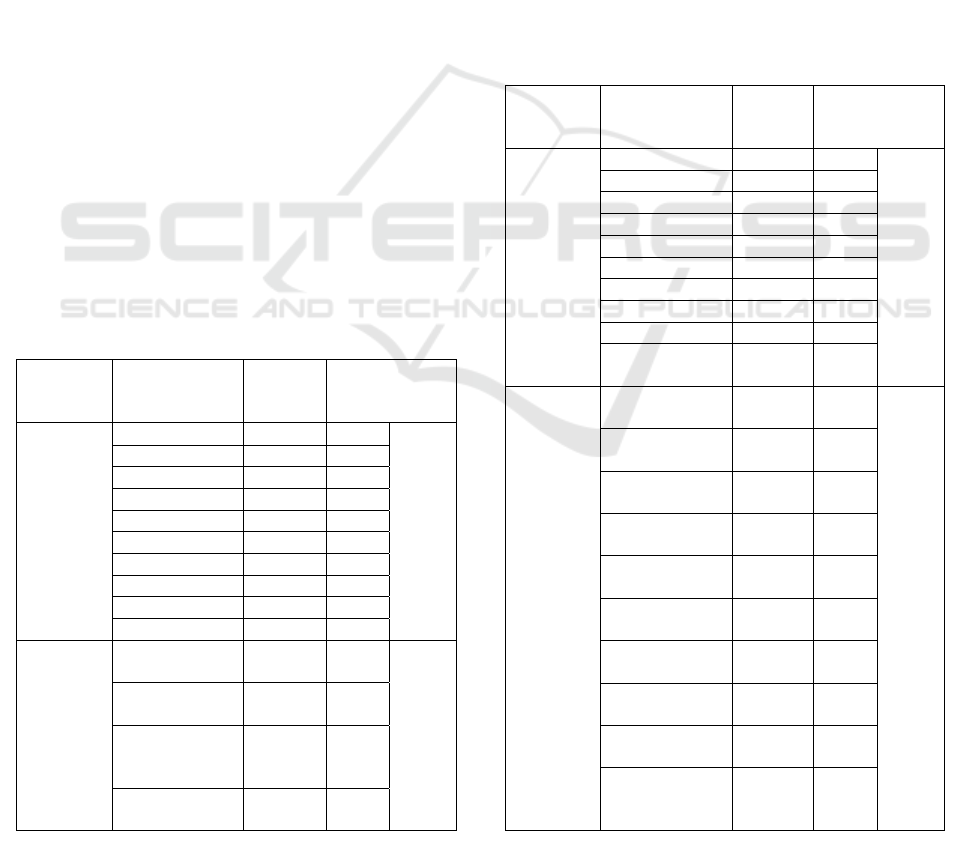
The antibiotic use of the patients in this study
presented in Tables 4 and 5. The mostly used single
antibiotics in pediatric case are cefotaxime, while
ceftriaxone is commonly prescribed to adult and
geriatric patients. Cefotaxime is the most preferred
antibiotics because of it is as effective as ampicillin-
sulbactam to treat pneumonia (Puspitasari et al., 2014).
Cefotaxim and ceftriaxone, the third generation of
cephalosporine, are a broad-spectrum antibiotic.
Patients with severe pneumonia should be treated with
broad-spectrum antibiotics before the etiologic
bacterial agent is detected (Stralin, 2008).
Nevertheless, a study confirms that there are no
differences in patient outcomes between the narrow-
spectrum and the broad-spectrum antibiotic treatment
(Williams et al., 2013).
Based on Tables 4 and 5, Ampicillin-gentamycin is
dominantly used in pediatric cases. In line with this
study, (Lodha et.al., 2013) suggest the combination
of ampicillin-gentamycin for pediatric inpatient with
severe and very severe pneumonia. When combined
with ampicillin, gentamycin produces a potent
bactericidal effect. It increases the drug uptake by the
inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis. Penicillin
alters the structure of the cell wall, allowing
gentamycin to penetrate easier into the bacteria
(Katzung, 2014).
Meropenem is an empirical antibiotic for severe
infection both in adult and pediatric patients (Baldwin
et al., 2008). Based on Table 5, the combination of
meropenem and metronidazole is the most prescribed
antibiotics in adult and geriatric patients. It is expected
to achieve broader therapeutic targets and optimum
ffects. Because these drugs work through the
mechanism of inhibiting protozoan DNA synthesis, it
Table 4: The empirical antibiotic use in pediatric patients
Types of
antibiotic
use
Antibiotics
Number
of use
(
N=47
)
%
Single
Cefotaxime 10 21.28
70.21
Mero
p
enem 7 14.90
Gentam
y
cin 5 10.64
Ceftazidime 3 6.38
Metronidazole 2 4.26
Cefixime 2 4.26
Cefazoline 1 2.13
Ceftriaxone 1 2.13
Ami
k
acin 1 2.13
Ampicillin 1 2.13
Combina-
tion
Ampicillin +
Gentam
y
cin
5 10.64
29.79
Meropenem +
Gentamycin
3 6.38
Meropenem +
Amikacin +
Metronidazole
1 2.13
Meropenem +
Ampicillin
1 2.13
Table 5: The empirical antibiotics use in adult and geriatric
patients
Types of
antibiotic
use
Antibiotics
Number
of use
(N=42)
(%)
Single
Ceftriaxone 9 21.43
69.05
Mero
p
ene
m
5 11.90
Cefotaxi
m
e 4 9.52
Ceftazidime 3 7.14
Gentamycin 2 4.76
Cefixime 2 4.76
Cotrimoxazole 1 2.38
Clindam
y
cin 1 2.38
Cefadroxil 1 2.38
Ampicillin/
Sulbacta
m
1 2.38
Combinat
ion
Meropenem +
Metronidazole
3 7.14
30.95
Ceftriaxone +
Metronidazole
2 4.76
Gentamycin +
Ceftriaxone
1 2.38
Gentamycin +
Mero
p
ene
m
1 2.38
Cefotaxime +
Gentamycin
1 2.38
Clindamycin +
Levofloxacin
1 2.38
Meropenem +
Metronidazole
1 2.38
Ceftriaxone +
Levofloxacin
1 2.38
Cefixime +
Metronidazole
1 2.38
Meropenem +
Metronidazole
+ Gentamycin
1 2.38
Empirical Antibiotics Study on Pneumonia in Intensive Care Unit
51

results in cell death (Fauziyah et al., 2011).
Meropenem is more effective than cefotaxime for
P.aeruginosa and isolated anaerobes. It is effective to
treat nosocomial infections (Mehtar et al., 1997). In
this study, a patient infected with Pseudomonas
aeroginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii recieved
meropenem as an empirical antibiotic.
The selection of antibiotics according to the
bacterial etiology can optimize the therapeutic effects
and reduce the risk of resistance. Unfortunately, this
study could not analyze the suitability of the empirical
antibiotic to deal with certain isolated bacteria because
the bacterial culture was not performed to all patients.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this study, Acinetobacter baumannii was the most
common isolated organism (42,11%), followed by
Klebsiella pneumonia and Pseudomonas aeruginosa
(15.79%). Meropenem was the most used single
antibiotic in pediatric cases (24%), while ceftriaxone
was most commonly prescribed adult patients
(16.22%). The most widely used combination of
antibiotics was ampicillin and gentamycin for pediatric
ICU patients (20%), and meropenem and
metronidazole in adult patients (13.51%). This study
also found that Acinetobacter baumannii was
completely resistant to Ampicillin-sulbactam and
partially resistant to the other beta-lactam antibiotics.
Both Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Klebsiella
pneumonia were completely resistant to Ampicillin
and Ampicillin-sulbactam.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors would like to thank the Fundamental
Grant, Universitas Sebelas Maret in 2018 for their
financial assiatance.
REFERENCES
Baldwin, C. M., Lyseng-williamson, K. A. and Keam, S. J.
(2008) ‘Meropenem A Review of its Use in the
Treatment of Serious Bacterial Infections’, Adis Drug
Evaluation, pp. 803–838.
Chawla, R. (2008) ‘Epidemiology, etiology, and diagnosis of
hospital-acquired pneumonia and ventilator-associated
pneumonia in Asian countries’, American Journal of
Infection Control, 36(4 SUPPL.). doi:
10.1016/j.ajic.2007.05.011.
Cilloniz, C., Martin-Loeches, Garcia-Vidal C., San Jose A
and Torres A. (2016) ‘Microbial etiology of pneumonia:
Epidemiology, diagnosis and resistance patterns’,
International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(12).
doi: 10.3390/ijms17122120.
Cukic, V. and Hadzic, A. (2016) ‘The Most Common
Detected Bacteria in Sputum of Patients with
Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) Treated In
Hospital’, Medical Archives, 70(5), p. 354. doi:
10.5455/medarh.2016.70.354-358.
Duszynska, W. Litwin, A. Rojek, S. Szczesny, A. Ciasullo,
A. Gozdzik, W.(2018) ‘Analysis of Acinetobacter
baumannii hospital infections in patients treated at the
intensive care unit of the University Hospital, Wroclaw,
Poland: A 6-year, single-center, retrospective study’,
Infection and Drug Resistance, 11, pp. 629–635. doi:
10.2147/IDR.S162232.
Eida, M.N, El-Maraghy M., Azab N., Khaled (2015) ‘Pattern
of hospital-acquired pneumonia in Intensive Care Unit of
Suez Canal University Hospital’, Egyptian Journal of
Chest Diseases and Tuberculosis. The Egyptian Society
of Chest Diseases and Tuberculosis, 64(3), pp. 625–631.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejcdt.2015.03.028.
Falagas, M. E., Mourtzoukou, E. G. and Vardakas, K. Z.
(2007) ‘Sex differences in the incidence and severity of
respiratory tract infections’, Respiratory Medicine.
Elsevier, 101(9), pp. 1845–1863. doi:
10.1016/j.rmed.2007.04.011.
Fauziyah, S. Radji, M. Nurgani, A (2011) ‘Hubungan
penggunaan antibiotika pada terapi empiris dengan
kepekaan bakteri di icu rsup fatmawati jakarta’. Jurnal
Farmasi Indonesia, 5(3), pp. 150–158.
Firmansyah, M A., Amin, Z., Loho, T. dan Shatri, H. 2015.
Predictors of Mortality in Comunity-Acquired
Pneumonia Inpatient in Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital,
Jakarta. International Journal of CHEST Critical and
Emergency Medicine, 2 : 45-53.
Gannon T., J. McCaran K, Christopher J. Pasquale,
Michaelter, Robert J. Napolitano, Lena M. (2004) ‘Male
gender is associated with increased risk for postinjury
pneumonia.’, Shock (Augusta, Ga.), pp. 410–414. doi:
10.1097/00024382-200405000-00003.
Harris, A.M, Bramley, A.M., Jain,S., Arnold, S.R., Ampofo,
K., Self, W.H., et.al., (2017). ‘Influence of Antibiotics
on the Detection of Bacteria by Culture-Based and
Culture-Independent Diagnostic Tests in Patients
Hospitalized With Community-Acquired Pneumonia’,
Infectious Disease Society of America: Open Forum
Infectious Disease, 30329: pp. 1-7.
Hazir T, Begum K, El Arifeen S, Khan AM, Huque MH,
Kazmi N, Roy S, Abbasi S, Rahman QS, Theodoratou E,
Khorshed MS, Rahman KM, Bari S, Kaiser MM, Saha
SK, Ahmed AS, Rudan I, Bryce J, Qazi SA, Campbell
H. (2013) ‘Measuring coverage in MNCH: a prospective
validation study in Pakistan and Bangladesh on
measuring correct treatment of childhood pneumonia.’,
PLoS medicine, 10(5). doi:
10.1371/journal.pmed.1001422.
Hsueh PR, Hoban DJ, Carmeli Y, Chen SY, Desikan S,
Alejandria M, et al., . 2011 Consensus review of the
MICH-PhD 2018 - 1st Muhammadiyah International Conference on Health and Pharmaceutical Development
52

epidemiology and appropriate antimicrobial therapy of
complicated urinary tract infections in Asia-Pacific
region, J Infect;63(2):114-23
Indonesian Health Ministry. Indonesian Health Profile 2013.
Indones Basic Res. 2014;1–100
Katzung, B. G., Masters, S. B. dan Trevor, A. J., (2014).
Basic and Clinical Pharmacology,12th Edition, 900-
1010, Mc Graw Hill Medical, New York.
Kosai, H. Tamaki, R. Saito, M. Tohma, K. Alday, P.P Tan,
A.G. Inobaya, M.T Suzuki, A. Kamigaki, T. Lupisan,
S.Tallo, V. Oshitani, Hitoshi (2015) ‘Incidence and risk
factors of childhood pneumonia-like episodes in Biliran
Island, Philippines - A community-based study’, PLoS
ONE, 10(5), pp. 1–19. doi:
10.1371/journal.pone.0125009.
Li, Guowei Cook, Deborah J. Thabane, Lehana Friedrich,
Jan O. Crozier, Tim M. Muscedere, John Granton, John
Mehta, Sangeeta Reynolds, Steven C. Lopes, Renato D.
Francois, Lauzier Freitag, Andreas P. Levine, Mitchell
A.H. (2016) ‘Risk factors for mortality in patients
admitted to intensive care units with pneumonia’,
Respiratory Research. Respiratory Research, 17(1), pp.
1–9. doi: 10.1186/s12931-016-0397-5.
Lodha R, Kabra SK, Pandey RM. Antibiotics for
community-acquired pneumonia in children. Cochrane
Database Syst Rev [Internet]. 2013 Jun 4 [cited 2018 Sep
29];(6)
Mehtar, S. Dewar, E.P. Leaper, D.J. Taylor, E.W. (1997) ‘A
multi-centre study to compare meropenem and
cefotaxime and metronidazole in the treatment of
hospitalized patients with serious infections’, Journal of
Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 39(5), pp. 631–638. doi:
10.1093/jac/39.5.631.
Puspitasari, D., Hasmono, D. and Rahman, T. (2014)
‘Ampicillin Sulbactam and Cefotaxime Are Similarly
Effective in Pediatric Pneumonia’, pp. 116–121.
Rozenbaum, M. H. Mangen, Marie Josee J. Huijts, Susanne
M. van der Werf, Tjip S. Postma, Maarten J. (2015)
‘Incidence, direct costs and duration of hospitalization of
patients hospitalized with community-acquired
pneumonia: A nationwide retrospective claims database
analysis’, Vaccine. Elsevier Ltd, 33(28), pp. 3193–3199.
doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.05.001.
Sileem, A. E., Said, A. M. and Meleha, M. S. (2017)
‘Acinetobacter baumannii in ICU patients: A prospective
study highlighting their incidence, antibiotic sensitivity
pattern and impact on ICU stay and mortality’, Egyptian
Journal of Chest Diseases and Tuberculosis. The
Egyptian Society of Chest Diseases and Tuberculosis,
66(4), pp. 693–698. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcdt.2017.01.003.
Stralin, K. (2008) ‘Usefulness of aetiological tests for
guiding antibiotic therapy in community-acquired
pneumonia.’, International journal of antimicrobial
agents. The Netherlands, 31(1), pp. 3–11. doi:
10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2007.06.037.
Uwingabiye, J. Frikh, M., Lemnouer, A. Bssaibis, F.,
Belefquih B., Maleb,A., Dahraoui S., Belyamani L., Bait
A., Haimeur C., Louzi L., Ibrahimi, Elouennass,
M.(2017) ‘Intensive care unit-acquired Acinetobacter
baumannii infections in a Moroccan teaching hospital:
epidemiology, risk factors and outcome’, Germs, 7(4),
pp. 193–205. doi: 10.18683/germs.2017.1126.
Williams, D. J. Hall, M. Shah, S. S. Parikh, K. Tyler, A.
Neuman, M. I. Hersh, A. L. Brogan, T. V. Blaschke, A.
J. Grijalva, C. G.. (2013) ‘Narrow Vs. Broad-spectrum
Antimicrobial Therapy for Children Hospitalized With
Pneumonia’, Pediatrics, 132(5), pp. e1141–e1148. doi:
10.1542/peds.2013-1614.
Empirical Antibiotics Study on Pneumonia in Intensive Care Unit
53
