
Hypertension Care Book (HYCAB) Enhancing Motivation and
Family Support toward a Healthy Lifestyle
Ninuk Dian Kurniawati
1
, Eva Diana
1
and Sylvia Dwi Wahyuni
1
1
Faculty of Nursing, Universitas Airlangga, Campus C UNAIR, Mulyorejo, Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: Hypertension, Health Education, Family Support, Healthy Lifestyle.
Abstract: Objectives: This study aimed to investigate Hypertension care book (HYCAB) in improving the family
support and the motivation of the hypertensive patients in performing a healthy lifestyle. Methods: This was
a quasi-experimental study employing 24 respondents who divided equally into the intervention and control
groups. The samples were recruited by simple random sampling technique. The independent variable was
the HYCAB, whereas the dependent variables were patients’ motivation and family support. The HYCAB
was a book developed by the researchers as a learning medium to accompany health education that given
thrice a week for two consecutive weeks. The book explains about hypertension and a healthy lifestyle
required to prevent future complications. In addition, this book also emphasizes the importance of family
support in supporting healthy lifestyles and how families can provide the support needed for patients
appropriately. Data were collected using a questionnaire and analysed with Wilcoxon signed rank test and
Mann Whitney U Test. Results: The results showed that the HYCAB improved family support and patients’
motivation significantly with p = 0.000 and p=0.02 respectively. Conclusions: HYCAB as a media of health
education enhanced family support and hypertensive patients’ motivation in performing a healthy lifestyle.
1
INTRODUCTION
Indonesia is one of the developing countries where
hypertension is one of primary death cause (Surabaya
City Health Office, 2016). Hypertensive patients’
poor health status is aggravated by the unhealthy
lifestyles include lack of physical activity, poor
management of stress, excessive salt consumption,
smoking, and consumption of caffeinated beverages
(Cosimo Marcello, Maria Domenica, Gabriele, Elisa,
& Francesca, 2018; Deaver, Kanika, Ramneek, &
Samuel, 2015; Talukder et al., 2010). Unhealthy
lifestyles are influenced by lack of motivation and
family support (Novian, 2013). Kenjeran Subdistrict
is a sub-district in Surabaya which has a higher
potential for exposure to sodium intake because
geographically the Kenjeran sub-district is bordered
by the Madura Strait. Research shows that the cause
of high hypertension is caused by a pattern of habits
of people who tend to marinate marine processed
foods. This causes a tendency for hypertension to
occur in coastal areas where sodium intake plays a
role in the incidence of hypertension (Cosimo
Marcello et al., 2018; Patnaik, Paul, Pattnaik, & Sahu,
2017). One of the puskesmas (Community Health
Centers) with the most hypertension patients (1387
people or 21.55%) is the Tambakwedi Health Center
(Dinas Kesehatan Kota Surabaya, 2018).
Hypertension sufferers in the Tambakwedi Health
Center experienced an increase in 2016 to 2177
people (Dinas Kesehatan Kota Surabaya, 2018). As
many as 100% of hypertensive patients at the
Tambakwedi Health Center lack family support and
80% have low motivation in implementing a healthy
lifestyle (Samuel, ., J. Deaver, & ., 2016).
Previous study shows that health education is
effective in increasing knowledge, self-management,
and controlling lifestyle habits that are detrimental to
hypertensive sufferers (Augustovski et al., 2018;
Beigi et al., 2014; Jafar et al., 2017). Hypertension
care book (HYCAB) is a medium offered as a new
innovation in health education media. Hypertension
care book (HYCAB) is a modification of booklet
media that is equipped with a monitoring table of
changes of daily lifestyle with the aim of evaluating
and monitoring lifestyle in patients. The purpose of
this study was to analyze the effect of Hypertension
care book (HYCAB) on family support and
motivation of hypertensive patients in implementing a
healthy lifestyle.
110
Kurniawati, N., Diana, E. and Wahyuni, S.
Hypertension Care Book (HYCAB) Enhancing Motivation and Family Support toward a Healthy Lifestyle.
DOI: 10.5220/0008205101100114
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference of Indonesian National Nurses Association (ICINNA 2018), pages 110-114
ISBN: 978-989-758-406-0
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
2
METHODS
This research was conducted in the working area of
Tambakwedi Community Health Center Surabaya in
July 2018. The design was a quasy experiment with
pre-post control group design. Sample of research
was 24 respondents selected by simple random
sampling technique. Respondents were divided to
control group and intervention group equally. The
control group received a standard nursing care
provided by the nurses of Tambakwedi Community
Health Center; whereas the intervention group
provided with the HYCAB.
HYCAB was a modification of a booklet that
explains about hypertension and its treatment
equipped with a table designed to monitor and to
evaluate patients’ daily lifestyle changes. To ensure
the patients understand the book well, the
researchers help the patients and family individually,
at the patients’ homes thrice a week for two
consecutive weeks. Both pre test and post test data
were collected by fellow researchers that had trained
prior to data collection to achieve similar
understanding.
The research instruments were questionnaires
and a Hypertension Care Book (HYCAB). There
were two questionnaires used to collect data: family
support and motivation. The family support
questionnaire was modified from Engeline (2016)
that used to measure the hypertensive geriatric
patients’ family support in Jakarta, Indonesia. The
motivation questionnaire derived from Mas’ulah
(2010) that investigated the motivation to control
routinely to health care facilities. The questionnaires
were tested for its validity and reliability prior the
study. The Cronbach alpha for family support
questionnaire was 0.854 showing that the
questionnaire was highly reliable while the
Cronbach alpha for motivation questionnaire was
0.768 indicating that the questionnaire was reliable.
Computer programs were used to process the
collected data. The analysis of the variables in this
study used the statistical test of Wilcoxon Signed
Rank Test and the Mann Whitney U Test. The
Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test was used to test results
between pre and post test within the same group;
whereas, the Mann Whitney U Test was used to
analyse the difference between pre or post test
results among groups.
3
RESULTS
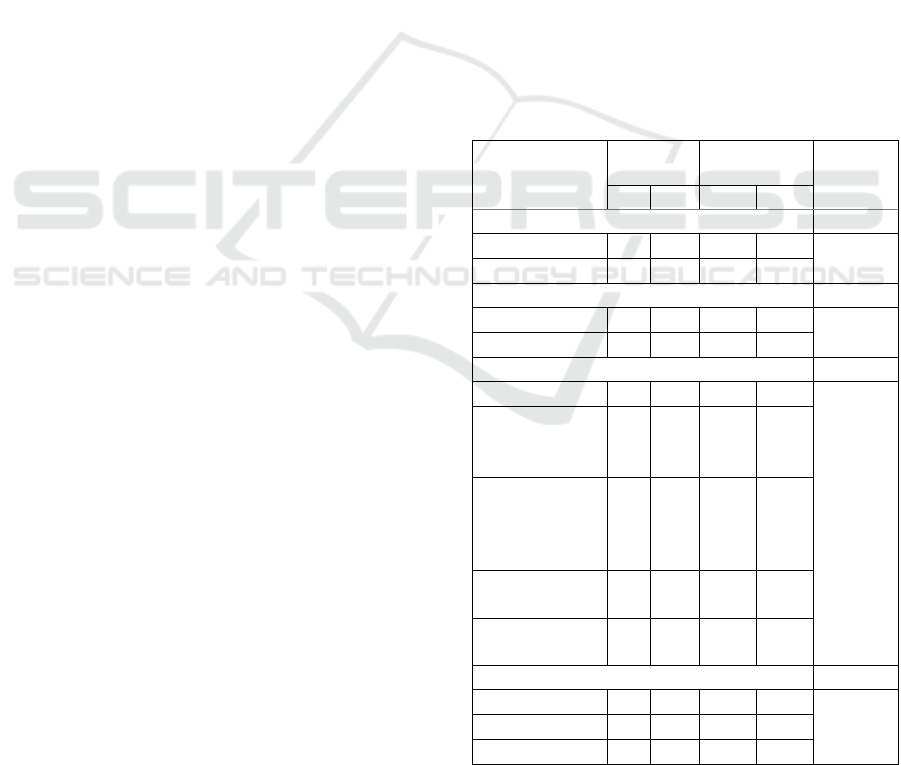
Table 1 shows the respondents’ characteristics: the
majority of the control group was 53-59 years old
(58%) with 75% of female sex, mostly employed
(75%) and 42% had a basic education. Moreover, it
can be seen from the table that most respondents
suffered from hypertension less than 5 years (75%)
and half of them had no family history of
hypertension (50%). While in the treatment group
most respondents (67%) were 53-59 years old with
female in sex (83%), as housewife (67%), mostly
suffered from hypertension less than 5 years (83%)
and had no family history of hypertension (58%).
Mann Whitney statistical analysis shows that all
variables had p value of more than 0.05, indicating
that respondents at both groups had the same
characteristics in terms of age, sex, education,
employment, length of hypertension and family
history of hypertension.
Table 1: Respondents’ Characteristics in control (n=12)
and intervention (n=12) groups of HYCAB enhancing
motivation and family support toward a healthy lifestyle.
Characteristics
Control
Group
Intervention
Group
p Value*
f
%
f
%
Age
45-52
5
42
4
33
0.799
53-59
7
58
8
67
Sex
Men
3
25
2
17
0.861
Women
9
75
10
83
Education
No education
4
33
5
42
1.000
Basic
education
(elementary)
5
42
3
25
Basic
education
(junior high
school)
0
0
2
16
Senior High
School
3
25
2
17
University
Education
0
0
0
0
Employment
None
0
0
1
8
0.857
House wife
3
25
8
67
Private
9
75
3
25
Hypertension Care Book (HYCAB) Enhancing Motivation and Family Support toward a Healthy Lifestyle
111
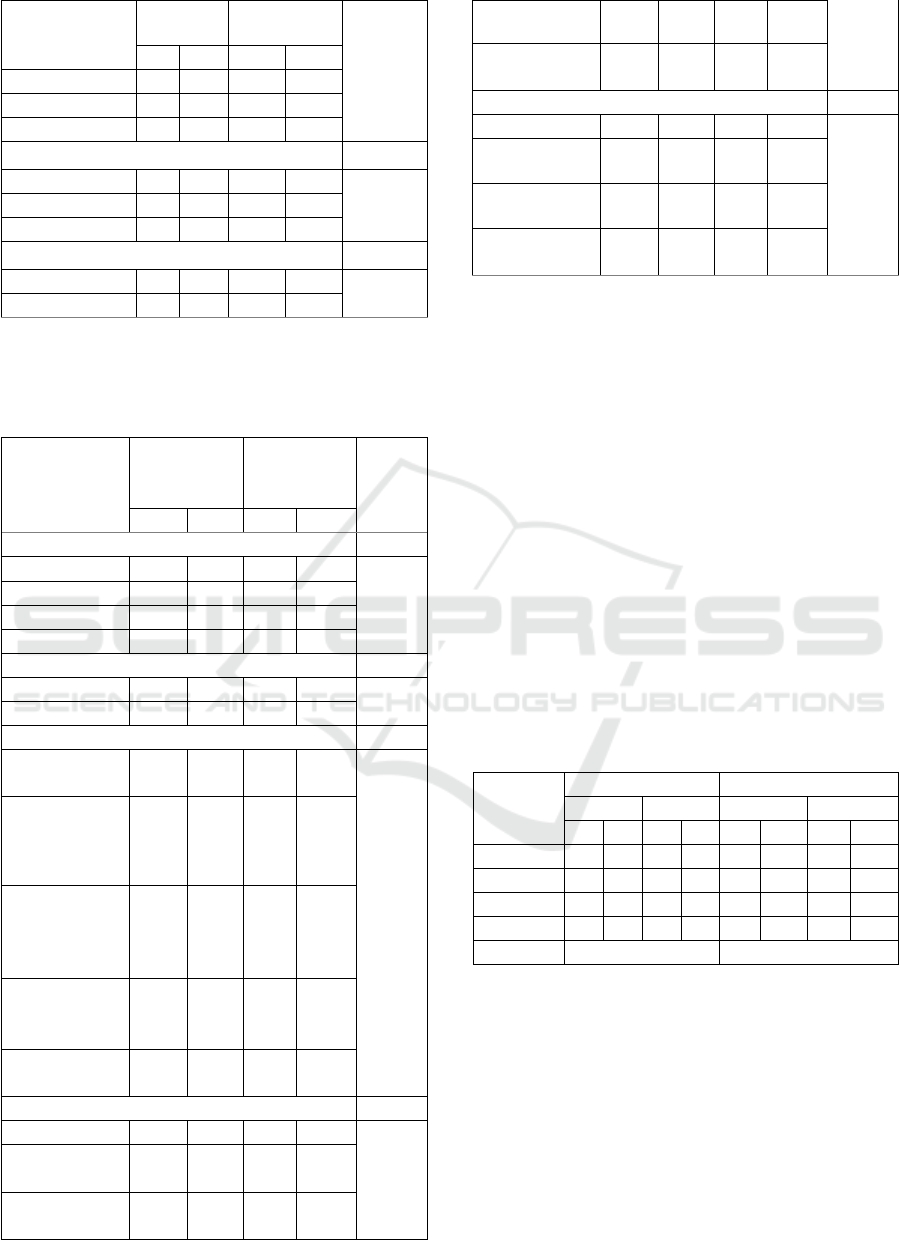
Characteristics
Control
Group
Intervention
Group
p Value*
f
%
f
%
sector
Interpreneur
0
0
0
0
Civil servant
0
0
0
0
Length of hypertension
< 5 y
9
75
10
83
0.081
5-10 y
3
25
2
17
> 10 y
0
0
0
0
Family History of Hypertension
Yes
6
50
5
42
1.000
No
6
50
7
58
*Mann Whithey statistical analysis.
Table 2: Family Characteristics of both in control (n=12)
and intervention (n=12) groups of HYCAB enhancing
motivation and family support toward a healthy lifestyle.
Characteristics
Control Group
Intervention
Group
p Value*
f
%
f
%
Age
25-29
6
50
2
17
0.388
30-39
1
8
3
25
40-49
2
17
1
8
50-59
3
25
6
50
Sex
Man
4
33
6
50
1.000
Woman
8
67
6
50
Education
No
education
0
0
1
8
1.000
Basic
education
(elementary)
4
33
3
25
Basic
education
(junior high
school)
2
17
5
42
Senior
High
School
5
42
2
17
University
Education
1
8
1
1
Employment
None
1
8
0
0
0.647
House
wife
5
42
3
25
Private
sector
6
50
7
59
Interpreneur
0
0
1
8
Civil
servant
0
0
1
8
Relationship with the respondent
Spouse
5
42
7
59
1.000
Grandchild
3
25
1
8
Son/daughter
4
33
3
25
Son/daughter
in law
0
0
1
8
*Mann Whithey statistical analysis.
Table 2 showed that the majority of families in
the control group aged 25-29 years old (50%) and
female (67%). This table also informs that nearly
half of the respondents had high school education
(42%) and working in private sectors (50%).
Respondents in intervention group aged of 50-59
year old (50%), female (50%), almost half educated
in junior high school (42%) and more than half
working in the private sector (59%). Additionally,
the largest proportion of family relationships
respondents were spouse (42% in treatment group
and 59% in control group). A statistical analysis
with Mann Whitney showed all variables had p >
0.05; thus, it can be concluded that all respondents’
characteristics between groups are similar.
Table 3: Family support in control (n=12) and intervention
(n=12) groups of HYCAB enhancing motivation and
family support toward a healthy lifestyle.
Family
Support
Intervention Group
Control Group
Pretest
Posttest
Pretest
Posttest
f
%
f
%
f
%
f
%
Good
0
0
10
83
1
8
1
8
Average
7
58
2
17
3
25
7
58
Low
5
42
0
0
8
67
4
33
Total
12
100
12
100
12
100
12
100
Wilcoxon
0.002
0.010
Table 3 shows the level of family support
received by the respondents. It can be seen in the
treatment group that the family support was
perceived as in moderate cathegory by 58% prior to
intervention while the rest of them perceived the
family support in low cathegory (42%). In the
control group, more than hal respondents (67%)
perceived the support provided by their family as in
low cathegory.
Moreover, from Table 3, it can be seen in the
treatment group that there was an increase in family
ICINNA 2018 - The 1st International Conference of Indonesian National Nurses Association
112
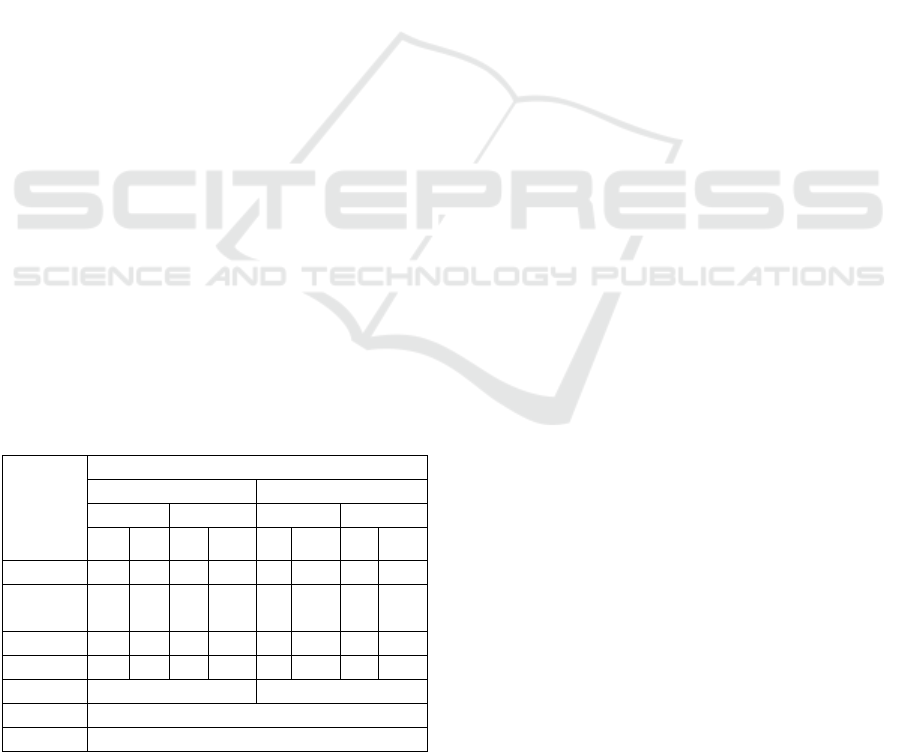
support after posttest where there were 10 people
(83%) with good category, while in the control
group there was an increase of family support with
moderate category of 7 people (58%). The
Wilcoxon test rank test in the treatment group was
0.002 <α 0.05, showing a significant increase in
family support during pretest and posttest as a result
of the education health education of hypertension
care book (HYCAB). Interestingly, both groups
show a significant difference of family support in
pre and post test, indicating the influence of
HYCAB media health education on family support
in treatment group.
The effect was also shown by the increase in
posttest results about family support in the treatment
group after HYCAB health education was provided.
As many as 100% of the families understand the
importance of family support as well as the
importance of practicing a healthy lifestyle to family
members who suffer from hypertension after health
education. This is in line with previous research
which states that there is an influence on the
extension of health education to increased
knowledge and family support (Purwati, 2014).
These significant changes confirm that the
provision of HYCAB media health education is
necessary to enable families to understand and
provide support to hypertension sufferers. As
stressed in the Mann Whitney U Test statistical test,
there was a significant different between groups
after health education with HYCAB media was
given. This is in line with the study Mardhiah, et al.
(2014) stating that health education media booklets
can enhance knowledge and family support.
Table 4: Motivation of both control (n=12) and
intervention (n=12) groups HYCAB enhancing motivation
and family support toward a healthy lifestyle.
Motivation
Group
Intervention
Control
Pretest
Posttest
Pretest
Post-test
f
%
f
%
f
%
f
%
Good
0
0
12
100
0
0
0
0
Average
12
100
0
0
8
67
12
100
Low
0
0
0
0
4
33
0
0
Total
12
100
12
100
12
100
12
100
p*
0.002
0.046
p**
0.201
p***
0.000
* Wilcoxon sign rank test
** Mann Whithey at pretest
*** Mann Whitney at posttest
Health education using a booklet or HYCAB
medium is more effective and the information
delivered visually is more acceptable to patients and
families.
Table 4 shows that at pretest, the motivation of
hypertension patients in applying healthy lifestyles
in the moderate category in the treatment group
(67%) and the low category in the control group
(33%). Lack of motivation was caused from
patients’s perception regarding hassles in
implementing the healthy lifestyle. At the posttest
the motivation increased to 100% in the treatment
group; while in the control group there were 12
people with still in moderate category. The results of
the statistical test showed that Mann Whitney U Test
in both groups significantly different (p = 0.000),
suggesting that there was influence of HYCAB
media health education on motivation in
hypertension and family members who received
HYCAB media health education.
4
DISCUSSIONS
The results of the study showed that the
interventions provided were successful in enhancing
family support. Family support is the assistance
provided in the form of instrumental support,
informal support, assessment support, and emotional
support from the family to individuals who need
support (Kuntjoro, 2012). Family support is
indispensable in the treatment of hypertension
patients in improving motivation in hypertension
patients in applying lifestyle. The family gives the
form of family support one of them is by facilitating
people with hypertension in the consumption of low
salt food. Family support is an important factor in
helping individuals solve problems. Family support
can add to self-confidence and motivation to deal
with problems and improve life satisfaction.
This study showed that HYCAB improved the
family support provided by the family to their family
member who suffered hypertension. Initially, the
majority of family were not well aware of the
importance of a healthy lifestyle hence the support
provided by the family was not optimal.
Additionally, the HYCAB also increase patients
motivation from poor to good. The Wilcoxon Signed
Rank Test test showed a significant different of the
patients motivation (average to good). This explains
that the provision of HYCAB media health
education is essential to hypertension patients to
increase motivation in applying healthy lifestyles
both internally and externally. This is in line with
Hypertension Care Book (HYCAB) Enhancing Motivation and Family Support toward a Healthy Lifestyle
113

research that explains that health education can
influence a person in acquiring knowledge and
motivation about health, including a healthy lifestyle
(Augustovski et al., 2018; Chaparro et al., 2015).
Health promotion can improve knowledge and
ability to maintain the certain behaviour needed for a
disease treatment (Hong, 2010).
The limitation of this study was the small sample
size due to the lack in number of patient and
patients’ family in the Puskesmas of Tambak Wedi
Surabaya.
5
CONCLUSIONS
Family support and patients’ motivation improved
after the intervention of the hypertension care book
(HYCAB) because the material contained in
HYCAB uses language that is easy to understand by
the patients and family. The monitoring table in
HYCAB also helps families in providing their
supportive forms of hypertension and indirectly
motivates hypertension sufferers to adopt a healthy
lifestyle.
REFERENCES
Augustovski, F., Chaparro, M., Palacios, A., Shi, L.,
Beratarrechea, A., Irazola, V., … Riviere, A., P.
(2018). Cost Effectiveness of a Comprehensive
Approach for Hypertension Control in Low-Income
Settings in Argentina: Trial-Based Analysis of the
Hypertension Control Program in Argentina. Value in
Health, 21, 1357–1364.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2018.06.003
Beigi, M. A. B., Zibaeenezhad, M. J., Aghasadeghi, K.,
Jokar, A., Shekarforoush, S., & Khazraei,
H. (2014). The Effect of Educational Programs on
Hypertension Management. International
Cardiovascular Research Journal, 8(3), 94– 98.
Chaparro, V., Chaves, G., Kieser, M., Gonzalez, G.,
Katus, H. A., Munzinger, J., … Bruckner, T. (2015).
Education to a Healthy Lifestyle Improves Symptoms
and Cardiovascular Risk Factors - AsuRiesgo Study.
Arquivos Brasileiros de Cardiologia, 347–355.
https://doi.org/10.5935/abc.20150021
Cosimo Marcello, B., Maria Domenica, A., Gabriele, P.,
Elisa, M., & Francesca, B. (2018). Lifestyle and
Hypertension: An Evidence-Based Review. Journal of
Hypertension and Management, 4(1), 1–10.
https://doi.org/10.23937/2474-3690/1510030
Deaver, U. J., Kanika, Ramneek, & Samuel, A. J. (2015).
Hypertension: Contributing Risk Factors and Lifestyle
Modification among Hypertensive Clients.
International Journal of Practical Nursing, 3(3), 115–
119.
Dinas Kesehatan Kota Surabaya. (2018). Profil Kesehatan
Kota Surabaya 2017. Retrieved from
http://www.depkes.go.id/resources/download/
profil/PROFIL_KAB_KOTA_2016/3578_Jati
m_Kota_Surabaya_2016.pdf
Engeline, S. A. (2016). Hubungan dukungan keluarga
dengan kejadian hipertensi pada lansia di BLUD
Puskesmas Kecamatan Kebon Jeruk Jakarta Barat.
Universitas Esa Unggul.
Hong, W. H. S. (2010). Evidence-based nursing practice
for health promotion in adults with hypertension: A
literature review. Asian Nursing Research, 4(4), 227–
245. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1976-1317(11)60007- 8
Jafar, T. H., Jehan, I., de Silva, H. A., Naheed, A., Gandhi,
M., Assam, P., … Kasturiratne, A. (2017).
Multicomponent intervention versus usual care for
management of hypertension in rural Bangladesh,
Pakistan and Sri Lanka: Study protocol for a cluster
randomized controlled trial. Trials, 18(1), 1–12.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-017-2018-0
Mas’ulah. (2010). Upaya Peningkatan Motivasi Penderita
Hipertensi dalam Melakukan Kunjungan Kontrol
Melalui Pemberian Pendidikan Kesehatan. Universitas
Airlangga. Novian, A. (2013). Jurnal Kesehatan
Masyarakat. Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat, 8(2), 113–
120. https://doi.org/ISSN 1858-1196
Patnaik, L., Paul, K. K., Pattnaik, S., & Sahu, T. (2017).
Lifestyle Pattern and Hypertension Related
Knowledge, Attitude and Practices among Diagnosed
Patients of Hypertension Attending a Tertiary Care
Hospital. Journal of Cardiovascular Disease
Research, 8(4), 108–111.
https://doi.org/10.5530/jcdr.2017.4.25
Samuel, A. J., R., J. Deaver, U., & K. (2016).
Hypertension: Contributing Risk Factors and Lifestyle
Modification among Hypertensive Clients.
International Journal of Practical Nursing, 3(3), 109–
113. https://doi.org/10.21088/ijpn.2347.7083.3315. 4
Talukder, M. A. H., Johnson, Wesley, M., Varadharaj, S.,
Lian, J., Kearns, P. N., El- Mahdy, Mo. A., … Zweier,
J. L. (2010). Chronic cigarette smoking causes
hypertension, increased oxidative stress, impaired NO
bioavailability, endothelial dysfunction, and cardiac
remodelling in mice. American Journal of Physiology:
Hear and Circulatory Physiology, 300(1), H388–
H396.
ICINNA 2018 - The 1st International Conference of Indonesian National Nurses Association
114
