
Study on Carbon Emission from Sludge Drying and Incineration
Process
Shasha Ji
*
Shanghai Urban Construction Design & Research Institute (Group) Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China
Keywords: Sludge, Drying and incineration, carbon emission
Abstract: In China, there is a lack of research on the carbon footprint of sludge treatment and disposal. This paper
studied the carbon emissions during sludge drying and incineration process In order to make the research
more practical, the carbon footprint of “ZhuYuan sludge incineration project” is calculated by the actual
measurement method and model estimation method. Using the model estimation method, the discharge
equivalent of CO
2
in the sludge incineration process is 1546.6~1709.9 kg CO
2
/t DS; Using the actual
measurement method, the discharge equivalent of CO
2
in the sludge incineration process is 3046.6 kg CO
2
/t
DS. The causes of the difference between the two methods were discussed. Finally, the optimization
strategy of reducing the carbon emission of the sludge drying and incineration process is put forward.
1 INTRODUCTION
It is estimated that by 2020, the amount of municipal
sludge will reach 6000~9000 million tons. The cost
of sludge disposal accounts for about half of the total
cost of sewage treatment. Sludge disposal and
management is one of the major challenges for the
global water industry (Zhou et al., 2013). The sludge
treatment process during sewage treatment has
become a major source of carbon emissions due to
its energy consumption and greenhouse gas
emissions. The carbon footprint is a new parameter
for the evaluation of the sludge technology route,
which reflects the possible greenhouse gases and
related climate changes that may be discharged
during the process of sludge treatment and disposal
(Brown et al., 2010).
In recent years, sludge drying and incineration
technology has shown explosive growth in China,
especially for some large cities with limited land
use. During the "13th Five-Year" period, all the new
construction projects of sludge treatment facilities in
the three major areas of Shanghai central urban area
were dry chemical incineration technology.
Sludge drying is designed to remove or reduce
the water content in the sludge. The removal process
is divided into two stages, namely, the vaporization
and evaporation process on the surface of the sludge
and the diffusion process of the water in the sludge.
It can reduce the sludge greatly, improve the sludge
calorific value, kill the harmful components and
create conditions for the utilization of resources.
Incineration is a complete combustion process,
especially suitable for large cities that are faced with
land restrictions. During the incineration process, the
combustible components in the sludge are rapidly
oxidized. The temperature required for complete
combustion is generally 760~820 ℃. One of the
main parameters of sludge incineration is the water
content of sludge. The sludge with solid ratio of
30%~50% could combustion without auxiliary fuel.
The sludge with solid ratio of 20%~30% needed to
add auxiliary fuel and pre-drying in the incinerator.
In addition, the low solid content will lead to the
increase of the flue gas treatment. Therefore, proper
solid ratio should be selected before incineration.
Another important parameter of sludge is the sludge
calorific value (Cao and Pawlowski, 2013).
At present, most of the research on carbon
footprint in China is mainly macroscopic. This paper
focuses on the carbon footprint research of sludge
treatment and disposal, and provides the basis for the
carbon emission reduction work of the sludge
industry.
Ji, S.
Study on Carbon Emission from Sludge Drying and Incineration Process.
DOI: 10.5220/0008188802730277
In The Second International Conference on Materials Chemistry and Environmental Protection (MEEP 2018), pages 273-277
ISBN: 978-989-758-360-5
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
273
2 METHODOLOGY
2.1 Project Introduction
At present, “ZhuYuan sludge incineration project” is
the largest sewage sludge drying and incineration
project that has been operated in China. The scale of
this project is 150 t/DS, and the Sludge calorific
value is 13700 kJ/kg. The project mainly includes
sludge receiving and storage system, sludge drying
system, sludge incineration system, waste heat
utilization system, flue gas treatment system and
auxiliary system. The sludge is dried by indirect
drying method, and the heat source is steam. The
sludge is incinerated by fluidized bed incinerator.
2.2 Boundary of Research System
In the study of sludge life cycle assessment, it is
generally regarded as the starting point of life cycle
evaluation, and the scope of the study includes the
whole process from production, transportation,
recycling, and treatment to final disposal. This paper
focuses on the research on the disposal and disposal
parts. Along with the sludge itself entering the
system, it also includes auxiliary energy and other
raw materials; the output of the system is useful
products and recycled energy.
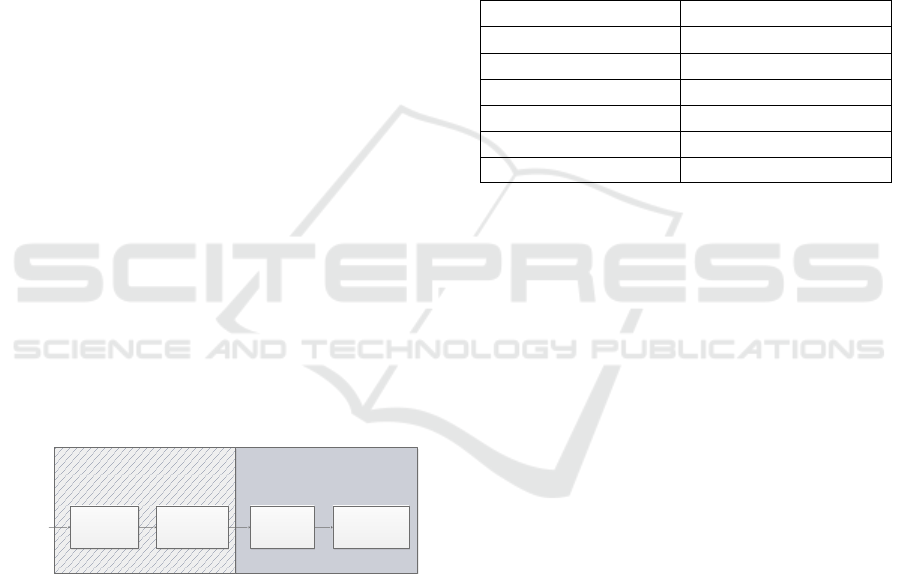
Sludge treatment processes and the disposal
route are presented in Figure 1. “Thickening” and
“Dewatering” process are finished in Waste water
treatment plant. “Drying” and “Incineration” process
are finished in Sludge treatment plants. Research
boundary is limited to sludge treatment plant.
Figure 1: Sludge treatment processes and disposal routes.
2.3 Carbon Footprint Method
The Carbon footprint is defined as the total amount
of greenhouse gases (GHG) produced to directly and
indirectly support human activities, usually
expressed in equivalent tons of carbon dioxide
(CO
2
). It is a common method to calculate the
impacts of human activities on Global Warming
(IPCC, 2006).
Although the study found many gases affecting the
climate system, only 6 major types of greenhouse
gases were included in the “Kyoto Protocol”,
including CO
2
, CH
4
, N
2
O, HFCs, PCFs and SF in
the carbon footprint assessment. As the
quantification of these gases cannot be directly
measured, they are estimated by calculating GHG
emissions of each processes involved in the studied
activities. The amount of each gas is then converted
with an emission factor in CO
2
equivalent (CO
2eq
)
according to their Global Warming Potential (GWP),
which showed in Table 1 (IPCC, 2006).
Table 1: Considered gases in carbon footprint and their
Global Warming Potential at 100 years (GWP
100
).
Formula
GWP
100
CO
2
1
CH
4
21
N
2
O
310
HFCs
124-14800
PCFs
7390-10300
SF
17200
GHG emission of sludge treatment can be divided
into direct part and indirect part:
Direct part: GHG emissions directly occurring
in sludge treatment and disposal.
Indirect part: GHG emissions caused by
electricity and fuel consumption during sludge
drying and incineration process.
2.4 Calculation Method
At present, the domestic calculation methods of
GHG emissions in sludge treatment and disposal
process are mainly divided into actual measurement
method and model estimation method.
The actual measurement method needs to
measure the relevant parameters of the emission
source or the operating equipment through the actual
testing method, and calculate the carbon emissions
by the measured data approved by the environmental
protection department. Most of calculations used
model estimation method. These studies are of great
guiding significance, but the results are largely
dependent on the hypothesis and scenario analysis.
In order to make the research more practical, the
carbon footprint of “ZhuYuan sludge incineration
project” is calculated by actual measurement method
and model estimation method.
Thickening
Dewatering
Drying
Incineration
Sludge
Waste water treatment plants
Sludge treatment plants
MEEP 2018 - The Second International Conference on Materials Chemistry and Environmental Protection
274

3 MODEL ESTIMATION
METHOD
3.1 Calculation Method of Drying
The carbon emission during the sludge drying
process is mainly energy consumption, and the
calculation method is as shown in Equation 1.
CO
2
=M1·(EC1·F
electric
+ EC2·F
natural gas
)
(1)
M1: The mass of water reduction during drying
EC1: Specific energy consumption (electric)
F
electric
: CO
2
emission factor (electric)
EC2: Specific energy consumption (natural gas)
F
natural gas
: CO
2
emission factor (natural gas)
3.2 Calculation Method of Incineration
Carbon emissions from sludge incineration include
Energy source CO
2
, Biogenic source CO
2
and
Alternative CO
2
, and the calculation method is as
shown in Equation (2) ~ (6).
CO
2
=M2·(EC3·F
electric
+ EC4·F
electric
)
(2)
M2: Dry sludge quality
EC3: Specific energy of Wet flue gas purification
system (electric)
EC4: Specific energy of SNCR (electric)
CO
2
=M2·CC·η1·44/12·
(3)
CC: Carbon content in sludge
η: Combustion carbon oxidation factor
CO
2CH4
=M2·F
CH4
·
(4)
F
CH4
: Emission factor of CH
4
CO
2N2O
=M2·F
N2O
·
(5)
F
N2O
: Emission factor of N
2
O
CO
2
=M2·Hv·η2·F
diesel
/Hvd
(6)
HV: Sludge calorific value
η2: Energy utilization rate
F
diesel
: CO
2
emission factor (diesel)
Hvd: Diesel calorific value
3.3 Estimation Result
In the model estimation method, the calculation
parameters of sludge drying and incineration process
are shown in Table 2. In the drying stage, due to the
different use of equipment and the actual operation,
it causes difference in energy consumption, and
there is still such a situation in the incineration stage,
that is, different flue gas treatment equipment and
different working conditions will lead to the
different energy consumption of the wet scrubbing
tower and the SNCR system (Liu et al., 2013).
The discharge equivalent of CO
2
in the sludge
incineration process is 1546.6~1709.9 kg CO
2
/t DS,
and the emission equivalent of the energy source
CO
2
is 737.7~988.0 kg CO
2
/t DS, and the emission
equivalent of the biological source CO
2
is 1432.5 kg.
Alternative CO
2
comes from the energy produced by
the sludge incineration. This part of the energy can
be used to compensate for the consumption of the
system (Showed as Table 3).
Table 2: Calculation parameters of GHG emission.
Unit
Category
Parameter
Value (Ministry of environmental
protection)
Drying
Energy source CO
2
M
2.5 kg
EC1
100-200 kWh/m
3
EC2
2750 kJ/kg
Incineration
Energy source CO
2
CC
36%
η1
95%
EC3
6~19 kWh/t DM
EC4
40~50 kWh/t DM
Biogenic source CO
2
F
CH4
24.25 g CH
4
/t DM
F
N2O
990 g N
2
O/t DM
Alternative CO
2
Hv
13700 kJ/kg
Hvd
43.0 TJ/Gg
η2
70%
Study on Carbon Emission from Sludge Drying and Incineration Process
275
Table 3: GHG emission.
Unit
Emission type
Emission value (kg)
GWP
CO
2
eq (kg CO
2
/t DS)
Drying
Energy source CO
2
t
684.9~916.9
1
684.9~916.9
Incineration
Energy source CO
2
49.8~71.1
1
49.8~71.1
Biogenic source CO
2
1125.1
1
1125.1
Emission of CH
4
0.024
21
0.504
Emission of N
2
O
0.99
310
306.9
Alternative CO
2
-710.6
1
-710.6
4 ACTUAL MEASUREMENT
METHOD
4.1 Energy Source CO
2
The energy source CO
2
emission from “ZhuYuan
sludge incineration project” mainly includes the
consumption of power, light diesel, activated carbon,
NaOH and Ca(OH)
2
. The specific value was showed
in Table 4. The discharge equivalent of energy
source CO
2
is 1891.96 kg CO
2
/t DS.
It is necessary to explain that the energy
generated by the sludge incineration is not sufficient
to support the drying of the sludge, so the external
energy is needed to fill the dry energy gap, and the
steam from the “Waigaoqiao power plant” is used in
this project.
Table 4: Energy source CO
2
emission.
Entry
Consumption
CO
2
eq (kg
CO
2
/t DS)
Power
578.97 kWh/t DS
537.28
External steam
(used for drying)
996.14 kWh/t DS
924.42
light diesel
124 kg/t DS
394.20
activated carbon
1 kg/t DS
6
NaOH
17.86 kg/t DS
20.90
Ca(OH)
2
9.41 kg/t DS
9.17
4.2 Biogenic Source CO
2
The average carbon content in dehydrated sludge
was 32%, and the average carbon content in fly ash
was 1.1% after burning. According to the estimated
method proposed by the IPCC (2006), the CO
2
emission of biological source was 1154.6 kg CO
2
/t
DS.
4.3 Alternative CO
2
Energy produced by the sludge incineration is all
self-used, one part is used for primary air heating in
incinerator and the other is used in the waste heat
boiler to produce steam to drying sludge, so it is no
longer included in the emission statistics.
5 METHOD COMPARISON
Using the model estimation method, the discharge
equivalent of CO
2
in the sludge incineration process
is 1546.6~1709.9 kg CO
2
/t DS; Using the actual
measurement method, the discharge equivalent of
CO
2
in the sludge incineration process is 3046.6 kg
CO
2
/t DS. It can be seen that there are large
differences in the calculation of CO
2
emission
equivalents by different methods. The main reasons
are as follows: 1. The power consumption in the
actual measurement method is the total power
consumption of the entire engineering operation
facility, which is greater than the power
consumption of the specified equipment in the
model estimation method; 2. The specific energy
consumption in the model estimation is greatly
affected by the assumptions, equipment and working
conditions, and there is a big difference with the
actual operating conditions. 3. The energy available
for sludge incineration after model incineration
depends on the assumed utilization value. For the
estimation, this is also quite different from the actual
use value of the energy in the measured method.
6 OPTIMIZATION SUGGESTION
Through analysis, it can be seen that the energy
source CO
2
emissions in the dry process and the flue
gas treatment process account for a large proportion.
Drying process is one of the most important links of
CO
2
emissions. The energy consumption of the
sludge drying technology is related to the dry form.
Therefore, the selection of a dry process with lower
energy consumption can effectively reduce CO
2
emissions.
MEEP 2018 - The Second International Conference on Materials Chemistry and Environmental Protection
276

The energy consumption of drying is still related
to the type of heat source chosen. From the
perspective of reducing carbon emissions, when the
flue gas temperature is high enough and transport
distance is relatively short, it is preferable to use
waste heat flue gas of large-scale industrial and
environmental protection infrastructure, such as
waste incinerator, power station, chemical facilities,
etc.
In addition, the energy utilization rate of the
incineration system should be increased, which can
increase the value of Alternative CO
2
.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Thanks for the support of scientific research project
of Shanghai science and Technology Commission
(18XD1422700).
REFERENCES
Brown, S., Beecher, N., Carpenter, A., 2010. Calculator
tool for determining greenhouse gas emissions for
biosolids processing and end use. Environ. Sci.
Technol. 44, 7.
Cao, Y., Pawlowski, A., 2013. Life cycle assessment of
two emerging sewage sludge-to-energy systems:
Evaluating energy and greenhouse gas emissions
implications. Bioresour. Technol. 127, 81–91.
IPCC, 2006. Guidelines for national greenhouse gas
inventories.
Liu, B., Wei, Q., Zhang, B., Bi, J., 2013. Life cycle ghg
emissions of sewage sludge treatment and
disposaloptions in tai lake watershed, china. Sci. Total
Environ., 447, 361–369.
Ministry of Environmental Protection. Guidelines for Best
Available Techniques for Sewage Treatment Plant
Sludge Treatment and Disposal Preparation of
research report [R].
Zhou, Y.Z., Zhang, D.Q., Le, M.T., Puah, A.N., Ng, W.J.
2013. Energy utilization in sewage treatment—A
review with comparisons. J. Water Clim. Chang 4, 1.
Study on Carbon Emission from Sludge Drying and Incineration Process
277
