
The Efficacy of Human Amniotic Membrane Mesenchymal Stem
Cells (hAMMSC) Plus Vitamin C for Treating Chronic Plantar Ulcer
in Leprosy Patient: A Case Report
Riyana Noor Oktaviyanti,
1
Rahmadewi,
1
Medhi Denisa Alinda
1
, Bagus Haryo Kusumaputra
1
, Linda
Astari
1
, M. Yulianto Listiawan, Indropo Agusni
1
, Fedik A. Rantam
2,3
and Cita Rosita Sigit
Prakoeswa
1
1
Departement of Dermatology Venereology, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Airlangga, Dr Soetomo General
Hospital, Surabaya, Indonesia
2
Stem Cell Research and Development Center, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia.
3
Virology and Immunology Laboratory, Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Universitas
Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: amniotic membrane stem cells, vitamin C, plantar ulcer, leprosy/MH
Abstract: Chronic plantar ulcer in Leprosy is a still a problem in term of patient’s medical and social aspect.
Amniotic membrane stem cell (AMSC) conditioned medium provide growth factors and sitokin for the
chronic ulcer’s healing. Vitamin C as antioxidant, anti inflamatory, dan collagen synthesis can be useful for
wound healing.
1 INTRODUCTION
Chronic plantar ulcers in Morbus Hansen (MH)
including level 2 defects, are the most common
cause of disability in MH patients. The prevalence of
level 2 deficiency in MH patients in Southeast Asia
increased from 2010 to 2011 by 2.5%. In Indonesia,
MH patients with disability level 2 also increased
during the year 2011-2012 by 10.11% (World
Health organization, 2012; Metro Tempo Co., 2013).
Approximately 30% of patients with Leprosy have
peripheral nerve damage, and 10-20% of them have
neuropathic ulcers due to peripheral nerve
damage. Chronic ulcers are a serious medical and
social problem. Patients experience decreased
quality of life, so wound healing management
continues to be investigated to deal with chronic
ulcers (Halim and Menald, 2010; Bauman, Girling,
and Brand, 1963). In chronic ulcers there is a
decrease in growth factors such as platelet derived
growth factor (PDGF) and growth factor
transformation (TGF) -β required in the healing
process, there is a high level of reactive oxygen
species (ROS), which can damage cells and collagen
degradation (Diegelmann and Evan, 2004).
Nowadays start developed therapy using
metabolite product from stem cell without the stem
cell. The use of this metabolite product is easier and
safer because it is aseluler. The AMSC metabolite
product was obtained at culture from AMSC, which
in this metabolite product contained several
cytokines and growth factors required for wound
healing (Lindenmair et al., 2012; Ennis, Sui, and
Bartholomew, 2013).
Vitamin C known as antioxidants and play role
in collagen synthesis. These functions are believed
to also be useful in wound healing. As an
antioxidant vitamin C neutralizing ROS that we
could found in chronic ulcers. Vitamin C also
directly stimulates collagen synthesis. One
derivative of vitamin C that is stable is sodium
ascorbyl phosphate (SAP) (Telang, 2013).
2 CASE
38- year-old female patient, working as a housewife
came with chief complaint ulcer at her right foot
since 1 years ago, painless and no itchy sensation. At
first the ulcer is small, then became bigger and
deeper by the time. Patients have been frequently
treated since the last 8 months for her complaints,
Oktaviyanti, R., Rahmadewi, ., Alinda, M., Kusumaputra, B., Astari, L., Listiawan, M., Agusni, I., Rantam, F. and Prakoeswa, C.
The Efficacy of Human Amniotic Membrane Mesenchymal Stem Cells (hAMMSC) Plus Vitamin C for Treating Chronic Plantar Ulcer in Leprosy Patient: A Case Report.
DOI: 10.5220/0008159104330436
In Proceedings of the 23rd Regional Conference of Dermatology (RCD 2018), pages 433-436
ISBN: 978-989-758-494-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
433

she got treatment for treating wounds with sterile
normal saline, antibiotics ointments and framycetin
gauze dressing (FGD) but no improvement.
The patient was suffering from borderline
leprosy since 3 years ago. She had already got
multibacillary multi-drug therapy for 12 months and
had finished the treatment 1 year ago. The result of
microbiology Mycobacterium leprosy examination
was bacterial index (BI) 0 and morphological index
(MI) was negative.
The initial treatment for the ulcer was sterile
normal saline and surgical debridement to remove
necrotic tissue, callus, and debris. After obtaining a
clean ulcer, wound area and wound depth
measurements were performed. Then the ulcer was
given FGD and sterile gauze above the FGD. On
subsequent visit, the ulcers begin to be given topical
hAMMSC-CM + Vit C gel and covered with
transparent film dressings. Application of gel was
done every 3 days, and weekly evaluation included
measurement of the size and the depth of the ulcer
was done. Initial measurements of the ulcer was 2 x
2 x 0.4 cm. Patient received hAMMSC-CM +
vitamin C gel for 7 weeks. After the therapy with
hAMMSC-CM + Vit C gel for 7 weeks, the ulcer
healed compeletely.
3 DISCUSSION
Since the early 20th century, amniotic membranes
have been used for the treatment of widespread
injuries, burns, chronic ulcers, deep ulcers, and
surgical wounds that are difficult to heal
completely. Studies on the human amniotic
membrane mesenchymal stem cells (hAMMSC) for
the repair and regeneration of cells showed good
results. The growth factors and cytokines can be
found in the tissue medium of stem cells in in
vitro conditions through its metabolite product so it
can be utilized as a useful modality in the process of
cell regeneration (Bauman, Girling, and Brand,
1963; Diegelmann and Evan, 2004).
The previous research has proved that injuries
that are difficult to heal in humans have high levels
of oxidative stress. Wounds or chronic ulcers often
show the increasing levels of reactive oxygen
species (ROS) or free radicals that can delay wound
healing process, inhibit the formation of granulation
tissue and epithelialization. Free radicals are formed
in response to tissue damage which then inhibits the
recovery process by attacking DNA, membranes,
proteins, and lipids from cells. Antioxidants are
believed to repair wounds by reducing the damage
caused by free radicals released by neutrophils in the
inflammatory phase of the wound healing process
Ennis, Sui, and Bartholomew, 2013; Telang, 2013).
Plantar ulcers in leprosy are neuropathic ulcers,
occurring due to prior nerve damage or sequelae.
Chronic ulceration results from one or more
extinctions of the wound healing phase (WHO,
2012). In a chronic wound, one may detect a
prolonged inflammatory response, elevated protease
activity and decreased growth factors. These
findings may account for the delayed wound healing
process. The prolonged inflammatory response may
be caused by infection or just inflammation. The
FGD is an antibiotic wound dressing that works in
the inflammatory phase of wound healing by treating
the infection and contra-acting the colonisation. It is
not effective in an inflammatory phase of wound
healing that is not caused by infection. It is also not
effective in the proliferative phase of wound healing
(Halim and Menald, 2010; Metro Tempo Co., 2013).
Prakoeswa et al (2018), study analytical
experimental approach comparing the topical
hAMMSC-CM and the framycetin gauze dressing
(FGD) applied every 3 days up to 8 weeks on the
healing of CPUL. Ulcer healing in the hAMMSC-
CM group was significantly better than that in the
FGD group with significant clinical and statistical
differences (p < 0.005 and p< 0.005).
The hAMMSCs contains many cytokines and
growth factors, which may be effective in the
inflammatory and the proliferation phase of the
wound healing. In the inflammatory phase of wound
healing, the pro-inflammatory cytokines in
hAMMSCs may influence the infection and
colonisation via its antimicrobial effect and the anti-
inflammatory cytokines in hAMMSCs will diminish
the inflammation (immunomodulatory effect). In the
proliferation phase of the wound healing, the growth
factors in hAMMSCs willstimulate proliferation and
migration of cells, induce angiogenesis, and
stimulate the formation of tissue granulation and
epithelialization (Bauman, Girling, and Brand, 1963;
Diegelmann and Evan, 2004).
RCD 2018 - The 23rd Regional Conference of Dermatology 2018
434
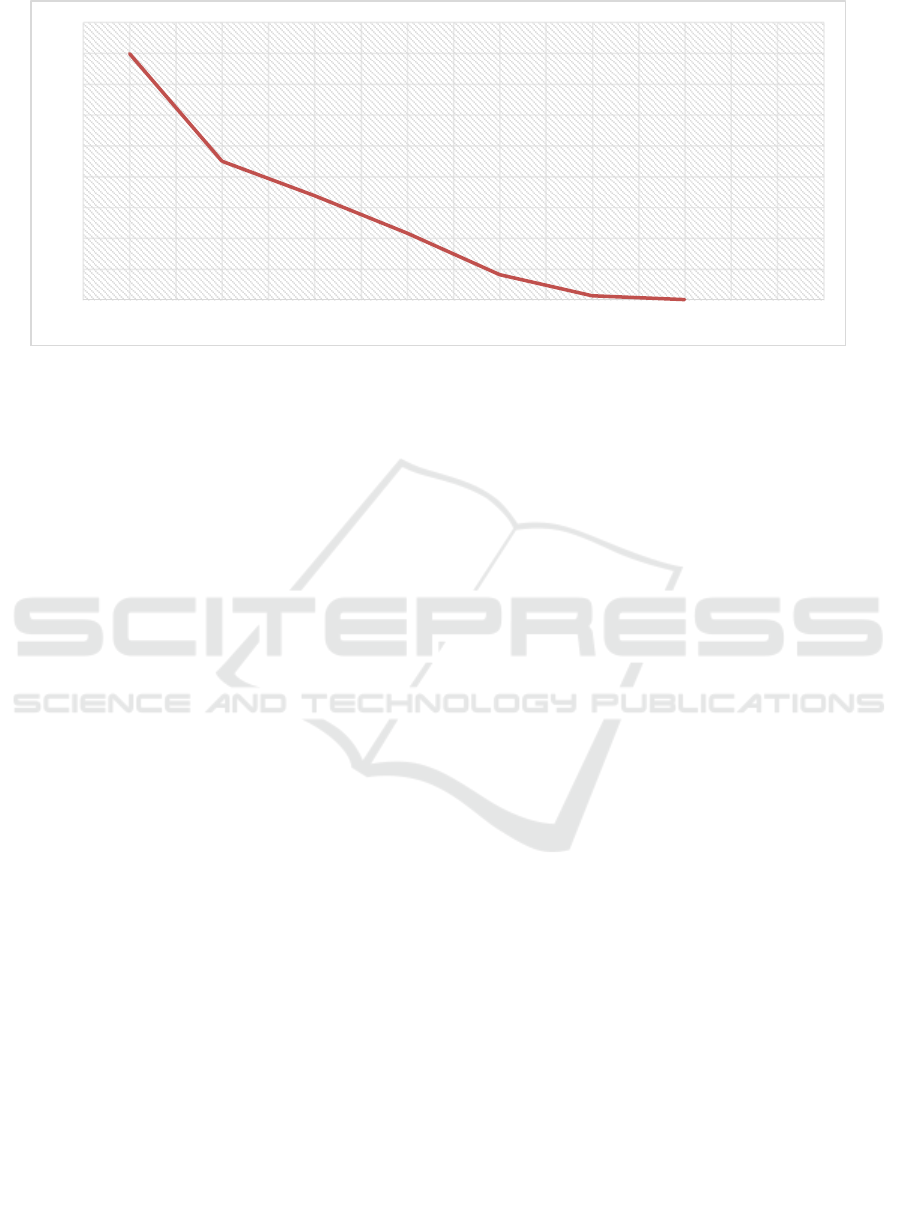
Figure 1: Healing progression. Ulcer treated hAMMSC-CM + Vit C healed completely at week 7
In the dermatology Vitamin C known as
antioxidants, and collagen synthesis. These functions
are believed be useful in wound healing. The
function of vitamin C as an antioxidant is beneficial
in neutralizing ROS present in chronic ulcers.
Vitamin C also directly stimulates collagen
synthesis. One derivative of vitamin C that is stable,
is sodium ascorbyl phosphate (SAP). This derivative
has the same function as vitamin C but has better
stability. The use of vitamin C and metabolite
products simultaneously is expected to accelerate
wound healing, with faster healing times that cost
less and the quality of life of patients increases
(Lindenmair et al., 2012; Ennis, Sui, and
Bartholomew, 2013).
Function of ascorbic acid as an antioxidant is
useful in inhibiting free radicals produced in the
inflammatory process (Moro, 1999; Telang, 2013).
Another study by Sarpoosh HR and colleagues
assessed the effectiveness of topical vitamin C in
necrotic tissue cause burns grade II. There were 30
patients with burns gr II divided into control groups
receiving sulfadiazine ointment and treatment group
receiving sulfadiazine ointment accompanied with
vitamin C. In the group of treatment the initial
necrotic tissue volume was 1.033 ± 0.182 and on day
14 the average volume was 1.233 ± 0.430, and in the
initial necrotic tissue volume control group was
1,000 ± 0,000 and at day 14 the average volume
became 1,700 ± 0.794. There was a significant
difference between the two groups, in the treatment
group, the mean difference of necrotic tissue volume
was less than the control group (Singh and Singh,
2012; Sarpooshi, Vaheb, Tabarayee, Sabzevar, and
Mortazavi, 2016)
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this case the function of vitamin C is SAP as
antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and
collagen synthesis can help wound healing where in
chronic injury disorders occur in the inflammatory
phase, and the proliferation phase. The combination
of PM-AMSC which contained several cytokines
and growth factor with vitamin C seemed to give
good results on the healing of chronic plantar ulcers
of leprosy, and in this case there were no side effects
in mixing PM-AMSC with vitamin C in chronic
leprosy ulcers.
The ulcer improvement within 7 weeks of
AMSC + vitamin C. There are several other factors
that also play a role in ulcer healing, age, type of
work and duration of ulcers may contribute to ulcer
healing.
REFERENCES
Bauman, J.H., Girling, J.P., Brand, P.W., 1963. Plantar
Pressure and tropic ulceration. The Journal Of Bone
And Joint Surgery, 4, 652-673.
Diegelmann, R.F., Evan, M.C., 2004. Wound healing : an
overview of acute, fibrotic and delayed healing.
Frontiers in Bioscience, 9, 283-289.
Ennis, W.J., Sui, A., Bartholomew, A., 2013. Stem cells
and healing: impact on inflammation. Adv Wound
Care, 7, 369-378.
Halim, L., Menald, S.L., 2010. Tata Laksana
Komprehensif Ulkus Plantar pada Pasien Lepra. Maj
Kedokt Indon, 60, 237-244.
Lindenmair, A., Hatlapatka, T., Kollwig, G.,
Hennerbichler, S., Gabriel, C., Wolbank, S., et al.,
1,6
0,9
0,676
0,432
0,162
0,025
0
0
0,2
0,4
0,6
0,8
1
1,2
1,4
1,6
1,8
Week1 Week2 Week3 Week4 Week5 Week6 Week7 Week8
The Efficacy of Human Amniotic Membrane Mesenchymal Stem Cells (hAMMSC) Plus Vitamin C for Treating Chronic Plantar Ulcer in
Leprosy Patient: A Case Report
435

2012. Mesenchymal stem or stromal cells from
amnion and umbilical cord tissue and their potential
for clinical applications. Cells, 1, 1061-1088.
Metro Tempo Co., 2013. (Internet). Jakarta. (cited Oktober
2015). Available
from:http://metro.tempo.co/read/news/2013/02/14/214
461169/penderita-kusta-indonesia-tertinggi-ketiga-
dunia
Moro, O., 1999. Biological activities of stable ascorbic
acid derivative, 2-0-a-D- glucopyrasonyl-L-ascorbic
acid (AA-2G) in cosmetics. Shiseido Research Center.
J ApplCosmetol, 18, 154-163.
Prakoeswa, C.R.S. et al., (in press). Efficacy of topical
human amniotic membrane mesenchymal stem cell-
conditioned medium (hAMMSC-CM) on the healing
of chronic plantar ulcers in leprosy: a controlled
prospective clinical trial.
Sarpooshi, H.M., Vaheb, M., Tabarayee, Y., Sabzevar,
A.V., Mortazavi, F., 2016. The effects of topical
vitamin C solution on the necrotic tissue volume of
burn wounds. Journal of Nursing and Midwifery
Science, 3(3), 11-17.
Singh, P., Singh, P., 2012. Role of topical ascorbic acid in
management of refractory corneal ulcer. IOSR Journal
of Pharmacy, 2, 1-4
Telang, P.S., 2013. Vitamin C in dermatology. Indian
Dermatol Online J., 4: 143–6.
World Health organization, 2012. Weekly Epidemiological
Record, 87, 317–328.
RCD 2018 - The 23rd Regional Conference of Dermatology 2018
436
