
The Effect of Media Exposure, Family Closeness, and Knowledge
about Sexually Transmitted Disease on Sexually Transmitted Disease
Risk Behaviors in Senior High School Students
Oki Wihardiyanto
1
, Flora Ramona Sigit Prakoeswa
2
, C. R. S. Prakoeswa
3
1
Faculty of Medicine Muhammadiyah University of Surakarta, Surakarta, Indonesia
2
Department of Dermatology and Venereology Muhammadiyah University of Surakarta-PKU Muhammadiyah Hospital,
Surakarta, Indonesia
3
Department of Dermatology and Venereology- Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Airlangga – Dr Soetomo General
Hospital, Surabaya, Indonesia
Keyword: Sexual Behaviour, Media Exposure, Family Closeness, Knowledge.
Abstract: Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) is one of the reproductive health problems that caused by unsafe
sexual behavior. STDscan be caused by multiplefactors, such as influenced by media exposure, family
closeness, and the knowledge about STDs. The aim of this research is to know the correlationbetween
media exposure, family closeness, and knowledge about STDs on STDs risk behaviors in senior high school
students.This study used cross sectional method, with 95 subjects of senior high school students, using
family closeness questionnaire, media exposure questionnaire, and sexual knowledge and behavior
questionnaire, the data were analyzed by wilcoxon test and logistic regression test.Based on the wilcoxon
test, the relation of media exposure, family closeness, and the knowledge about STDswith STDs risk
behaviors obtained z scores 3.316 (p = 0.001), -8.352 (p = 0,000), -5,000 (p = 0,000), respectively. The
regression test showed a correlation value between media exposure, closeness, and the knowledge about
STDs with STDs risk behavior of each 3,561 (p=0,040), 1,417 (p=0,011), 5,553 (p=0,037). There is a
relationship between media exposure, family closeness, and the knowledge of STDs on STDs risk behaviors
in senior high school students. Knowledge about STDs is the most influential factor in STDs-risk behavior
compared to media exposure and family closeness.
1 INTRODUCTION
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) is the
pandemics that caused health, social, and economic
problems. STDs is one of the reproductive health
problems that caused by unsafe sexual behavior.
Based on data from the World Health Organization
(WHO) there are more than one million people
affected by STDs every day and 357 million cases
occur each year
(WHO, 2016). In Indonesia, the
incidence of STDs in 2016 is about 41.259 cases
(Indonesian Ministry of Health, 2016).
Smith (2015) stated that the transmission of
STDs can be prevented with a safe sex (Smith,
2015). But the result of Crosby’s (2012) research
showed that the safe sex is less effective than avoid
the high risk of behaviour in preventing STDs
(Crosby, 2012). According to the data of Indonesian
population and family information network
(BKKBN) 62,7% students in Indonesia had a high
risk of sexual behaviour
(BKKBN, 2015).
The high risk of sexual behaviour can be
trigerred by several things, such as social
enviroment, media exposure of pornography, family
bonding, and the knowledge of STDs (Departemen
Kesehatan Republik Indonesia, 2016). In order to
prevent the high risk of sexual behaviour and STDs
we need to know which factors that have a greater
influence of sexual behaviour.
2 METHODS
This study used cross sectional method. The number
of subject calculated with slovin formula :
Wihardiyanto, O., Prakoeswa, F. and Prakoeswa, C.
The Effect of Media Exposure, Family Closeness, and Knowledge about Sexually Transmitted Disease on Sexually Transmitted Disease Risk Behaviors in Senior High School Students.
DOI: 10.5220/0008156002950298
In Proceedings of the 23rd Regional Conference of Dermatology (RCD 2018), pages 295-298
ISBN: 978-989-758-494-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
295
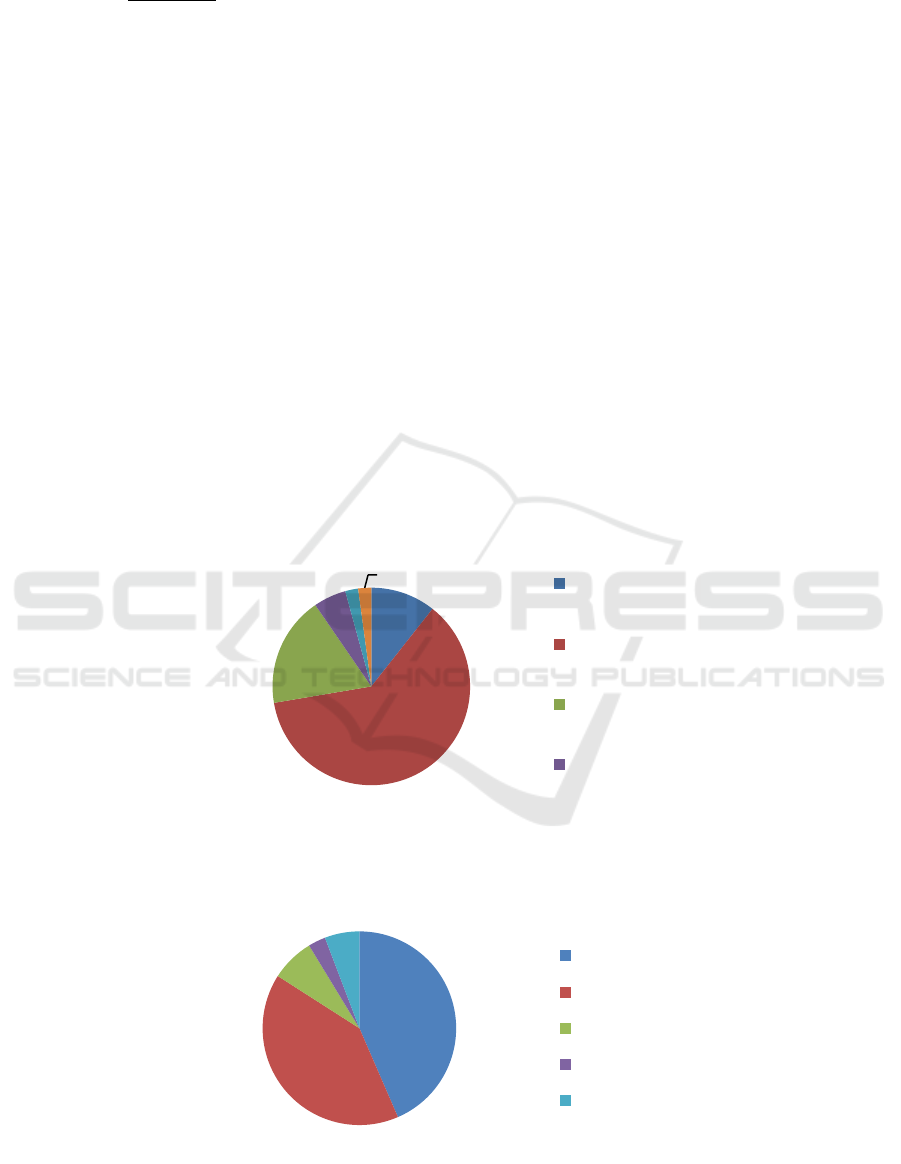
43%
41%
7%
3%
6%
internet
film/video
television
book/magazine
others
𝑛
𝑁
1𝑁
𝑑
1
and obtain the minimum number of subject is 92
students (𝑛 minimum sample, N = population, d
= maximum tolerantion) . To be included, subject of
this study had to meet three criteria. First, the subject
must be aged 14 – 19 years old. Second, the subject
had the score of L-MMPI less than 10. Third, the
subject is not a boarding student.
The data was colected using family
questionnaire, media exposure questionnaire, and
sexual knowledge and behavior questionnaire. The
data were analyzed by wilcoxon test and regression
logistic test. The wilcoxon test used to knowing the
correlation between the variables. The regression
logistic test used to look for which variable that has
the highest influence of STDs and to predict the
amount of influence from each variable.
3 RESULTS
The number of subject with a high risk of STDs
from this study is 7,4% and the low risk of STDs is
amount 92,6%. The distribution of media exposure
showed that 7,4% subjects never had a exposure of
pornography, 69,5% subjects had a moderate
exposure of pornography, and 23,1% subjects had a
high exposure of pornography. About the family
closeness, there are 11,6% of subjects which had a
bad relation with teir family. The distribution of
knowledge about STDs on subject showed that 6,3%
subjetcs had a bad knowledge, 38,9% subjects had
an intermediate knowledge, and 54,7% subjects had
a good knowledge.
All the variables of this study had a significance
correlation to STDs risk behaviour with the p value
less than 0,005. The subject with a high exposure of
pornography had a higher responsibility to do a
sexual risk behaviour 3,561 point (p value: 0,04)
than the others. The less closeness with family
improved the responsibility to do a sexual risk
behaviour at the point 1,417 (p value: 0,011). The
less knowledge about STDs also improved the
responsibility to do a sexual risk behaviour at the
point5,553 (p value:0,037).
Figure 1: Distribution of sexual activity in senior high school students.
Figure 2: Distribution of pornoghraphy exposure in senior high school students.
11%
62%
18%
5%
2% 2%
None
Masturbation
Kissing
Petting
RCD 2018 - The 23rd Regional Conference of Dermatology 2018
296
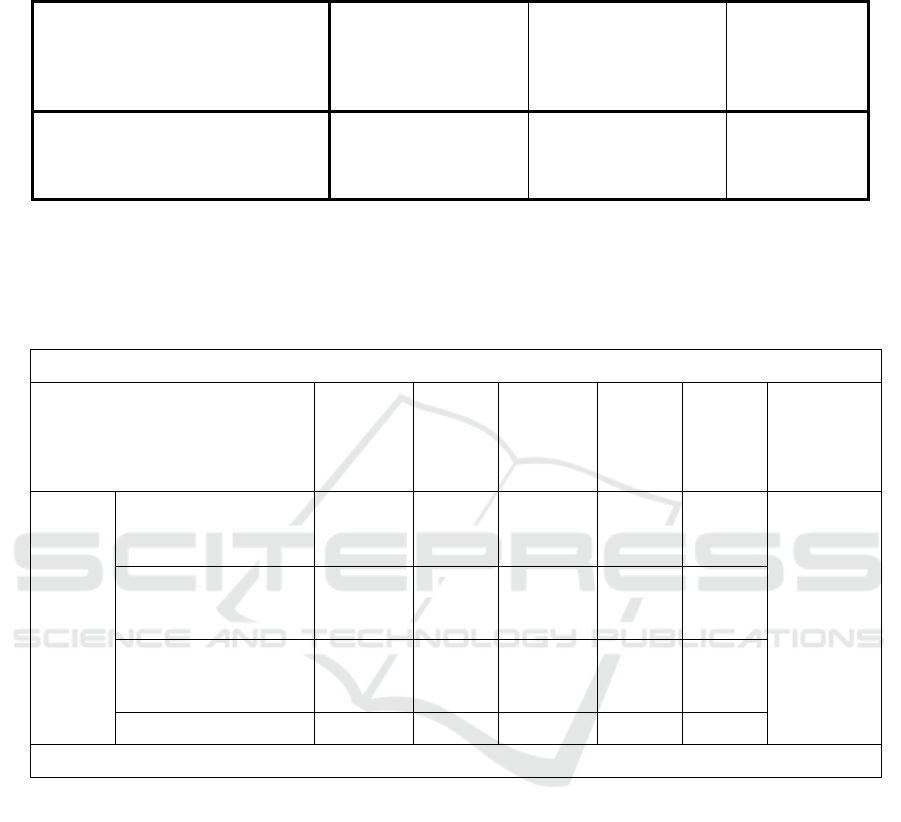
Table 1: Univariate test of variable.
Test Statistics
a
STDs Risk Behaviour –
Family Closeness
STDs Risk Behaviour –
Media Exposure
STDs Risk
Behaviour –
Knowledge of
STDs
Z– score
-8,352
b
3,316
c
-5,000
c
Asymp. Sig. (2-tailed)
,000 ,001 ,000
a. Wilcoxon Signed Ranks Test
b. Based on negative ranks.
c. Based on positive ranks.
Table 2 : Correlation between media exposure, family closeness, and knowledge about STDs on STDs risk behaviour.
Variables in the Equation
B S.E. Wald Sig. Exp(B)
Nagelkerke
R Square
Step 1
a
Family closeness
-4,06 1,598 6,452 0,011 1,417
0,692
Media exposure
0,579 1,276 0,206 0,04 3,561
Knowledge about STDs
-1,875 0,899 4,354 0,037 5,553
Constant
5,491 4,408 1,552 0,213 242,59
a. Variable(s) entered on step 1: Family closeness, Media exposure, Knowledge about STDs.
4 DISCUSSION
The number of subjects with a high risk of STDs
from this study is 7,4%. The family closeness from
this group categorized as a low family closeness
with a score of family closeness questionaire less
than 50%. Less score on family closeness can
increased the risk of STDs from the subjects 1,417
point. It can be occured because the low of family
closeness will make the adolescent have a low
function of enviromental control
(Mahmudah, 2016).
The recent study showed that the low of family
closeness can increase the risk of STDs 4,65 point
(Yusuf, 2017). Based on Abraham Harold Maslow’s
theory about human behaviour, behaviour can be
occured from the natural needs from the human. In
this case, if the natural needs from the adolescents
about bonding with family can not fulfilled, the
adolescents will vent their needs on the other
behaviour such as sexual behaviour
(Sarwono,
2012). Family closeness had a significant effect ti
reduce the STDs risk behaviour. Previous study
showed that family intervention can reduce the risk
of STDs on adolescents up to 20%
(Prado, 2012).
Media exposure from the subjects with high risk
of STDs is categorized as a massive exposure. The
subject with a high risk STDs had a 15,7% higher
exposure than the subject with low risk of STDs.
From this study, media exposure couldincrease the
risk of STDs from the subjects 3,561 point. Based on
The Effect of Media Exposure, Family Closeness, and Knowledge about Sexually Transmitted Disease on Sexually Transmitted Disease
Risk Behaviors in Senior High School Students
297

Green Behaviour theory, media exposure include in
enabling factor of human behaviour. Massive
exposure from the enabling factor will lead the
human to had a behaviour which accordance with
the exposure. The other theory said that the human
behaviours are based on human experience and
insight. In other word, if adolescents get a massive
exposure about pornography, it can lead them to had
a high risk sexual behaviour than the others
(Burke,
2001; Sarwono, 2012)
The knowledge of STDs from the subjects with
high risk of STDs is categorized as low knowledge
with the score less than 50%. The low of knowledge
about STDs could increase the risk of STDs 5,553
point. The recent study showed that subjects with
high knowledge about STDs will decrease the risk of
STDs 8,3% compared with subjects with low
knowledge about STDs. Based on cognitive theory,
knowledge will make someone knowthe positive and
negative effect from their deeds. The higher
knowledge about STDs will make someone
understand the negative effects from unsafe sexual
behaviour. If someone know the negative effect
from unsafe sexual behaviour, it can lead them to
avoid the sexual risk behaviour
(Burke, 2001;
Mahmudah, 2016). Previous research showed that
intense intervention about knowledge of STDs can
decrease the incidence of STDs up to 19%
(Kusnan,
2016).
The knowledge of STDs is the most influence
factors on STDs risk behaviour between media
exposure and family closeness.This happens because
the knowledge is the major pradisposing factor in
behavioral theory. As a major predisposing factor,
knowledge will affect attitudes, individual values /
individual norms, and sociodemographic factors.
Accordingly, the low level of knowledge will lead
someone to get an inappropriate behaviours
(Burke,
2001; Sarwono, 2012).
5 CONCLUSION
There is a relationship between media exposure,
family closeness, and the knowledge of STDs on
STDs risk behaviors in senior high school students.
The knowledge about STDs is a more influential
factor in STDs-risk behavior (odd ratio: 5,553)
compared to media exposure (odd ratio: 3,561) and
family closeness (odd ratio:1,417).
Family closeness and knowledge about STDs
had a negative effect on STDs risk behaviour. The
lower family closeness and knowledge about STDs
will increase the risk of STDs. While media
exposure had a positive effect on STDs risk
behaviour. The more often subjects exposed with
pornography media then the risk of STDs will also
increase. To get a better result, author advises the
next researchers to find out the effect of intensive
intervention of family closeness, media exposure,
and knowledge of STDs on sexual risk behaviour in
students.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The researcher presents his sincere appretiation to
Muhammadiyah University of Surakarta which has
been facillitated this study and to Capital investment
and service agency integrated one door province of
central java (DPMPTSP) for allowing us to condust
this study in Surakarta Regency.
REFERENCES
BKKBN: Survei Demografi Kesehatan Indonesia, 2015.
Indonesia Ministry of Health.
Burke, P. 2001. History of Social Theory. Jakarta:
Yayasan Pustaka Indonesia
Data dan Informasi Kesehatan Profil Kesehatan Indonesia,
2016. Departemen Kesehatan Republik Indonesia.
Health Data and Information dan Informasi Kesehatan
Profil Kesehatan Indonesia, 2016.Departemen
Kesehatan RI. Health Data and Information:
Indonesian Health Profile. Jakarta: Indonesian
Ministry of Health.
Kusnan, A., 2018. Analysis of the Determinant Factors
Related to the Prevalence of Sexual Infectious
Infection Disease of the Prostitutes in Kendari, Bau-
Bau and Muna Year 2012. Jurnal Kesehatan.
Mahmudah, Yaunin, Y. and Lestari, Y. 2016. Correlating
Factors of Sexual Behaviour In Adolescents In
Padang. Jurnal Kesehatan Andalas.
Prado, G., Pantin, H., Huang, S., Cordova, D., Tapia, M.
I., Velazquez, M. R., ... & Jimenez, G. L., 2012.
Effects of a family intervention in reducing HIV risk
behaviors among high-risk Hispanic adolescents: A
randomized controlled trial. Archives of Pediatrics &
Adolescent Medicine, 166(2), pp. 127-133.
WHO. Int., 2016.Sexually Transmitted Disease Infection,
The Importance of a Renewed Commitment in a
Achieving Global Sexual and Reproductive Health.
Yusuf, A., Khoridatul, B., Endang, H., and Wiyono, A.,
2017. Correlation Between Family Closeness and
Social Environement to Adolescents Sexual
Behaviour. Journal Ners, pp.14-21
RCD 2018 - The 23rd Regional Conference of Dermatology 2018
298
