
Indonesia's First: Botulinum Toxin Procedure as a Modality of
Successful Vaginismus Treatment
Robbi Asri Wicaksono
1*
, Merlinda Nur Annissa
2
.
1
Obstetric and Gynecology, Limijati Woman and Children Hospital, Bandung, Indonesia
2
Dermatology and Venereology, Limijati Woman and Children Hospital, Bandung, Indonesia
Keywords: vaginismus, botulinum toxin
Abstract: Vaginismus is a common female sexual dysfunction, but mostly unknown among clinicians, that continues
to be ignored by many medical schools, residency programs and is rarely discussed at medical meetings.
Patients with vaginismus had involuntary spasm of the pelvic muscles surrounding of the vagina.
Penetration such as tampons, finger, vaginal dilators, gynecological exams, and intercourse is often painful
or impossible. This article aims to bring attention to the understanding and treatment of vaginismus.
Vaginismus patients came to Limijati Hospital between January and December 2017. Diagnosis was made
based on history taking and physical examination of vaginal spasm. The severity of vaginismus was ranked
1-5 according to Lamont-Pacik classification. Seventeen patients underwent the procedure consists of total
intravenous anesthesia, botulinum toxin (botox) injections, and progressive dilation, with 100% same day
successful self dilation using 4 inch silicone dilator, and 82.3% achieved sexual intercourse in average of
4,5 weeks after the procedure. Botox along with other modalities appear to be a promising result for
vaginismus treatment. Awareness among clinicians about diagnosis and treatment of vaginismus is
extremely needed.
1 INTRODUCTION
Vaginismus thought to be one of the most common
female sexual dysfunction (Pacik, 2014).
Approximately 1-7% of female worldwide suffer
with this condition, and in a clinical setting has been
estimated as 5% to 17% (Pacik, 2011). Vaginismus
patients usually remain silent, feels taboo, rarely
exposed in community nor clinicians (Pacik 2011;
Pacik and Gelatta, 2017), make patients become
neglected in many aspects.
Vaginismus is a physical disorder as noted by
vaginal spasm (Pacik, 2010; Pacik, 2014), persistent
or recurrent difficulty in allowing vaginal entry of
the penis, finger, or any object, despite the woman’s
expressed wish to do so. It is a condition in which
the muscles in the vagina spasm involuntarily
preventing any vaginal penetration. Or, if
penetration is possible, it can be very
painful(Bertolasi et al., 2009; Pacik, 2010).
The cause of vaginismus is unknown (Berek,
2007; Pacik, 2011; Pacik, 2014). Vaginismus is a
very serious problem for the patients. It is poorly
understood, and many physicians across a number of
specialties have limited experience with this entity.
It is hoped that with additional awareness,
physicians will have yet another modality for the
treatment of vaginismus (Pacik, 2015).
Severity of vaginismus was ranked 1-5 according
to Lamont-Pacik classification(Pacik, 2011; Pacik
and Gelatta, 2017). The treatment for vaginismus
depends on the severity, includes education, sexual
counseling, Kegel’s exercises, dilation with dilators,
hypnotherapy, lubricants (Pacik, 2010; Pacik, 2014),
use of local anesthesia, incision of spasmodic
perivaginal muscles, intravaginal botox injection
(Shafik and El-Sibaik, 2000; Ghazizadeh and
Nikzad, 2004; Bertolasi et al., 2009; Fageeh, 2011;
Pacik and Gelatta, 2017).
Botox type A is a neurotoxin produced by
Clostridium botulinum that paralyzes muscles by the
prevention of acetylcholine release and has been
shown to be useful in treating conditions associated
with neuromuscular dysfunction such as muscles
hyperactivity and spasms (Ghazizadeh and Nikzad,
2004). There was no reporting case in Indonesia
about vaginismus nor the therapy. This is the first
research about botox modalities as vaginismus
204
Wicaksono, R. and Annissa, M.
Indonesia’s First: Botulinum Toxin Procedure as a Modality of Successful Vaginismus Treatment.
DOI: 10.5220/0008154002040208
In Proceedings of the 23rd Regional Conference of Dermatology (RCD 2018), pages 204-208
ISBN: 978-989-758-494-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reser ved

treatment in Indonesia. This procedure is adapted
from a procedure developed by Peter T. Pacik, MD.,
FACS (Plastic Surgery Center, Manchester, NH,
USA) who has received approval from the United
States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to
continue studies on the use of botox to treat
vaginismus.
2 METHODS
2.1 Assessment
Vaginismus patients initially contacted me without
hesitation through social media which dedicated for
vaginismus information, they know that they are
having vaginismus, since they have experienced
difficulties on penile penetration in sexual
intercourse during their marriage or acitive sexually.
A scheduled appointment for initial consultation and
physical examination was offered to each patient.
Until this paper is submitted, total 141 patients have
contacted me (from all over Indonesia, including 2
patients from Malaysia, and 1 patient from Nigeria),
admitting that they have penetration difficulties.
Fourty-nine patients came to my office for initial
examination and consultation, to get their
vaginismus and the severity confirmed, also for
determining therapy options. Fourty one of them
(83.6%) are candidates for the procedure (3rd to 5th
degree vaginismus). Nineteen patients underwent the
procedure.
Vaginismus diagnosis is based on history taking
and physical examination. When a patient complains
that attempted intercourse feels like it is ‘‘hitting a
wall’’, suggestive of spasm at the level of the
introitus, this is a symptom that helps differentiate
vaginismus from dyspareunia, vulvodynia and
provoked vestibulodynia (vestibulitis). A Q-tip test
is performed to ruled out vulvodynia by pressing the
wet Q-tip against the vestibule at the 2, 4, 6, 8, and
10 o’clock positions to determine if there is
provoked pain. If Q-tip test is negative, vulvodynia
is ruled out.
Next, simple finger penetration attempt
by examiner was perfomed to determine the vaginal
spasm (Goldstein, Pukall, and Goldstein, 2009).
Patients with 3rd-5th degree was adviced to
undergo the assisted dilation procedure enabling
them to start the successful self dilation using
silicone dilator.
Table 1: Severity of vaginismus
Grade Description
Lamont grade 1 Patient is able to relax for pelvic examination
Lamont
g
rade 2 Patient is unable to relax for
p
elvic examination
Lamont
g
rade 3 Buttocks lift off table. Earl
y
retreat
Lamont
g
rade 4 Generalized retreat: buttocks lift u
p
, thi
g
hs close,
p
atient retreats
Pacik grade 5 Generalized retreat as in level 4 plus visceral reaction, which may result in any one or
more of the following: palpitations, hyperventilation, sweating, severe trembling,
uncontrollable shaking, screaming, hysteria, wanting to jump off the table, a feeling of
b
ecomin
g
unconscious, nausea, vomitin
g
, and even a desire to attack the docto
r
(references : Lamont Pacik Classification)
Once the diagnosis and severity of vaginismus
had been determined, treatment options can be
discussed. Basically, if a patient can tolerate finger
penetration it means that they can start self dilation
immediately. But when a patient cannot tolerate any
kind of simple penetration, assisted dilation
procedure is the most suitable option for them. Other
characteristics such as age, duration of marriage or
active sexually, previous treatment, and minimal
progress of self dilation, are also used for procedure
consideration.
Some women choose the more traditional
treatment of dilation. Dilation consists of using
several dilators over time in increasing size. A
dilator is inserted into the vagina to gradually stretch
the vaginal muscles. Some patients become frustated
with the dilation process and prefer Botox procedure
so they can progress to the larger sized dilators.
Other women, seek the botox procedure directly.
Most women have tried dilation at home and were
either unsuccesful progressing to the larger sized
dilators or were too fearful to even begin
treatment.
2.2 Assessment
In the operating room, patients are given total
intravenous anesthesia. A pelvic exam performed to
assess vaginal tightness and anatomical
abnormalities, speculum is placed inside the vagina,
initially for inspection of vagina and cervix. Then
total of 100 units botox injected throughout the
vaginal vault, 50 units of Botox injected into the
Indonesia’s First: Botulinum Toxin Procedure as a Modality of Successful Vaginismus Treatment
205
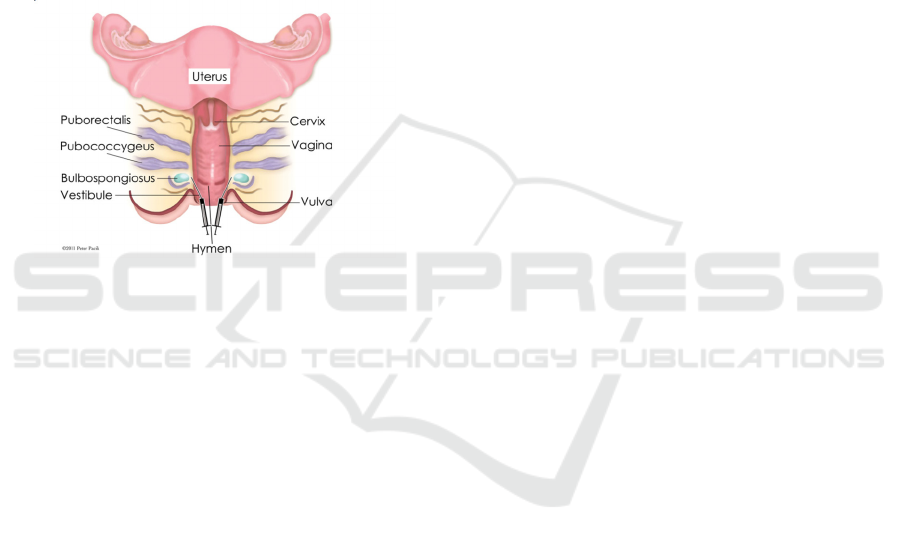
puborectalis and pubococcygeus muscles; divided
into four clumns of thhree injections bilaterally.
After that, 18 ml of local anesthetic (0,25%
marcaine with epinephrine 1:400.000) then injected
throughout the vault in a similar distribution to the
previous botox injections.
The bulbocavernosus then injected in three
columns; one proximal, one inferior and one distal
bilaterally. A largest dilator (number 6) which had
covered with xylocaine gel and natural lubricant
inserted and remain in placed as the patient brought
to the recovery room. This allows patients to wake
up in recovery with pain-free experience for the first
time while a static penetration using largest dilator
happened.
Figures 1. Area of botox injection
7
Patients transported to her room for dilation
excercise. For the next 3-4 hours, patient has some
rest and recover for maximum alertness. The dilator
was totally removed for the first time as preparation
for urinating after the procedure. After that, patient
is able to successfully reinsert the dilator without
any significant pain and fear. During that process,
doctor supervised dilation process all the time, and
also give them positive direction and encouragement
as form of psychological support. Patients must do
the dilation using method and movement as
instructed in a certain time, such as rotating, move
back forward, and changing size. At night, number 4
dilator was worn through the night while she was
sleeping.
On the next day, doctor evaluate the progress of
the dilation and gave patient and her spouse
counseling about transition from dilation to sexual
intercourse. They were discharged with a dilation
program at home with typical method and
movement. First follow up is one month after the
procedure. Patient will undergo a simulation of
several vaginal examination, such as pelvic
examination, speculum examination, and
transvaginal ultrasound. Patients are allowed to have
direct communication to make doctor keep informed
about their problem and progress.
3 RESULTS
Fourty one patients (83.6%) with 3-5 level of
vaginismus are candidates for the procedure, 17
patients underwent the procedure. Seventeen
patients (100%) achieved nonsexual penetration and
self dilation at same day as procedure. Seventeen
patients (100%) have successful vaginal ultrasound
and pelvic examination in 1 month post procedure
follow up. For penile penetration in sexual
intercourse, 14 patients (82.3%) achieved it within
average of 4,5 weeks after the procedure.
4 DISCUSSIONS
Vaginismus is a more common sexual problem than
previously reported (Lamont, 1978). There is no data
about vaginismus di indonesia. This is the first study
about vaginismus in Indonesia.
Vaginismus is a subset of the genito-pelvic pain
and penetration disorders and is currently defined by
the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental
Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-V) as a penetration
disorder (Pacik, 2014), in accordance in ICD-10
definition as involuntary spasm of the pelvic
muscles surrounding the outer third of the vagina,
spesifically the perineal muscles and the levator ani
muscles (Lamont, 1978; Pacik, 2014). In severe
cases of vaginismus the adductors of the thighs, the
rectus abdominis, and the gluteus muscles may be
involved (Lamont, 1978). The diagnosis of
vaginismus is made by history and physical
examination (Pacik, 2014).
Patient came mostly for their unconsummated
marriage and infertility. Two patients referred by
dermatologists. Nineteen vaginismus patient treated
with botox procedure in this study has the range of
marriage duration between 6 months and 9 years. All
of them never had penile penetration, they
complains that attempted intercourse feels like it is
‘‘hitting a wall’’, suggestive of muscles spasm at
surrounding vagina.
The first reported use of Botox to treat
vaginismus was in 1997 (Ghazizadeh and Nikzad,
2004). Mechanism action of botox is the toxin enters
the nerves by binding to surface protein receptors
and undergoing into internalized vesicles. The light
chain is released into the nerve cytosol, and the
RCD 2018 - The 23rd Regional Conference of Dermatology 2018
206

SNARE (soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor
attachment protein receptor) protein complex is
cleaved to inhibit exocytosis of the neurotransmitters
such as acethylcholine (Goldsmith, Katz, and
Gilchrest, 2012) at the neuromuscular junction
(Shafik and El-Sibaik, 2000). The end result is a
chemodenervation of the cholinergic neurons, either
motor nerves or autonomic nerves, leading to
localized absence of muscle activity (Goldsmith,
Katz, and Gilchrest, 2012).
Botox produces its effect
by causing muscle paralysis, thus will inhibit
muscles spams in vaginimus. Improvement in
vaginismus is presumably due to paralysis of the
bulbospongiosus muscle. The latter appears to be
responsible for closure of the vaginal introitus on
trial of vaginal penetration. The other pelvic floor
muscles, levator ani and puborectalis muscles are
apparently not involved during vaginalpenetration as
the levator ani is inserted into the vaginal fornices
while the puborectalis is related to the lower part of
the vagina (Shafik and El-Sibaik, 2000).
Ghazizadeh and Nikzad reported the used of
Botox in the treatment of refractory vaginismus in
24 patients. In this study, Dysport (150 to 400 mIU)
was used. Twenty three patients were able to have
vaginal examinations 1 week after the procedure,
showing little or no vaginismus. One patient refused
vaginal examination and did not attempt coitus. Of
the 23 patients, 18 (78%) achieved satisfactory
intercourse, four (17%) had mild pain, and one was
unable to have intercourse because of her husband’s
impotence.
Botox procedure in this study consist of botox
injection in bulbospongiosus muscle, dilation with
the biggest dilator under anesthesia. The results were
100% patients have successful painfree penetration
without muscle spasm through self dilation using 4
inch silicone dilator at the same day of the
procedure, and 82,3% achieved sexual intercourse in
average of 4,5 weeks after the procedure.
Dilation, in the treatment of vaginismus is a
simple method buy may require long-term therapy
and fail in persistent cases (Shafik and El-Sibaik,
2000). Most women have tried dilation at home and
were either unsuccesful progressing to the larger
sized dilators or were too fearful to even begin
treatment (Pacik and Gelatta, 2017). Likewise,
behavioural therapy and psychotherapy, besides
being lengthy and expensive, may not succeed in
cureing the condition, especially in persistent and
severe degree of vaginismus. Meanwhile, botox
procedure is a simple, easy, rapid, and effective
treatment for vaginismus.
Side effects of botox including minor discomfort,
bruising (Goldsmith, Katz, and Gilchrest, 2012), dry
mouth, dysphagia, paresis extremities, or urine
incontinence (Shafik and El-Sibaik, 2000). Two
patients in this study report temporary mild urine
incontinence, this expected gone by the time botox
loses its effectiveness.
Botox is a safe drug when used according to the
manufacturer’s recommendations. During the past
20 years, Pacik has treated thousands of patients
using botos for dynamic facial wrinkles, excessive
sweating, migraine headhaches, and vaginismus,
with only rare minor untowards effects mostly the
result of migration of botox to nearby tissues.
Around 391 vaginismus patient were treated with
this botox procedure, there only few minor untoward
events such as temporary mild stress incontinence
(Pacik and Gelatta, 2017), same as this study. No
permanent sequele were noted.
Botox has a long duration of action up to 6
months,
loses its effectiveness within 4 to 6 months
(Goldsmith, Katz, and Gilchrest, 2012), but another
repeated botox procedure is usually not needed. At
this time period, patient has made the transition from
post-operative dilation to intercourse. In this study,
no patient was in need of re-procedure and there was
no reccurence during the follow-up period. Botox
procedure effected cure in all of the vaginismus
patients with no complications or recurrence.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Botox procedure appears to be safe and effective as
vaginismus treatment. This procedure has helped
many women to immediately start effective dilation
and also end their unconsummated marriage. It is
important for health care providers to know more
about vaginismus. Medical school, residency
program, and medical meetings are needed to spread
the knowledge about vaginismus and its treatment.
REFERENCES
Berek, J.S., 2007. ed. Berek & Novak’s Gynecology. 14th
ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Bertolasi, L., Frasson, E., Cappelletti, J.Y., Vicentini, S.,
Bordignon, M., Graziottin, A., 2009. Botulinum
neurotoxin type A injections for vaginismus secondary
to vulvar vestibulitis syndrome. Obstet Gynecol,
114(5), pp. 1008-1016,
doi:10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181bb0dbb.
Fageeh, W.M.K., 2011. Different treatment modalities for
Indonesia’s First: Botulinum Toxin Procedure as a Modality of Successful Vaginismus Treatment
207

refractory vaginismus in western saudi arabia. J Sex
Med, 8(6), pp. 1735-1739, doi:10.1111/j.1743-
6109.2011.02247.x.
Ghazizadeh, S., Nikzad, M., 2004. Botulinum toxin in the
treatment of refractory vaginismus. Obstet Gynecol,
104(5), pp. 922-925,
doi:10.1097/01.AOG.0000141441.41178.6b.
Goldsmith, L.A., Katz, S.I., Gilchrest, B.A., 2012.
Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 8th
editio. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Goldstein, A.T., Pukall, C.F., Goldstein, I., 2009. eds.
Female Sexual Pain Disorders. 1st editio. Oxford:
Blackwell Publishing.
Lamont, J., 1978. Vaginismus. Am J Obs Gynecol.
Pacik, P.T., 2010.When Sex Seems Impossible. (Cole JB,
ed.). Manchester NH: Odyne Publishing.
Pacik, P.T., 2011. Vaginismus: Review of current
concepts and treatment using botox injections,
bupivacaine injections, and progressive dilation with
the patient under anesthesia. Aesthetic Plast Surg,
35(6), pp. 1160-1164, doi:10.1007/s00266-011-9737-
5.
Pacik, P.T., 2014. Understanding and treating vaginismus:
a multimodal approach. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor
Dysfunct, pp. 25(12):1613-1620, doi:10.1007/s00192-
014-2421-y.
Pacik, P.T., 2015. OnabotulinumtoxinA as part of a
multimodal program to treat vaginismus. J Appl
Biobehav Res, 20(1), pp. 25-36.
doi:10.1111/jabr.12037.
Pacik, P.T., Geletta, S., 2017. Vaginismus Treatment :
Clinical Trials Follow Up 241 Patients. Sex Med, pp.
1-10, doi:10.1016/j.esxm.2017.02.002.
Porst, H., Buvat, J., 2008. Standard Practice in Sexual
Medicine, doi:10.1002/9780470755235.
Prakash, V., Garg, N., 2017. SM Gr up SM Dermatology
Intractable Vaginismus - Management by Incision of
Spasmodic Perivaginal Muscles and Resurfacing with
Labia Minora fl aps - New Appraoch, 3(4) , pp.3-5.
Shafik, a., El-Sibai, O., 2000. Vaginismus: results of
treatment with botulin toxin. J Obstet Gynaecol, 20(3),
pp. 300-302, doi:10.1080/01443610050009674.
RCD 2018 - The 23rd Regional Conference of Dermatology 2018
208
