
The Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Conditioned Medium (Adipose-
Derived and Wharton's Jelly-Derived) on the Prevention of
Hypertrophic Scar Formation
Gita Hening Bunga
1
, Retno Dwi Utami
1
, Erlina Pricilla Sitorus
1
, Novan Adi Setyawan
2
, Indah
Julianto
1,3
, Moerbono Mochtar
1
1
Dermatoveneorology Department Faculty of Medicine Sebelas Maret University, Surakarta, Indonesia
2
Pathology Anatomy Department Faculty of Medicine Sebelas Maret University, Surakarta, Indonesia
3
Dermama Biotechnology, Surakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: ADSC-CM, hypertrophic scar, scar elevation index, WJSC-CM
Abstract: The process of wound healing can lead to the formation of varied outcomes, from scarless healing to excessive
fibrosis (hypertrophic) or atrophic scar. Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) had been shown to prevent the growth
of fibrosis tissue. Conditioned media (CM) is the medium where stem cells are cultured. Adipose-Derived
Stem Cell Conditioned Medium (ADSC-CM) and Wharton’s Jelly Stem Cell Conditioned Medium (WJSC-
CM) are MSC-CM reported to contain growth factors, some of which plays a role in the formation of
hypertrophic scar such as TGFβ1 and VEGF, and some in the prevention of scar formation, such as bFGF.
This in vivo study conducted using 24 mice, divided into 4 groups: group I given Dulbecco's Modified Eagle
Medium (DMEM), group II ADSC-CM, group III WJSC-CM, and group IV without any treatment (control).
Before the injection, wound was made on the back of each mice with a 1 cm punch biopsy. On day 28th,
rebiopsy was done on the scar area, the tissue stained with hematoxyllin eosin staining to assess the Scar
Elevation Index (SEI). The SEI score showed that WJSC-CM group showed the lowest percentage of
hypertrophic scar formation (50%) compared to ADSC-CM (66.67%), DMEM (83.33%) or control
group(100%), although statistically the difference was not significant. This study showed that WJSC-CM
injection had a greater potential in preventing the formation of hypertrophic scar than ADSC-CM. It is thought
to be related to higher bFGF levels as well as lower TGFβ1 in WJSC-CM.
1 INTRODUCTION
The wound healing process can cause the formation
of fibrosis tissue, also known as scar. Scar tissue
consist of a collection of cells (especially fibroblasts)
and an irregular extracellular matrix (mainly
composed of collagen) (Gurtner et al., 2008).
Hypertrophic scar is a fibroproliferative dermis
disorder with typical features of excessive collagen
deposition in the dermis and subcutaneous layer. The
occurrence of hypertrophic scar indicates an
excessive wound healing process, including
migration and cell proliferation, inflammation,
increased of synthesis and secretion of cytokines and
extracellular matrix proteins, also remodeling of new
matrices that form to excessive deposition of
extracellular matrix (Meenakshi et al., 2005).
Several experimental and pre-clinical studies have
reported the potential of mesenchymal stem cells
(MSCs) to preventthe growth of fibrosis tissue (Dong
et al., 2015; Li, Zhang and Fu, 2016). Mesenchymal
stem cells may be present in both embryonic and adult
tissue such as adipose tissue, muscle, peripheral
blood, lung, heart, corneal stroma, dental pulp,
placenta, endometrium, amniotic membrane and
Wharton's jelly (Kalaszczynska et al., 2015).
The use of stem cell-conditioned media,
compared to direct stem cells, provides a better
solution in overcoming the limitations of cell-based
therapies (Jayaraman et al., 2013). Potapova et al
proved that the media used to culture stem cells, so-
called conditioned media, was useful for survival,
proliferation, invasion of extracellular matrix, and in
vitro endothelial cell migration (Potapova et al.,
2007). The conditioned media also contains a number
of cytokines and growth factors that are directly
146
Bunga, G., Utami, R., Sitorus, E., Setyawan, N., Julianto, I. and Mochtar, M.
The Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Conditioned Medium (Adipose-Derived and Wharton’s Jelly-Derived) on the Prevention of Hypertrophic Scar Formation.
DOI: 10.5220/0008152701460149
In Proceedings of the 23rd Regional Conference of Dermatology (RCD 2018), pages 146-149
ISBN: 978-989-758-494-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
related to the wound healing process (Jayaraman et
al., 2013).
Zhang et al showed that adipose-derived stem cell
(ADSC) intralesional injection can reduce the
formation of hypertrophic scar in rabbit ears by
decreasing the expression of α-SMA genes and
collagen type I, as well as reducing collagen
deposition (Zhang et al., 2015). Yun et al also
conducted research using ADSC injection on full-
thickness defects made on pig's back and found that
ADSC injection reduce the size, color and soften the
scars that arise. The ADSC injection also decreases
mast cell activity and inhibits the transformational
growth factor β (TGFβ), and stimulates scar
remodeling by increasing the expression of matrix
metalloproteinase (MMP) (Yun et al., 2012).
Kitajima et al conducted studies using umbilical
cord blood (UCB-MSC) mesenchymal stem cells and
wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells (WJ -MSC)
injected in full thickness wounds in nude rats.
Although the results showed no significant difference
between injection of UCB-MSC and WJ-MSC on
scar formation, the scar tissue in the WJ-MSC group
showed smaller and thicker areas (Kitajima et al.,
2016).
The various descriptions above underlay the
researcher to examine the effect of injection of
mesenchymal stem cell conditioned-medium
(adipose-derived and wharton's jelly-derived) in
preventing hypertrophic scar formation.
2 RESEARCH METHODS
This experimental research using mice and was
conducted at the Animal House of Pharmacology
Department Faculty Of Medicine Gajah Mada
University Yogyakarta between April-Mei 2016. As
many as 24 mice were used divided into 3 treatment
groups and 1 control group. Group I was given
Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM)
injection 0.2 ml perilesion, Group II injected with
ADSC-CM 0.2 ml perilesion, Group III given WJSC-
CM 0,2 ml perilesion, and group IV as negative
control not given any injection. Before the injection
was performed, wound were made on the back of
each mice with a 1 cm diameter punch biopsy (day 0).
On day 28th, re-biopsy was done on the scar area, the
tissue taken was stained with Hematoxyllin Eosin in
Pathology Anatomy Laboratory of Gajah Mada
University and analyzed with Image J to assess the
Scar Elevation Index (SEI) of each scar. If the SEI >
1 = hypertrophic, while if SEI < 1 the scar is normal
(eutrophy). The result were statistically analyzed with
one way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with the
significance value of p < 0.05.
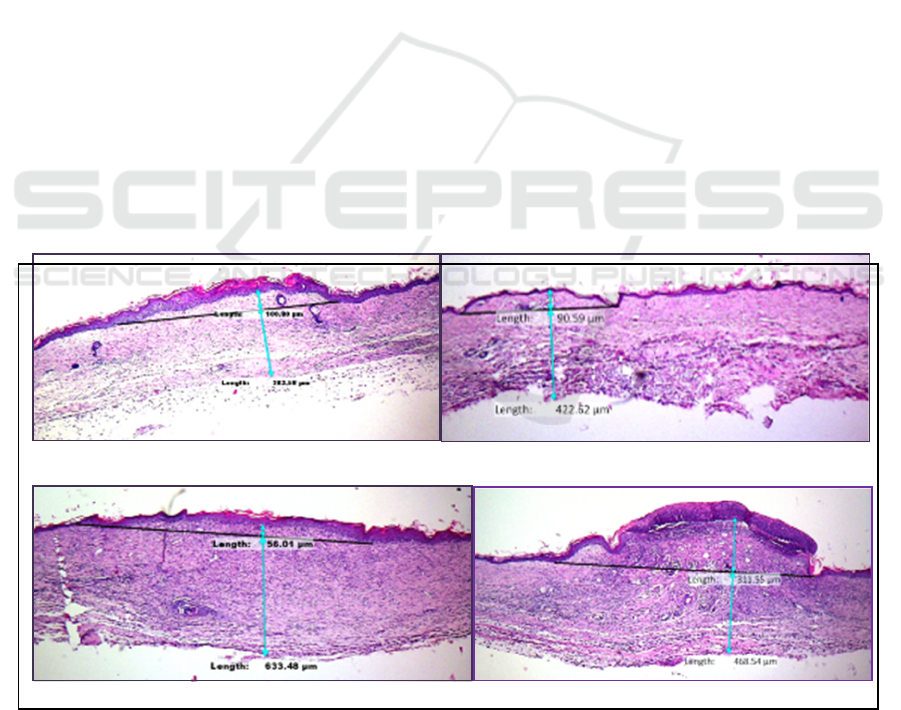
DMEM ADSC-CM
WJSC-CM Negative Control
Figure 1. Histopathology Image and Scar Elevation Index (SEI) Measurement.
The Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Conditioned Medium (Adipose-Derived and Wharton’s Jelly-Derived) on the Prevention of
Hypertrophic Scar Formation
147
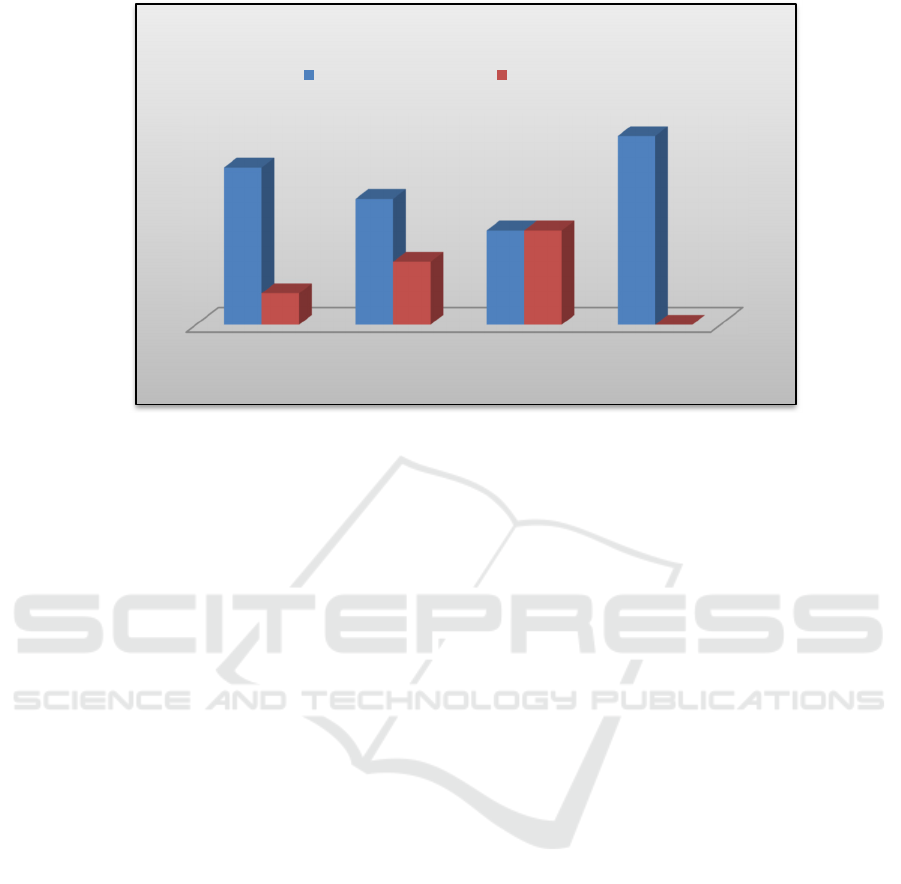
Figure 2. Scar Elevation Index Percentage.
3 RESULTS
ANOVA analysis from SEI measurements showed
no significant differences between groups (p >
0.05). For the percentage of scar formed the result
showed that in group I (DMEM) hypertrophic scar
formed as much as 83,33%, group II (ADSC-CM)
66,67%, group III (WJSC-CM) 50% and in group
IV (control) all of the scar was hypertrophic. 100%.
The data showed that WJSC-CM had the lowest
percentage of hypertrophic scar formation
compared to ADSC-CM, DMEM or without
treatment, although statistically the difference was
not significant.
4 DISCUSSION
In the SEI measurements there was no significant
difference between the treatment groups
statistically. However, it can be seen that the
percentage of hypertrophic scar most in group IV
(without treatment) equal to 100% and smallest in
group III (given WJSC-CM) as much as 50%.
The Enzym-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
(ELISA) examination of growth factor content
contained in ADSC-CM and WJSC-CM revealed
the content of bFGF, TGFβ1 and VEGF in both of
the conditioned media. The content of bFGF at
WJSC-CM (7,141 pg / ml) is higher than ADSC-
CM (6.376 pg/ml), whereas the TGFβ1 content of
WJSC-CM (7.596 pg/ml) is lower than ADSC-CM
(8,176 pg/ml) . Similarly, the WJSC VEGF content
(3.645 pg / ml) is lower than ADSC-CM (7.287 pg
/ ml).
Several studies have proven the role of bFGF in
the process of wound healing and prevention of
hypertrophic scar formation (Spaccapelo, 2016).
Ono et al injected basic fibroblast growth factor
(bFGF) in postoperative wounds and showed that
bFGF injection may inhibit the formation of
hypertrophic scars and inhibit the widening of
postoperative scar size (Ono et al., 2007). In this
study it appears that the administration of WJSC-
CM, which contains higher bFGF levels, showed a
lower percentage of hypertrophic scar formation
slightly compared to ADSC-CM, DMEM media or
without treatment. This is in accordance with the
theory that bFGF can prevent the formation of
hypertrophic scars.
Transforming growth factor β1 (TGFβ1) is
known to have an important role in the formation of
hypertrophic scars (Lu et al., 2005). WJSC-CM-
conditioned media known to contain lower levels of
TGFβ1 than ADSC-CM. It is estimated that the
lower TGFβ1 levels are also a factor that plays a
smaller percentage of WJSC-CM hypertrophic
scarred than ADSC-CM.
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a
growth factor that played a role in angiogenesis of
wound healing process. In angiogenesis process it is
estimated that dermis endothelial cells can stimulate
expenditure of TGFβ, CTGF or other profibrotic
factors that can stimulate scar tissue formation by
fibroblasts. The process of remodeling the
DMEM ADSC-CM WJSC-CM Negative
Control
83,33%
66,67%
50%
100%
16,67%
33,33%
50%
0%
Scar Elevation Index (SEI) Percentage
Hypertrophic Scar Eutrophic Scar
RCD 2018 - The 23rd Regional Conference of Dermatology 2018
148

extracellular matrix that accompanies angiogenesis
also indirectly can stimulate the formation of scar
tissue. Thus VEGF can act as a link between
angiogenesis and scar formation, by directly
stimulating both endothelial cells and dermal
fibroblasts (Wilgus et al., 2008). In this study
WJSC-CM, which contained lower VEGF, showed
the lowest percentage of hypertrophic scar. It is
estimated that low levels of VEGF also affect these
results, in addition to higher levels of bFGF and
lower TGFβ1.
5 CONCLUSION
WJSC-CM injection has a greater potential in
preventing the formation of post-wound
hypertrophic scarring than ADSC-CM. It is thought
to be related to higher bFGF levels, as well as lower
TGFβ1 in WJSC-CM used in this study.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This research was supported by Dermama
Biotechnology Laboratory Surakarta. We thank our
colleagues Dermama Biotechnology Laboratory
Surakarta who provided insight and expertise that
greatly assisted the research.
REFERENCES
Dong, L.H., Jiang, Y.Y., Liu, Y.J., Cui, S., Xia, C.C., Qu,
C., Jiang, X., Qu, Y.Q., Chang, P.Y., Liu, F., 2015.
The anti-fibrotic effects of mesenchymal stem cells
on irradiated lungs via stimulating endogenous
secretion of HGF and PGE2. Scientific Reports 5.
doi:10.1038/srep08713
Gurtner, G.C., Werner, S., Barrandon, Y., Longaker,
M.T., 2008. Wound repair and regeneration. Nature.
453(7193), p.314-21. doi:10.1038/nature07039
Jayaraman, P., Nathan, P., Vasanthan, P., Musa, S.,
Govindasamy, V., 2013. Stem cells conditioned
medium: A new approach to skin wound healing
management. Cell Biology International 37, 1122–
1128. doi:10.1002/cbin.10138
Kalaszczynska, I., Ferdyn, K., Kalaszczynska, I., Ferdyn,
K., 2015. Wharton’s Jelly Derived Mesenchymal
Stem Cells: Future of Regenerative Medicine? Recent
Findings and Clinical Significance. BioMed Research
International 2015, 1–11. doi:10.1155/2015/430847
Kitajima, Y., Doi, H., Luo, L., Yan, C., Tateishi, S., Ono,
Y., Urata, Y., Goto, S., Mori, R., Masuzaki, H.,
Shimokawa, I., Hirano, A. and Li, T. 2016. Potency
of umbilical cord blood- and Wharton’s jelly-derived
mesenchymal stem cells for scarless wound healing.
Scientific Reports, 6(1), p.18844.
Li, Q., Zhang, C. and Fu, X. 2016. Will stem cells bring
hope to pathological skin scar treatment?.
Cytotherapy, 38(2), pp.1-14.
Lu, L., Saulis, A.S., Liu, W.R., Roy, N.K., Chao, J.D.,
Ledbetter, S., Mustoe, T.A., 2005. The temporal
effects of anti-TGF-β1, 2, and 3 monoclonal antibody
on wound healing and hypertrophic scar formation.
Journal of the American College of Surgeons 201,
391–397. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2005.03.032
Meenakshi, J., Jayaraman, V., Ramakrishnan, K. and
Babu, M. 2005. Keloids and hypertrophic scars: a
review. Indian Journal of Plastic Surgery, 38(2),
p.175.
Ono, I., Akasaka, Y., Kikuchi, R., Sakemoto, A., Kamiya,
T., Yamashita, T., Jimbow, K., 2007. Basic fibroblast
growth factor reduces scar formation in acute
incisional wounds. Wound Repair and Regeneration
15, 617–623. doi:10.1111/j.1524-475X.2007.00293.x
Potapova, I.A., Gaudette, G.R., Brink, P.R., Robinson,
R.B., Rosen, M.R., Cohen, I.S., Doronin, S.V., 2007.
Mesenchymal Stem Cells Support Migration,
Extracellular Matrix Invasion, Proliferation, and
Survival of Endothelial Cells In Vitro. Stem Cells 25,
1761–1768. doi:10.1634/stemcells.2007-0022
Spaccapelo, L. 2016. Rationale for basic FGF in wound
healing and review of therapeutic applications. ejpmr,
3(5), pp.51-59.
Wilgus, T.A., Ferreira, A.M., Oberyszyn, T.M., Bergdall,
V.K., Dipietro, L.A., 2008. Regulation of scar
formation by vascular endothelial growth factor.
Laboratory investigation; a journal of technical
methods and pathology 88, 579–90.
doi:10.1038/labinvest.2008.36
Yun, I.S., Jeon, Y.R., Lee, W.J., Lee, J.W., Rah, D.K.,
Tark, K.C., Lew, D.H., 2012. Effect of human adipose
derived stem cells on scar formation and remodeling
in a pig model: a pilot study. Dermatologic surgery :
official publication for American Society for
Dermatologic Surgery [et al.] 38, 1678–88.
doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2012.02495.x
Zhang, Q., Liu, L.N., Yong, Q., Deng, J.C., Cao, W.G.,
2015. Intralesional injection of adipose-derived stem
cells reduces hypertrophic scarring in a rabbit ear
model. Stem Cell Research and Therapy 6.
doi:10.1186/s13287-015-0133-y
The Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Conditioned Medium (Adipose-Derived and Wharton’s Jelly-Derived) on the Prevention of
Hypertrophic Scar Formation
149
