
Study on Nano ZnO Photocatalytic Treatment of
Chlortetracycline Hydrochloride Pollution in Aquaculture
Waste Water
J H Liu, X C Yu
*
, M C Guo, L P Wang, Z W Nie and H Yang
College of Ocean Technique and Environment department, Dalian Ocean University,
China
Corresponding author and E-mail: Xiaocai Yu, xiaocyu@dlou.edu.cn
Abstract. The Nano ZnO photocatalyst has been successfully prepared and characterized by
XRD, SEM and other testing methods. A self-made nano ZnO was successfully used for the
photocatalytic treatment of chlortetracycline hydrochloride pollution in aquaculture waste
water. The effects of six factors such as dosage of photocatalysts ,calcining temperature of
photocatalysts, calcining time of photocatalysts, H
2
O
2
concentration, reaction time and initial
concentration of chlortetracycline hydrochloride under UV irradiation were discussed. The
optimal experimental conditions for photocatalytic treatment of chlortetracycline
hydrochloride pollution in aquaculture waste water which was determined by orthogonal
experiments are as follows: when the concentration of chlortetracycline hydrochloride in the
ultraviolet light was 0.01 g/L, calcining temperature of nano ZnO at 250°C , calcining time at
1h, dosage of nano ZnO at 0.5 g/L, H
2
O
2
concentration at 0.4 g/L and reaction time at 4 h,
the optimized removal rate of chlortetracycline hydrochloride in aquaculture waste water
occurred , which can reach 79.10%.
1. Introduction
In recent years, seafood has become more and more popular among people and aquaculture industry
has been greatly developing. Large doses of antibiotics are added to the aquaculture environment to
prevent fish diseases and promote fish growth and development[1]. But only a small percentage of
the antibiotics put into aquaculture can be absorbed and transformed by the fish themselves, most of
which are released into the natural environment with excrement[2]. Tetracycline antibiotics, mainly
including soxytetracycline, chlortetracycline, tetracycline and some synthetic antibiotics[3], are often
used in aquaculture field, which has produced a large amount of aquaculture waste water containing
antibiotics, causing some harm to the environment[4].
The bandgap of ZnO is narrow, so it can make good use of ultraviolet light to generate photo-
induced electron-hole pairs, which possesses strong redox ability to decompose inorganic and
organic pollutants into simple non-toxic inorganic substances. Besides, there is no secondary
pollution in the process of degradation. ZnO is an environment-friendly photocatalyst and plays an
important role in the governance of environmental pollution[5]. ZnO is used to degrade amoxicillin,
ampicillin, chlorcellicillin and benzazepine in water with a good effect by scholars[6-7]. Li Di and
358
Liu, J., Yu, X., Guo, M., Wang, L., Nie, Z. and Yang, H.
Study on Nano ZnO Photocatalytic Treatment of Chlortetracycline Hydrochloride Pollution in Aquaculture Waste Water.
In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering (IWEMSE 2018), pages 358-367
ISBN: 978-989-758-344-5
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reser ved

Shi Weidong have found that photocatalytic treatment of antibiotics has good prospects[8]. In this
paper, Nano ZnO was employed to carry out a photocatalytic degradation study on chlortetracycline
hydrochloride which was extensively used in aquaculture. This paper is aimed at providing a
scientific and effective way to treat antibiotics in aquaculture waste water.
2. Experimental
2.1. Experimental apparatus
Muffle furnace, centrifuge, magnetic stirrer, oven, 752 UV-Vis spectrophotometer, SU8010 scanning
electron microscope, D/MAX-2500 X ray diffractometer, indoor UV visible photocatalytic device.
Due to the wide bandgap of ZnO, the illumination used was completely UV light source, which can
provide a stronger light energy to excite ZnO to generate photoelectron electron-hole pairs, thereby
generating more hydroxyl radicals and superoxide radicals on the degradation of chlortetracycline
hydrochloride.
2.2. Experimental reagents
Zinc nitrate (AR), sodium hydroxide (AR), 30% H
2
O
2
(AR), absolute ethanol (AR) and
chlortetracycline hydrochloride (USP).
2.3. Preparation of Nano ZnO photocatalyst
Nano ZnO can be prepared by a precipitation method[9-10]. A certain amount of zinc nitrate
hexahydrate was dissolved in pure water and stirred. Then, a certain concentration of sodium
hydroxide solution was slowly added dropwise to the zinc nitrate solution to produce a uniform zinc
hydroxide precipitate, which was centrifuged, washed with anhydrous ethanol and pure water for
several times, and dried in an oven at 105°C . The dried solids were ground and finally calcined at
different temperatures in a muffle furnace to obtain nano-ZnO photocatalysts. The prepared
photocatalyst was characterized by SEM, XRD and other testing methods.
2.4. Experimental methods
To simulate the preparation of aquaculture waste water containing chlortetracycline hydrochloride:
the sea water was taken from the Dalian Ocean University, and suctioned by filtration. Different
quantities of chlortetracycline hydrochloride were prepared according to the experiment needs and
dissolved in sea water. The content of chlortetracycline hydrochloride was estimated by UV
spectrophotometry.
A certain amount of simulated aquaculture waste water was taken into the reaction vessel.
Chlortetracycline hydrochloride, Nano ZnO dosage, H
2
O
2
concentration and reaction time were
adjustable according to the experimental conditions. The experiment was carried out under the
condition of magnetic stirrer and UV irradiation. Before the photocatalytic reaction was carried out, it
was stirred for one hour in the dark to bring it to equilibrium after adsorption. The light source is then
turned on for photocatalytic reaction. After the reaction, the supernatant was taken to measure the
absorbance at a wavelength of 275 nm with a UV-visible spectrophotometer and the degradation rate
of chlortetracycline hydrochloride was calculated.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. X-ray diffraction characterization (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
The XRD and SEM characterization results were shown Figure 1.
It could be concluded from the analysis of Figure 1 that the peak value was obvious when 2θ was
31.7348°, 34.3994°, 36.2102°, 56.5351°, 61.7981° or 47.4826°, and the sample was a hexagonal
wurtzite structure in comparison with the standard JCPDS card (JCPDS 36-1541). The average
Study on Nano ZnO Photocatalytic Treatment of Chlortetracycline Hydrochloride Pollution in Aquaculture Waste Water
359
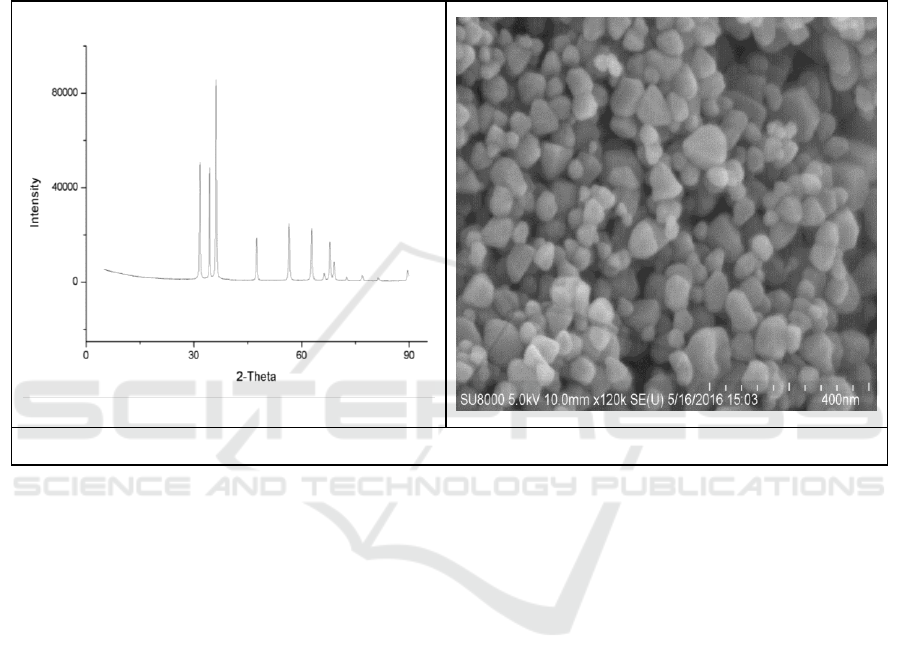
crystallite size of nanometer ZnO photocatalyst could be calculated by Scherrer formula. The lattice
constants a, b and c of ZnO were 3.2539Å, 3.2539Å and 5.2098Å, respectively. By calculating the
(111) diffraction peak, the average crystallite size of the nanometer ZnO photocatalyst was 34.14 nm,
which was similar to the partical size of ZnO in SEM image.
It could be observed from the scanning electron micrograph image that the ZnO crystal presented
an elliptical structure with uniform distribution and good particle dispersion while the particle size
was consistent with the characterization result of XRD pattern.
Figure 1.The XRD pattern and SEM image of as-prepared ZnO photocatalyst.
3.2. Photocatalytic degradation of antibiotic pollution in aquaculture wastewater with Nano –ZnO
photocatalyst
Each reaction vessel was added 50 mL simulated aquaculture wastewater , calcination temperature
at 250 ℃, calcination time at 1.5 h,dosage of ZnO at 0.4 g/L, concentration of chlortetracycline
hydrochloride at 0.02 g/L and concentration of H2O2 at 0.3 g/L. The reaction lasted two hours under
ultraviolet light illumination.
IWEMSE 2018 - International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering
360
(a)
(b)
Removal rate
The remaining
amount
Removal rate
The remaining
amount
Study on Nano ZnO Photocatalytic Treatment of Chlortetracycline Hydrochloride Pollution in Aquaculture Waste Water
361
(c)
(d)
Removal rate
The remaining
amount
Removal rate
The remaining
amount
IWEMSE 2018 - International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering
362
(e)
(f)
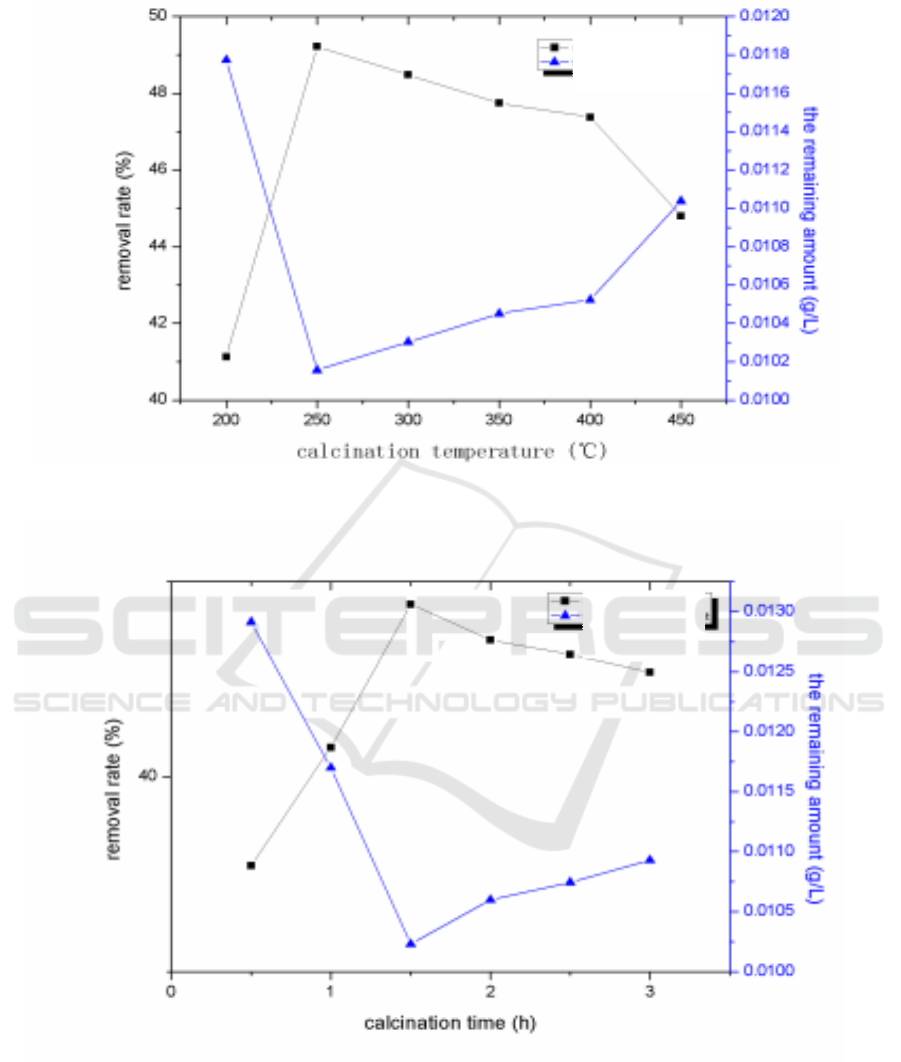
Figure 2. Effects of calcination temperature (a), calcination time (b), dosage (c), concentration of
H
2
O
2
(d), initial chlortetracycline hydrochloride concentration (e), and illumination time (f) on
photocatalytic degradation.
3.3. Effect of calcination temperature of nanometer ZnO photocatalyst on the degradation of
antibiotic pollution in aquiculture wastewater
The results were shown in Figure 2 (a). When the calcination temperature of nano-ZnO increased
gradually, the removal rate of chlortetracycline hydrochloride increased first and then decreased,
indicating that the crystal phase of nanometer ZnO has not been fully matured at a low calcination
temperature. As the calcination temperature increased with the gradual maturity of crystal phase of
Removal rate
The remaining
amount
Removal rate
The remaining amount
Study on Nano ZnO Photocatalytic Treatment of Chlortetracycline Hydrochloride Pollution in Aquaculture Waste Water
363

nanometer ZnO, the sites of photosensitizing adsorption to chlortetracycline hydrochloride increased.
Thus, the removal rate of chlortetracycline hydrochloride increased continuously when the
calcination temperature was from 250 °C to 450 °C . When the calcination temperature was 250 °C ,
the removal rate reaches the maximum of 49.22%. Higher calcination temperature was not conducive
to the formation of nano-ZnO crystals for the reduction of the photosensitive adsorption sites to
chlortetracycline hydrochloride.
3.4. Effect of calcination time of nanometer ZnO photocatalyst on the degradation of antibiotic
pollution in aquiculture wastewater
The results were shown in Figure 2(b). When the calcination time of nano-ZnO increased dgradually,
the removal rate of chlortetracycline hydrochloride first increased and then decreased, indicating that
the degree of maturity of nano-ZnO crystalline was affected by the calcination time. With the gradual
growth of calcination time, the crystalline phase of nano-ZnO became more mature, and the photo-
adsorption sites of nano-ZnO as well as the photocatalytic kinetic energy gradually increased when
the calcination time was from 0.5 h to 3 h. When the calcination time reached 1.5 h, the
photocatalytic activity of the catalyst was the optimal. An increase of calcination time was not
conducive to the formation of the catalyst, weakening the photocatalytic degradation of
chlortetracycline hydrochloride.
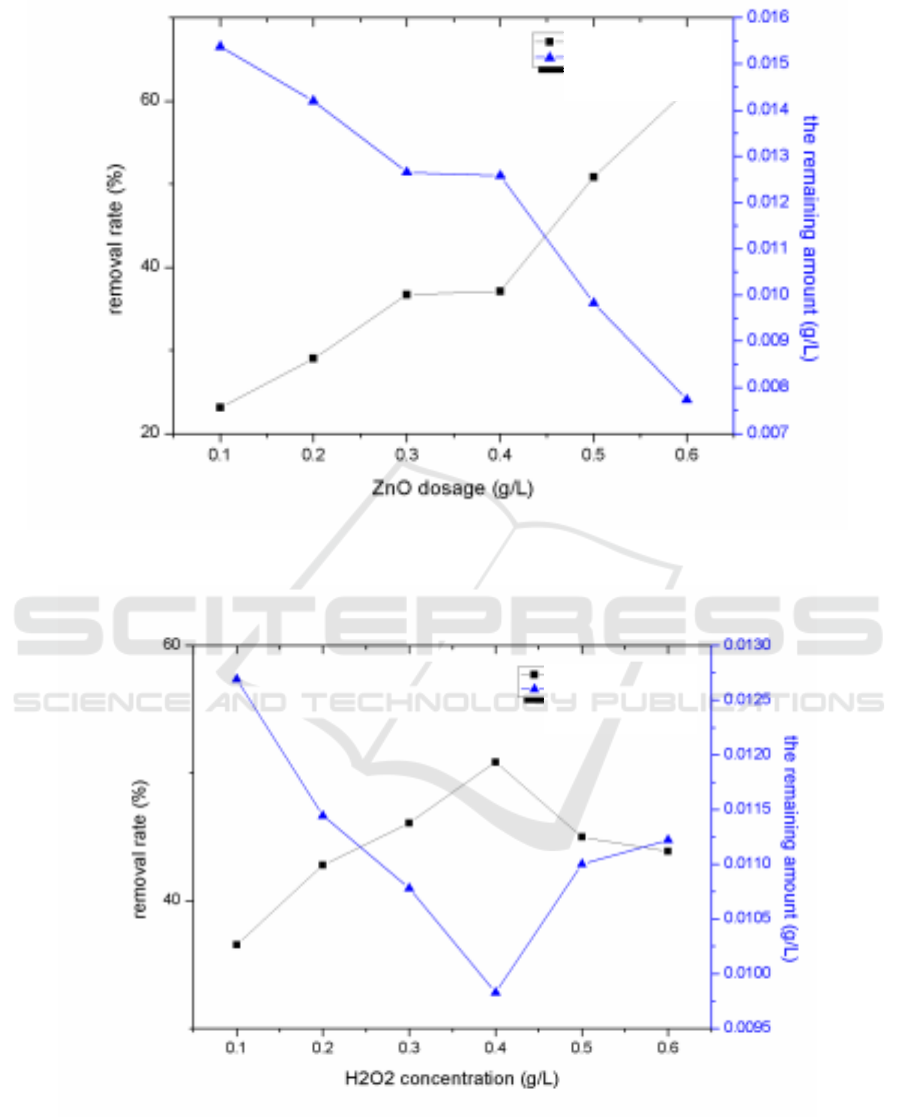
3.5. Effect of dosage of ZnO on the degradation of antibiotic pollution in aquaculture wastewater
treatment
The results were shown in Figure 2(c). The removal rate of chlortetracycline hydrochloride showed a
positive correlation with the dosage of nano-ZnO. When the concentration of pollutants was constant,
the increase of the dosage of nano-ZnO improved the photo-absorption sites of nano-ZnO under UV
light , and enhanced the utilization rate of photo-generated electrons and promotes the generation of
hydroxyl radicals and oxidation of substances[11-13], so as to improve the removal rate of
chlortetracycline hydrochloride. Due to the concentration of chlortetracycline hydrochloride was
constant, when the dosage of nano-ZnO was too large, the particles would have diffuse reflection to
light and the the photosensitive adsorption site utilization of nano-ZnO was too low to improve the
removal of hydrochloric chlortetracycline.
3.6. Effect of H
2
O
2
concentration on the degradation of antibiotic contamination in aquaculture
wastewater
The results were shown in Figure 2(d). When the H
2
O
2
concentration gradually increased, the
removal rate of chlortetracycline hydrochloride first increased and then decreased. The effect of
adding H
2
O
2
was to promote photogenerated electron-hole pairs of ZnO photocatalysts to generate
more hydroxyl radicals and superoxide radicals and improve the degradation rate of chlortetracycline
hydrochloride. But excessive H
2
O
2
was not conducive to the reaction.
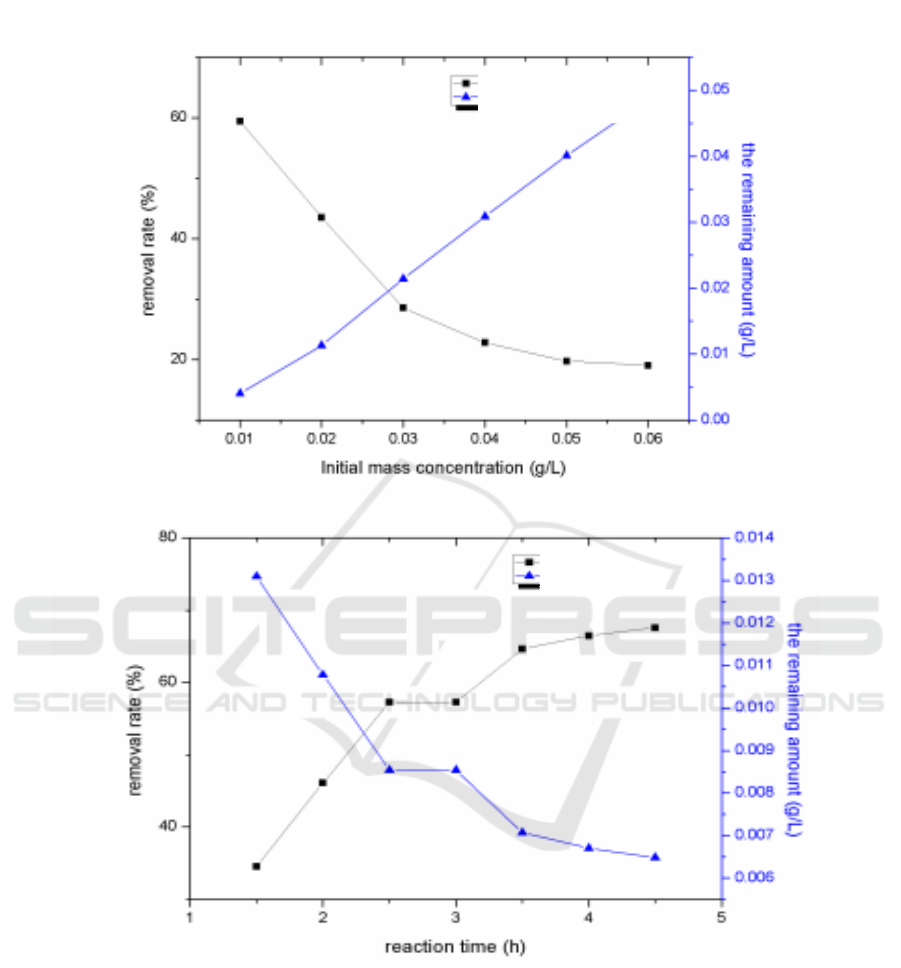
3.7. Effect of initial chlortetracycline hydrochloride concentration on the degradation of antibiotic
contamination in aquaculture wastewater
The results were shown in Figure 2(e). The removal rate of chlortetracycline hydrochloride and the
initial concentration of chlortetracycline hydrochloride were negatively correlated. When the dosage
of nano-ZnO was constant the photo-sensitive adsorption sites on the photocatalyst remained
unchanged. The initial concentration of chlortetracycline hydrochloride gradually increased and the
photo-adsorption sites on the photocatalyst gradually saturated, which affected the further removal of
chlortetracycline hydrochloride. Besides, too much chlortetracycline hydrochloride would cover the
surface of the nano-ZnO, producing shading and diffuse effect to the ultraviolet light[8]. It would
IWEMSE 2018 - International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering
364

have effect photocatalysts on the utilize of ultraviolet light and weaken the removal of
chlortetracycline hydrochloride .
3.8. UV irradiation reaction time on the treatment of aquaculture wastewater antibiotic
contamination
The results were shown in the Figure 2(f). The results showed that with the increase of reaction time,
the removal rate of chlortetracycline hydrochloride increased gradually. The removal rate reached
66.49% when the reaction time was 4 h. The removal rate tended to be gentle when the reaction time
was longer than 4 h. The results also showed that the effective contact with ZnO was low when the
residual concentration of chlortetracycline hydrochloride was low, and the photocatalytic activity of
nanometer ZnO was weak. It was difficult for ZnO to remove a very low concentration of
chlortetracycline hydrochloride. The removal rate tended to be stable.
3.9. Optimization of photocatalytic treatment of chlortetracycline hydrochloride wastewater
Six factors and five levels table was designed. The orthogonal experimental data was shown in Table
1.
Table1. Design matrix and experimental results for orthogonal array.
Experime
nt
Calcination
temperature(℃)
Calcination
time(h)
Dosage
(g/L)
Concentration
of H
2
O
2
(g/L)
Illumination
time(h)
Iinitial chlortetracycline
hydrochloride
concentration(g/L)
Removal
rate
( %)
1
250
1
0.2
0.1
2
0.1
54.65
2
250
1.5
0.3
0.2
2.5
0.2
65.57
3
250
2
0.4
0.3
3
0.3
47.65
4
250
2.5
0.5
0.4
3.5
0.4
52.56
5
250
3
0.6
0.5
4
0.5
52.57
6
300
1
0.3
0.3
3.5
0.5
29.67
7
300
1.5
0.4
0.4
4
0.1
69.35
8
300
2
0.5
0.5
2
0.2
52.34
9
300
2.5
0.6
0.1
2.5
0.3
38.83
10
300
3
0.2
0.2
3
0.4
18.51
11
350
1
0.4
0.5
2.5
0.4
33.91
12
350
1.5
0.5
0.1
3
0.5
27.09
13
350
2
0.6
0.2
3.5
0.1
77.44
14
350
2.5
0.2
0.3
4
0.2
56.93
15
350
3
0.3
0.4
2
0.3
28.91
16
400
1
0.5
0.4
4
0.3
71.17
17
400
1.5
0.6
0.5
2
0.4
25.83
18
400
2
0.2
0.1
2.5
0.5
5.41
19
400
2.5
0.3
0.2
3
0.1
71.19
20
400
3
0.4
0.3
3.5
0.2
62.26
21
450
1
0.6
0.4
3
0.2
58.95
22
450
1.5
0.2
0.5
3.5
0.3
35.28
23
450
2
0.3
0.1
4
0.4
22.52
24
450
2.5
0.4
0.2
2
0.5
2.84
25
450
3
0.5
0.3
2.5
0.1
57.23
K1
273
248.35
170.78
148.5
164.57
329.86
K2
208.7
223.12
217.86
235.55
200.95
296.05
K3
224.28
205.36
220.92
253.74
223.39
221.84
K4
235.86
222.35
260.39
280.94
257.21
153.33
K5
176.82
219.48
253.62
199.93
272.54
117.58
R
96.18
42.99
89.61
132.44
107.97
212.28
Study on Nano ZnO Photocatalytic Treatment of Chlortetracycline Hydrochloride Pollution in Aquaculture Waste Water
365

The order of these factors magnitude of effects on the removal rate was the following: initial
concentration of chlortetracycline hydrochloride> hydrogen peroxide concentration> reaction time>
calcination temperature> dosage of catalyst> calcination time. The optimal experimental condition
for the photocatalytic degradation of chlortetracycline hydrochloride using nano-ZnO was: the
chlortetracycline hydrochloride was 0.01 g/L, the calcination was 250 ℃, the calcination time was 1
h, the catalyst dosage was 0.5 g/L, the hydrogen peroxide was 0.4 g/L and the reaction time was 4 h.
Verification tests under the above conditions were carried out and the removal rate reached 79.10%.
The experimental results were shown in the Table 2.
Table 2. Verification test.
Experiment
Calcination
temperature(
℃)
Calcination
time(h)
Dosage (g/L)
Concentration of
H
2
O
2
(g/L)
Illumination
time(h)
Iinitial
chlortetracycline
hydrochloride
concentration(g/L)
Removal
rate
( %)
Average
removal
rate(%)
1
250
1
0.5
0.4
4
0.01
77.63
79.10
2
250
1
0.5
0.4
4
0.01
78.02
3
250
1
0.5
0.4
4
0.01
78.92
4
250
1
0.5
0.4
4
0.01
79.91
5
250
1
0.5
0.4
4
0.01
81.02
4. Conclusions
(1) The nano-ZnO photocatalyst was successfully prepared. The average particle size of the nano-
ZnO photocatalyst was 34.14nm. The prepared nano-ZnO can be used as a photocatalyst to degrade
the chlortetracycline hydrochloride pollutants in aquaculture wastewater efficiently under the
ultraviolet light with low concentration of chlortetracycline hydrochloride.
(2) The optimum reaction conditions obtained by orthogonal test were as follows: when the
concentration of chlortetracycline hydrochloride was 0.01 g / L, the photocatalyst calcination
temperature of nano ZnO was 250 °C , the calcination time was 1 h, the dosage was 0.5 g / L, the
concentration of H
2
O
2
was 0.4g / L and the reaction time was 1 h, in which case the average removal
rate reached 79.10% under ultraviolet light.
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by a grant from Marine research and special funds public service
sectors of State Oceanic Administration People’s Repubic of China (201305002), Liaoning Province
large equipment and equipment sharing service platform capacity building funds, Department of
Science and Technology of Liaoning (2016LD0105),Science Foundation of Department of Ocean
and Fisheries of Liaoning Province (201733),and Liaoning Science and Technology Public Welfare
Fund(20170002)
References
[1] Wang W B and Ding W G 2012 Talking about the Harm of Antibiotic Residues in Fisheries
and the Precautionary Measures Kexue Zhongyang 06:53-54
[2] Yao Y, Qian C and Yue Z J 2008 Briefly describe the problem of antibiotic pollution in water
Scientific and Technological Innovation 09:165
[3] He D C, Xu Z C, Wu G Y and et al 2011 Research on environmental behavior of tetracycline
antibiotics Progress in Veterinary Medicine32(4):98-102
[4] Gao P, Mao D, Luo Y and et al 2012 Occurrence of sulfonamide and tetracycline resistant
bacteria and resistance genes in aquaculture environment Water Research46 ( 7) : 2355-
2364
IWEMSE 2018 - International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering
366

[5] Song Y N and Guan W S 2012 Photocatalytic degradation of antibiotic with ZnO /CNTs
composite photocatalyst Applied Chemical Industry41(07):1172-1175
[6] Elmolla E S and Chaudhuri M 2010 Degradation of amoxicillin, ampicillin and cloxacillin
antibiotics in aqueous solution by the UV /ZnOphotocatalytic process Journal of
Hazardous Materials 173: 445-449
[7] Hilal H S, G Al-Nour Y M, Zyoud A and et al 2010 Pristine and supported ZnO-based
catalysts for phenazopyridine degradation with direct solar light Solid State Sciences12( 4) :
578-586
[8] Li D and Shi W D 2016 Recent developments in visible-light photocatalytic degradation of
antibiotics Chinese Journal of Catalysis37(06):792-799
[9] Chen J F 2015 The preparationof compound nanometer ZnO and the research
ofmechanismand application of photocatalyst Dalian Ocean University
[10] Zhang J, H Liu Y, Ji Q Y and et al 2016 Preparation of a pholocatalyst nanometer SnO 2 and
its photocatalyticdegration of marine diesel pollution Journal of Dalian Ocean
University31(04):438-443
[11] Chen J F, Yu X C, Wu Y Y and et al 2014 Study on the Photo-Catalytic Degradation of Waste
Water fromSeafood Processing Using Nano-Zinc Dioxide Journal of Ocean
Technology33(03):61-67
[12] Liu L W, Wu X L, Wu C H and et al 2012 Photocatalytic degradation of quinolone antibiotics
in water using TiO
2
Journal of Central South University(Science and
Technology)43(8):3300-3307
[13] Ge L K, Chen J W, Zhang S Y and et al 2010 Photodegradation of fluoroquinolone antibiotic
gatifloxacin in aqueous solutions.Chinese Science Bulletin55(11): 99-1001
Study on Nano ZnO Photocatalytic Treatment of Chlortetracycline Hydrochloride Pollution in Aquaculture Waste Water
367
