
Application of Decision Support Systems
for Selection of Radiotherapy Methods Breast Cancer Patients
Rafli Filano and Boy Subirosa Sabarguna
Biomedical Engineering Study Program, Faculty of Engineering, Universitas Indonesia, Jl Kampus UI, Kukusan, Beji, Kota
Depok, Jawa Barat 16424
Keyword: Decision Support System, Breast Cancer, Radiotherapy, 3D-CRT, IMRT, VMAT.
Abstract: Radiotherapy is a treatment against malignant tumor or cancer by using ionizing radiation, such as X-rays,
gamma rays or high-energy electrons. Radiotherapy methods include 3D-CRT, IMRT, VMAT. Decision-
making in the selection of radiotherapy methods in case of breast cancer is unique to each patient so doctors
need consideration. Selection of radiotherapy method for breast cancer patients so that it becomes optimal
with support of decision support system. Analytical Hierarchy Process's decision support system helps solve
complex problems by structuring a hierarchy of criteria, stakeholders, outcomes and displaying considerations
to develop possible options. The purpose of this research is the application of AHP-based aids decision system
that can be used by doctors as an alternative selection tool from existing radiotherapy methods and educational
facilities of prospective doctors in learning about radiotherapy methods in breast cancer patients. The resulting
of decision support system is used in the selection of radiotherapy methods in breast cancer patients that
greatly assist the physician in selecting decisions. Suggested software applications need to develop step
instructions and questions to be more complex and tailored to the condition of patients and hospitals.
1 INTRODUCTION
Breast cancer is a degenerative disease resulting from
cells in the breast tissue dividing and growing
uncontrollably (Miranda, et al 2013). According to
data Globacan, International Agency for Research on
Cancer (IARC) in 2012 found that breast cancer ranks
first as the most common type of cancer suffered by
women in the world. Breast cancer accounts for 25%
of all newly diagnosed overall cancer cases (Infodatin
Kemenkes, 2015). Breast cancer has a contribution of
30% and is the most dominant type of cancer in
Indonesia, beating cervical cancer that contributes
24% (DepKes RI, 2013).
One treatment of cancer is to use radiotherapy
where Radiotherapy is a recognized therapy, and 45-
50% of cancer patients are cured, radiotherapy plays
a role in the healing. New and growing radiotherapy
methods are used for breast cancer therapy, which is
radiation using 3DCRT (Three-dimensional
Conformal Radiation Therapy) techniques, IMRT
(Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy) techniques, and
VMAT (Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy)
techniques (Liu, et al 2013).
Decision-making in the selection of breast cancer
therapy using various methods of radiotherapy is
often a problem that is often faced for a doctor
(clinician) and a patient / patient with breast cancer,
including cancer stage, surgery that has been done,
radiation target, and total dose of radiation.
Therefore, one of the methods that can be
implemented in the health world is a decision-based
system based on Analytical Hierarchy Process.
Decision support system based on Analytical
Hierarchy Process that can be used in determining the
selection of the best alternative radiotherapy methods
and becomes very important in providing knowledge
and learning about radiotherapy methods.
The purpose of this research is the selection of
radiotherapy method for breast cancer patients so that
it becomes optimal with the support of decision
support system based on Analytical Hierarchy
Process and can know the limitations of radiotherapy
method selection manually.
944
Filano, R. and Sabarguna, B.
Application of Decision Support Systems for Selection of Radiotherapy Methods Breast Cancer Patients.
DOI: 10.5220/0007554509440950
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School (ICPS 2018), pages 944-950
ISBN: 978-989-758-348-3
Copyright
c
2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is principally a malignant tumor of one
of the skins on the outside of the chest cavity. The
armpit lymph gland forms the lymphatic drainage
system for both upper quadrants of the body, as well
as the breasts including both arms (Jong, 2005).
Breast cancer is a malignancy of breast tissue that
may originate in the ductal and lobular epithelium.
Breast cancer is one of the most cancer types in
Indonesia.
Based on Pathological Based Registration in
Indonesia, Breast Cancer ranks first with relative
frequency of 18.6% (Cancer Data in Indonesia Year
2010, according to Histopathological data, Cancer
Registry Agency of Indonesian Pathology Specialist
Association and Indonesian Cancer Foundation
(YKI)). It is estimated that the incidence rate in
Indonesia is 12 / 100,000 women, whereas in the
United States are about 92 / 100,000 women with a
fairly high mortality of 27 / 100,000 or 18% of deaths
found in women. This disease can also be suffered in
men with frequency about 1%. In Indonesia, more
than 80% of cases are found to be in an advanced
stage, where treatment efforts are difficult. Therefore,
it is necessary to understand about prevention efforts,
early diagnosis, curative and palliative remedies as
well as good rehabilitation efforts, so that the service
in patients can be done optimally (Komite
Penanggulangan Kanker Nasional DepKes RI, 2015).
2.2 Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy is an utilization of ionizing rays in a
therapeutic attempt by providing a precise dose of
radiation to a determined tumor volume by reducing
normal surrounding tissue damage to a minimum.
The principle of radiotherapy is to kill cancer cells by
giving the appropriate dose to the targeted tumor or
target and to keep the radiation effect on healthy
tissue to a minimum (Murat, et al, 2010).
Radiotherapy is a treatment against malignant
cancer or cancer by using ionizing radiation, such as
X-rays, gamma rays or high-energy electrons (Sarkar,
et al 2012). Radiotherapy is a recognized therapy, and
45-50% of cancer patients are cured, radiotherapy
plays role in the healing (Susworo, 2007).
2.3 Radiotherapy Methods
2.3.1 3D-CRT Method (3 Dimension
Conformal Radiation Theraphy)
3D-CRT (Conformal Radiation Theraphy) is a
radiotherapy irradiation method based on 3D
anatomical information and uses the appropriate dose
distribution for volume targets in the case of adequate
doses of target volume and minimal doses of healthy
tissue. With the computer system work 3D-CRT
method can know the shape, size, and location of
tumors and can calculate the virtual three-
dimensional tumor.3D-CRT inidimana planning and
delivery treatment based on 3 dimensions of
volumetric image data with each radiation field in
accordance with the form of target volume
conformity (Khan, 2014).
2.3.2 IMRT Method (Intensity Modulated
Radiotheraphy)
The principle of IMRT is to provide irradiation to the
patient with some amount of irradiation direction with
a non-uniform pitch which has been optimized to give
the maximal dose to the target organ and provide
minimal dosage to the surrounding organ. Radiation
The IMRT method may be provided by the operation
of MLC (Multi Leaf Collimator) from one of the three
bases; The segmented MLC, or so-called step and
shoot, dynamic MLC or often called sliding, and
intensity modulated arc therapy (IMAT). In the MLC
step and shoot, there is a field inside the radiation
field, the MLC will move to cover the already enough
dose, and the radiation will come out if the MLC
finishes moving. In dynamic MLC, MLC will
continue to cover the part of organ that has enough
dose, as long as it is also radiation out. In the IMAT
(VMAT), MLC will move following the organ shape
and the gantry will rotate around the patient (Levitt,
et al, 2012).
2.3.3 VMAT Method (Rapid Arc)
VMAT was first introduced in 2007 and is described
as a new radiation method that allows simultaneous
variation of three parameters during treatment, ie
gantry rotation speed, aperture form of treatment
through MLC leaf movement and dose rate (Teoh, et
al, 2011). RapidArc uses the Volumetric Modulated
Arc Therapy (VMAT) Method, in which treatment is
given at a dose for the overall volume of the cancer
(Cimasi. RJ, 2014). RapidArc is a dynamic treatment
by way of radiation with 360-degree gantry rotation
around a given patient with complex planning
Application of Decision Support Systems for Selection of Radiotherapy Methods Breast Cancer Patients
945

whereby the velocity of the gantry, dose rate, and
shape of the irradiation field will change following
the shape of the tumor itself using a device called
MLC or Multi Leaf Collimator. The rotating gantry
and irradiation of the radiation field following the
overall shape of the tumor reduces the irradiation
times compared to the conventional Modulated
Radiotherapy (IMRT) Method. Besides reducing the
exposure time, the use of RapidArc is also very useful
in reducing the doses received by the risky organs
around without reducing the radiation that reaches the
target organ.
2.4 Decision Support System
Decision Support System as a set of model-based
procedures for processing and assessment data to help
managers make decisions. Decision support systems
have the primary goal of helping decision makers
through several stages of each decision-making
process through the exploitation of computerized
information systems (Hartono. AA, 2014).
Decision support system has three main sub
system, namely database management subsystem,
model subsystem, and dialog subsystem. These three
subsystems are important elements in modeling and
decision-making simulations to provide more
appropriate decision alternatives using the AHP
(Analytical Hierarchy Process) method (Shaot. A, et
al, 2014).
The basis for thinking of the AHP method is the
numerical forming process to rank each decision
alternative based on how the alternative should be
matched against the decision-making criteria
(Supriyono, 2007). This AHP method helps solve
complex problems by structuring a hierarchy of
criteria, stakeholders, outcomes and by drawing
considerations for developing weights or priorities.
Thus AHP is used when decisions are taken
involving many factors, when decision makers have
difficulty in determining the weight of each factor.
AHP will solve a complex, unstructured situation into
several components in a hierarchical arrangement. By
giving subjective values about the relative importance
of each variable, and specifying which variable has
the highest priority aims to influence the outcome of
the situation when the decision will be taken.
The steps or procedures on the AHP method are:
(Saaty. TL, 2004)
Figure 1: Flowchart procedure on AHP.
3 METHODS
This research uses qualitative method with
experimental quasi, with approach of longitudinal
research because in research implementation not at
certain period of time. The research was carried out
from August to November 2017 at the Radiotherapy
Installation of MRCCC Siloam Jakarta and the
Biomedical Technology Campus of FTUI Salemba,
Jakarta. Samples taken purposively based on
assessment by programmers and doctors PPDS
Radiation Oncology at RSCM Hospital Jakarta.
Tools and materials used in this research are:
a. Computers / Laptops, with AMD A8 processor
specifications or Intel core-i7 processors and
RAM memory of 2-3 GB.
b. Programming language
1) Front base: Html 5, CSS, Bootstrap, JS
2) Back base: Php
3) Database: Mysql
Data collection methods used are:
a. Literature Review
b. Interview
c. Preparation of Analytical Hierarchy Process
d. Systems Analysis and Design
e. Creation of Application software
f. Trials
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
946
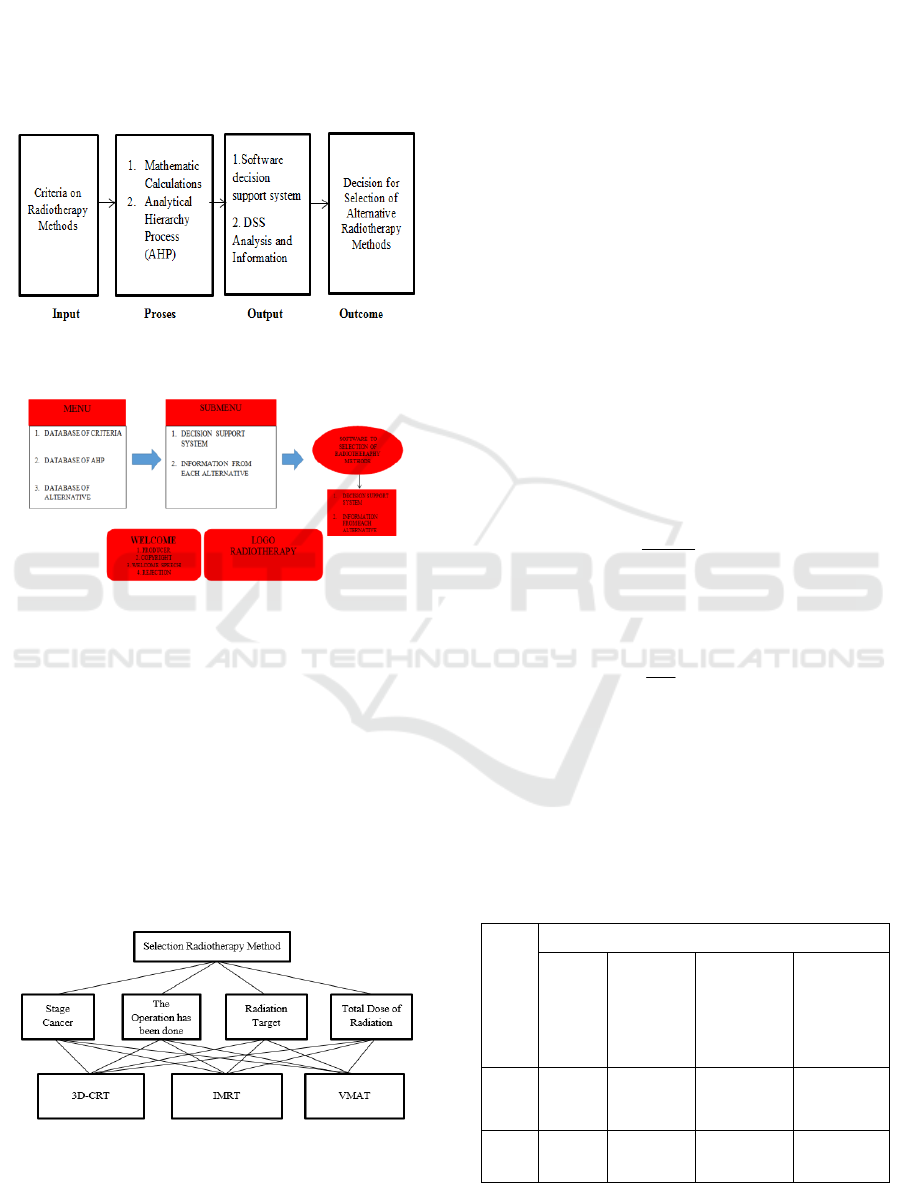
4 RESULTS
4.1 Analysis and Design System
A system architecture design is done by doing the
analysis so that the proposed system will be made.
Figure 2: System interconnection.
Figure 3: Interface design system.
4.2 Application of AHP
4.2.1 Define the Problem and Determine the
Desired Solution, then Determine the
Hierarchy.
First we have to define the situation carefully,
include as many relevant details as possible, then
arrange the model in a hierarchy consisting of
several levels of detail, ie the focus of the problem,
criteria, and alternatives.
Figure 4: Structure of AHP.
4.2.2 Creating a Pairwise Matrix Matrix
Matrix of pairwise comperition is made by
comparing the setlap of alternative pairs against the
criteria tested.
4.2.3 Synthesizing Comparisons
Synthesis aims to obtain the priority of all decision
alternatives after all data in the benchmark matrix is
performed. Synthetic is done by comparing the
matrix normalization, which is obtained by dividing
each entry by the number of columns in the
corresponding entry. The number of each column
will be equal to one. From a normalized matrix,
multiply the relative priority value with each entry in
the corresponding column in the benchmark matrix.
Add the multiplication in a row.
Next on the row number column, for each entry
with the entry corresponding to the priority vector, the
result is a consistency vector. The lambda value is the
average of the consistency vector. And then
calculated consistency index (CI) which n used in this
research that is 3 (number of alternative compare).
1−
−
=
n
n
CI
λ
………...…
(1)
For n = 3, the random index (RI) is 0.58, so the
consistency ratio (CR) is:
R
I
CI
CR =
…………….
(2)
The CR result in the example shows that CR =
0.011 means that the response is quite consistent and
true, and does not need to re-evaluate the comparative
matrix that has been made because CR <10% (0.1)
Analytical Hierarchy process process that has been
done got the final result that is:
Table 1: Final summary.
Alte
rnati
ve
Prioritas
Stage
Cance
r
The
Operatio
n has
been
done
Radiation
Target
Total
Dose of
radiation
3D-
CR
T
0.16
(*3)
0.16 (*3) 0.13 (*3) 0.55 (*1)
IMR
T
0.59
(*1)
0.30 (*2) 0.38 (*2) 0.18 (*3)
Application of Decision Support Systems for Selection of Radiotherapy Methods Breast Cancer Patients
947

VM
AT
0.25
(*2)
0.54 (*1) 0.54 (*1) 0.27 (*2)
4.3 Implementation of Interface
For implementation of interface design assisted by
programmer. There are three views in Interface:
login menu (Username and user password), current
patient data menu (data already done decision system
decision process), patient input menu (included
patient data and existing medical resume, and start of
Decision Support System for selection method of
radiotherapy in breast cancer patients).
4.3.1 Display Login Menu
Figure 5: Menu login.
4.3.2 Recent Patient List Menu Display
Contains the latest patient data set intended to make
it easier for doctors to find information from their
current patients.
Figure 6: Recent patient data.
4.3.3 Display of Patient Form
The Patient Form is the first part of a series of
therapeutic end-points determination for patients.
Here is an example of a patient form:
Figure 7: Patient form.
After that just go into the questionnaire is
arranged hierarchically from one to ten questions,
with some examples of the display are:
a. Does Patient Have Breast Cancer?
b. Does the patient include an early stage?
c. Does the patient include an advanced stage?
d. Is the patient already in surgery?
e. Has the patient been fully operational
(Mastectomy)?
f. Has the patient been partially surgically removed
(Lumpectomy)?
g. Does the patient need radiation on the chest
wall?
g. Does the patient need radiation on all breasts?
h. Does the patient need radiation on the regional
lymph nodes?
i. Does the patient need Booster on a tumor bed?
After the process on each question is completed
then ultimately boils down to the result.
4.4 Trial and Verification Test
4.4.1 The Test Results on the Programmer
Trials are Conducted on Three
Programmers to Assess Whether the
Program is Working or not, and
Compliance with Programming.
Figure 8: Programmer trial.
4.4.2 The Test Results on User
Trials were conducted on three physicians PPDS
Radiation Oncology FKUI for general and
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
948
comprehensive assessments by assessing whether the
program can run or not, the suitability of the content,
provide an overview of information and software
usability.
Figure 9: User trial.
4.4.3 Verification Test Results
Software verification verification conducted by 3
doctor PPDS specialist Radiation oncology FKUI at
Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital. PPDS doctors are
tested on how they can make quick and precise
decisions on the choice of radiotherapy methods to
breast cancer patients directly and manually without
the use of software that has been created and fill out
the form provided. However, PPDS doctors
specializing in radiation oncology are still getting
difficulties such as knowledge and field experience is
still lacking and limitations in making consideration
questions, such as: Questions are good, Questions are
added to be more specific, choice of radiotherapy
method is added according to the type of therapy that
has been undertaken by the patient, Questions and
references added for treatment recommendations.
At this time the doctors ppds specialist radiation
oncology in decision-making radiotherapy method
selection is still done manually with the mindset and
condition of the patient, the choice of radiotherapy
methods are also still experiencing many difficulties,
especially in cases of breast cancer. So with the
software system decision aids for the selection of
radiotherapy methods in breast cancer patients and
this software can be used by PPDS radiation
oncologists to facilitate in taking a decision quickly
and precisely.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The results of this research in the form of web based
application software that is a decision-based system
Analytical Hierarchy Process in the selection of
radiotherapy methods in breast cancer patients. This
research produces an overview and helps / facilitates
the specialist radiation oncologist ppds physicians in
making decisions for the selection of rapid,
appropriate and appropriate radiotherapy methods
from several available alternatives and provides
appropriate information as reference materials for the
choice of radiotherapy methods, and the resulting
decision support system and recommended in the
system directly by the program as well as any
permanent decisions of a specialist doctor or radiation
oncologist specifies even though in making decisions
the choice of radiotherapy methods is still done
manually and also still experiencing many
difficulties, especially in cases of breast cancer.
Suggested Further research software application
needs to develop step instructions and questions to be
more complex and tailored to the condition of patients
and hospitals.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Hereby, we would like to express our gratitude to the
DRPM Universitas Indonesia who has funded the
participation on International Conference
Postgraduate School Universitas Airlangga 2018
through the PITTA's Grant 2018
REFERENCES
Cimasi RJ. 2014. Healthcare Valuation, The Financial
Appraisal of Enterprises, Assets, and Services. Willey
Finance Series.
Depkes RI. 2013. Penderita Kanker Diperkirakan Menjadi
Penyebab Utama Beban Ekonomi Terus Meningkat.
Kementrian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia
Hartono, AA. 2014. Sistem Pendukung Keputusan Pada
Penjurusan Siswa. Cilacap: JNTETI, Vol. 03 no. 3
Jong, Wim de. 2005. Kanker, apakah itu? Pengobatan,
Harapan Hidup, dan Dukungan Keluarga. Arcan.
Jakarta
Khan F, Gibbons (Jr) MJP. 2014. Khan's The Physics of
Radiation Therapy. 5th ed. Philadelpia: Lippincott
Williams & Wilkins.
Komite Penanggulangan Kanker Nasional. 2015. Panduan
Penatalaksanaan Kanker Payudara.Kementrian
Kesehatan Republik Indonesia.
Levitt, S. H., & Purdy, J. A. 2012. Technical Basis of
Radiation Therapy 5th Edition.London: Springer
Liu. X, et al. 2017. Dosimetric Comparison of Helical
Tomography, VMAT, Fixed-FieldIMRT and 3D-
Conformal Radiotheraphy. Radiation Oncology
Biomed Central. DOI 10.1186/s13014-017-0812-1
Miranda, R, Khoury JD, Medeiros LJ, 2013. Atlas of Lymph
Node Pathology. Texas: Springer.
Murat, B., Ozygit, G., & Ebruli, C. 2010. Basic Radiation
Oncology. Berlin: Springer Heidelberg.
Application of Decision Support Systems for Selection of Radiotherapy Methods Breast Cancer Patients
949

Saaty, T.L. 2004. Decision making-the analytic hierarichal
process and theanalytic network process. Journal of
Systems Science and Systems Engineering. Vol 13 (1):
35.
Sarkar A, Chiocca EA. 2012. Glioblastoma and Malignant
Astrocytoma. Brain Tumors. 384–407.
Supriyono, dkk. 2007. Sistem Pemilihan Pejabat Struktural
dengan Metode AHP. Yogyakarta: Prosiding Seminar
Nasional III. ISSN 1978-0176
Susworo, R. 2007. RADIOTERAPI ''Dasar-Dasar
Radioterapi Tata Laksana Radioterapi Penyakit
Kanker”. Jakarta: Universitas Indonesia (UI-Press).
Teoh. M, Clark. CH, Wood. K, Whitaker. S, Nisbel. A.
2011. Volumetric Modulated Arc Theraphy.Br J Radiol.
2011 Nov; 84(1007): 967–996. doi: 10.1259/bjr/
22373346
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
950
