
Competency Development of Traits and Motives in Case of Salt
Farmer in Galis, Sub-district of Pamekasan Regency
Sukron Ma’mun, Windijarto and Sutinah
¹Magister Postgraduate School Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: Competence Development, Traits and Motives, Peasant Salt People.
Abstract: The purpose of this research was to determine the development of competency traits and motives of
smallholder salt farmers in Galis Subdistrict, Pamekasan Regency. In improving the competence of
smallholder, salt farmers in Galis Subdistrict Pamekasan Regency developed the competence by providing
training and guidance to them. One of the competence development that can be done is the development of
competence of traits and motives. According to Spencer & Spencer (1993) cited by Emmyah (2009) in
Sutoto, competencies in aspects of personal characteristics/traits include: self-control competence, self-
confidence, flexibility, organizational commitment, and competence in the aspect of motives include
organizational awareness competence, relationship building, and achievement orientation. This research
used qualitative methods with data collection techniques through interviews and observations. The results of
research that have been found that smallholder salt farmers in Galis Subdistrict, Pamekasan Regency
already have the competence of traits and motives, but still need development because until now the
smallholder salt farmers in Galis Subdistrict are only able to produce coarse salt (krosok) with low quality,
so that such development can increase the ability of salt farmers to produce people's salt in Galis Subdistrict,
Pamekasan Regency.
1 INTRODUCTION
Madura as part of East Java provincial region holds
a considerable amount of natural resource potential
including; the terrestrial biodiversity and marine
biodiversity. One of the more value of the natural
resources potential of Madura Island when
compared with other areas in East Java Province is
salt which Madurese people often called "white
gold". Salt is one of the commodities that became
one of the icons on the island of Madura other than
bull racing and Madura tobacco. The salt potential in
Madura Island has not been able to improve the
welfare of its people and develop its human
resources, especially to improve the living standards
of the people's salt farmers on the island of Madura,
so the island of Madura is known to be the largest
producer of salt in Indonesia.
Suhelmi IR, et al (2013) reveals that total area of
salt land in Madura, about 11,695 ha, it means that
Madura has the largest salting area in all of
Indonesia, because that is why since a long time
Madura also known as salt island. In fact, the largest
salt farm area in Madura throughout Indonesia has
not been able to improve the lives and economics of
salt farmers in Madura Island that are still
experiencing ups and downs, as well as the human
resources of the salt peasants of the people in
Madura who also have not experienced significant
progress and progress.
Makhfud E, et al (2012) reveals that in general
until now the peasant salt people in Madura are only
able to produce raw salt or commonly called low-
quality salt krosok from their salt land, the peasant
salt people in Madura in general still not able to
produce quality and ready salt people to be
consumed or even ready for use with certain brands,
quality, and packaging, because their knowledge,
skills and abilities are still limited and far behind
when compared to the ability of PT. Garam and salt
factories or private salt companies in Madura that
are already developing in the process of producing
and producing quality salt. If such circumstances
remain left unchecked and do not take action to
make changes, then in the long run the salt area in
Madura, one day will not be used again to improve
the welfare of the peasant’s salt farmers in Madura,
790
Maâ
˘
A
´
Zmun, S., Windijarto, . and Sutinah, .
Competency Development of Traits and Motives in Case of Salt Farmer in Galis, Sub-district of Pamekasan Regency.
DOI: 10.5220/0007551507900794
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School (ICPS 2018), pages 790-794
ISBN: 978-989-758-348-3
Copyright
c
2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

and things like that very unfortunate if happened to
the area that got the nickname of salt island.
One of the districts on the island of Madura that
has a large salt area is Pamekasan Regency is
geographically located Regency is the second from
the eastern end of the island of Madura after
Sumenep Regency. In Pamekasan District, there are
several sub districts in which the majority of the
people work as peasant salt people, one of them is
Galis Sub-district. Galis Sub-district of Pamekasan
Regency is a Sub-district that has the widest width
of people's salt area in all areas of Pamekasan
Regency, so it can be ascertained that the largest
number of peasant salt farmers in Pamekasan
Regency is in Galis Sub-district.
The majority of people in Galis Subdistrict,
Pamekasan Regency, where they live around salt
fields, work as community salt farmers, but based on
preliminary studies conducted by researchers in the
field, researchers found that the ability to manage
the people's salt they have is still low, the article is
almost entirely salt produced by smallholder salt
farmers in Galis Subdistrict has a low quality and is
still in the form of raw salt (krosok). Based on the
background of the above problems, the researchers
are interested to conduct research by taking the
location of research in Galis Subdistrict of
Pamekasan Regency, and examined the development
of competence traits and motives peasant salt people
in District Galis Pamekasan.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW AND
METHOD
According to Spencer and Spencer, (1993),
competence is the underlying characteristic of a
person and is related to the effectiveness of the
individual's performance in his work. Underlying
characteristics that contain the meaning of
competence are part of a deep and attached
personality to a person as well as predictable
behavior on various circumstances and work tasks.
Causally related has the meaning of competence is
something that causes or predicts behavior and
performance. Criterion referenced implies that the
competence actually predicts who is performing
well, measured by the criteria or standard used.
Hogg (1993), in Seema Sanghi (2007) defines
competence as a manager characteristic that leads to
a demonstration of skills and abilities that result in
effective performance within the work area.
Competence also manifests capacity to transfer skills
and abilities from one field to another. Other
definitions that are also relevant and widely accepted
among human resources experts in the corporate
environment suggest that competence is a
fundamental characteristic of someone who
produces effective performance or superior
performance in his work Klemp 1980, in Seema
Sanghi (2007).
A more detailed definition synthesized from the
suggestion of several hundred experts in human
resource development who attended a conference on
competency issues in Johannesburg in 1995, stated
that competence is a collection of interrelated
knowledge, skills and attitudes that affect the
majority of one's work (the role or responsibility)
that correlates with workplace performance, which
can be measured against well-received standards and
can be improved through training and development,
Parry (1996) in Seema Sanghi (2007).
Furthermore, Wibowo (2007) argued that the
competence as the ability to perform or perform a
job or task based on the skills and knowledge of
work demanded by the job. Thus, the competence
shows the skills or knowledge that is characterized
by professionalism in a particular field as the most
important. Competence as a person's characteristics
is related to effective performance in a job or
situation. Each competence is seen in individuals at
various levels. Competencies include the deepest
human characteristics such as motives, traits and
attitudes or are observable and observable
characteristics such as skills and knowledge. The
existence of the level of competence proposed by
Spencer and Spencer in Wibowo (2007) like the
iceberg where there are visible on the surface, but
some are not visible on the surface. Based on figure
1 below, it can be seen that the knowledge and skills
aspect are competency aspect which tends to be
visible and relative on the surface, while self-
concept, personal traits and motives are aspects of
competence that tend to be hidden, and do not
appear on the surface.
Competency Development of Traits and Motives in Case of Salt Farmer in Galis, Sub-district of Pamekasan Regency
791
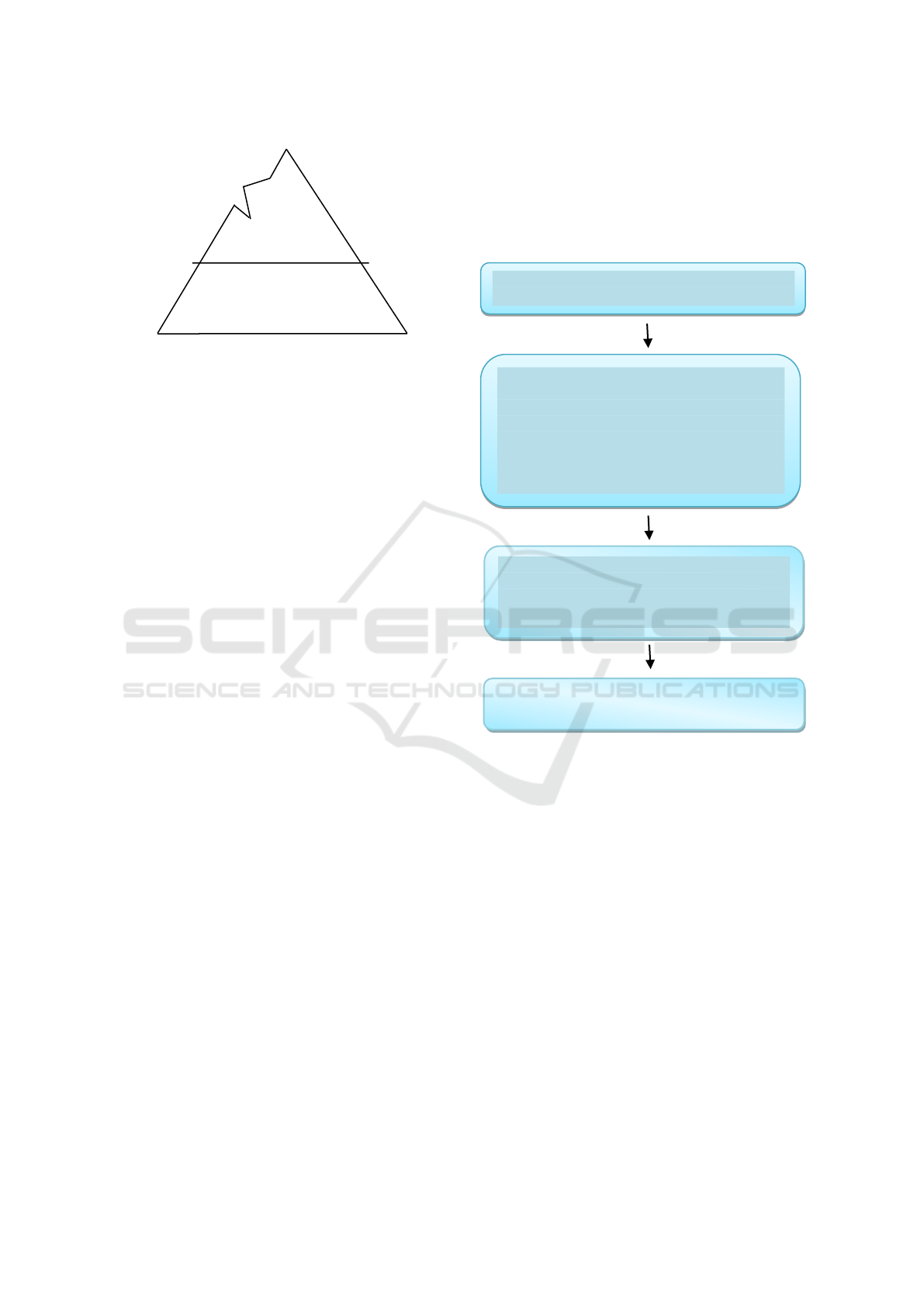
Visible
Skills- Knowledge
Self-concept
Hidden Traits
Motives
Figure 1 : The iceberg model.
Source: Spencer and Spencer in Wibowo (2007)
In this research, the researcher uses qualitative
method because it intends to get the description of
the phenomenon that occurs in the field that is about
the development of competence of traits and motives
of peasant salt in Galis Sub-district, Pamekasan
Regency, and intends to get a deep picture about
competence development of traits and motives of
salt farmers people in Galis Sub-district Pamekasan
District, the type of research used in this study is the
type of survey, which aims to find out directly about
the development of competence traits and motives
peasant salt people in Galis Sub-district Pamekasan
The type of research used in this study is a more in-
depth descriptive (thick description) that will try to
depict in depth a research object at the present
moment based on facts that appear as they are.
Furthermore, in order for the research results to have
a high weight, this research will be done by
identifying the dimensions that are quite influential
and relevant to note, and then the facts found given
interpretation. This research, using unit of individual
analysis with research object of competence
development of traits and motives of peasant salt in
Galis Sub-district Pamekasan Regency.
Determination of informants in this research is based
on research subjects who master the problem, have
data and willing to provide data to researchers. The
adequacy of data is based on the depth of data
obtained at the time of research data collection,
while saturation of data is based on the similarity
and uniformity of data and information obtained
from the informants at the time of data collection in
the field. Informants in this research amounted to 9
people, namely: 8 people salt farmers who come
from each different Hamlet in the village that has a
salt peoples land area in Galis Sub-district, which
consists of: 2 people salt farmers who come from the
Village Polagan Galis Sub-district, 2 peasant salt
people from Konang Village, Galis Sub-district, and
4 peasant salt people from Lembung Village, Galis
Sub-district, and 1 supporting informant that is
Chairman of Garam Commission Pamekasan
Regency. Data collection technique used in research
are: in-depth interviews and observation. The
conceptual framework in this research is presented
in figure 2.
Figure 2: Conceptual framework.
Based on conceptual framework, this research
uses the theory of competence proposed by Spencer
and Spencer (1993) cited by Emmyah (2009) in
Sutoto, which states that competence as the
underlying characteristic of a person and related to
the effectiveness of individual performance in his
work (an underlying characteristic of an individual
which is causally related to criterion referenced
effective and or superior performance in a job or
situation). Spencer and Spencer (1993), stated that
competence consists of five characteristics namely:
knowledge, skills, self-concepts, traits, and motives.
The development of the competence of smallholder
salt farmers in Galis Sub-district Pamekasan
Regency. in this research, focused on the aspects of
personal characteristics/ traits that include self-
control competence (SCT), self-confidence (SCF),
flexibility (FLX), organizational commitment (OC)
and aspects of motives that include organizational
Competence traits and motives peasants salt farmers
Galis Sub-district of Pamekasan Regency
Characteristics of competence according to
dictionary competence Spencer & Spencer:
clusters of personal characteristics / traits include
self-control (SCT), self-confidence (SCF),
flexibility (FLX), and organizational commitment
(OC). Cluster motives includes: organizational
awareness (OA), relationship building (RB), and
achievement orientation (ACH).
The development of competence of traits and
motives of peasant salt refers to Spencer &
Spencer's competence theory, cited by Emmyah
(2009) in Sutoto
Competence traits and motives of peasant salt
people Galis Subdistrict of Pamekasan Regency
increased
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
792

awareness (OA), relationship building (RB), and
achievement orientation (ACH) competencies,
because both aspects of the competency can still be
developed. Whereas the other three aspects, namely
aspects of knowledge, skills, and self-concept, will
not be examined by researchers so that the results of
their research are more focused. With a frame of
mind, it is expected to produce directed and
consistent research, able to answer problems that
will be examined accurately, so that this research
will be useful for the Pamekasan Regency
government, for the Pamekasan Salt Commission,
and for small salt farmers in Galis Subdistrict,
Pamekasan Regency.
3 RESULT OF THE STUDY
The results of this research indicate that the
competence of personal characteristics/ traits of the
salt farmers of Galis Sub-district of Pamekasan
Regency is still need development, especially the
personal characteristic competence/ traits that is still
not good for example the peasant salt people who
have not followed the training and coaching working
on salt land is generally still done traditionally or
without using polybag, and dependence on weather
or sunlight is still very high.
The salt farmers of the people in Galis Sub-
district also need to pay attention to the environment
around the people's salt land which can also affect
the development of personal characteristics/ traits of
smallholder salt farmers which will ultimately affect
the quality and quantity of people's salt produced.
The development of personal characteristics/ traits
of smallholder salt farmers in Galis Sub-district can
be carried out through training and coaching carried
out periodically by the Pamekasan Regency
government, namely by the Fisheries and Marine
Service of Pamekasan Regency to develop the
competence of personal characteristics/ traits of
smallholder salt farmers. in Galis Sub-district, so
that with the training and guidance, the competence
of personal characteristics/ traits of salt farmers in
Galis Sub-district has increased.
In addition, this study shows that the competence
of the motives (peasant farmers) in the Subdistrict of
Galis Pamekasan still need development.
Development of the competence of people's salt
farmers in Galis Sub-district Pamekasan Regency
can be done if the salt farmers in Galis District also
have confidence to develop the competence of
motives that they have today. In addition, the salt
peasant farmers in Galis Sub-district should also be
more active in supporting the development of the
competence of the people's salt farmer’s motives in
Galis Sub-district. The development of the
competence of salt farmers motives in Galis Sub-
district can also be done through training and
guidance to the peasant salt farmers in the Sub-
district of Galis conducted by the government of
Pamekasan Regency, Fisheries and Marine Office of
Pamekasan Regency, to develop the competence of
the salt farmers motives people in Sub-district Galis
Pamekasan Regency.
The results of this research also indicate that the
availability of human resources in developing the
competence of farmers' motives in the Subdistrict of
Galis, especially the willingness of smallholder salt
farmers in Galis Subdistrict in developing the
competence of motives is also still not good. In
general, the results of this study indicate that the
development of competence traits and motives
peasants salt farmers in Subdistrict Galis Pamekasan
Regency is still not running well, so the government
of Pamekasan District in this case the Department of
Fisheries and Marine Pamekasan Regency should
conduct training and coaching to develop
competence traits and the motives of peasant salt
people in Galis Sub-district, Pamekasan Regency.
The people salt farmers in Galis Sub-district must
also have confidence in the training and guidance
done by the Fisheries and Marine Service of
Pamekasan Regency, and also have the willingness
to participate in the training and development as it
aims to develop the competence of personal
characteristics/ traits and competence development
motive of peasant salt people in Sub-district Galis
Pamekasan Regency.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Research on the development of competence of traits
and motives of peasant salt in Galis Sub-district of
Pamekasan Regency has the following conclusions:
1) In general, the people's salt farmers in Galis
Sub-district Pamekasan Regency already have the
competence of traits and motives in producing
people salt, but the competence of traits and motives
owned by farmers salt people in Galis Sub-district
Pamekasan Regency still need further development.
The development of competence of traits and
motives of salt farmers in Galis Subdistrict can be
done through training and guidance activities to
smallholder salt farmers in Galis Sub-district, so that
the development of competence of traits and motives
owned by smallholder salt farmers in Galis Sub-
Competency Development of Traits and Motives in Case of Salt Farmer in Galis, Sub-district of Pamekasan Regency
793

district can support the ability of smallholder salt
farmers in Galis regency in producing the salt of the
people they have acquired from generation to
generation from their own parents.
2) In developing competence of traits and
motives of peasant salt in Galis Sub-district of
Pamekasan Regency, Fishery and Marine Office of
Pamekasan Regency as training and coach to
develop competence of traits and motives owned by
peasant salt farmer in Galis Sub-district until now,
training and sustainable development to all peasant
salt people in Galis Sub-district Pamekasan
Regency, it is evident with still found most of the
people salt farmers in Galis Sub-district Pamekasan
Regency which until now still have not followed the
training and coaching activities conducted by the
Department of Fisheries and Marine District
Pamekasan. Until now there are still many people
salt farmers in Galis Sub-district Pamekasan
Regency that competence traits and motives has not
developed and still produce people's salt with the
ability obtained by hereditary from their parents, so
the quality and productivity of the people's salt they
produce is still low.
3) In developing the competence of traits and
motives owned by peasant salt people in Galis Sub-
district Pamekasan Regency, Fishery and Marine
Office of Pamekasan Regency have coordinated and
cooperated with the power holder or government
under it, such as Sub-district Head of Galis Sub-
district and its staff and at the level Village Heads,
Village Devices, Community Leaders, Religious
Leaders, and other influential people in conducting
training and fostering activities to smallholder salt
farmers in Galis Subdistrict, so that training and
coaching activities can be done well.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The researcher is grateful to Postgraduate School of
Universitas Airlangga for giving him the opportunity
to present this paper at the 2018 International
Conference of Postgraduate School, Universitas
Airlangga, Surabaya.
REFERENCES
Adi, Tukul R, Agus Supangat, Budi Sulistiyo, Bangun
Muljo S, Husni Amarullah, Tri Heru Prihadi, Sudarto,
Eddy Soentjahjo, Agustin Rustam. 2012. Buku
Panduan Pengembangan Usaha Terpadu Garam dan
Artemia. Pusat Penelitian dan Pengembangan
Sumberdaya Laut dan Pesisir, Badan Penelitian dan
Pengembangan Kelautan dan Perikanan, Jakarta.
Bungin, Burhan. 2013. Metodologi Penelitian Sosial &
Ekonomi: Format-Format Kuantitatif dan Kualitatif
untuk Studi Sosiologi, Kebijakan Publik, Komunikasi,
Manajemen, dan Pemasaran. Kencana Prenada Media
Group, Cetakan ke Satu, Jakarta.
Efendy, Makhfud, Firman Farid Muhsoni, Rahmad Fajar
Shidiq, Ahmad Heryanto. 2012. Garam Rakyat
Potensi dan Permasalahan. UTM Press, Universitas
Trunojoyo Madura. Bangkalan.
Efendy, Makhfud, Ahmad Heryanto, Rahmad Fajar Sidik,.
2014. Korporatisasi Usaha Garam Rakyat: Perspektif
Teknis Sosial Ekonomis. UTM Press, Universitas
Trunojoyo Madura. Bangkalan.
Emmyah. 2009. Analisis Faktor–Faktor Kinerja Pegawai
Pada Politeknik Negeri Ujung Pandang. Makassar:
STIA-LAN RI.
Irianto, Jusuf. 2016. “Kebijakan dan Manajemen Sumber
Daya Manusia Sektor Publik (KMSDM-SP)”.
Indomedia Pustaka, Cetakan Pertama, Yogyakarta.
Laporan Akhir Pengembangan Demplot Garam Aditif
Adirama. 2012. Dinas Perindustrian dan Perdagangan
Kabupaten Pamekasan bekerjasama dengan Fakultas
Pertanian Universitas Trunojoyo Madura. Bangkalan.
Moleong, Lexy J. Metodologi Penelitian Kualitatif.
Remaja Rosdakarya, Cetakan Kedua Puluh Dua,
Bandung: 2007.
Pusat Penelitian dan Pengembangan Sumberdaya Laut dan
Pesisir. 2012. Buku Panduan Pembuatan Garam
Bermutu, Pemberdayaan Lahan Kering Kawasan
Pesisir untuk Industri Garam Rakyat. Cetakan ke -3.
Pusat penelitian dan Pengembangan Sumberdaya Laut
dan Pesisir, Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan
Kelautan dan Perikanan, Jakarta.
Sanghi, Seema, 2007. The Handbook of Competency
Mapping: Understanding, Designing and
Implementing Competency Models in Organizations,
Second Edition. Response Books. New Delhi.
Sekretariat Pugar. 2012. Laporan Akhir Pemberdayaan
Usaha Garam Rakyat Tahun 2013. Direktorat
Jenderal Kelautan, Pesisir dan Pulau pulau Kecil,
Kementerian Kelautan dan Perikanan.
Sugiyono. 2017. Metode Penelitian: Kuantitatif,
Kualitatif, dan R&D. Alfabeta, Bandung.
Suhelmi, Ifan Ridho, Erish Widjanarko, Hariyanto
Triwibowo, Sophia L Sagala, Hari Prihatno, Ahmad
Najid, Aris Wahyu Widodo, Rikha Bramawanto.
2013. Garam Madura: Tradisi dan Potensi Usaha
Garam Rakyat. Pusat Penelitian dan Pengembangan
Sumberdaya Laut dan Pesisir, Badan Penelitian dan
Pengembangan Kelautan dan Perikanan, Jakarta.
Wibowo, 2007. Manajemen Kinerja, PT. Raja Grafindo
Persada. Jakarta.
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
794
