
The Potential of Antigenic Protein of Sarcoptes scabiei as a
Serological Diagnostic Candidate for Scabies in Goats
Nunuk Dyah Retno Lastuti
1,2
, Dony Chrismanto
3
, Poedji Hastutiek
2
and Agus Sunarso
2
1
Postgraduate School, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya
2
Dept. of Parasitology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya
3
Animal Health Program, Faculty of Vocational Education, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya
Keywords: Antigenic Protein, Goat, Sarcoptes scabiei, Serological diagnostic.
Abstract: In Indonesia, the prevalence of scabies on goat cattle is still high, which shows that scabies is still not
handled properly. It is now considered as an emerging/re-emerging parasitic disease that threatens human
and animal health globally. The scabies disease has been known for a thousand years, and it is a persistent
problem on public health and also livestock. Yet, until today a serological diagnostic tool is sensitive and
specific is not available, especially for goat cattle in Indonesia. In recent years, an indirect antibody enzyme-
linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) has been available, which has higher sensitivity and specificity than
traditional diagnostic methods. In order to overcome those problems preventive actions need to be
undertaken through research for serological diagnostic development as an alternative for scabies prevention
in goats in Indonesia. The purpose of this research is doing sensitivity and specificity tests towards the
antigenic protein of Sarcoptes scabiei isolated from goat as diagnostic material for scabies in goats. The
method was comprised of deciding the gold standard for positive and negative scabies, checkerboard test
toward antigenic protein, and ELISA test for measuring sensitivity and specificity. The research results
showed that S. scabiei antigenic protein with molecular weight of 57.3 kDa can be recognized by serum
antibody of goat that infested with scabies with sensitivity level of 96% and specificity of 86,6%. From that
result, it can be recommended that S.scabiei with a molecular weight of 57.3 kDa is the specific antigenic
protein that can be used as a candidate of serological diagnostic material for scabies isolated from
Indonesian local goat.
1 INTRODUCTION
Scabies disease is already known for thousand years
ago and is persistently harming the health of people
as well as cattle. However, until today a sensitive
and specific tool for serological diagnostic which is
specially provided for goat livestock in Indonesia
has not been found yet. Diagnosis of scabies
nowadays is still conventional, which is based on
clinical symptoms and microscopic examination
from the skin scraping results done by scraping until
the deep layer skin is peeled off. The diagnosis is not
very practical if the number of livestock is high and
the livestock is less sensitive because the clinical
symptoms are similar to other skin disease like
caused by other mites (psoroptes, notoedres and
chorioptes), fungus, and ticks, which cause atopic
dermatitis, itching, and alopecia (Soulsby, 1986;
Walton and Currie, 2007; Yu Zheng, 2016). A
definite diagnosis (skin scraping) by finding
Sarcoptes scabiei mites will meet difficulties,
especially if the number of mites is low in the
infected animals and the success level is only 30-
50% (Arlian, 2000; Lower et al., 2001; Tarigan,
2004; Walton and Currie, 2007). As an effort to
resolve the problem, it is necessary to develop
diagnostic material serologically to enable early
therapy to prevent broader transmission. Some
countries, such as Australia, Germany and the
Uniteds States, have developed serological diagnosis
(ELISA) for dogs and pigs, it is very possible
because S.scabiei could induce a humoral antibody
response on the infected host (Lower et al., 2001;
Arlian et al., 2004; Tarigan, 2004; Vercruysse, 2004;
Walton and Currie, 2007; Lastuti, 2017; Lastuti,
2018).
Lastuti, N., Chrismanto, D., Hastutiek, P. and Sunarso, A.
The Potential of Antigenic Protein of Sarcoptes scabiei as a Serological Diagnostic Candidate for Scabies in Goats.
DOI: 10.5220/0007546505370540
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School (ICPS 2018), pages 537-540
ISBN: 978-989-758-348-3
Copyright
c
2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
537
2 MATERIAL AND METHODS
2.1 Determination of Gold Standard
The determination of gold standard for positive
control and negative controls was based on
microscopic examination of goat skin scraping
infected with scabies. Positive results were declared
if the researchers found S.scabiei mites under the
goat skin by scraping examination, which would
then be used as positive control. Meanwhile, the
negative control comes from healthy goats, which
were previously examined by skin scraping and did
not contain any mites. The number of samples for
gold standard was 40 samples consisting of 25
positive samples of scabies and 15 negative samples
of scabies (Lastuti, 2017).
2.2 Indirect ELISA assay
The checkerboard result of antigenic protein of
S.scabiei (57.3 kDa) was examined through indirect
ELISA test to test the ability to detect antibody
reaction towards positive control and negative
control performed as follows: a microtiter plate
consisting of 96 wells, with each well being coated
with 100 μl of antigen solution with a concentration
of 10 μg/ml in buffer coating, was incubated at 4 ºC
overnight. The next day, the well was washed with
buffer washing (NaCl-Tween) 200μl three times.
Furthermore, the well was blocked using a 4%
creamer (in PBS-Tween) of 200 μl/well and
incubated at 37 ºC for one hour, then microtiter plate
will be washed the same way three times. The next
step is that the well was added with goat serum from
positive control and negative controls and also added
with PBS tested on 1/100 dilution for as much as
100 μl per well. Work was done in duplo. As per the
standard for counting antibody titers, the dilution of
antibody for which the positive control antibody titer
was known was done at dilutions of 1/25 to 1/51200
and 100 μl was added per well. Then, the plate was
incubated at 37 ºC for an hour and washed again.
The next step is the addition of anti-goat conjugate
(IgG anti-goat) at1/5000 dilution for as much as 100
μl each well and incubated at 37 ºC for one hour.
The plate was washed again and added pNPP
substrate in substrate buffer (diethanolamine 1
mg/ml) of 100 μl per well. Then, the well was
incubated at room temperature in a dark room within
15 to 45 minutes. The reaction was stopped by the
addition of 50 μl NaOH 3N solution per well, then
the plate was read using the ELISA reader with a
wavelength of 405 nm (Lastuti, 2018). The value of
OD obtained in positive and negative controls would
determine the sensitivity and specificity of the tested
antigens.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The results of the indirect ELISA test showed that
the antigenic protein identified by the gold standard
antibody sample was a molecular weight protein of
57.3 kDa. The number of samples was 40, which
consists of positive controls with 25 samples and
negative controls with 15 samples. The average
value of Optical Density (OD) and the antibody titer
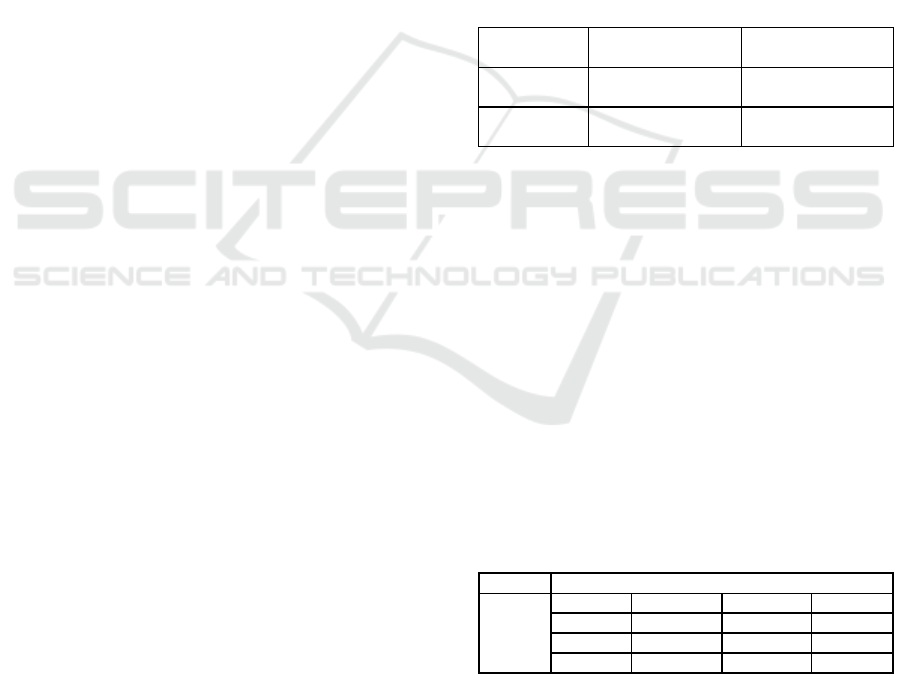
were listed in table 1 below.
Table 1. Average OD values and gold standard sample
antibody titer which recognized the S.scabiei protein 57.3
kDa
Sample
Value of OD
(mean SD)
Antibody Titer
(mean SD)
Positive
0.281
a
0.096
712,000
a
451.220
Negative
0.166
b
0.020
26,666
b
70,373
Annotation: A different superscript on the same column
showed a very significant difference (p <0.01).
Based on the ELISA indirect test, the value of
OD and antibody titer was used as the basis for
testing the sensitivity and specificity of proteins with
a molecular weight of 57.3 kDa. The test results
showed that 57.3 kDa protein serum antibodies
could be recognized by a goat, with the following
results: out of 25 positive samples of gold standard,
24 samples were positive (true positive) and one
sample was negative (false positive). Meanwhile,
from 15 negative samples of gold standard, 13
negative samples and 2 positive samples (false
negative) were found. The results are summarized in
Table 2 below.
Table 2: Sensitivity and Specificity Tests of S.scabiei
Protein 57.3 kDa.
Skin Scraping Examination
Elisa
test
+
-
Total
+
24
2
26
-
1
13
14
Total
25
15
40
Note: Skin scraping: conventional method for scabies
diagnostic ELISA test: serological test used to develop
scabies diagnostic.
The calculation results of sensitivity test, which
is the positive number of ELISA test divided by the
positive number of scraping examination, is: 24/25 =
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
538

96%, while the specificity test result is the negative
number of ELISA test divided by the number of total
negative examination of gold standard scraping is:
13/15 = 86.6%. These results indicated that S.scabiei
antigen protein with a molecular weight of 57.3 kDa
could be identified by scabies infected goat serum
antibody with 96% sensitivity level and specificity
level of 86.6%. From the results, it can be
recommended that the S.scabiei protein goat isolates
with a molecular weight of 57.3 kDa is a specific
antigenic protein that could be used as a serological
diagnostic candidate for scabies in goats.
Based on the results of Tarigan's research
(2004a) that goat infected with S.scabiei showed a
high IgG response ten days after infection and the
high level of IgG could be maintained for up to 20
days after receiving ivermectin. The antibody was
able to recognize antigen with molecular weight of
43 to 220 kDa with four highly prominent antigens
being 180, 60, 38 and 37 kDa. Sensitivity test results
of 96% and a specificity of 86.66% showed an
accurate diagnosis result exceeding 80% (Bornstein,
2006; Lower et al., 2001). The development of
serological diagnostic tests that have been performed
to diagnose scabies in various animals have been
undertaken by researchers, including a diagnosis
developed by ELISA techniques to detect S.scabiei
antibody. Serological test results showed not much
different levels of sensitivity and specificity as they
did Lower et al (2001) for serologic diagnosis in
dogs with ELISA assay, which found a sensitivity
level of 84.2% and specificity of 89.5%, in which
antigen was used to detect antibodies in dogs who
had received scabies treatment for 1 to 4.5 months
and the ELISA test was recommended for the
diagnosis of scabies in dogs. The same test had been
evaluated by serological test with ELISA indirect
test against scabies in red fox (Vulpes vulpes), which
showed a sensitivity level of 95.4% and specificity
level of 100% and based on these results it was
concluded that ELISA test was used for diagnosing
and studying the epidemiology on scabies on red fox
(Bornstein, 2006). Similarly, Rambozzi et al (2004)
performed a serological test for detecting antibodies
induced by S. scabiei in chamois (Rupicapra spp)
with asymptomatic symptoms in the outbreak region
of the scabies showing 97% sensitivity level with
ELISA assays. Based on the exploratory results of
S.scabiei protein, it has been proved that S.scabiei
contains a protein, which is capable of inducing
humoral and cellular immune responses and has high
sensitivity and specificity level (> 80%), which can
be used as serological diagnostic candidate kits for
scabies in goats.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Antigenic protein of S. scabiei with a molecular
weight of 57.3 kDa could be recognized by serum
antibody of goat infested with scabies and had high
sensitivity and specificity level (> 80%). From the
results, it can be recommended that S.scabiei with a
molecular weight of 57.3 kDa is the specific
antigenic protein that can be used as a candidate of
serological diagnostic material for scabies isolated
from Indonesian local goat.
REFERENCES
Arlian LG and Morgan MS, 2000. Serum antibody to
Sarcoptes scabiei and house dust mite prior to and
during infestation with S.scabiei. Vet Parasitol
90:315-326.
Arlian LG, Morgan MS, Estes SA, Walton SF, Kemp DJ
and Currie BJ, 2004. Circulating IgE in patients with
ordinary and crusted scabies. J Med Entomol 41:
74-77.
Bornstein S, Frossling J, Naslund K, Zakrisson G and
Momer T, 2006. Evaluation of a serological test
(indirect ELISA) for the diagnosis of sarcoptic mange
in red fox (vulpes vulpes). Vet Dermatol 17: 411.
He R, Shen N, Zhang H, Ren Y, He M,
Xu J, Guo C, Xie
Y, Gu X, Lai W, Peng X, and Yang G. 2017.
Molecular characteristics and serodiagnostic
potential of chitinase-like protein from Sarcoptes
scabiei. Oncotarget. Oct 13; 8(48): 83995–84005.
Lastuti NDR, Abdul Rantam FA, Hastutiek P and
Chrismanto D. 2017. Protein of Sarcoptes scabiei
var.caprae inducing rabbit’s immune response and
Toll Like Receptor-2 (TLR-2) as marker. Proceeding
of 1st International Conference in One Health (ICOH
2017) Advances in Health Sciences Research
(AHSR), volume 5, 79-83.
Lastuti, NDR., Yuniarti, WM., Hastutiek P., Suwanti
LT., Chrismanto D. 2018. Humoral and cellular
response induced by antigenic protein of
Sarcoptes scabiei var.caprae. Veterinary World
journal. Vol II/No. 1168, 18823/ISSN 2231-
0916.
Lower KS, Medleau LM, Hnilica K and Bigler B, 2001.
Evaluation of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
(ELISA) for the serological diagnosis of sarcoptic
mange in dogs. Vet Dermatol 12: 315-
Rambozzi L, Menzano A, Lavin S and Rossi L, 2004.
Biotin-avidin amplified ELISA for detection of
antibodies to Sarcoptes scabiei in chamois
(Rupicapra spp). Vet Res 35: 701-708.
Soulsby EJL, 1986. Helminths, arthropods and protozoa
of domesticated animal. 7
th
ed. The English and
protozoa of society and Baillire, Tindall, London, pp
504-506.
The Potential of Antigenic Protein of Sarcoptes scabiei as a Serological Diagnostic Candidate for Scabies in Goats
539

Tarigan S, 2004. Ingestion of host immunoglobulin by
Sarcoptes scabiei. JITV 10:35-40.
Virchow F and Bigler B, 2004. Allergy-Diagnosis and
Allergy Testing. Cross-reactivity between house dust,
sarcoptic and storage mites in dogs with atopic
dermatitis. Vet Dermatol 15:37-40.
Walton SF and Currie BJ, 2007. Problems in diagnosing
scabies, a global disease in human and animal
populations. Clin Microbiol Reviews 20: 268-279.
Zheng Y, He R, He M, Gu X, Wang T, Lai W, Peng X and
Yang G. 2016.Characterization of Sarcoptes
scabiei cofilin gene and assessment of recombinant
cofilin protein as an antigen in indirect-ELISA for
diagnosis. BMC Infectious disease, 16:21.
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
540
