
Low Cost Dual Frequency Impedance Analysis for Measuring
Internal and External Celluler Fluid
Khusnul Ain
1
, R. Arif Wibowo
2
, Soegianto Soelistiono
1
, Lailatul Muniroh
3
, Tri Agggono
2
, and
M.Rizky Yusdy
1
1
Biomedical Engineering, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia
2
Physics, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia
3
Public Health, Airlangga University, Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: Bioimpedance, dual frequency, extracellular, intracellular, low cost
Abstract:
The regulation of body fluid balance is a major concern in body health. Disruption of body fluid balance is a
major factor responsible for changes in cell volume. It can affect cell function and survival. Intracellular
fluid (ICF), extracellular fluid (ECF) and total body fluid (TBW) have been used as information on body fat
levels, dengue indications and some chronic diseases. The design and development of dual frequency
bioelectrical impedance analysis prototype are used as a candidate for intracellular and extracellular fluid
measuring instrument. The device was built using sine wave generator from ICL8038 which can produce 20
kHz and 75 kHz voltage controlled current source (VCCS) and from LF412 which can generate 0.5 mA
from Howland dual op-amp method, potential was measured by instrument amplifier from AD620 and
AD536 was used as AC to DC converter. The device performance was tested on 10 volunteers. The
performance indicator is the relationship of ICF and ECF calculations to H
2
/Z. The analysis of intracellular
fluid (ICF) was obtained from used the measurement of total body impedance at high frequency of 75 kHz.
It has excellent linearity with R² = 0,9636. Meanwhile, analysis of extracellular fluid (ECF) was obtained
from the measurement of total body impedance at low frequency of 20 kHz. It has a very good linearity with
R² = 0.9579..
1 INTRODUCTION
Dengue fever is an acute disease caused by dengue
virus infection carried by mosquitoes Aedes aegypti
and Aedes albopictus. The virus causes disruption of
the capillary blood vessels in the blood clotting
system resulting in bleeding. The dengue virus
transmitted through the bite of Aedes aegypti and
Aedes albopictus was previously infected by dengue
virus from other dengue fever patients with 4 related
antigens, but different serotypes (DENV-1, DENV-
2, DENV-3, and DENV-4) including the genus
Flavivirus, family Flaviviridae (WHO, 2009).
The classification and definition of dengue fever
is divided into dengue fever and dengue
hemorrhagic fever. Dengue fever begins with a
sudden increase in temperature with headache,
myalgia, macular rash, loss of appetite, nausea,
vomiting, abdominal pain, changes in psychological
state, and thrombocytopenia, then if initial clinical
management or appropriate fluid therapy is not
provided, dengue fever will become a dengue
hemorrhagic fever that begins with a fever that
subsides but increases micro vascular permeability,
decreases plasma volume, and is aggravated by
hypotension and shock, lastly if appropriate therapy
is not available, circulatory failure will occur, then
dengue hemorrhagic fever will become dengue
shock syndrome which is a fatal classification and
definition of dengue that begins with a rapid and
weak pulse.
Therefore, delays in the management of fluid
therapy may lead to death (Deen et al., 2006). The
number of cases of dengue fever every year and the
absence of vaccines and antiviral drugs that can stop
dengue virus infection, result in broad loss impact,
especially on economic and health aspects (WHO,
2009). Dengue virus that enters the body will infect
immune cells in the skin tissue then enter the
lymphatic system, thus, triggering a strong
inflammatory reaction. During the incubation period,
the virus replicates locally then spreads into the
504
Ain, K., Wibowo, R., Soelistiono, S., Muniroh, L., Anggono, T. and Yusdy, M.
Low Cost Dual Frequency Impedance Analysis for Measuring Internal and External Celluler Fluid.
DOI: 10.5220/0007545905040510
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School (ICPS 2018), pages 504-510
ISBN: 978-989-758-348-3
Copyright
c
2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
bloodstream which is commonly referred to as
viremia. In some patients, especially children,
dengue virus infection can lead to severe clinical
manifestations. The most severe clinical
manifestations can cause blood vessels to become
permeable resulting in leakage of plasma which
ultimately requires intensive hospital care. The
phase and clinical symptoms when experiencing
dengue fever is the first phase of high fever which is
characterized by high fever reaches 40
o
C with
symptoms caused by severe headache, back pain in
the eyes, nausea, vomiting, swollen glands, rash,
pain muscles and joints. This is a sign that a person
is infected with dengue virus after being bitten by an
infected mosquito and an incubation period of
dengue virus for 4 - 10 days, in this phase usually
occurs for 2 - 7 days.
Accurate diagnosis and monitoring of dengue
fever condition is needed to identify the severity
level in providing appropriate treatment. In order to
handle and control cases of dengue, there are many
methods that have been developed and used to
diagnose and monitor the risk of dengue fever. One
of them is to observe the onset and progression of
plasma leakage of dengue fever patients by
measuring the increase in total hematocit or
hemoglobin (WHO, 2009). The advantage of this
method is not only to diagnose dengue fever but also
to distinguish dengue fever as well, then by
monitoring the number of thrombocyte of dengue
fever patients and liver function. Although this
conventional method has been able to provide an
accurate diagnosis, it takes a long time, is invasive,
and can harm patients, since this conventional
method requires frequent invasive blood sampling,
which can lead to further injury to the subcutaneous
tissues and potentially harmful to people with
dengue fever (Ibrahim et al., 2005 and Ibrahim et
al., 2007). In addition, this conventional method can
only be done in inpatients at the hospital only, but
not all patients with dengue fever can undergo
hospitalization because the facility in the hospital
itself is not able to handle all patients with dengue
fever in a very large number (Ibrahim et al., 2005).
The facts show that cases of dengue fever are
often misdiagnosed with other diseases, such as flu
or typhoid. This is because the symptoms of dengue
virus infection in the early stages may not have a
distinctive feature (Ginanjar, 2008). So far, the
majority of society and health practitioners in
Indonesia still do not understand the difference
between fever caused by dengue virus infection and
common fever caused by other infections. This is
what causes the number of morbidity (mortality rate)
and mortality (Mortality Rate), because the success
of the handling of dengue fever case is largely
determined by early detection of dengue virus
manifestations in patients so that it can be done case
management in the form of management therapy
effective fluids. Early detection of dengue fever
patients with non-invasive method, one of them can
be done through body temperature analysis because
at the time of dengue fever patient experiencing high
fever phase until critical phase, they will have fever
which has characteristic marked with horse saddle
graph produced by body temperature.
Multi-frequency bioelectrical impedance analysis
(MF - BIA) method can diagnose the manifestation
of dengue virus in dengue fever patient. This method
uses a constant electric current at low frequencies of
5 kHz to 1000 kHz through the body, and produces a
potential difference value (V) to obtain an
impedance value (Z), using four electrodes (Jaffrin
et. al., 2008). The results showed that there was a
correlation between the frequency value of body
fluid measurements, where the low frequency values
represent extracellular fluid values (ECF) and high
frequency values represent intracellular fluid values
(ICF), so the total body water (TBW) was obtained
based on the sum of the fluid value extracellular
(ECF) and intracellular fluid value (ICF). Several
studies have been conducted to determine the
intracellular and extracellular fluids (Moissl et al.
2006).
2 METHODS
In this research, the design and development of
intracellular cell and extracellular cell impedance
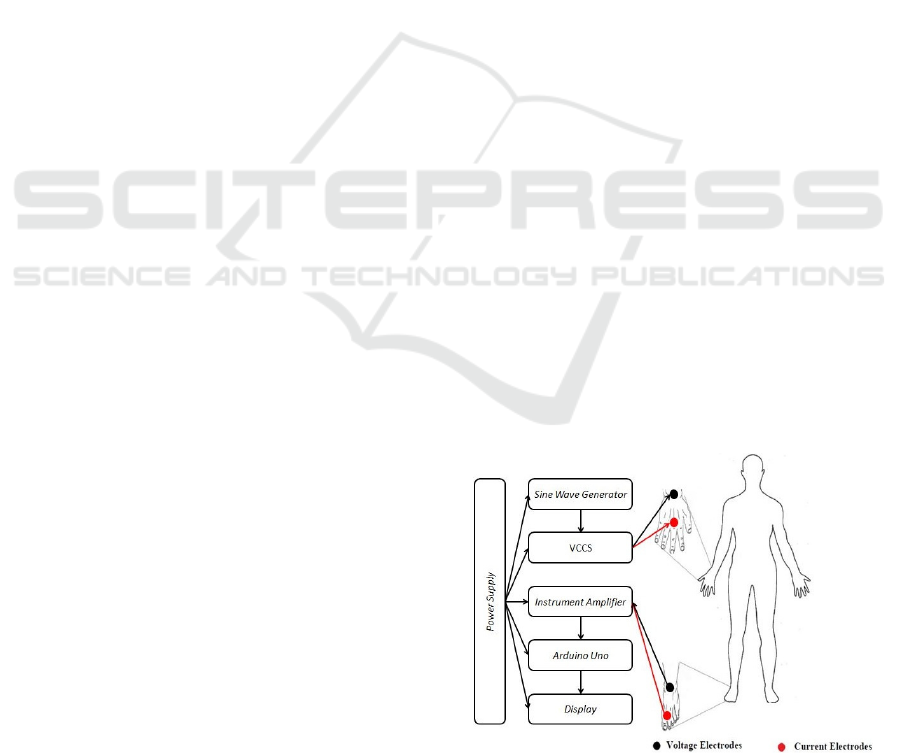
measuring device. The design of the device is shown
in Figure 1.
Figure 1 : Block diagram of Bioelectrical Impedance
Analysis
Low Cost Dual Frequency Impedance Analysis for Measuring Internal and External Celluler Fluid
505
The device consists of a sine wave generator,
VCCS, voltage meter and microcontroller. Sine
wave generator circuit was used as a generator of
sinus voltage signal using IC IC8080 which was
then connected with resistor and capacitor to
produce sine voltage of 20 kHz and 75 kHz which
can be seen in Figure 2.
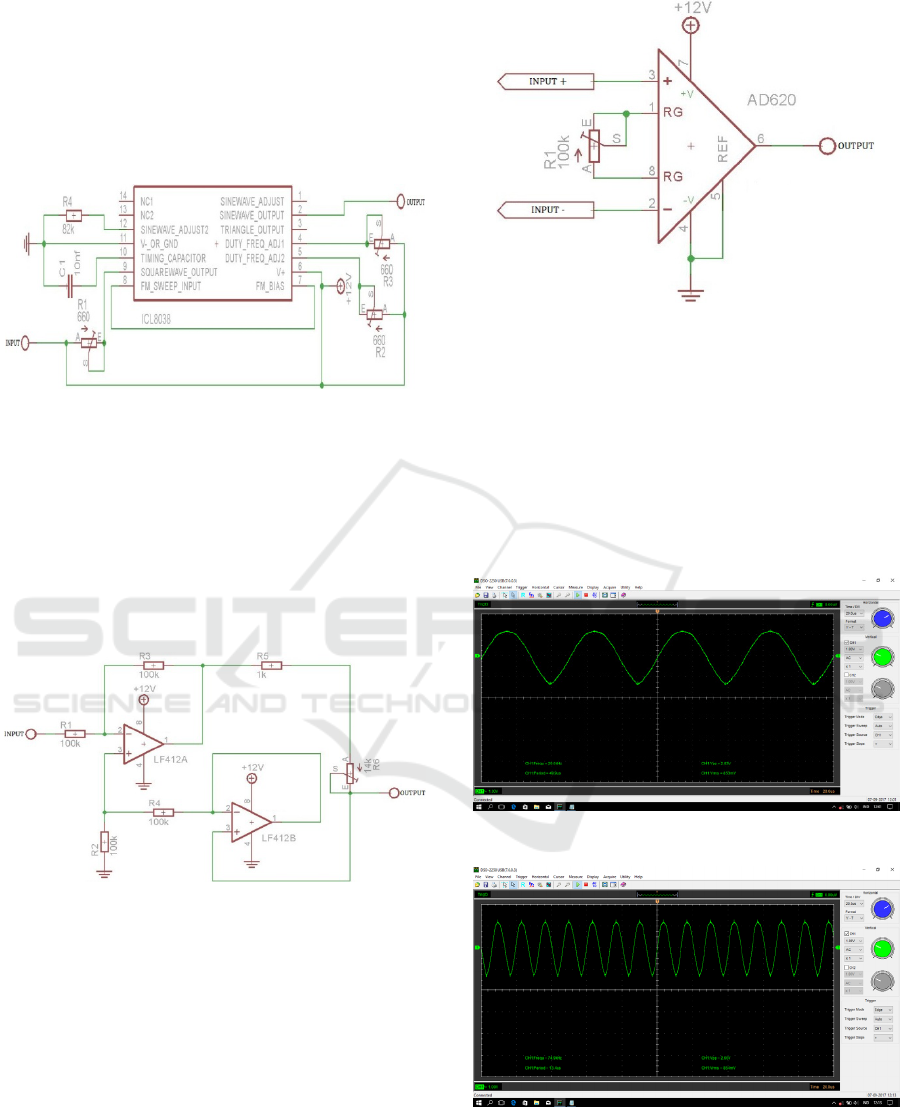
Figure 2 : Design of sine wave generator
Voltage Controlled Current Source (VCCS)
circuit functions as electric current source based on
input voltage signal. The VCCS circuit uses a dual
opamp built from IC LF412 coupled with a resistor
that can serve as a current source of 0.5 mA, as
shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3 : Design of Voltage Control Current Source
(VCCS).
The Instrument Amplifier circuit was used as a
comparison of two input voltages into one output
using IC AD620 which is then connected to the
resistor as a reinforcement source, as in Figure 4.
Figure 4 : Design of Instrument Amplifier
3 RESULT
Sinus generator built from IC IC8080 was coupled
with capacitor 10 nF, resistor of 1650 Ω and 440 Ω
respectively to produce sine voltage of 20 kHz and
75 kHz. The output signal generated by the circuit
can be observed through the oscilloscope, as shown
in Fig. 5 and Fig. 6.
Figure 5 : Signal 20 kHz from sine wave generator
Figure 6 : Signal 75 kHz from sine wave generator
The output signal of the sine wave generator
circuit produced a direct voltage (DC) that fluctuated
from 4.80 V until 7.84 V. The VCCS circuit was
used as an electric current generator based on input
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
506
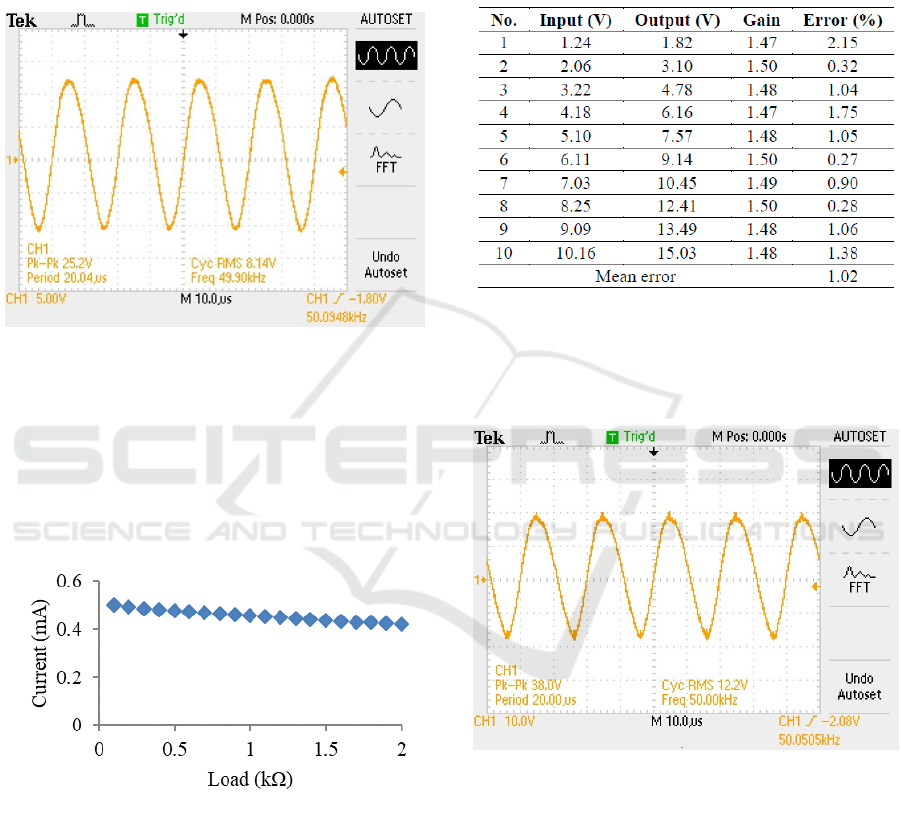
voltage using LF412 IC. The circuit requires a
supply voltage of ± 15V and a resistor to produce an
electric current with a frequency of 20 kHz and 75
kHz with an electrical current ≤ 0.5 mA that is safe
for the body. The output signal generated by the
VCCS circuit can be observed through the
oscilloscope shown in Figure 7.
Figure 7 : The signal output from VCCS circuit
Based on the signal in the oscilloscope, it can be
seen that the output signal from the VCCS circuit
was a DC electric current that fluctuated from 3.52
V to 6.56 V. Furthermore, the VCCS circuit test
showed the electric current generated against the
load changes given in Figure 8.
Figure 8. Graph between current and load at 50 kHz
The instrument amplifier circuit serves as a
comparator of two inputs voltage into one output
voltage. The circuit used an IC AD620 and ± 15V
supply voltage connected to the resistor as the
amplifier. The circuits used to tap the potential
difference of the body from the electric current 20
kHz and 75 kHz. The circuits were channeled into
the body using disposable electrodes that were
bonded on the body surface. Based on the results
shown in the oscilloscope, it appears that the output
signal of the instrument amplifier circuit produced a
DC voltage that fluctuated from 3.84 V to 7.36 V.
The amplification of the instrument amplifier circuit
is 1.5 as shown in Table 1.
Table 1 : Test of instrument amplifier
The signal generated by the instrument amplifier
circuit can be observed through the oscilloscope, as
displayed in Figure 9.
Figure 9 : Output signal from Instrument Amplifier
Dual frequency of bioelectrical impedance
analysis tool as diagnostic candidate of dengue fever
consists of hardware and software. The hardware
was used as a generator of 20 kHz and 75 kHz sine
wave signals with an electric current of ≤ 0.5 mA.
Furthermore, the electric current was used to
determine the impedance (Z) of the body.
The measurement of the potential difference (V)
generated from the 20 kHz and 75 kHz sine wave
signals was received by the instrument amplifier and
processed by arduino uno microcontroller with the
software. The software functions as a viewer and
Low Cost Dual Frequency Impedance Analysis for Measuring Internal and External Celluler Fluid
507
data processor obtained from hardware. The
software will read the potential of the body. The
analog data were converted into bits. The bit was
converted by arduino software IDE 1.6.9 into a volt /
potential (V), the last result of the measurement of
the potential (V) was processed by the software into
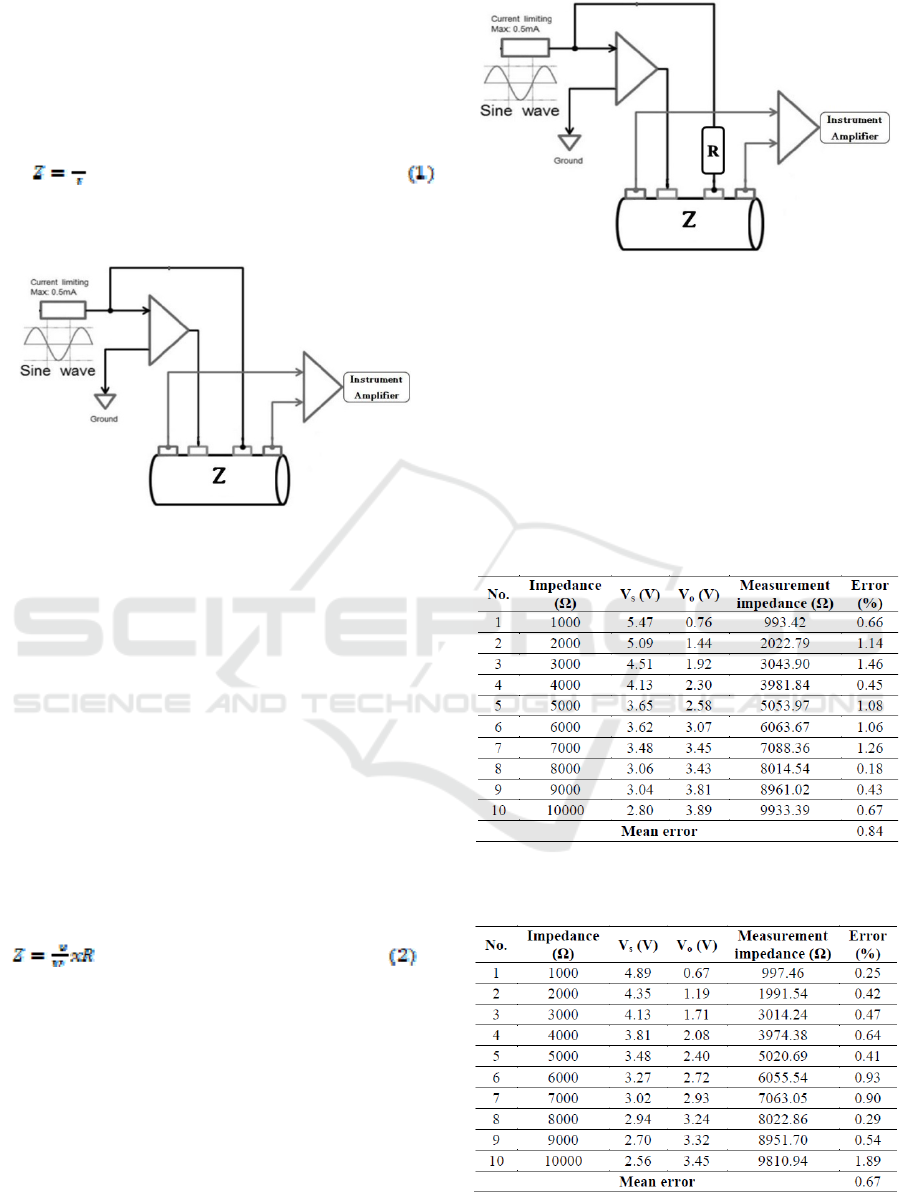
an impedance using Equation (1).
Equation 1 was obtained based on Figure 10.
Figure 10 : Analogies of conventional calculations
The measurement of body impedance (Z) using
Equation (1) was conducted by dividing the injected
electric current (I) and the potential body (V)
obtained from the instrument amplifier circuit. The
problem that occurred when measuring the body
impedance (Z) using equation (1) was when the
electric current (I) was considered constant, because
in fact in testing the voltage controlled current
source (VCCS) circuit in which the electric current
(I) is smaller when the load gets bigger. So when
measuring the body impedance (Z) using equation
(1) and assuming the value of electric current (I)
constant at ≤ 0.5 mA, the resulting body impedance
(Z) is not valid. Voltage divider approach is a valid
method that can be used in measuring body
impedance (Z), that is by using equation (2).
Equation (2) was obtained from Figure 11.
Figure 11 : Analogies of modification calculations
The measurement of body impedance (Z) using
equation 2 was done by dividing the voltage (Vo)
obtained from the reading of the potential at meeting
point (R) and (Z) and the voltage of the current
source Vs obtained from the reading the potential at
point (R) then multiplied by the resistance (R) used.
The results of device testing with variations of
measurable barriers can be seen in Table 2 and 3.
Tabel 2 : Device testing with various loads at 20 kHz
Tabel 3 : Device testing with various load at 75 kHz
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
508
After the device was well-tested, it was used to
measure impedances of 10 volunteers at frequencies
of 20 kHz and 75 kHz. The data test were taken by
measuring weight, height, and total body impedance.
The data were then used to determine the
intracellular fluid (ICF), extracellular fluid (ECF),
and total body water (TBW), while the results of
data retrieval device that has been done can be seen
in Table 4.
The measuring body fluids is based on the
equation obtained by Hoffer et al., in his journal
entitled Correlation of Whole - Body Impedance
with Total Body Water Volume (1969). The
equation relates between total body impedance and
total body fluids calibrated by dissolution techniques
tritium in-vivo. Furthermore, the equation was used
on 10 Volunteers. This is the example of the x
volunteer:
• Height (H) = 168 cm
• Weight (W) = 70 kg
• It is obtained impedance (Z) = 937 Ω when
Frequency was 20 kHz and impedance (Z)
= 682 Ω was obtained when Frequency was
75 kHz
The calculation of intracellular fluid (ICF),
extracellular fluid (ECF), and total body water
(TBW), along with percentage of intracellular fluid
value (ICF) and extracellular fluid (ECF) to total
body fluids (TBW) is,
• Intracelular Cell Fluid (ICF)
Y = 0.5855(X) + 1.9878
ICF = 0.5855 x (168
2
/682) + 1.9878
ICF = 26.22
• Extracelular Cell Fluid (ECF)
Y = 0.5855(X) + 1.9878
ECF = (0.5855 x (168
2
/937) + 1.9878)
ECF = 19.62
• Total Body Water (TBW)
TBW = ICF + ECF
TBW = 26.22 + 19.62
TBW = 45.84
• Percentage of ICF and ECF
¾ Percentage of ICF
%ICF = (ICF/TBW) x 100%
%ICF = (26.22/45.84) x 100%
%ICF = 57%
¾ Percentage of ECF
%ECF = (ECF/ TBW) x 100%
%ECF = (19.62/45.84) x 100%
%ECF = 43%
The results of data collection analysis from 10
volunteers to be shown on the graph and linearity
graph between H
2
/Z and intracellular fluid (ICF) and
extracellular fluid (ECF) which can be seen in Table
4 and Figure 12 and 13.
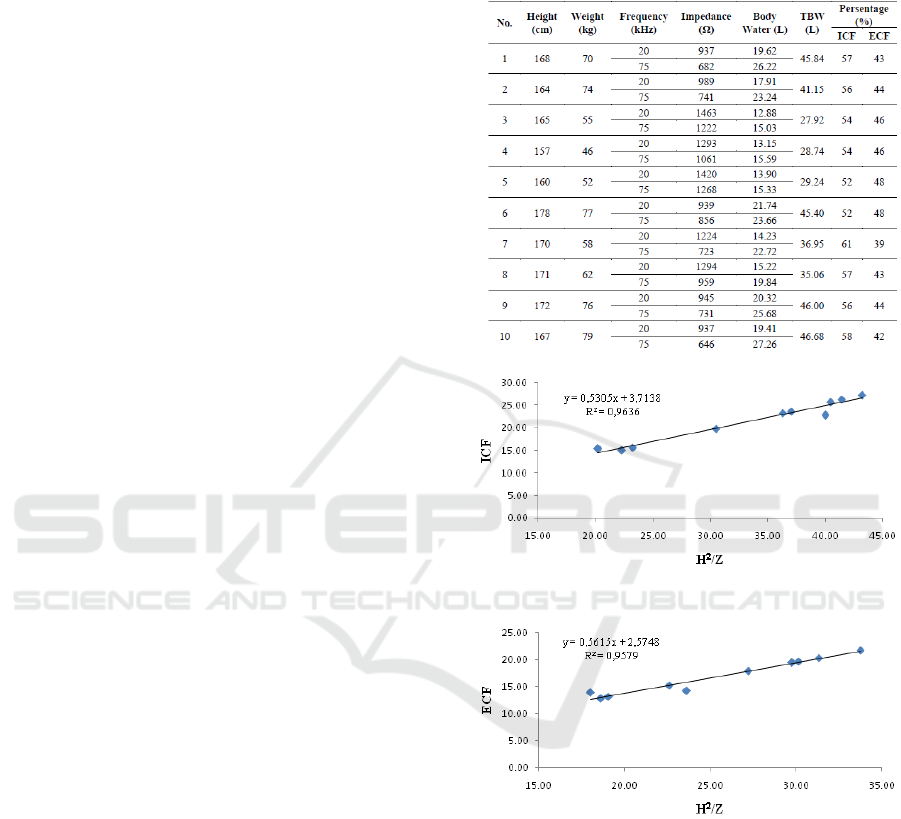
Tabel 4 : Data device and analysis
Figure 12 : Graph of linearity between H
2
/Z and ICF
Figure 13 : Graph of linearity between H
2
/Z and ECF
4 CONCLUSIONS
The dual frequency bioelectrical impedance as
diagnostic candidate for dengue fever patient can be
used to monitor the percentage of intracellular fluid
(ICF) and extracellular liquid (ECF). The
intracellular fluid (ICF) was obtained from the
measurement of total body impedance value at high
frequency (75 kHz) with linearity of R² = 0.9636
and extracellular liquid (ECF ) was obtained from
the result of measuring total body impedance value
Low Cost Dual Frequency Impedance Analysis for Measuring Internal and External Celluler Fluid
509

at low frequency (20 kHz) with linearity of R² =
0.9579.
REFERENCES
Deen J et al. 2006. The WHO Dengue Classification
and Case Definitions : Time for a
Reassessment. Lancet., 368 : 170 – 173.
Ginanjar, Genis. 2008. Demam Berdarah, a Survival
Guide. Yogyakarta : B – First.
Hoffer et al. 1969. Correlation of Whole – Body
Impedance with Total Body Water Volume. J.
Appl. Physiol, 27, 531 – 534.
Ibrahim et al. 2005. A Novel Approach to Classify
Risk in Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (DHF)
Using Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA).
IEEE Transactions On Instrumentation And
Measurement, Vol. 54, No. 1.
Ibrahim et al. 2007. A New Approach to Classify
Risk in Dengue Infection Using Bioelectrical
Impedance Analysis. Dengue Bulletin – Volume
31.
Jaffrin et al. 2008. Body Fluid Volumes
Measurements by Impedance : A Review of
Bioimpedance Spectroscopy (BIS) and
Bioimpedance Analysis (BIA) Methods. Med.
Eng. Phys., 30, 1257 – 1269.
Moissl et al. 2006. Body Fluid Volume
Determination via Body Composition
Spectroscopy in Health and Disease. Physiol.
Meas., 27, 921 – 933.
World Health Organization. 2009. Dengue :
Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention
and Control. Switzerland : WHO Press.
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
510
