
Resistance Test of Vibrio sp. From Milkfish (Chanos chanos) in
Fishpond Jabon Sidoarjo to Heavy Metals and Antibiotics
Pratikah Verdianti
1
, Fitriyati Mukhlishoh
1
, Tuty Putri
2
,and Ayu Puspitasari
2
1
Forensics Science, Postgraduate School, Universitas Airlangga, Jl. Airlangga No. 4 -6, Surabaya, East Java, Indonesia
2
Study Program of Medical Laboratory Technology, Health Polytechnic Surabaya, Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: Vibrio sp, Resistance test, Lead (Pb), Cadmium (Cd), Tetracycline antibiotic, Chloramphenicol antibiotic.
Abstract: The milkfish (Chanos chanos) obtained from Fishponds Jabon Sidoarjo contained heavy metals such as Pb
and Cd. Heavy metals pollution can be controlled by bioremediation. The objective of this research is to
determine the resistance of Vibrio sp isolated from milkfish to heavy metals Pb, Cd, at various
concentrations and to know the resistance of these bacteria to antibiotics such as tetracycline and
chloramphenicol. Resistance tests of Vibrio sp were performed using dilution and pour plate method. The
Nutrient agar media used in this study contained heavy metals PbCl
2
and CdCl
2
with concentrations of 5
ppm, 10 ppm, 25 ppm. Heavy metals-resistant Vibrio sp was tested its antibiotic resistance with diffusion
method using antibiotic disks such as Tetracycline 30 μg and Chloramphenicol 30 μg. The results showed
that Vibrio sp was resistant to heavy metals Pb and Cd at all concentrations. Antibiotic sensitivity test using
chloramphenicol 30 μg showed that Vibrio sp was resistant to chloramphenicol at concentration of 5ppm.
Pb-resistant Vibrio sp was shown resistant to chloramphenicol at concentration of 10 ppm and 25 ppm. Pb-
and Cd-resistant Vibrio sp were shown resistant to Tetracycline 30 μg at all concentrations.
1 INTRODUCTION
In 2014, there were approximately 79% rivers with
status of slight, moderate, and severe pollution,
while in 2015 there was increasing number of
polluted rivers. One of polluted rivers in East Java
was Porong River in Kabupaten Sidoarjo due to
disposal of lapindo mud by Lapindo Brantas Inc.
This led to reduction of ecosystem caused by heavy
metals contamination such as Lead (Pb) and
Cadmium (Cd).
Kholidiyah (2010) stated that concentrations of
heavy metals in the water of Porong river and
lapindo mud exeeded the standard level, showing
Lead (Pb) at concentration of 7,2876 mg/L in
lapindo mud and 0,6949 mg/L in the water of
Porong river, whereas Cadmium (Cd) contained in
lapindo mud were at concentration of 0,3063 mg/L
and of 0,0271 mg/L in the water of Porong river.
This caused pollution of nearby fishponds.
Both Lead (Pb) and Cadmium (Cd) are heavy
metals that can accumulate inside the body of living
creatures especially fishes in water contaminated
with heavy metals, potentially become toxic. If those
fishes are consumed by human, toxic will
accumulate inside tissues of human body and
endanger their health (Nuhman, 2003) One of the
known contaminated fishes is Bandeng or Milkfish
(Chanos chanos), a brackish water fish commonly
bred in fishponds.
Larasati (2015) in her research stated that
milkfish bred in fishpond Jabon Sidoarjo located at 5
km, 10 km, and 15 km away from lapindo mud
showed average concentration level of Pb of 1,0985
mg/kg, 1,3408 mg/kg, and 1,0839 mg/kg. Based on
those results it could be concluded that milkfish was
contaminated with Pb at concentration exceeding
standard of heavy metal concentration according to
SNI 7387:2009 which is 0,3 mg/kg. Screening test to
detect heavy metals contained in milkfish living in
fishpond Jabon Sidoarjo (2017) showed the result as
much as 4,82 ppm and 6,11 ppm of Pb, while Cd
was as much as 2,63 ppm and 3,24 ppm.
One of methods to overcome contamination
caused by heavy metals is by bioremediation, a
technique using certain microorganisms to eliminate
effect of contaminants (toxic substances), in order to
reduce contaminating substances (Sitanala, dkk.,
2008). Microorganisms which can be used in
bioremediation are those resistant to heavy metals.
Verdianti, P., Mukhlishoh, F., Putri, T. and Puspitasari, A.
Resistance Test of Vibrio Sp from Milkish (Chanos chanos) in Fishpond Jabon Sidoarjo to Heavy Metals and Antibiotics.
DOI: 10.5220/0007543203710375
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School (ICPS 2018), pages 371-375
ISBN: 978-989-758-348-3
Copyright
c
2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
371

After screening test of bacterial isolation from
milkfish (2017) was performed, the result showed
that Vibrio sp was contained inside the milkfish.
Vibrio sp, according to Utomo (2016) is indigenous
bacteria naturally found in fish.
Ayu (2013) stated that if certain microorganisms
contain any substances resistant to heavy metals and
antibiotics, they will negatively affect to human’s
health as treatment failure. Therefore, it is necessary
to perform resistance test using antibotics, a
chemical substance produced by certain
microorganisms that inhibit growth or kill other
microorganisms. (Simangunsong, et al., 2015).
Antibiotics often used in medical treatment are
tetracycline with wide spectrum for certain
indication from bacteria (BPOM, 2015) and
chloramphenicol which is a preferred antibiotic for
treating infection of gram-positive and gram-
negative bacteria (Uddin, et al., 2016).
Based on facts above, It was necessary to
perform a study about resistance of Vibrio sp
isolated from Milkfish (Chanos chanos) in fishpond
Jabon Sidoarjo to heavy metals such as Lead (Pb)
and Cadmium (Cd) and to antibiotics such as
Tetracycline and Chloramphenicol.
The aim of this study was to identify the
resistance of Vibrio sp to Pb and Cd at
concentrations of 5 ppm,10 ppm and 25 ppm, and to
identify the resistance of heavy metals-resistant
Vibrio sp to Tetracycline and Chloramphenicol.
2 RESEARCH METHOD
2.1 Type of Research
This study used explorative descriptive method.
2.2 Place and Time
This study took place in Microbiology Laboratory of
study program of Medical Laboratory Technology,
Health Polytechnic Surabaya starting from January
until June 2017.
2.3 Tools and Materials
Tools used in this study were autoclave, incubator,
inoculating loop, spirit burner, laboratory tripod,
erlenmeyer flask, petri dish, laboratory cottons,
analytical balance, glass stirring rod, sterile alcohol
swab, pH-indicator papers, graduated cylinder,
laboratory funnel, tweezers, rubbers, alumunium
foil, volumetric flask, beaker glass, and watch glass.
Materials used in this study were isolates of
Vibrio sp from milkfish, NA (Nutrient Agar) media,
PbCl
2
, CdCl
2
, NB (Nutrient Broth) media, MH
(Mueller Hinton Agar) media, Mc Farland
standards, antibiotic sensitivity disks Tetracycline 30
µg and Chloramphenicol 30 µg.
2.4 Procedures
2.4.1 Isolatioan of Bacteria from Milkfish
Milkfish firstly was cleaned from bones and mashed.
Serial dilution of fish samples then was performed
using saline solution to create dilution of 10
-3
. The
diluted samples were inoculated on Mac Conkey
Agar and incubated on 37
o
C for 24 24 hours.
Colonies grown on Mac Conkey Agar were picked
off and inoculated on Eosin Methylene Blue Agar
media, incubated on 37
o
C for 24 hours. Colonies
grown on EMB media were inoculated on Triple
Sugar Iron Agar media, incubated on 37
o
C for 24
hours. Colonies on TSIA media were further
identified using IMViC test (Indol, Methyl Red,
Voges Proskauer and Citrate) and Semi solid.
2.4.2 Resistance Test to Heavy Metals
Isolates of Vibrio sp were diluted until 10
-5
then
poured into NA-PbCl
2
and NA-CdCl
2
media with
concentrations used were 5 ppm, 10 ppm and 25
ppm. In addition, NA-PbCl
2
and NA-CdCl
2
media
were used as negative controls in the absence of
vibrio sp isolates. After 24 hours of incubation, the
grown isolates were shown to be resistant to Pb and
Cd, and negative controls media. Then, CFU
(Colony Forming Unit) was determined by
comparing the number of colony in media test amd
that of negative control media.
2.4.3 Resistance test to Antibiotics
Resistance tests of Vibrio sp to antibiotics were
performed by inoculating heavy metals-resistant
bacteria on MH (Mueller Hinton) media, putting
tetracycline disk and chloramphenicol using sterile
tweezers on the surface of media inoculated with
bacteria, and incubating those media for 24 hours.
Transparent zones were measured and results were
interpreted.
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
372
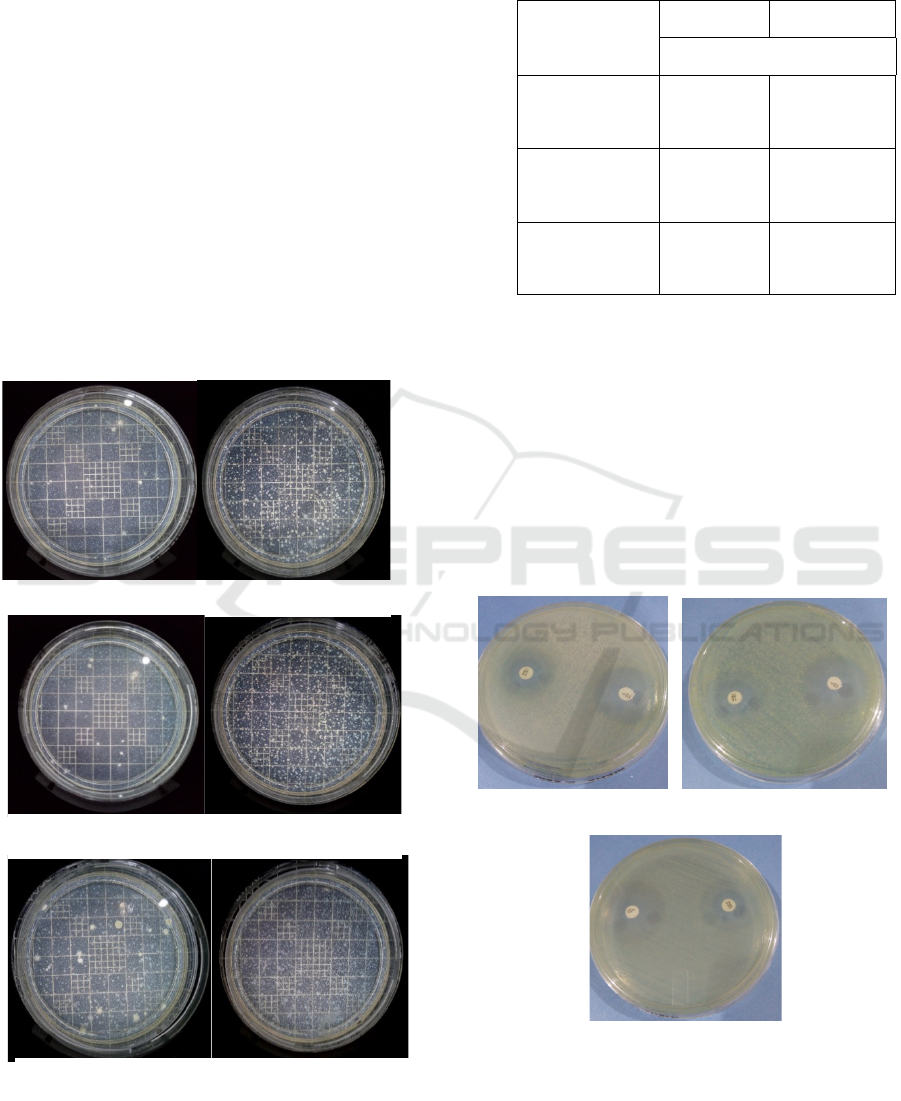

3 RESULT
3.1 Resistance Test to Heavy Metals
Resistance tests of Vibrio sp to heavy metals were
performed by determining the viability of Pb- and
Cd-resistant Vibrio sp. The CFU/ml of Vibrio sp
isolates treated with Pb (Table 1) showed constant
number at all concentrations, while the CFU/ml of
Vibrio sp isolates treated with Cd showed certain
decline at concentration of 5 ppm, 10 ppm and 25
ppm (Table 1).
Isolates of Vibrio sp from milkfish were able to
grow on Pb- and Cd- containing media with
concentration of 5 ppm, 10 ppm, and 25 ppm (Figure
1). According to Zulaika et.al (2012), bacteria
isolated from heavy metals-contaminated
environment were resistant to surrounding heavy
metals.
Figure 1: Result of inoculation of Vibrio sp to Pb and Cd
with concentration of 5 ppm (a), 10 ppm (b), 25 ppm (c).
Table 1: Result of resistance test of Vibrio sp to Pb and
Cd.
3.2 Antibiotic Sensitivity Test
Result of antibiotic sensitivity test shown in Figure 2
and Table 2 showed that Pb-resistant Vibrio sp was
resistant to Tetracycline 30 µg at all concentrations
of heavy metals and was resistant to
Chloramphenicol at Pb concentration of 10 ppm and
25 ppm. Meanwhile, Pb-resistant Vibrio sp was
susceptible to Chloramphenicol 30 µg at Pb
concentration of 5 ppm.
(c)
Figure 2: Result of antibiotic sensitivity test of Pb-
resistant Vibrio sp.
Concentrations
of heavy metals
Pb Cd
CFU/ml
5 ppm 13,55 x 10
6
30,0 x 10
6
10 ppm 13,3 x 10
6
16,55 x 10
6
25 ppm 13,7 x 10
6
12,2 x 10
6
(
a
)
(
b
)
(c)
(a) (b)
Resistance Test of Vibrio Sp from Milkish (Chanos chanos) in Fishpond Jabon Sidoarjo to Heavy Metals and Antibiotics
373
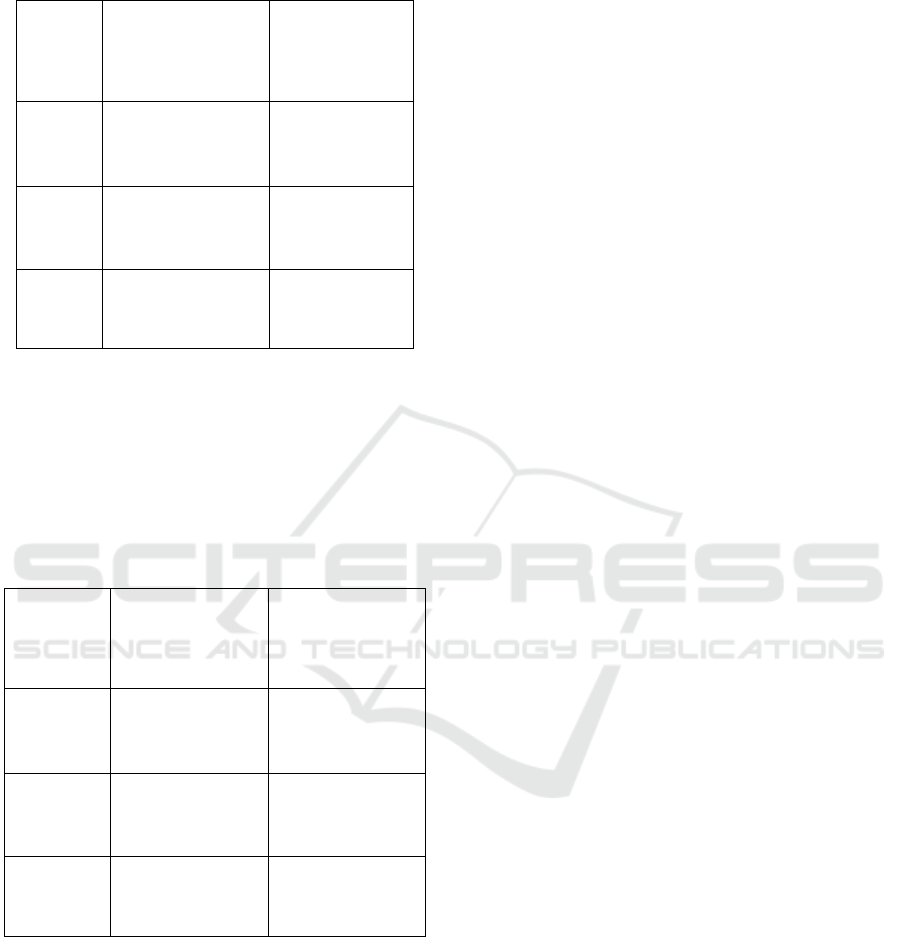
Table 2: Result of antibimicrobial resistance test of Pb-
resistant Vibrio sp.
Pb
Inhibition zone
diameter of
Tetracycline
30 µg
Inhibition zone
diameter of
Chloramphenico
l 30 µg
5 ppm
17 mm,
resistant
29 mm,
susceptible
10 ppm
18 mm,
resistant
16 mm,
resistant
25 ppm
16 mm,
resistant
15 mm,
resistant
Antibiotic sensitivity test of Cd-resistant Vibrio
sp to Tetracycline 30 µg and Chloramphenicol 30 µg
using Cd at concentration of 5 ppm, 10 ppm, and 25
ppm showed that Cd-resistant Vibrio sp was resistant
to Tetracycline 30 µg and Chloramphenicol 30 µg at
all concentrations of Cd (Table 3).
Table 3: Result of antibiotic sensitivity of Cd-resistant
Vibrio sp.
Cd
Inhibition zone
diameter of
Tetracycline
30 µg
Inhibition zone
diameter of
Chloramphenico
l 30 µg
5 ppm
6 mm,
resistant
17 mm,
susceptible
10 ppm
6 mm,
resistant
15 mm,
resistant
25 ppm
6 mm,
resistant
15 mm,
resistant
4 DISCUSSIONS
4.1 Resistance Test to Heavy Metals
Vibrio sp was able to grow in such condition by a
mechanism called biotransformation.
Biotransformation is a process of enzyme production
possessed by microorganisms through a chemical
alteration of pollutants in order to modify toxic
pollutants. This process will lead to biodegradation
process which is the ability of microorganisms to
cleave chemical structure of toxic pollutants into
noncomplex substances with low toxicity (Perdana,
2012). Biodegradation is classified into two types,
namely extracellular and intracellular. Extracellular
mechanism is the ability of bacteria to detoxify the
effect of heavy metals with the availability of
polyphosphate precipitates or by forming
nonspecific bond with extracellular polysaccharides
or natural polymers in the cell wall whereas
intracellular mechanism of heavy metals is
unactivated through precipitation by polyphosphate,
binding to Metallothionein (MT), and efflux system
(Jaroslawiecka and Seget, 2014).
4.2 Antibiotic Sensitivity Test
Based on the results above, Pb and Cd-resistant
Vibrio sp were all resistant to Tetracycline 30 µg,
shown by inhibition zone diameters less than 18
mm. According to Byarugaba (2009) resistance can
naturally occur because microorganisms are not
easily affected by antibiotics. This statement was
supported by Johnson et.al (2011) stating that
mechanisms of antimicrobial are classified into two,
namely nongenetic mechanism caused by loss of
specific targeted structures and genetic mechanism
caused by chromosomal/ extrachromosomal
resistance in bacteria.
In addition to Tetracycline, chloramphenicol 30
µg was also used for antibiotic sensitivity test. Based
on the results above, it was found that Pb-resistant
Vibrio sp was resistant to Chloramphenicol at
concentration of 10 and 25 ppm and was resistant to
Cd at all concentrations, shown by inhibiton zone
diameters less than 19 mm. In contrast, Pb-resistant
Vibrio sp was susceptible to Chloramphenicol at
concentration of 5 ppm, shown by inhibition zone
diameters more than 19 mm. This was caused by the
wide-spectrum ability of antibiotics to effectively
inhibit growth of gram-negative bacteria by blocking
the activity of enzyme peptidyl transferase. This
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
374

enzyme plays a role in the process of forming
peptide bonds between new amino acids attached to
tRNA and the last amino acids which are still
developing in the bacteria. As the result, protein
synthesis in bacteria will be completely interrupted
(Pratiwi, 2008).
Gram-negative bacteria are more resistant to
drugs compared to gram-positive bacteria due to
efflux system possessed by gram-negative bacteria.
This system allows accumulated drugs inside cells to
be carried out, enabling drug concentration to be
reduced. The antibiotic sensitivity test showed that
bacteria can modify themselves to reduce effectivity
of certain drugs. As the result, the bacteria can
survive living and reproduce themselves to be more
endangering (Dwyana and Fahruddin, 2012).
5 CONCLUSIONS AND
SUGGESTIONS
5.1 Conclusions
According to study above, it could be concluded
that:
1. Vibrio sp was resistant to heavy metals such as
Pb and Cd at concentration of 5 ppm, 10 ppm,
and 25 ppm, suggesting that the bacteria could
survive living in the water regardless the
availability of Pb dan Cd.
2. Antibiotic sensitivity test showed that Pb-
resistant Vibrio sp was resistant to Tetracycline
30 µg at all concentrations but susceptible only
to Chloramphenicol 30 µg at concentration of 5
ppm. Antibiotic sensitivity test showed that Cd-
resistant Vibrio sp was resistant to Tetracycline
30 µg and Chloramphenicol 30 µg at all
concentrations.
5.2 Suggestions
1. Society should not excessively consume milkfish
due to side effect of heavy metals contained in
water where it lives and due to bacteria in it
which are resistant to heavy metals.
2. We suggest that the next researchers perform a
study using Pb and Cd with higher concentration
and do resistance test using different strains of
bacteria, heavy metals, and antibiotics.
REFERENCES
Ayu, Dwi R., 2013. Isolasi dan Uji Resistensi Antibiotik
Bakteri Resitensi Merkuri (Hg) dari Kawasan Pantai
Losari Makassar. http://repository.unhas.ac.id/.
Badan Pengawas Obat dan Makanan Republik Indonesia.,
2015. Tetrasiklin. http://pionas.pom.go.id/ioni/bab-5-
infeksi/51-antibakteri/513-tetrasiklin.
Byarugaba, Denis K., 2009. Mechanisms of Antibiotic
sensitivity. www.springer.com.
Dwyana S. and Fahruddin., 2012. Isolasi dan Uji
Resistesni Antibiotik Bakteri Resistensi Merkuri (Hg)
dari Kawasan Pantai Losari Makassar.
http://repository.unhas.ac.id
Jaroslawiecka, Anna and Seget, Zofia Piotrowska., 2014.
Lead Resistance In Micro-organisms. Microbiology.
160, 12-25.
Johnson, G., et.al,. 2011. Mikrobiologi dan Imunologi.
Binarupa Aksara. Pamulang-Tangerang Selatan. Edisi
ke 5
Kholidiyah, Noviana., 2010. Respon Biologis Tumbuhan
Eceng Gondok (Eichhornia Crassipes Solms) Sebagai
Biomonitoring Pencemaran Logam Berat Cadmium
(Cd) Dan Plumbum (Pb) Pada Sungai Pembuangan
Lumpur Lapindo, Kecamatan Porong, Kabupaten
Sidoarjo. Fakultas Sains dan Teknologi. Universitas
Islam Negeri (Uin) Maulana Malik Ibrahim Malang.
Skripsi.
Larasati, U., 2015. Analisa Kadar Timbal Pada Ikan
Bandeng (Chanos chanos) yang Dibudidayakan di
Tambak Kalisogo Sidoarjo Setelah Perebusan
Menggunakan Belimbing Wuluh (Averrhoa bilimbi).
Jurusan Analis Kesehatan. Politeknik Kementrian
Kesehatan Surabaya. Karya Tulis Ilmia.
Nuhman., 2003. Kandungan Kadmium pada Udang Windu
(Penaeus monodon) Hasil Budidaya Secara Intensif
dan Tradisional. Majalah Ilmiah Kelautan: Neptunus,
Universitas Hang Tua Surabaya, Vol. 1. No. 1.
Perdana, Jeremia., 2012. Uji Resistensi dan Uji
Biodegradasi Logam berat (Pb,Zn, dan Hg) Oleh Isolat
Bakteri Lumpur Pantai Kenjeran. Faklutas Sains dan
Teknologi. Universitas Airlangga Surabaya. Skripsi.
Simangunsong., 2015. Uji Resistensi Bakteri
Pseudomonas Sp yang Di Isolasi dari Plak Gigi
Terhadap Merkuri dan Tetrasiklin. Vol. 3. No. 2.
Sintala, Arsyad, and Rustiadi, Ernan., 2008. Penyelamatan
Tanah, Air, dan lingkungan. Crestpent Press. Bogor.
Uddin, Mohammad Nasir., 2016. Simultaneous
Determination Of Amoxicillin And Chloramphenicol
And Their Drug Interaction Study By The Validated
UPLC Method. Jurnal of Taibah University for
science. 10 (755-765).
Utomo, Trisno., 2010. Ikan sebagai Pangan (3): Waspadai
Bakteri Patogen.
http://www.kompasiana.com/lhapiye/ikan-sebagai-
pangan-3-waspadai-bakteri
patogen_57468de17293733b1caa3c9a.
Zulaika, Enny., et.al., 2012. Bakteri Resisten Logam Berat
yang Berpotensi Sebagai Biosorben dan
Bioakumulator. ISBN 978-602-95595-4-5.
Resistance Test of Vibrio Sp from Milkish (Chanos chanos) in Fishpond Jabon Sidoarjo to Heavy Metals and Antibiotics
375
