
Analysis the Effect of Third Party Funds, Non Performing Financing,
Capital Adequacy Ratio, and Bank Indonesia Sharia Certificates
toward Financing
Case Studies of Indonesia Islamic Banking Period 2010-2015
Novelinda Nurul Firdaus, Sri Iswati, and Amalia Rizki
Universitas Airlangga, Jl. Airlangga 4 Surabaya, Indonesia 60285
Keywords: Financing, DPK, NPF, CAR, SBIS, Islamic Bank
Abstract: This study aims to determine the effect of Third Party Funds, Non Performing Financing, Capital Adequacy
Ratio, and Bank Indonesia Sharia Certificates towards financing. The population and also the sample used
was the entire Islamic Bank in Indonesia that was established in 2010-2015. The type of data in this research
was a quantitative that uses secondary data derived from financial statements published by Bank Indonesia.
The analytical method used is pooled data regression analysis with a significance level of 5%. This research
used financing as dependent variable and Third Party Funds (DPK), Non Performing Financing (NPF),
Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR), and Bank Indonesia Sharia Certificates (SBIS) as independent variables.
Based on the research that has been done, it was found that Third Party Funds has significant positive effect.
Non Performing Ratio has a negative and insignificant. Capital Adequacy Ratio has insignificant negative
effect. While Bank Indonesia Sharia Certificates has significant negative effect towards financing of Islamic
Banks in Indonesia.
1 INTRODUCTION
Islamic Bank is an institution that acts as an
intermediary for financial services (financial
intermediary), has the main task to collect funds
from the public and then distribute it back to the
community in the form of financing. The
fundamental difference between the Islamic Bank
and conventional bank are Islamic bank conducts its
business activities are not based on the interest
(interest fee), but based on profit and loss sharing
principle. This makes Islamic banks need to be able
to survive and not be liquidated during the monetary
crisis that occurred in 1998. The Islamic bank is not
obliged to pay interest on deposits to its customers.
Islamic banks only pay for results in accordance
with profits earned from the investment bank does.
Islamic banks get more adequate legal base after
the deregulation of the banking sector, Act 10 of
1998 in lieu of Law No. 7 of 1992 which is refined
into Law No. 21 of 2008 concerning Islamic banking
regulate in detail the legal basis and the types of
businesses that can be operated and implemented by
Islamic Bank. The law also addresses the dual
banking system, which means providing the
opportunity for conventional commercial banks to
open branch offices to conduct banking operations
based on Islamic principles.
One key to the success of the bank's management
is how to serve the best their excess money and save
money in the form of demand deposits, time deposits
and savings, as well as serving the needs of the
community through the provision of credit money
(Noneng, 2009). Financing is an indicator for
measuring progress or growth in market share of
Islamic banking. One of the main activities and
become a major revenue source for a bank through
the activity distribution of financing, but the greatest
risk in the bank is also sourced from loans.
Therefore, a bank must have a good credit
management and should also studied factors that
influence the magnitude of the amount of financing
provided to the public by a financial institution of
Islamic banking.
Third Party Funds (DPK) are sources of funds of
a bank originating from the public in the form of
demand deposits, deposits and savings deposits.
According to Dendawijaya (2005: 49), funds
Nurul Firdaus, N., Iswati, S. and Rizki, A.
Analysis the Effect of Third Party Funds, Non Performing Financing, Capital Adequacy Ratio, and Bank Indonesia Sharia Certificates toward Financing.
DOI: 10.5220/0007540102010209
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School (ICPS 2018), pages 201-209
ISBN: 978-989-758-348-3
Copyright
c
2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
201

collected from the community are the largest source
of funds most relied on by banks that can reach 80%
-90% of all funds managed by banks. This DPK is
then used to encourage economic growth through
credit distribution.
The results of Maula's (2008) study stated that
third party fund deposits had a negative and
significant effect on murabahah financing. Different
results were found by Francisca (2008) where DPK
had a positive and significant effect on lending.
Further research that obtained similar results was
also found by Khatimah (2009), Pratama (2010), and
Andraeny (2011) who concluded that Third Party
Funds had a positive and significant effect on
financing volume.
Non Performing Financing (NPF) is a ratio used
to measure a bank's ability to cover the risk of
failure to repay a loan by a debtor (Darmawan,
2004). The higher the NPF level, the greater the
credit risk borne by the bank (Ali, 2004). The high
NPF results in banks having to provide greater
reserves, so that ultimately the bank's capital will be
eroded. Though the amount of capital greatly
influences the size of credit expansion.
Through Maula's research (2008), concluded that
NPF had a negative and significant influence on
financing channeled by Islamic banking in
Indonesia. Similar results were found by
Nurapriyani (2009) and Pratama (2010) which
obtained negative and significant results. However,
different results were found by Andraeny (2011),
Khatimah (2009), and Francisca (2008) which
obtained insignificant results.
Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) is a ratio that
shows the ability of banks to provide funds for
business development needs and accommodate the
risk of loss of funds caused by bank operations (Ali,
2004). One of the main activities in bank operations
that contain or generate risk is the distribution of
funds in the form of credit. CAR will increase
banking confidence in channeling credit. With CAR
above 20%, it will increase bank credit growth by
20-25% per year (Wibowo, 2009).
Noneng (2009), stated that CAR has a positive
and significant influence on credit given to Bank
Permata. While Pratama (2011), concluded that
CAR has a negative and significant influence. The
different thing that was discovered by Francisca
(2008) that received a positive result was not
significant towards lending.
Other variables considered to have an effect on
financing distribution are Bank Indonesia Sharia
Certificates (SBIS). SBIS is one of the Indonesian
bank monetary instruments intended for Islamic
banks in Indonesia with the aim of being a place of
excess liquidity. Funds placed by banks in the SBIS
will reduce the credit disbursed. The higher the SBIS
fund is placed, the amount of financing disbursed
will decrease.
Nurapriyani's research (2009) concluded that
SBIS partially has a significant negative influence
on financing. Different results were found by
Khatimah who received no significant positive
results.
The difference between the results of previous
research that has been described above, is interesting
to be tested again which can be used as a problem in
this study. Based on the above, the formulation of
the research problems is:
1. Does Third Party Funds have an effect on the
distribution of financing?
2. Does Non Performing Financing have an effect
on the distribution of financing?
3. Does Capital Adequacy Ratio have an effect on
the distribution of financing?
4. Does Bank Indonesia Sharia Certificates have an
effect on the distribution of financing?
The purpose of this study was to examine the
influence of Third Party Funds, Non Performing
Financing, Capital Adequacy Ratio and Bank
Indonesia Sharia Certificates to the distribution of
financing.
2 LITERATURE
2.1 Islamic Bank
Islamic bank is a bank that operates without relying
on interest. Bank Islam or commonly called the bank
without interest, is a financial institution / bank
operations and products are developed based on the
Qur'an and the Hadith of the Prophet SAW. It
concluded that Islamic Bank is the main business of
financial institutions that provide financing and
other services in payment traffic and circulation of
money that its operation adapted to the principles of
Islamic law (Muhammad, 2004:1).
2.2 Financing
Financing is one of the bank's main task, namely
providing facilities for provision of funds to meet
the needs of those who are deficit units (Antonio,
2001: 160). Definition of financing widely according
to Muhammad (2002: 260), means financing or
expenditure is the funding that issued to support the
planned investment, either by themselves or run by
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
202

someone else. In a narrow sense, the financing used
to define the funding committed by financial
institutions, such as Islamic banks to customers.
Furthermore, in the regulation of Islamic bank,
Islamic Banking Act No. 21 of 2008, stated the
definition of financing is the provision of funds or
bill equivalent to the form:
1. Profit and Loss sharing transaction in the form of
mudharabah and musyarakah;
2. Leasing transaction in the form of Ijarah or lease
purchase in the form of Ijarah muntahiya
bittamlik;
3. Sale and purchase transaction in the form of
murabahah, salam, and istishna’;
4. Borrowing transaction in the form of receivables
qardh; and
5. Lease services transaction in the form of Ijarah
for multiservice transaction;
2.3 Third Party Funds
Third party funds are usually more familiar with
public funds, the funds raised by banks from the
public in the broadest sense, encompassing
individual communities, and business entities. Bank
offers deposit products to the public in raising funds
(Ismail, 2010: 43). According Dendawijaya (2005:
49), the funds collected from the community is the
largest funding source of the most reliable bank that
can reach 80% -90% of all funds managed by the
bank. Banks do not give a reward in the form of
interest on funds deposited by customers in the bank.
The payoff is given on the basis of the principle of
sharing (Budisantoso and Triandaru, 2006).
2.4 Non Performing Financing
Non performing financing is a condition in which
the customer is no longer able to pay part or all
liabilities to banks as it has been agreed (Kuncoro
and Suhardjono, 2002: 462). NPF ratio reflects the
bank's ability to cover risks of failure of loan
repayment by the debtor (Darmawan, 2004). If not
handled properly, then the problem of financing is a
source of potential losses for banks. Therefore, we
need a systematic and sustainable handling
(Mahmoeddin, 2004: 5). NPF is very influential in
controlling costs and at the same time also affects
the financing policies that would do the bank itself.
NPF can bring adverse impact, especially if the NPF
in large quantities. By looking at previous NPF (t-1),
the bank may consider how much funding will be
distributed now.
2.5 Capital Adequacy Ratio
The capital adequacy ratio (CAR) is a measure of a
bank's capital. It is expressed as a percentage of a
bank's risk weighted credit exposures. The level of
capital adequacy can be measured by comparing the
capital with third-party funds and capital compared
with risk assets (Arifin, 2009: 162).
2.6 Bank Indonesia Sharia Certificates
In order for the implementation of open market
operations can be run properly, it is necessary to
create a device controlling the money supply in
accordance with the principles of Sharia in the form
of Bank Indonesia Sharia Certificates (SBIS). The
device can be used as a short-term fund deposits,
especially for banks that have excess liquidity.
Islamic banks that have idle funds, can invest their
funds in these instruments. Bonuses obtained and the
absence of risk factors, SBIS attractive for Islamic
banking compared channeled through financing
(Nurapriyani, 2009).
2.7 Effect of Third Party Fund (DPK)
on the distribution of Financing
Collection and distribution of funds is the main
focus of activities of Islamic banks. Therefore, in
order to optimally distribute the funds, the bank
must have the ability to raise funds for Third Party
Fund (DPK). Because it is the major source of
Islamic bank financing. Deposits or Third Party
Fund (DPK) is the funds raised by banks from the
public, both individuals and business entities that
obtained by using various instruments deposit
products such as wadiah current accounts, wadiah
saving accounts, mudharabah saving accounts, and
mudharabah deposits accounts.
Once the funds have been collected by a third
party bank, then according to his function then the
intermediary bank is obliged to distribute these
funds back to communities in need, namely in the
form of loans or can be referred to as financing
(Kasmir, 2008). Funds that have been collected from
the community is the largest funding source of the
most reliable by banks and have a strong influence
on the financing (Dendawijaya, 2008).
Francisca (2008), stating that the higher DPK
will increase financing expansion in the banking
system. Similarly, Khatimah (2009), Nurapriyani
(2009), Pratama (2010), and Andraeny (2011) which
state that the higher third party funds that have been
Analysis the Effect of Third Party Funds, Non Performing Financing, Capital Adequacy Ratio, and Bank Indonesia Sharia Certificates
toward Financing
203
collected by the banks, will encourage an increase in
the amount of financing that can be distributed.
H1: Third Party Fund (DPK) Variable has a positive
effect on the distribution of financing.
2.8 Effect of Non Performing
Financing (NPF) on the distribution
of Financing
Non Performing Financing (NPF) is the ratio
between the amount of financing that is troubled by
the total amount of financing. The ratio is used to
measure the bank's ability to cover risks of failure of
loan repayment by the debtor (Darmawan, 2004).
NPF reflect the credit risk, the higher the level of
NPF, the greater the credit risk borne by the bank
(Ali, 2004). NPF height is strongly influenced by the
bank's ability to execute with good credit granting
process and in terms of credit management,
including monitoring measures after the loans were
disbursed and control measures when there are
indications of irregularities or indications of
defaulted loans.
Nurapriyani (2009) states that high
non-performing financing will result in a decreased
level of profit sharing distributed to owners of funds
and losses due to non-receipt of returned funds have
been disbursed. The higher NPF then the worse the
quality of bank assets that will affect the cost and
capital of the bank. Due to the high NPF make the
bank has the obligation and have to incur costs to
meet the PPAP (Allowance for Earning Assets) were
taken from the bank's capital itself. Though the
amount of capital greatly affects the amount of
credit expansion.
H2: Non Performing Financing (NPF) Variable has a
negative effect on the distribution of financing.
2.9 Effect of Capital Adequacy Ratio
(CAR) on the distribution of
Financing
The quality of the bank refinancing operations can
be measured quantitatively by using financial ratios,
one of the ratio is the Capital Adequacy Ratio
(CAR). CAR is an analytical tool used to determine
how much capital is sufficient to support its
operations and reserves to absorb losses that might
occur (Kuncoro and Suhardjono, 2002: 562). The
higher CAR, the greater the financial resources that
can be used for business development and anticipate
potential losses caused by the operations of the bank,
one of which is financing (Ali, 2004).
H3: Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) Variable has
positive effect on the distribution of financing.
2.10 Effect of Bank Indonesia Sharia
Certificates (SBIS) on the
distribution Financing
Use of SBIS addition to being a tool for controlling
the money supply is also used as a short-term care
facility, especially for banks that have excess
liquidity fund. SBIS issued and administered without
paper (script less) and cannot be traded
(non-negotiable). Although the advantage given of
SBIS just a bonus, but at a certain moment SBIS
attractive for Islamic banking to invest their funds in
these instruments compared channeled through
financing due to various factors, including risk
factors (Nurapriyani, 2009).
Results of Nurapriyani study (2009) revealed that
SBIS has a significant negative effect on the
financing. If the SBIS bonus increases, the banks
will be interested to invest their funds in SBIS
makes decreasing the amount of financing. It
concluded that SBIS negatively affect financing. If
the larger funds allocated for SBIS, then the amount
of resources that can be channeled by Islamic
banking will be reduced.
H4: Bank Indonesia Sharia Certificates (SBIS)
Variable has a negative effect on the distribution of
financing.
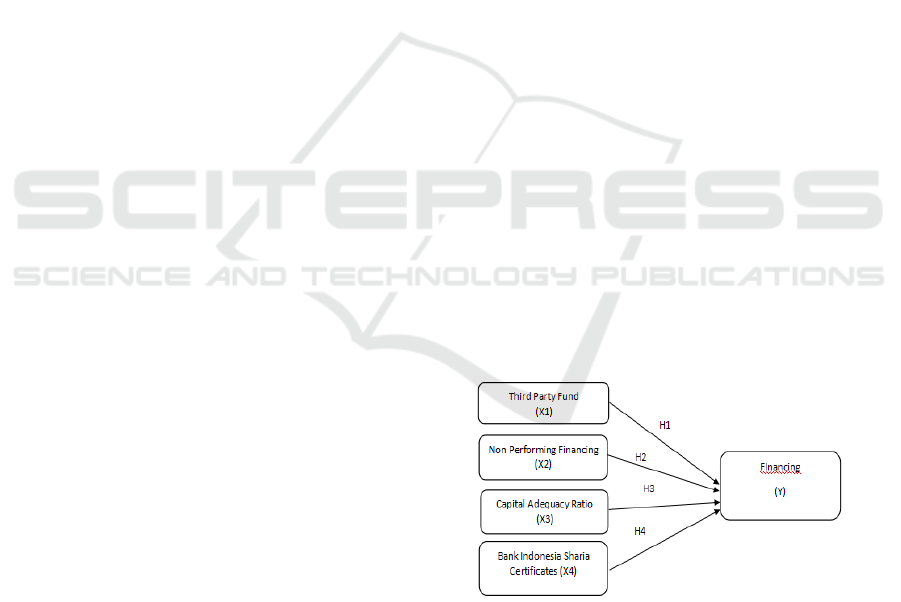
2.11 Research Model
Research Model shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Research Model.
3 RESEARCH METHODS
Variables used in this analysis can be divided into
two, namely dependent variable and the independent
variable. Dependent variable on this research is
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
204

financing denoted by Y, while the independent
variables and its notation consist of:
1. Third Party Funds (DPK)
2. Non Performing Financing (NPF)
3. Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR)
4. Bank Indonesia Sharia Certificates (SBIS)
3.1 Operational Definition
The operational definition of each variable used in
this study is as follows:
1. Financing is the distribution of funds by Islamic
banks with the principle of profit sharing which
consists of financing the form of mudharabah
and musyarakah, the principle of sale and
purchase which consists of financing the
murabahah, salam, and istishna 'contracts,
financing under the lease principle (ijarah), the
principle of social loans in the form of qardh
receivables, and financing with complementary
contracts. The data used is the total amount of
financing channeled by Islamic banking in
Indonesia which is stated in units of millions of
Rupiah.
2. Third Party Funds (DPK) are defined as funds
collected by banks originating from the
community based on Akad wadi'ah or other
contracts that do not conflict with Sharia
Principles in the form of wadi'ah current
account, wadi'ah savings, mudaraba savings, and
deposits mudharabah which is stated in units of
millions of Rupiah.
3. Non Performing Financing (NPF) is defined as
the ratio between the amount of financing that is
problematic which is classified as substandard,
doubtful, and loss with the total amount of
financing based on Bank Indonesia regulations.
The data used is annual calculation data which is
expressed in percent.
4. Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) is defined as the
amount of bank capital that indicates the bank's
ability to provide funds to support its operational
activities and reserves to cover the risk of
possible losses. The data used is expressed in
percent.
5. Bank Indonesia Sharia Certificate (SBIS) is
defined as a monetary instrument that is used in
controlling the money supply to be used as a
short-term safekeeping facility, especially for
banks that experience excess liquidity funds
stated in millions of Rupiah.
3.2 Population and Sample
The population used in this study are all the Islamic
Banks registered in Indonesia from the period of
2010 to 2015. The total amount of population and
sample at the same time are 11 Islamic Banks.
3.3 Data Analysis Technique
3.3.1 Panel Data Regression Methods
This study uses pooled data regression analysis
techniques. Pooled data is a combination of time
series and cross section data. The number of
observations will increase significantly without any
treatment of the data.
According Widarjono (2007: 251), there are
three approaches in the data panel, the Pool Least
Square (PLS) or called Common Effect, Fixed
Effect (FE), and Random Effects (RE). Firstly, Pool
Least Square (PLS) estimating pooled data just by
combining data time series and cross section
regardless of differences over time and individuals.
Second, the approach Fixed Effect (FE), assumes
that considers the behavior of an individual or a
different cross section in the same period, or it can
be said to have a different intercept but the slope
fixed (constant). Fixed Effect model technique
estimating panel data using dummy variables to
account for differences in the intercept (Widarjono,
2007: 253). Thirdly, the approach Random Effect
(RE) estimating pooled data where disturbance
variables may be interconnected across time and
between individuals.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Chow test (F Test)
The first test was conducted in this study is the
Chow test or F test to choose the best model among
the models Pooled Least Square (PLS) or Fixed
Effect Model (FEM). The Following hypothesis of
this test are:
Ho: The model used is the Pooled Least
Square (PLS)
H1: The model used is the Fixed Effects
Model
Analysis the Effect of Third Party Funds, Non Performing Financing, Capital Adequacy Ratio, and Bank Indonesia Sharia Certificates
toward Financing
205
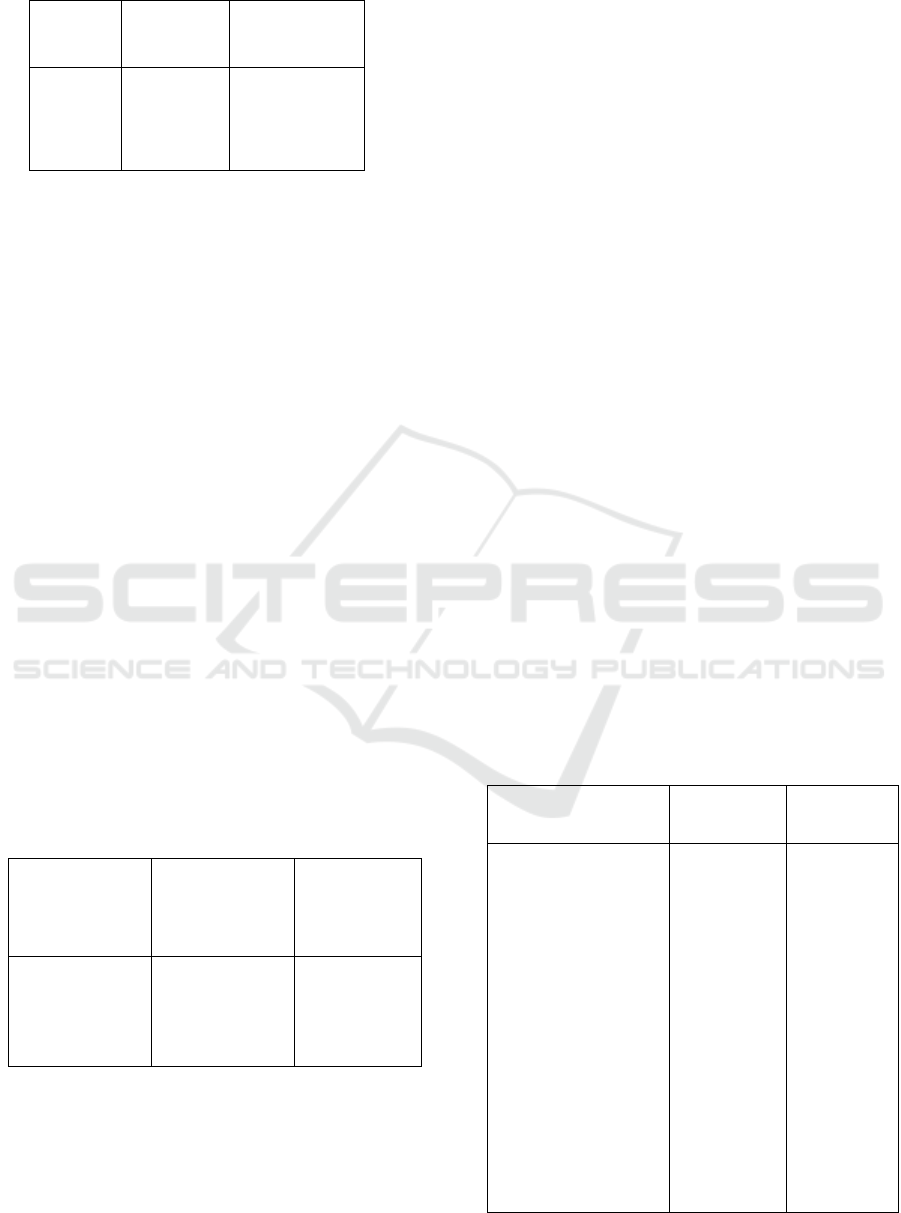
Table 2: Model Selection between PLS and FEM.
Source: Test Result with Eviews
Based on Table 2 shows that the value of F
count> F table, so that Ho refused and accept H1,
which means with the degree of confidence (α =
5%), the technique of estimation model chosen is a
method Fixed Effect Model (FEM).
4.2 Hausman Test
The next test is the test of Hausman Test to
determine the best model between the Fixed Effects
Model (FEM) or Random Effect Model (REM). The
Following hypothesis of this test are:
Ho: The model used is the Random Effect
Model
H
1:
The model used is the Fixed Effect Model
The results of the calculations in this study
resulted Chi-Square statistic value at 1.023846 and
Chi-Square table value of 0.9062. Chi-square
statistic value is greater than the value of Chi-Square
table, then the hypothesis Ho is rejected and accept
H1, which means that the model selection Fixed
Effect Model (FEM) is more appropriate when
compared with Random Effects Model (REM) in
this study.
Table 3: Model Selection between FEM and REM.
Chi-Square
table (α=5%)
Chi-Square
statistic
Estimation
Model
Selected
0.9062 1.023846 Fixed Effect
Model
(FEM)
Source: Test Result with Eviews
4.3 The Determination Coefficient (R2)
The regression analysis of pooled data in this study
obtained the coefficient of determination (R2),
which demonstrates the ability of all the independent
variables are jointly able to explain further variation
of the dependent variable changes. The results of
processing the data obtained by the coefficient of
determination (R2) is 0.936229. This suggests that
the distribution of financing levels as the dependent
variable in this research model is 93.6229% can be
explained by the independent variable in the model
of research that third party funds, non-performing
financing, capital adequacy ratio, and Bank
Indonesia Sharia Certificates, while the rest
influenced by other variables outside the model in
the study amounted to 6.3771%.
4.4 F Test
F test conducted to prove the influence of
independent variables (independent) together on the
dependent variable (dependent). Based on the results
of test calculations obtained F statistic value
53.48125 while significance value of 0.000. It can be
concluded that with 95% of independent variables
DPK, NPF, CAR, and SBIS together significantly
influence the distribution of financing Islamic bank
in Indonesia 2010-2015.
4.5 T Test
Proof pooled data regression analysis partial to the
independent variable on the dependent variable with
a degree of confidence (α = 5%) in this study
through the partial coefficient t test can be seen at
the following table.
Table 4: Panel Data Regression T Test Results.
Independent
Variable
Prob
t-statistic
Significan
ce (α=5%)
Third Party Fund
(DPK)
Non Performing
Financing (NPF)
Capital Adequacy
Ratio (CAR)
Bank Indonesia
Sharia Certificates
(SBIS)
0.0000
0.6463
0.5257
0.0146
Significan
ce
(α=5%)
Insignifica
nce
(α=5%)
Insignifica
nce
(α=5%)
Significan
ce
(α=5%)
F
table
(α=5%)
F
statistic
Estimation
Model Selected
0.0000 14.376225 Fixed Effect
Model
(FEM)
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
206

Source: Test Result with Eviews
Based on Table 4 it can be seen that the DPK
variable and SBIS have a significant influence on
the distribution of ffinancing Islamic bank in
Indonesia 2010-2015. While the independent
variables consisting of NPF and CAR did not have a
significant effect on the distribution of ffinancing
Islamic bank in Indonesia period 2010-2015.
5 DISCUSSION
Based on the description of the calculation results of
the regression model of pooled data in this study
shows that the coefficient of determination (R2) is
equal to 0.936229 which means that the independent
variables consisting of DPK, NPF, CAR, and SBIS
in this study were able to describe and explain the
dependent variable that finance portfolio amounted
to 93.6229%, while the remaining amount of
6.3771% is explained by other variables outside the
model in this study. All of these variables together
have a significant effect on the dependent variable in
this study. Pooled data regression model obtained in
this study are:
Financing = 525362.7 + 0.340257DPK –
87076.36NPF – 6045.185CAR - 0.568229SBIS.
DPK as an independent variable has positive effect
on the dependent variable, each 1% increase in third
party funds it will raise the level of the finance
portfolio amounted to 34.0257%. Then every
increase of 1% NPF, CAR, and SBIS will reduce the
level of distribution of financing.
5.1 Effect of Third Party Fund (DPK) on
the Distribution of Financing
Regression analysis showed that the Third Party
Fund (DPK) variable has significantly affect the
amount of financing provided by the bank. It can be
seen from the significant value of the t test for 0000
is smaller than the error level (α) of 5% or 0:05. The
regression coefficient is positive in deposits
amounted to 0.340257. This shows that when the
value of regression coefficient other variables are
constant, the increase in deposits amounted to 1
rupiah will cause the number of Islamic banks from
financing increased by IDR 0.340257.
The positive regression coefficient indicates the
direction a unidirectional relationship. This means
that with the increase in deposits will cause an
increase in the funds owned by banks in order to
allocate the finance portfolio. DPK has significant
influence because of DPK is the biggest donor in the
Islamic banking financing activities. Most of the
sources of the funds raised by the Islamic banking
community allocated to financing.
The results support the previous research
Francisca (2008), Khatimah (2009), Pratama (2010)
and Andraeny (2011) which states that the greater
third party funds collected, the greater the volume of
financing that can be distributed. It is also consistent
with the theory that an increase in deposits would
affect the increasing number of financing disbursed.
The greater the number of third-party funds
collected, the greater the funds that can be allocated
by the Islamic banks to the real sector in the form of
financing. The result is consistent with research
conducted by Francisca (2008) which states that the
variable CAR cannot be used to predict the volume
of credit because of the partial test results showed no
significant relationship between these variables with
loan volume.
5.2 Effect of Non Performing Financing
(NPF) on the Distribution of
Financing
Based on the results of regression analysis showed
that in the Islamic banking firm, NPF variable does
not affect the amount of financing provided by the
bank. It can be seen from the significant value of t
test of 0.6463 which is greater than the standard
error (α) 0:05. The regression coefficient for NPF is
negative, the value is -87076.36 indicate when other
variables are constant, then the change NPF one unit
will cause a decrease in the amount of financing
disbursed IDR 87076.36.
NPF did not have a significant effect on the
financing, because NPF Islamic banks is relatively
small compared to conventional bank that is not a
major consideration in offering financing. The
results are consistent with research conducted by
Francisca (2008) which states that the variable NPL
(non-performing loans) cannot be used to predict the
volume of credit because of the partial test results
show a negative effect but not significant.
Analysis the Effect of Third Party Funds, Non Performing Financing, Capital Adequacy Ratio, and Bank Indonesia Sharia Certificates
toward Financing
207

5.3 Effect of Capital Adequacy Ratio
(CAR) on the Distribution of
Financing
Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) has a negative
influence on the amount of financing provided by
the bank. From the regression results, indicate that
when the variable CAR rose one unit, will lead to a
reduction disbursed IDR 6045.185, assuming all
other variables held constant. Negative regression
coefficient indicates the opposite direction of the
relationship. This means that an increase in CAR
result in reduced distribution of the financing
provided by Islamic banks.
CAR has no significant effect on the financing,
which means that the higher the CAR, the higher the
ability of bank capital to maintain the possibility of
losses from its business activities but did not
significantly affect the increased distribution of
Islamic bank financing.
5.4 Effect of Bank Indonesia Sharia
Certificates (SBIS) on the
Distribution of Financing
Based on the results of regression analysis showed
that the variables SBIS has a significant effect on the
amount of financing provided by the bank. It can be
seen from the significant value of t test of 0.0146
which is smaller than the error level (α) 0:05.
Variable SBIS have a negative regression coefficient
that is equal to -0.568229. If it is assumed bonus
SBIS rupiah rose by 1, then the loan amount will
decrease by 0.568229 rupiahs, if the value of the
regression coefficient other variables is constant.
Thus, variable direction SBIS has a negative
relationship to the number of Islamic banking
financing.
SBIS has a significant influence negatively on
the distribution of funding. The results support the
research Nurapriyani (2009) which states that if the
higher level of bonus SBIS resulting in increasing
the funds allocated for SBIS, then the amount of
resources that can be channeled by Islamic banking
will be reduced
.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the analysis and hypothesis testing that has
been done in previous chapters, some conclusions
can be drawn from this study are: DPK has a
positive effect, NPF has no effect, CAR has no
effect, SBIS has a negative effect on the distribution
of financing Islamic bank in Indonesia period
2010-2015.
REFERENCES
Ali, Mashud. 2004. Asset Liability Management :
Menyiasati Risiko Pasar dan Risiko Operasional.
Jakarta: PT. Gramedia.
Andraeny, Dita. 2011. Analisis Pengaruh Dana Pihak
Ketiga, Tingkat Bagi Hasil, dan Non Performing
Financing terhadap Volume Pembiayaan berbasis
Bagi Hasil pada Perbankan Syariah di Indonesia.
Jurnal Simposium Nasional Akuntansi XIV.
Antonio, Muhammad Syafi’i. 2001. Bank Syari’ah dari
Teori ke Praktik. Jakarta: Gema Insani.
Arifin, Zainul. 2009. Dasar-Dasar Manajemen Bank
Syariah. Jakarta: AlvaBet.
Budisantoso, Totok dan Triandaru, Sigit. 2006. Bank dan
Lembaga Keuangan Lain. Jakarta: Salemba empat.
Darmawan, Komang. 2004. Analisis Rasio-rasio Bank.
Info Bank, hlm 18-21.
Dendawijaya, Lukman. 2005. Manajemen Perbankan.
Jakarta: Ghalia Indonesia.
Francisca.2008. Pengaruh Faktor Internal Bank terhadap
Volume Kredit pada Bank yang Go Public di
Indonesia. Skripsi Universitas Sumatera Utara.
Ismail. 2010. Manajemen Perbankan: Dari Teori Menuju
Aplikasi. Jakarta: Prenada.
Kasmir. 2008. Bank dan Lembaga Keuangan Lainnya.
Jakarta: PT. Raja Grafindo Persada.
Khatimah. 2009. Analisis Faktor-faktor yang
mempengaruhi Penyaluran Dana Perbankan Syariah
di Indonesia Sebelum dan Sesudah Kebijakan
Akselerasi Perbankan Syariah Tahun 2007/2008.
Jurnal Optimal Vol.3, No.1. Maret 2009
Kuncoro, Mudrajad dan Suhardjono. 2002. Manajemen
Perbankan Teori dan Aplikasi Edisi Pertama.
Yogyakarta: BPFE.
Mahmoeddin, As. 2004. Melacak Kredit Bermasalah.
Jakarta: Pustaka Sinar Harapan.
Maula, Khodijah Hadiyyatul. 2008. Pengaruh Simpanan
(Dana Pihak Ketiga), Modal Sendiri, Margin
Keuntungan, dan Non Performing Financing terhadap
Pembiayaan Murabahah pada Bank Syariah Mandiri.
Skripsi Universitas Islam Negeri Sunan Kalijaga
Yogyakarta.
Muhammad. 2011. Manajemen Bank Syari’ah.
Yogyakarta: UPP STIM YKPN.
Muhammad. 2004. Manajemen Dana Bank Syariah.
Yogyakarta: Ekonisia.
Noneng. 2009. Analisis Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR)
dan Return On Assets (ROA) Pengaruhnya terhadap
Kredit yang diberikan Studi Kasus Pada PT Bank
Permata TBK yang Terdaftar di BEI. Jurnal
Universitas Komputer Indonesia.
Nurapriyani, Dwi. 2009. Faktor-faktor yang
Mempengaruhi Pembiayaan Murabahah di Bank
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
208

Syariah Mandiri Periode Tahun 2004-2007. Skripsi
Universitas Negeri Sunan Kalijaga Yogyakarta.
Pratama, Billy Arma. 2010. Analisis Faktor-faktor yang
Mempengaruhi Kebijakan Penyaluran Kredit
Perbankan. Semarang
Analysis the Effect of Third Party Funds, Non Performing Financing, Capital Adequacy Ratio, and Bank Indonesia Sharia Certificates
toward Financing
209
