
Experimental Research on Effect of CNC Machining Parameters on
Surface Roughness of Workpieces
Chang guo Lu
1
Jing bo Wang
1
,
*
1
Yingkou Institute of Technology
,
Bowen Road,Yingkou, China
Keywords: The surface roughness, CNC machining, the amount of cutting.
Abstract: The surface roughness of a mechanical part is one of the accuracy of parts processing. A Cutting parameter
in CNC machining is a important factor that would affect the surface roughness of parts. From an
experimental point of view, the writers have studied the influence of the cutting amount on the surface
roughness in CNC machining, and the result could be used to guide the machining.
1 INTRODUCTION
The term surface roughness refers to the smaller
pitch of the machined surface and the unevenness
between peaks and valleys. The lower the surface
roughness is, the smoother the surface is. The
surface roughness of a part is a parameter that
characterizes the micro-geometry of the part surface,
to measure the accuracy of the part surface.
According to GB/T 1031-2009"Surface Structure
Profile Method Surface Roughness Parameters and
Its Value", the arithmetic average deviation Ra and
the contour maximum height Rz are used as the
evaluation parameters in the sampling length. When
used, the part’ surface roughness will affect its wear
resistance, fatigue strength, corrosion resistance and
tolerances and fits and so on.
In the cutting process, the surface roughness of
the workpiece will be affected by a lot of factors,
such as cutting amount, tool geometric parameters,
workpiece material, cutting fluid, vibration during
cutting, formation of built-up edge or not, and so on.
In the numerical control machining process, some
influence factors are fixed relatively, such as the
workpiece material, cutting fluid, vibration and
built-up edge. The others are need to be selected
according to different processing conditions, such as
and the cutting amount and tool geometric
parameters etc. The standard tools are used in CNC
machining. When a certain tool type is selected, the
geometric parameters are also determined. So as to
the actual cutting parameters,then there is only one
is actually to be selected,that is the cutting amount
in the actual machining process.
The cutting amount includes the cutting speed
vc,the back engagement of the cutting edge ap, and
the feed amount f and so on. When increasing one of
them , the cutting efficiency will be more and
influence by the tool condition and the machine tool
performance. Because changing the cutting amount
parameters will affect the quality of the part
machining surface, so it is more important for us to
study the relationship between the cutting
parameters and the surface roughness of the
workpiece for ensuring the quality of the NC
machining while improving the cutting efficiency.
2THE THEORETICAL CAUSE OF
SURFACE ROUGHNESS
The term theoretical roughness is the tool surface
geometry and the workpiece surface roughness
caused by cutting motion. That is residual areas
formed between the contours of the adjacent tool
paths due to the geometry of the tool during
machining. Here,we take turning processing as an
example as shown in Figure 1.
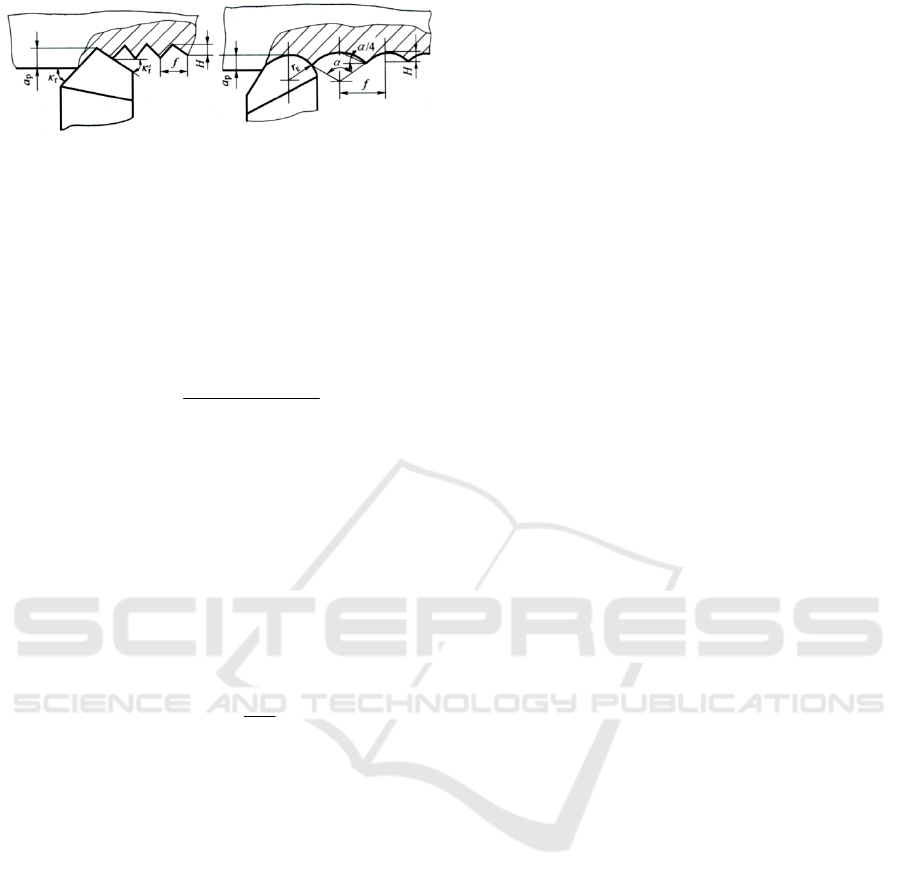
(a) (b)
Figure 1 Surface area remaining on turning workpiece.
The value of surface roughness in cutting process
is mainly based on the height of the cutting residual
area. When tools with corner radius
r
=0, the height
of the workpiece surface remained (Referring to
Figure 1a).
rr
f
H
cotcot
(1)
Where
f
- Feed amount (mm/r);
r
- Lead angle (≠90°);
r
'
- Deflection angle (≠90°).
When tools with corner radius
r
≠0, the height
of the workpiece surface remained (Referring to
Figure 1b).
r
f
H
8
2
(2)
Based on the above equations (1) and (2) ,the
height of the residual area can be reduced by
decreasing
f
、
r
、
r
'
orincreasing
r
.
Certainly, the microscopic geometric
deformation generated on the workpiece surface is
more than the theoretical roughness in the actual
cutting process, because of the friction between the
tool and the workpiece surface, the plastic
deformation of the workpiece surface, and the high
frequency vibration in the process system.
3THE ESTABLISHMENT OF AN
EXPERIMENTAL MODEL
It is long for theoretical and experimental research
on the influence of the three factors of cutting
amount on the roughness of the workpiece surface. It
is shown that the amount of feed has a significant
effect on the value of the surface roughness by a lot
of studies and the Long-term production. That is the
value of the surface roughness will increase after the
feed increases. And the effect of cutting speed on the
surface roughness of the workpiece is related to the
formation of built-up edge in the cutting process.
When cutting plastic material in the medium-speed
(vc =20-40m/min),the built-up edge is easy to be
formed, then the surface roughness value of the
workpiece increases;While in low-speed or high-
speed, it is not and the roughness value of workpiece
surface is less ;The effect of the amount of the
back engagement of the cutting edge on the
workpiece surface roughness is not very obvious. Of
course, the results are based on ordinary metal
cutting process. CNC cutting machining is similar to
it, but it still has some specific features. Here, the
actual conditions of modern CNC cutting processing
is be used to determine the corresponding
experimental methods and parameters in the paper.
We intend to machine the workpiece with CNC
machining and CNC milling separately, then
measure the value of the surface roughness of the
workpiece, and finally analyze the measurement data
and results from them in this experiment. Based on
the actual production habits, the parameters are set
as follows:
①CNC turning: Specimenφ18×40,Q235; 93
degree turning tool ; ap(mm)0.1,0.2,0.5,1.0 ;
f(mm/r)0.05,0.08,0.10,0.12,0.20 ;
n(r/min)500,800,1000,1200;
② CNC milling: Specimen 64×16 , Q235 ;
φ80End mill,φ20、φ16、φ10 End mill,R5Ball
end mill;ap(mm)0.1,0.2,0.3,0.5,1.0,2.0;
F(mm/min)50 , 100 , 200 , 300 ; n(r/min)500 ,
800,1000,1200
,1800,2000.
4THE EXPERIMENTAL DATA
After machining, wetested specimen in the way of
contour contact measurement using a 2205 Surface
Roughness Gauge. The data are listed in Table 1 and
Table 2 (Excerpts) respectively. The 2205 Surface
Roughness Gauge can measure multiple surface
roughness parameters. This experimental is only
based on the most widely used contour arithmetic
average deviation Ra.
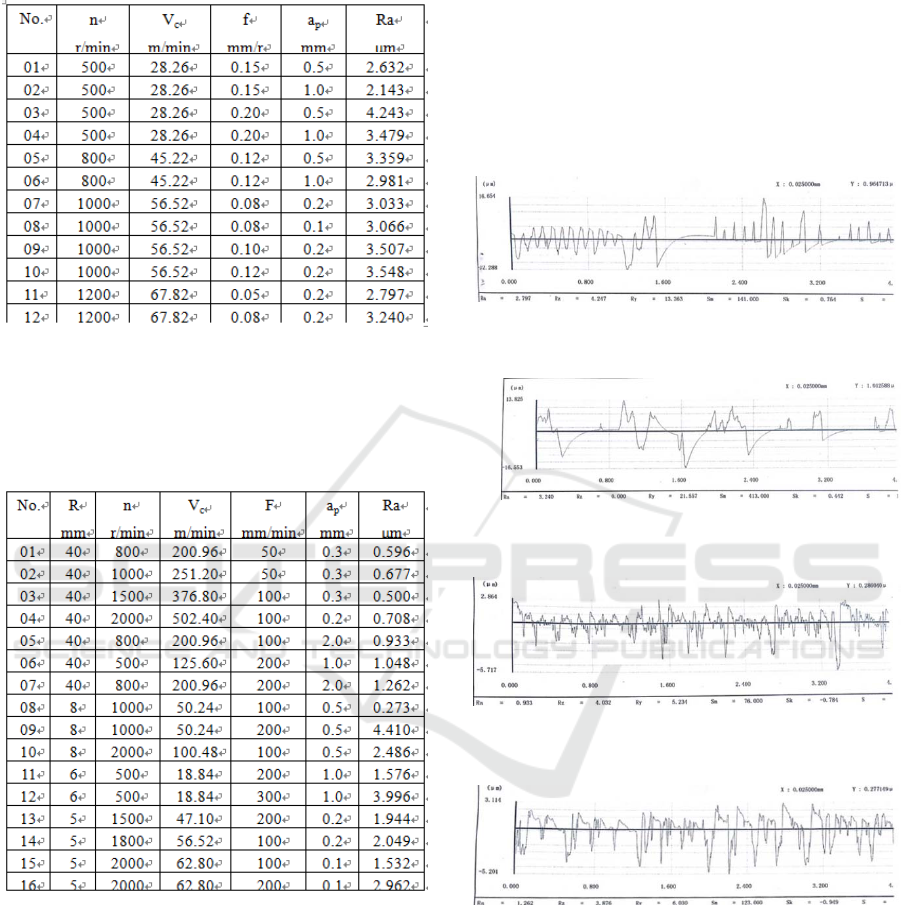
Table 1: Surface Roughness Measurement Results of CNC
Lathe Machining Test Pieces (Extract).
Note: Spindle speed n, feed amount f, and the
back engagement of the cutting edge a
p
refer to the
common CNC turning parameters selection.The cutting
speed Vc is a converted value (Vc=πdn/1000).
Table 2 :Surface Roughness Measurement Results of NC
Milling Test Pieces (Excerpt).
Note: Spindle speed n, feed speed F, and the
back engagement of the cutting edge ap refer to the
common CNC milling parameters selection.The cutting
speed Vc is a converted value (Vc=2πRn/1000).
5THE ANALYSIS OF DATA
There are 83 valid samples of CNC turning and
milling. Some data are eliminated by taking into
account the effects of random errors and
measurement errors during cutting. After studying
the conclusions are as follows:
① The feed or feed rate has a significant effect
on the workpiece surface roughness. Under the same
cutting conditions, the workpiece surface roughness
value will increase while the feed or feed rate
increases. Referring the number 02, 03 and 08, 09
and11,12 in Table 1; the 05, 07 and 11 ,12 and15 ,16
in Table 2.In Fig. 2 and Fig. 3 are the measured
results of the surface roughness of the workpieces of
the CNC turning; In Fig. 4 and Fig. 5 are the CNC
milling.
Fig. 2 Surface roughness measurement results of CNC
turning workpiece 11(n1200,f0.05,ap0.2).
Fig. 3 Surface roughness measurement results of CNC
turning workpiece 12(n1200,f0.08,ap0.2).
Fig. 4 Surface roughness measurement result of NC
milling workpiece 05(R40,n800,F100,ap2).
Fig. 5 Surface roughness measurement result of NC
milling workpiece 07(R40,n800,F200,ap2).
②The parameter back engagement of the cutting
edge has not a significant effect on the value of the
surface roughness of the workpiece. When in the
same condition in addition to the back engagement
of the cutting edge, the surface roughness value of
the workpieces keep unchanged basically either
CNC turning or milling. Referring 01,02 and 03,04
in Table 1, the value the of surface roughness of the
workpiece decreases when the back engagement of

the cutting edge increases, because of the affecting
by the turning radius of tool cutting edge of the
turning tool.
③ The cutting speed has an effect on the surface
roughness of the workpiece, but it is less than the
feed or feed rate. During in high-speed, the value of
the surface roughness of the workpiece decreases
when increasing the cutting speed, referring to 14,15
in Table 2, and 14, 15 and 02, 03, 04.when the
cutting speed Vc> 200m/min, the average value of
the surface roughness of the workpiece is some
0.628μm; and when Vc = 50~60m/min, the value is
about 2.122μm. However, if the spindle speed of the
machine tool is too high, the value of the surface
roughness of the workpiece will increase due to the
accuracy of the machine itself and the effects of
cutting vibration,. Such as when the spindle speed of
the economical CNC lathe reaches 1200r/min and
the CNC milling machine reaches 2000r/min.
6CONCLUSIONS
After CNC machining and milling, we tested the
value of the surface roughness of the sample pieces
and then study the effects on them by the cutting
parameters (the cutting speed vc, the
back engagement of the cutting edgeap, the feed f )
in this experiment, the conclusions are as follows:
①The feed has a significant effect on the value
of the surface roughness of the workpiece. the more
the feed, the bigger the value.
②The cutting speed effects on the value of the
surface roughness of the workpiece. the more the
speed, the less the value during high-speed cutting.
③ Theback engagement of the cutting edge has
little effect on the value of the surface roughness of
the workpiece.
④Usually, if to make the value of the workpiece
surface roughness Ra= 1.6 ~ 3.2μm, the ideal
turning amount in CNC turning: vc = 30 ~ 60m/min,
ap = 0.5 ~ 1.0mm, f = 0.05 ~ 0.12mm / r; In CNC
milling: vc = 20 ~ 100m/min, ap = 0.2 ~ 2.0mm, F =
50 ~ 200mm/min. When a large diameter end is sued
in CNC milling, and F = 50 ~ 100mm/min, the Ra is
up to 0.8μm.
⑤When the spindle speed of the machine tool is
too high, the value of the surface roughness value of
the workpiece will increase due to machine tool
accuracy and cutting vibration. Otherwise, if
theback engagement of the cutting edge is too small,
the value will increase due to the influence of the
turning radius of tool cutting edge.
REFERENCES
1. Liu Hui. ,2006.Interchangeability and Technical
Measurement. East China University of Technology
Press.Shanghai.
2. Wang Qiping.,1999. Mechanical Manufacturing
Technology. Harbin University of Technology
Press.Harbin .
3. Eung-Suk Lee,Suk-Hwan Suh and Jin-wook
Shon.,1998.A comprehensive method for calibration of
volumetric positioning accuracy of cnc-
machines.Advanced manufacturing
technology,1998,14(1):43~49.
4. Dufour P,Groppetti R.,2000.Computer aided accuracy
improvement in larger NC machine
tools.M.T.D.R.Conferrence Proceedings,
5. Lu Changguo, Duan Zhenyun. ,2016.
6. Technical basis of Mechanical Manufacturing. Dalian
University of Technology Press.Dalian.
