
Analysis of Mechanical Properties of Cement Concrete Mixed with
Waste Asphalt Mixture Powder
Desheng Jia
1
, Weiwei Han
1
and Na Li
1
1Xi'an Highway Research Institute, Xi'an, Shanxi, China
Keywords: Waste asphalt mixture powder cement concrete mechanical properties.
Abstract: In order to solve the problem of reutilization of waste asphalt mixture, at the same time, in order to improve
the mechanical properties of cement concrete, such as flexural tensile strength and so on, In this paper,
based on the test of waste asphalt mixture powder obtained by special crushing and screening equipment, it
replaces the quality of part of sand in cement concrete, and analyzes the influence of waste asphalt mixture
powder on the mechanical properties of cement concrete. Through tests, it has been shown that the flexural
tensile strength of cement concrete after replacing the 15% sand content in cement concrete with waste
asphalt mixture powder is significantly improved, and the elastic modulus is decreased.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the gradual extension of the time of the
road input and operation in China, the asphalt
pavement of the early construction has entered the
maintenance period, and the reutilization of the
waste asphalt pavement material has been paid much
attention. With the continuous popularization and
application of cement concrete pavement, the quality
requirements of the surface concrete material in the
opposite layer are increasing. It is required that the
surface concrete material should have higher
flexural strength and lower elastic modulus. So as to
avoid the occurrence of cracks in the early stage of
pavement construction, improve the performance of
cement concrete and prolong the service life of
pavement. This article starts with these two common
topics, blending waste asphalt mixture powder into
cement concrete, and analyzing the effect of waste
powder on the mechanical properties of cement
concrete.
2 PRODUCT FEATURES OF
WASTE ASPHALT MIXTURE
POWDER
The waste asphalt mixture used in this experiment is
used as the waste asphalt pavement milling material,
and the waste asphalt mixture with grain size below
2.36mm is obtained by the self-made crushing and
screening equipment.
2.1 Test of Waste Material Extraction
and Three Major Index Tests
The test adopts the centrifugal asphalt mixture fast
extraction instrument and takes the dry sample
1500g. According to the requirements of the test,
three parallel tests are carried out, the average value
is taken, finally obtains the asphalt content in the
waste asphalt mixture powder to be 9.5%.
In order to characterize the properties of the
waste material powder, the three indexes for
recovering the asphalt were tested after the
extraction test. The results are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Extraction and recovery of asphalt properties.
inde
x
25℃penetrati
on (0.1mm)
15℃ductility
(cm)
softening point(ring
and ball method)(℃)
Valu
e
28.6 1.2 56.2
2.2 Screening Test of Waste Asphalt
Mixture Powder
In order to analyze the performance of waste
material and determine its gradation, sieving test
was carried out. Prior to each screening test, a small
amount of lumps in the waste material powder were
crushed, and then a certain amount of waste material
powder was taken and fully stirred and then
sampled, two parallel tests were performed each
time and a dry screening method was used. The test
results are shown in Table 2.
Table 2 Results of screening test for waste material
powder.
Screen size
(mm)
2.36 1.18 0.6 0.3 0.15
0.07
5
Percentage
passing
(%)
100 99.0 87.7 76.0 46.7 26.7
3 ANALYSIS OF MECHANICAL
PERFORMANCE OF CEMENT
CONCRETE MIXED WITH
WASTE POWDER
In this paper, the effect of waste material powder on
the flexural tensile strength and elastic modulus of
cement concrete is mainly analyzed. At the same
time, the change of concrete compressive strength is
analyzed, and the best dosage of the best waste
material is summed up. The test program is based on
the use of waste material powder instead of sand
0%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25% five different mixing
ratio of the mechanical properties of the test.
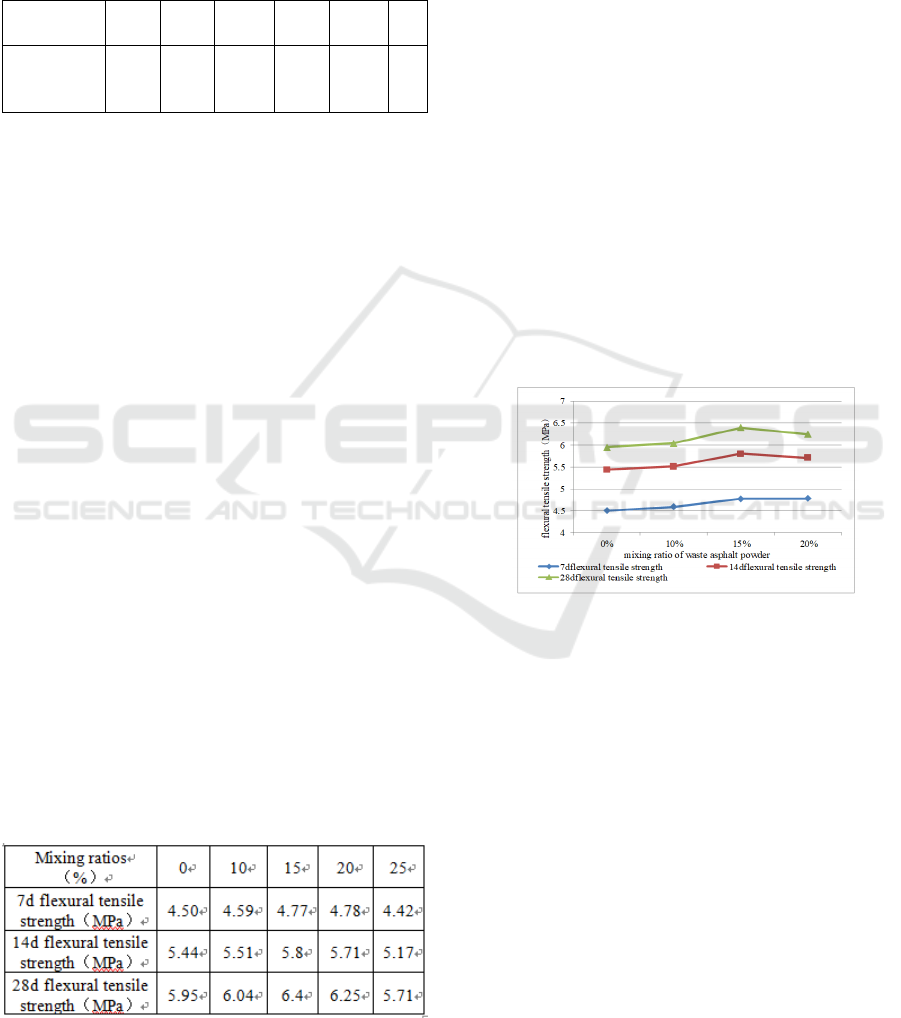
3.1 Flexural Tensile Strength
The flexural tensile strength of cement concrete for
road pavement is the main strength index, and the
compressive strength is used as a reference strength
index. So when evaluating the performance of road
cement concrete, we should first analyze whether its
flexural strength meets the requirements. Through
indoor standard test, the flexural tensile strength of
concrete is shown in Table 3.
Table 3 The flexural tensile strength of concrete with
different mixing ratios and ages.
From Table 3 and Figure 1, we can see:
(1)When the mixing ratio is less than 20%,
the flexural tensile strength of cement concrete
mixed with waste material is improved, and when
the proportion of mixing is 25%, the flexural tensile
strength of the concrete is reduced to a certain
extent.
(2)When the curing period was 7 days, the
concrete flexural strengths of 10%, 15%, and 20%
were higher by 2.0%, 6.0%, and 6.2%, respectively,
than those of the concrete without blended waste
powder.
( 3 ) With a curing period of 14 days, the
concrete flexural strengths of 10%, 15%, and 20%,
respectively, increased by 1.3%, 6.6%, and 5.0%,
respectively, compared with the concrete without
undoped waste powder.
(4)When the curing age is 28 days, when the
proportion of waste powder mixed is 15%, the
concrete tensile flexural strength increases by 7.6%;
the blending ratio is 20%, and the concrete flexural
strength increases by 5.0%. Therefore, the integrated
early concrete flexural tensile strength and 28-day
standard strength, the best mixing ratio of waste
powder is 15%.
Figure 1 The flexural tensile strength of concrete with
different mixing ratios and ages.
3.2 Elastic Modulus
Elastic modulus is one of the important mechanical
properties of concrete. It reflects the relationship
between concrete stress and its strain. It is one of the
parameters necessary to calculate the deformation of
concrete structure, crack cracking and temperature
stress. In this paper, the compressive elastic modulus
of cement concrete prism is analyzed, and the
mechanical properties of cement concrete mixed
with waste material powder are evaluated. The
experimental results are shown in Table 4.
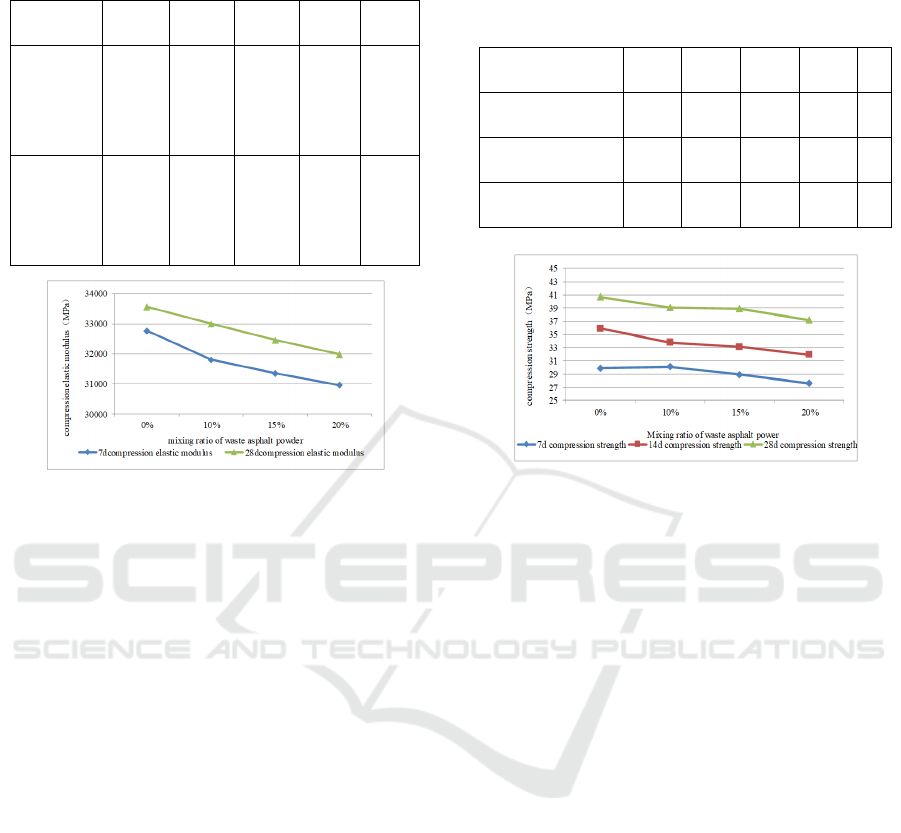
Table 4 Concrete compression elastic modulus with
different mixing ratios and ages.
mixing
ratios(%)
0 10 15 20 25
7d
compression
elastic
modulus(
MPa)
32760 31797 31348 30959 31774
28d
compression
elastic
modulus(
MPa)
33560 32996 32453 31983 32587
Figure 2 Concrete compression elastic modulus with
different mixing ratios and ages.
From Table 4 and Figure 2 we can see:
( 1 ) The compressive elastic modulus of
cement concrete mixed with waste material is lower
than that of the concrete without waste material,
However, as the curing age continues to increase,
the decrease in the elastic modulus at the later stage
of the concrete becomes smaller, that is, the decrease
in elastic modulus at the later stage is less obvious
than at the early stage.
( 2 ) When the proportion of waste powder
mixed is 20%, the compressive elastic modulus of
cement concrete decreases by a maximum of 4.7%
over 28 days.
Combine the change rule of the compressive
elastic modulus of the concrete of each age, and
determine the best proportion of the waste material
mixed is 20%.
3.3 Compressive Strength
According to the standard method, this test was
made of cubic compressive specimens of 150mm x
150mm x 150mm, which were cured under standard
curing conditions for 7d, 14d, and 28d. Their
ultimate compressive load was measured according
to the standard method. The test results are shown in
Table 5.
Table 5 Concrete compression strong with different
mixing ratios and ages.
mixing ratios(%
)
0 10 15 20 25
7d compression
strength(MPa)
29.9 30.1 28.9 27.6 25.3
14d compression
strength(MPa)
35.9 33.8 33.1 31.9 30.2
28d compression
strength(MPa)
40.7 39.1 38.9 37.2 36.1
Figure 3 Concrete compressive strength with different
mixing ratios and ages.
From Table 5 and Figure 3, it can be seen that
the compressive strength shows a different degree of
decline, and as the proportion of blending increases,
the decrease extent increases. At curing age of 28
days, the compressive strength of concrete with a
content of more than 20% decreased by
10%.Therefore, in order to ensure the compressive
strength requirements of road concrete, it is
recommended that the mixing ratio of waste material
should not exceed 20%.
3.4 Mechanism of Action Analysis
( 1 ) Influence of waste powder on flexural
tensile strength of cement concrete
From the observation of the truncation of the test
specimens of concrete flexural tensile strength test,
it can be seen that compared with the ordinary
concrete specimens, the cross section color is
relatively dark, the surface pores are relatively small,
and the sand on the surface is relatively less.
The following analysis of the mechanism of
action of waste powder in concrete from three
aspects:
①Filling mechanism. The strength of concrete
depends mainly on the strength of the cement slurry,
and the porosity is a decisive factor in the strength of
the cement slurry, so the porosity of the concrete

structure is an important factor affecting its strength.
The waste material used in this test is a kind of
powder like mineral powder on the particle size. It
effectively fills the void in cement concrete structure
in cement concrete structure, making the whole
structure of concrete more dense and improving the
flexural strength.
②Viscoelastic mechanism. The old asphalt in
the waste material has a certain bonding effect,
which forms a chain or reticular structure inside the
concrete structure under the effect of temperature.
On the one hand, this kind of bonding can reduce the
appearance of early micro cracks or prevent the
further expansion of the cracks. On the other hand,
the waste material powder, as an elastic medium,
exists in the concrete. The strain of the material is
buffered under the stress action, that is, a certain
buffer action is played when the micro cracks appear
under the action of load and temperature.
③Reaction mechanism. Along with the
hydration of cement, the bitumen and mineral
powder in the waste material will react with the
concrete and the aggregate minerals in a series of
physical and chemical reactions mainly by acid and
alkali neutralization reaction. It is mainly reflected
in the hydration and exothermic environment. The
acid aging asphalt in the waste material is reacted
with the cement to produce some kind of material.
At the same time, the mineral powder reacts with
some minerals of the aggregate in the concrete, and
the physical and chemical changes occur.
( 2 ) Influence of waste powder on elastic
modulus of cement concrete
The waste asphalt mixture powder that replaces
part of the sand in this test is a powdery substance
with a particle size of 2.36 mm or less and has
viscoelastic properties. After mixing with cement
paste in concrete, it is equivalent to increasing the
fluidity of the mixture and exerting its viscoelastic
characteristics, thus reducing the modulus of
elasticity of concrete.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Through the mechanical performance test and
analysis, we can get the following conclusions.
(1)The waste material which is replaced by
sand 15% can obviously improve the flexural
strength of cement concrete, and its modulus of
elasticity has a downward trend, and has little effect
on the decline of compressive strength.
(2)After processing the waste asphalt mixture
through the special crushing and screening
equipment, the waste material is obtained. Replacing
some of the sand in the cement concrete can
obviously improve the mechanical properties of the
concrete, such as the flexural tensile strength and so
on, thus reducing the production of pavement cracks
and prolonging the life life of the pavement.
REFERENCES
1. Huang, X.M. Zhao, Y.L., et al. Analysis of Asphalt
Pavement Recycling Test [J], Chinese Journal of
Geotechnical Engineering, 2001(04):468-471.
2. Wang, H.P. Research on crack resistance of cement-
stabilized macadam with mixed waste materials[D],
Chang’an University, 2011.
3. Liu, Z.H. Research on the Recovery Test and
Recycling Technology of Used Asphalt Pavement [D],
Chongqing traffic University, 2012.
4. Zhang, D.S. Wang, H.P., Research on Crack
Resistance of Cement Stabilized Crushed Stones
Mixed with Waste Old Asphalt Mixtures[J].China
Foreign Highway,2006(05):221-225.
5. Bi, H.J., Zhang, X.H., The recycling of used asphalt
mixture[J], Traffic World, 2006(01):70-73.
6. Ru. B., continued macro. Application of asphalt
milling material regeneration technology [J], Shanxi
Architecture: 2003(06):111-112.
7. Qu, Q.Y., Zhang, L.J., Fu, C.C., The performance of
self-compacting concrete mixed with used asphalt
mixture[J], Subgrade Engineering, 2017(02):118-121.
8. Shang, H.S., Zhao, Y.G., Research on the Test of
Waste Stabilized Bituminous Mixtures[J].Journal of
Gansu Sciences,2016(06):85-88.
9. Wang, H.P., Zhang, D.S., Lu, J.J., Impact of mixed
fine asphalt mixture on the compressive strength of
cement stabilized macadam [J], Highway,
2012(06):204-208.
10. JTG E30-2005. Test protocol for cement and cement
concrete in highway engineering [S], Beijing: China
Communications Press, 2005.
