
Effect of Enzyme on Harmful Components Reduction in
Reconstituted Tobacco
T H Huang
1
, Q S Shi
2,3
, K Wei
1
, J P Gui
2,3
and L S Zheng
2,3, *
1
China Tobacco Guangxi Industrial Co. LTD., Guangxi, 530001, China
2
School of Biological Science and Medical Engineering, Beihang University, Key
Laboratory for Biomechanics and Mechanobiology of Ministry of Education, Beijing,
100083, China
3
Beijing Advanced Innovation Centre for Biomedical Engineering, Beihang
University, Beijing, 100083, China
Corresponding author and e-mail: L S Zheng, lishazheng@buaa.edu.cn
Abstract. To explore the influence of the composite enzymes on harmful components in
reconstituted tobacco, we developed compound enzymes which included power of cellulose
(23-41%, 100,000U/g), xylanase (10-23%, 100,000U/g), complex protease (41-57%,
100,000U/g), pectinase (5-6%, 100,000U/g) and amylase (1.5-3.8%, 10,000U/g). The
compound enzymes were added to the reconstituted tobacco (0.4% enzymes, incubated for 1
h at 45 ± 5°C). We evaluated the quality of the reconstituted tobacco using physical and
chemical indices. The results show that protein and pectin contents were effectively reduced,
with improved taste of the cigarette smoke, and harmful ingredients were reduced, such as
ammonia and hydrogen cyanide, in the mainstream smoke of the composite enzyme treatment
group compared with the untreated control group. This approach will reduce the danger of
mainstream smoke in reconstituted tobacco.
1. Introduction
Papermaking process reconstituted tobacco (RTL) is a type of tobacco product that utilizes
papermaking technology to produce a tobacco product. RTL uses tobacco stems and fines as the
major raw material. The main process of producing RTL includes placing the reconstituted tobacco
raw material in water, immersing and extracting the soluble material, and separating the insoluble
material. Secondly, a sheet is produced from a fiber base of insoluble material using a paper machine.
The insoluble substances are made into substrates, such as base paper, using a similar paper-making
method. Then, concentrated soluble substances are added with other additives to the substrate, which
becomes RTL after drying. A certain amount of recycled tobacco is added to the cigarette as a filling
material, which saves tobacco, reduces the cost of the cigarettes, and adjusts and improves the
physical properties and chemical composition of the cigarette [1-4]. However, biological
macromolecules, such as proteins, starch, and pectin, may affect the quality and effect of recycled
tobacco. Both domestic and overseas researchers have used bio-enzymes to transform and degrade
cellulose, lignin, pectin, proteins, starch, and other bio-macromolecules that influence the quality of
reconstituted tobacco to reduce the content of these macromolecules, which reduces the impurities
Huang, T., Shi, Q., Wei, K., Gui, J. and Zheng, L.
Effect of Enzyme on Harmful Components Reduction in Reconstituted Tobacco.
In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Materials, Chemistry and Engineering (IWMCE 2018), pages 351-356
ISBN: 978-989-758-346-9
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
351

and irritation and improves the quality of the RTL [5-8]. In this study, we used protease, cellulase,
pectinase, and other biological enzyme preparations to treat reconstituted tobacco leaf extract to
study the effect of the enzyme preparation on the regeneration of tobacco leaves and flue gas,
particularly the release of harmful components in tobacco leaves.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Materials
Tobacco stems and tobacco powder was supplied by Guangxi Zhongyan Industrial Co., Ltd. The
compound enzyme was developed by Beihang University. Other reagents are analytically pure.
2.2. Method
Preparation of the reconstituted tobacco extract. Tobacco stems: tobacco powder (4: 6) samples was
weighed after being broken by a micro-plant crusher (FZ102 Miniature plant crusher, Taisite, China)
and was formed into a 1:10 solid-liquid ratio at 65 ± 5°C (HH-4 Constant temperature water bath,
Hannuo, China). After stirring for 40 min, the supernatant and residue were collected and the residue
was extracted three times. The supernatant was concentrated by a vacuum rotary evaporator and
concentrated to give the extract.
Extraction with the enzyme preparation. A compound enzyme preparation was added to the
extract at a rate of 0.4% of the total mass of the raw material (the end of the tobacco powder+
tobacco stems), and the mixture was prepared as blank samples and tested. The reaction was carried
out at 45 ± 5°C (TRH-300-GD Humidity Chamber, Thermoline, Australia) for 1 h and heated at
100°C for 10 min. After inactivating the compound enzyme, the extract was concentrated to the
original 1:9 volume at a density of 1.03–1.04 g/ml and made into a coating solution.
Preparation of cigarettes. Compound enzyme 5 was produced and prepared at Beihang University
and used to produce reconstituted tobacco at the proportion of 0.4%; tobacco stems, fines and other
material are used for extracting, concentrating, mixing, papermaking, coatings, drying, perfuming,
and other processes on the production lines of Guangdong Golden Leaf Technology Development
Co., Ltd. They were coated on the same substrate with a coating solution and the compound
enzyme-treated coating solution, respectively. The coating rate was set to 40 ± 2%. After drying at
105°C (FED240 Electric thermostatic drying oven, Binder, Germany), the flake reconstituted tobacco
was prepared. We used slices for the tobacco primary processing, rolling, and linking assembly units
to reforge the tobacco leaf materials, and packaged the reforged tobacco on the production lines of
Guangxi Zhongyan Co., Ltd.
Test methods. The extract was analyzed using physical and chemical indices. The protein content
was determined in accordance with National Food Safety Standards of China GB 5009.5-2010
“Determination of Protein in Foods”. The Kjeldahl digestion in analytical chemistry is a method for
the quantitative determination of nitrogen contained in organic substances plus the nitrogen in tuck
ammonia and ammonium (NH3/NH4+) [9]. Pectin content was determined in accordance with the
“Raw Fiber Material-Determination of Pectin Content (GB/T 10742-2008)”. A method is described
for the determination of pectin content in tobacco pectin by carbazole colorimetric method,
experiment conditions were investigated in detail and the optimum conditions were found as follows:
sulphuric acid 6.0mL, hydrolytic temperature 70°C , hydrolytic time 20min, 0.15% carbazole absolute
ethanol's solution 0.5mL, color reactions were carried out under room temperature, reaction time
30min, The method has been applied successfully to actual samples [10]. Total cellulose was
determined in accordance with “Fibrous Raw Material-Determination of Total cellulose (GB/T
2677.10-1995)”. The Van Soest is a method for the quantitative determination of Total cellulose in
tobacco [11].
IWMCE 2018 - International Workshop on Materials, Chemistry and Engineering
352
Tobacco smoke analysis: Nicotine, carbon monoxide, water, tar, total particulate matter,
crotonaldehyde, phenol, hydrogen cyanide, ammonia, benzo(a)pyrenes, N-nitrosamines, and other
substances were determined in the total particulate matter of cigarette smoke using the national
tobacco industry standard or relevant national standard methods.
Sensory quality analysis: The taste sense was evaluated by aroma, irritation, coordination,
impurities, and aftertaste of the cigarettes in accordance with the National Industry Standard
YC/T138 “Tobacco and Tobacco Products-the Sensory Evaluation Methods”.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Effects of the compound enzyme on protein content in the extract
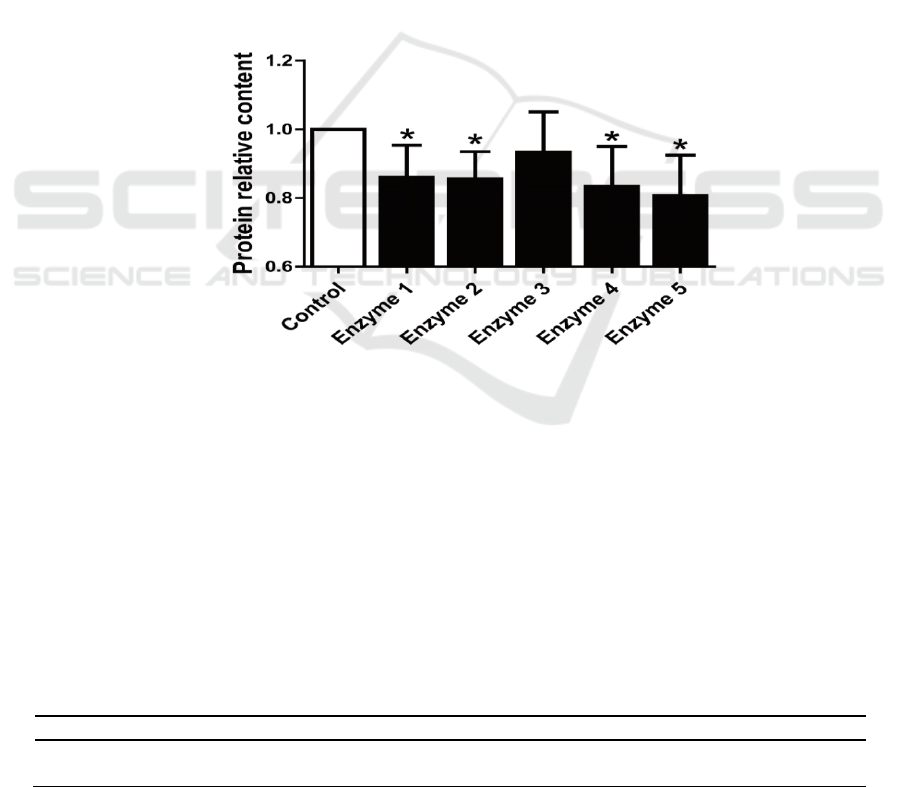
The protein content in the reconstituted tobacco extracts all decreased after being treated by
compound enzyme (Figure 1). Compound enzyme 5 provided the greatest decrease of about 20%.
Compound enzyme 4 reduced protein content in the extract by about 17%. The effects of compound
enzyme 1 and compound enzyme 2 were similar at about 15%. The effect of compound enzyme 3
was the poorest at only 7%. The effects of compound enzymes 3 did not reach statistical significance.
Considering the cost of the enzyme preparation and other factors, compound enzyme 2 and 5 were
selected for follow-up experiments because of their stable results.
Figure 1. Changes in protein content of the extraction solution based on the composite enzyme
treatment.
3.2. Effects of the compound enzymes on pectin and cellulose contents in the extract
Pectin and total cellulose contents in the extract changed after treatment with the compound enzymes
(Table 1). Pectin and cellulose contents did not change after treatment with compound enzyme 2,
indicating that compound enzyme 2 had good degradation efficiency for protein but was not ideal for
pectin or cellulose. Compound enzyme 5 also had good degradation efficiency on pectin by about
12%, but the efficiency of cellulose was not ideal. The reaction conditions for cellulose degradation
require further exploration. The conditions and process needs optimization.
Table 1. Content of pectin and ensemble cellulose in extracting solution by composite enzyme
treatment (%).
Control group
Enzyme group 2
Enzyme group 5
pectin
0.384
0.386
0.338
Total cellulose
0.04
0.043
0.064
Effect of Enzyme on Harmful Components Reduction in Reconstituted Tobacco
353
3.3. Effects of the compound enzymes on the sensory evaluation
We used cigarettes with reconstituted tobacco leaves made from the compound enzyme-treated
extract for the sensory evaluation analysis (Table 2). According to the results, cigarettes in enzyme
groups 2 and 5 improved taste quality, mainly sweetness and impurities, compared with the untreated
control group. Enzyme group 5 had fewer impurities, more abundant fragrance, and shorter residue
time as an aftertaste than the control group and the enzyme 2 group. The analysis showed that
enzyme group 5 was superior to enzyme group 2 and the control group.
Table 2. Results of cigarette smoking sensory quality assessment.
Sample
Sensory quality assessment result
Control group
Woody impurity gas; aftertaste with granular sensation.
Enzyme group 2
Gentle gas; clear sweet aroma; good abundance; slight woody smell;
aftertaste with slight granular sensation.
Enzyme group 5
Smooth gas; great abundance; but less volume of aroma; more sweet feeling;
slight impurity; slight irritation.
3.4. Optimization of conditions for the compound enzyme treatment
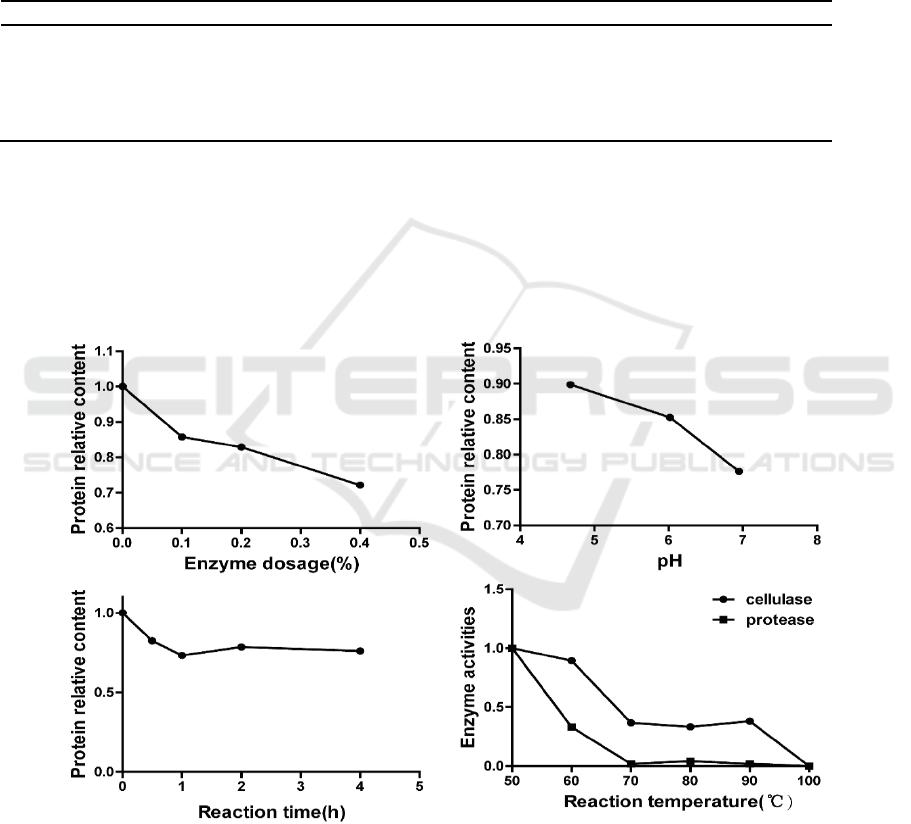
The effects of enzyme dosage, pH, reaction time, and reaction temperature were investigated. The
results are shown in Figure 2.
The amount of enzyme used in the extract had a significant effect on degradation of protein. After
considering the degradation of protein and the price of the compound enzyme, the mass fraction of
0.4% was chosen as the optimal amount of compound enzyme to use.
Figure 2. Effects of enzyme dosage, pH, reaction time, and temperature on protein degradation.
The pH value of the leaf extract had an important effect on the degradation of protein by the
compound enzyme (Figure 2). When the pH value was close to neutral, the effect of the enzyme
preparation was more obvious, indicating that the compound enzyme preparation (at least the
IWMCE 2018 - International Workshop on Materials, Chemistry and Engineering
354
protease component) pH was close to pH 7, so pH 7 was selected as the pH for the complex enzyme
reaction system.
The protein content in the tobacco leaf extract required a certain reaction time. Protein content
decreased rapidly within 1 h. Protein content did not change with a reaction time more than 1 h.
Although protein content of the reaction was lower than that of the reaction at 30 h, the protein
content was less than that of the reaction at 1 h, so a reaction time of 1 h was chosen, taking into
account practical factors, such as production efficiency.
After the reaction, the enzyme preparation must be completely inactivated, or the flavor of
cigarettes in storage will continue to change. Temperature is essential for the inactivating enzyme
preparations. The changes in protease and cellulase activities in the complex enzyme were studied at
different temperatures.
The results showed that protease activity was almost nil at 70°C, while cellulase was relatively
inactive, and the activity decreased to a low level (0.4) at 70°C and was maintained at a lower state
until 100°C when activity was reduced to nil, so the choice of inactivation temperature was 100°C.
3.5. Effect of enzyme treatment on the extract reconstituted tobacco mainstream smoke
According to the detection method described in section 1.2.4, the results of the three indices in the
main flue gas of the flue-cured tobacco (Table 3) show that a similar amount of tar, nicotine, and
carbon monoxide were released in the enzyme treatment group compared with the control group.
Table 3. Three indicators of mainstream smoke in reconstituted tobacco.
sample
TPM
(mg/a
cigarette)
Nicotine
(mg/a
cigarette)
Moisture
(mg/a
cigarette)
Tar
(mg/a
cigarette
)
CO
(mg/a
cigarette)
Number of suction
ports(mouth/a
cigarette )
Control group
8.40
0.53
1.15
6.7
15.4
5.2
Enzyme
group 5
8.12
0.48
1.21
6.4
15.4
4.9
We further investigate the harmful components of mainstream smoke in reconstituted tobacco.
The results show that the release of hydrogen cyanide (HCN) in the flue gas of the test group was
lower than that of the control sample (P < 0.05) (Table 4). The results show that HCN decreased by
10.5%, ammonia decreased by 21.3%, and the hazard index of tobacco leaf was reduced by 0.2.
Table 4. Harmful components of mainstream smoke in reconstituted tobacco.
Sample
CO
(mg/a
cigarette)
HCN
(ug/a
cigarette)
NNK
(ng/a
cigarette)
NH
3
(ug/a
cigarette)
B[a]P
(ng/a
cigarette)
Phenol
(ug/a
cigarette)
Crotonald-ehyde
(ug/a cigarette)
Hazard
Index
Control group
13.9
85.5
10.8
4.7
6.1
2.7
17.4
8.2
Enzyme group 5
14.5
76.5
11.2
3.7
5.7
2.7
17.0
8.0
HazardIndex=(CO/14.2+HCN/146.3+NNK/5.5+NH3/8.1+B[a]P/10.9+phenol/17.4+Crotonaldehyde/18.6)*10/7.
4. Conclusions
Yang found that the optimum compound enzymes was composed of 0.5g/kg neutral proteinase,
0.1g/kg papaya proteinase and 0.5g/kg pineapple proteinase based on the weight of treated tobacco
leaves. By treating with the compound proteinase, the protein of tobacco was decreased by 13%
[12].Yao found that the neutral proteinase was the most effective enzyme for reducing the protein in
Effect of Enzyme on Harmful Components Reduction in Reconstituted Tobacco
355

tobacco. 120U/g neutral proteinase decreased protein to 12% [13]. Cellulase and pectinase compound
enzymes could degraded the cell wall material into sugars. It could degrade the cell wall material by
5% - 10% [14]. Deng used pectinase storing at 50°C for 12 hours. The results showed that the pectin
was reduced by 18.15% [15].Compared with our results, protein decreased to maximal 20% and
pectin decreased by 12%. It is better than the previous results.
The compound enzyme in this study reduced the release of harmful components in reconstituted
tobacco leaves. Compound enzyme 5 was added, and the extract was reconstituted. The protein
content of the extract was reduced by 20% and pectin content was reduced by 12%. Harmful
components, such as HCN gas, were reduced by 10.5%, ammonia was reduced by 21.3%, and the
hazard index decreased by 0.2 compared with the control cigarette. In conclusion, treating the extract
with a compound enzyme reduced protein and pectin contents as well as the release of harmful
components in reconstituted tobacco leaves, which is beneficial for improving the quality of
reconstituted tobacco.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant numbers
11572030], National Key R&D Program of China [2017YFC0108505].
References
[1] Chen Z G, Cai B, Wang J X, Ye M Q and Xiong B 2002 Tobacco Science & Technology 2
4-10
[2] Sun X Y, Sun B, Li D L and Zhang Z H 2011 Biomass Chemical Engineering 45 49-56
[3] Bai T, Yi A R, Tang J G, Zhu L H and Meng Z Y 2013 J of Anhui Agricultural Sciences 41
11512-11515
[4] Potts R J, Bombick B R, Meckley D R, Ayres P H and Pence D H 2010 Experimental and
Toxicologic Pathology 62 117-126
[5] Mao Y, Liu Z C, Yao Y J, Wang F L, Wang L and Xie Y M 2011 Tobacco Science
&Technolog 6 48-51
[6] Duan M, Li X, Li Z Y, Che J, Wang C, Hu W Y, Zhou J and Liu W J 2009 Chinese Tobacco
Science 30 69-72
[7] Huang T H, Gui J P, and Zheng L S 2015 J of Northeast Agricultural University 10 102-108
[8] Zheng X G, Zhao C Z, Wei X L, Wang Y X, Li J F, Han X C and Wang A C 2010 Shandong
Food Ferment 1 11-13
[9] Ding J D, Zhang X H, Yao X C, Huang W Y and Lin C W 2010 Food Research &
Development 11 138-140
[10] Shi W, Sun Y and Xu Z B 2013 Grain Science & Technology & Economy 5 31-32
[11] Gao X, Chen K L, Zhang H, Peng L C and Liu Q X 2014 Bioresources 3 4094-4107
[12] Yang Z C, Liu X Z, Ye J B, Xi J Q, Shen H T, Xu H, Peng Y F, Hao H, Wang G F and Yang
Y F 2016 Journal of Henan Agricultural University 5 683-687
[13] Yao G M 2000 Tobacco Science & Technology 9 6-8
[14] Yan K Y and Liu F Z 2011 Biotechnology 4 19-22
[15] Deng G B, Li X M, Li C B, Zhou J and Zhang Z 2003 Tobacco Science & Technology 11
17-18
IWMCE 2018 - International Workshop on Materials, Chemistry and Engineering
356
