
Experimental Study on the Strength and Durability of Concrete
with Treated Rubber Particles
M M Wu, Y Xie, X R Su, H X Wang and D M Luo
*
Department of Civil Engineering, Foshan University, 528000, Guangdong
Corresponding author’s e-mail address: D M Luo, dongmei_luo@126.com
Abstract. In this study, the rubber particles are treated by the water and NaOH before adding
into the concrete, and the Rubber Concrete (RC) specimen is manufactured by mixing the
treated 10 mesh rubber particles with the mass fraction of 5% ~ 35% into the plain cement,
and the cube compressive strength, axial compressive strength and flexural strength of RC are
tested for the specimen with the age of 28d. The results show the content of 3% of NaOH is
reasonable to obtain the higher strength growth ratios for different specimens. At the same
time, the freeze-thaw resistance and anti-sulfate properties of treated RC are investigated. The
results show that the strength and freeze-thaw resistance of the treated RC can be improved
when the content of NaOH is lower than 5%, and the optimal NAOH content is 3% for the
improvement of strengths, and the treatment of rubber particles with NaOH have little action
on the improvement of anti-sulfate.
1. Introduction
RC is a kind of recycled concrete material in which the fine aggregate is replaced by crumb rubber
with different mass fractions. Although the existed experimental studies reported that the
compressive strength, tensile strength and modulus of elasticity of RC decreased obviously
compared to conventional concrete [1-2] , it is expected to obtain high toughness, good ductility and
light weight to improve the long term service life of RC [3-4]. Some researchers have investigated
the method to improve the ductility of rubber concrete [5-7]. Topcu and Demir [8] investigated the
influence of rubber aggregates on the freeze-thaw resistance of concrete, and they concluded that the
crumb rubber with the size from 1 to 4 mm can improve the freeze thaw durability of concrete when
the content of rubber in concrete is limited to 10% by volume. In fact, the hydrophobic nature of
rubber leads to the weak bonding strength between the rubber surface and cement paste [9], which
result in the strength of concrete would be decreased with added rubber particles [10]. In order to
eliminate the negative effects of the rubber particles on the properties of concrete, the rubber could
be pre-treated to enhance its adhesion to cement paste before adding it into concrete. Many studies
[11-12]
have proven that treated rubber aggregate with NaOH solution can improve the compressive
and flexural strength of RC, but the durability of the concrete containing treated rubber aggregate is
seldom investigated. This study tries to investigate the influence of the treated rubber particles with
water and NaOH solution on the strength and the durability of RC.
Wu, M., Xie, Y., Su, X., Wang, H. and Luo, D.
Experimental Study on the Strength and Durability of Concrete with Treated Rubber Particles.
In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Materials, Chemistry and Engineering (IWMCE 2018), pages 307-312
ISBN: 978-989-758-346-9
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
307

2. Material preparation for rubber composites
Brand sea snail P·O42.5R Cement and medium size sands with the density of 2600kg/m
3
were used
in the study. The aggregates are the natural stone with the density of 2800kg/m
3
. Rubber particles for
10 mesh with the density of 1100kg/m
3
was produced by Zhejiang Enxiang Building Materials
corporation. NaOH solution treatment could provide a weak alkali condition around the rubber
particles, and the cement hydration around rubber can be improved when the treated rubber is
incorporated into cement. The NaOH powder with different content is obtained by adding water to
the NaOH solution of 0% (only washed by water and without NaOH solution), 1%, 3%, 5% and 10%
respectively in this study. The cleaned rubber particles were first soaked in 1N NaOH solution for 45
min at room temperature, then the rubber particles were took out from NaOH solution, and washed
with tap water repeatedly until the pH is equal to 7. To prevent NaOH residues, the rinsed rubber is
still immersed in water for 30 minutes before the test. At last, the treated rubber particles were air
dried at ambient temperature.
Modification mechanism of sodium hydroxide satisfied the following equation:
))(()(24)(
42351723517
OHZnNaCOOHCNaNaOHCOOHCZn
(1)
Where,
COOHC
3517
is saturated carboxylic acid, and its structural formula is
COOHCHCH
1623
)(
with the unsaturation of 1, which is not so easy to break.
Based on the procedure for ordinary concrete mix design (JGJ55-2000), the mechanical properties of
RC were studied by adding rubber particles with different size and volume fraction. The water
cement ratio is 0.45, and the test match ratio is shown in Table 1.
Table 1.
Mix ratio of rubber concrete.
designation
water
(kg)
cement
(kg)
sand
(kg)
rubber particles
(kg)
replacement rate
(%)
Stone
(kg)
RC-0
185
411
678
0
0
1106
RC-5-10
185
411
644.1
14.34
5
1106
RC-15-10
185
411
576.3
43.03
15
1106
RC-25-10
185
411
508.5
71.7
25
1106
RC-35-10
185
411
440.7
100.38
35
1106
Note:The number meaning (take RC-15-10 as an example ). 15 show rubber incorporation, 10 show rubber
particle size.
3. Result and discuss
3.1. Strength test
The test for compressive strength and flexural strength of RC were carried out according to <Test
methods of mechanical properties for the ordinary concrete> (GB/T 50081-2011). The pressure is
applied along the vertical direction of the specimen with the speed of 0.5MPa per second until the
specimen is damaged. The test for durability were carried out according to “Standard for test methods
of long-term performance and durability of ordinary concrete” (GB/T 50082-2009). For the concrete
with the treated and untreated rubber particles, the cube compressive strength, axial compressive
strength and flexural strength have been measured in the test. The strength growth ratio is defined as
IWMCE 2018 - International Workshop on Materials, Chemistry and Engineering
308
the ratio of the difference between the strengths for treated and the untreated RC divided by the
strength of untreated RC in this paper.
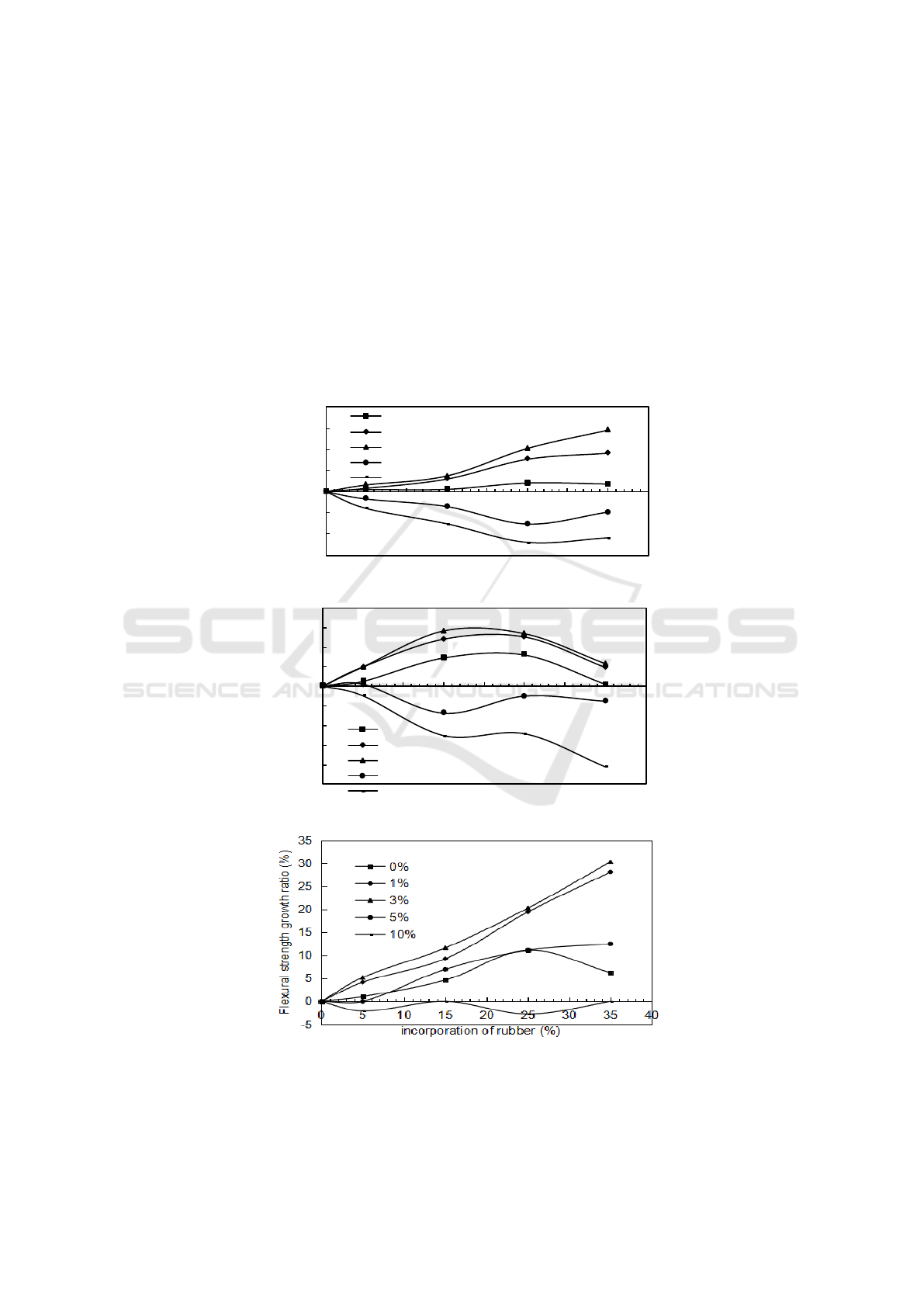
As shown in Figure 1, the results show that the axial and cube strength growth rates are negative
growth when the content of NaOH solution is more than 5%, and the flexural strength growth rate is
negative growth for the case of the content of NaOH is 10%. It means that if the content of NaOH is
too high, the strengths will lower than that of the ordinal concrete. The strength growth rates
increased with the fastest speed for three kinds of test (axial, cube and flexural) when the content of
NaOH is 3%. The peak value of strength growth rate for cube test is 14.11% when the mass fraction
of treated rubber particles is 15%, and it is 29.09% for axial test and 30.31% for flexural test at the
rubber mass fraction of 35%, and the strength growth ratio increases with the increase of the mass
fraction of the treated rubber particles for axial test and flexural test,but the strength growth ratio is
the highest at the mass fraction of 15% for cube test, then it decreases with the increase of the mass
fraction of treated rubber particles.
Figure 1. Strength growth ratio of concrete with treated rubber particles for compressive and
flexural test.
-30
-20
-10
0
10
20
30
40
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
Axial compressive
strength grow th ratio (%)
incorporation of rubber (%)
0%
1%
3%
5%
10%
-25
-20
-15
-10
-5
0
5
10
15
20
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
Cube compressive strength
grow th ratio (%)
incorporation of rubber (%)
0%
1%
3%
5%
10%
Experimental Study on the Strength and Durability of Concrete with Treated Rubber Particles
309
3.2 Freeze and thaw analysis
The experiment was carried out in accordance with the rapid freezing method of SL352-2006 “Test
code for hydraulic concrete”. The specimen is a cube with the dimension of 150*150*150, and the
average cube strength is obtained from three groups test. At first, the specimen is cured in the curing
room about 4 days, then they are removed to soak in the water with the temperature of 20
3 ° C for
4 days. A freezing and thawing cycle lasted 2.5-4 h, and by the end of the heating and cooling, the
temperature in specimen center should be controlled in 17
2 ° C and 8
2 ° C, respectively. The
temperature in the center and surface of specimen is less than 28 ° C. After the test, the specimen was
taken out from the box, and the water in surface of the specimen was wiped off, and the mass of
samples was measured throughout the freeze-thaw test.
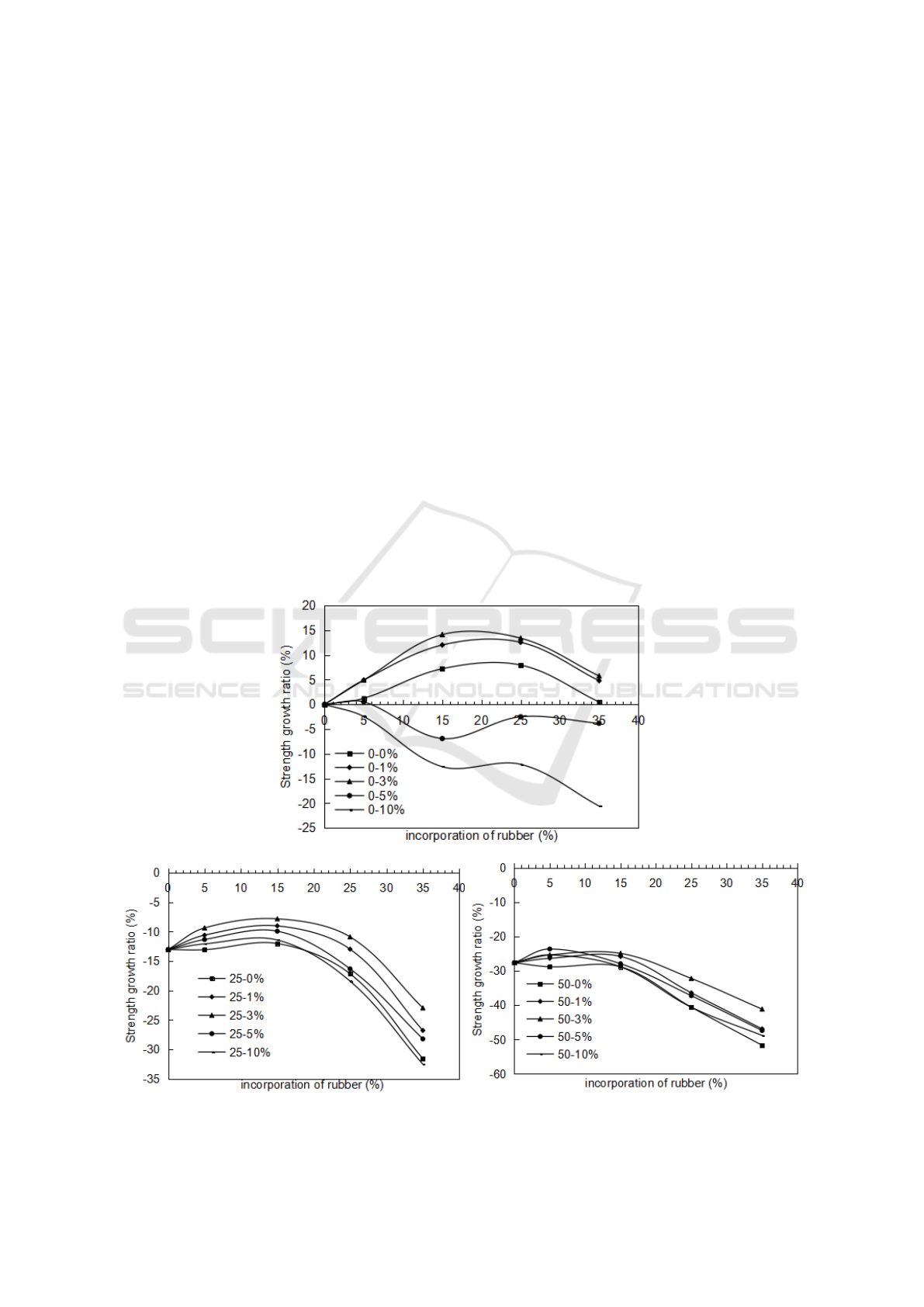
The cube strength growth ratio in Figure 2 shows the ratio of the difference between the strengths
for treated and the untreated RC divided by the strength of untreated RC with different cycling times.
The results show that the strength growth rate increases for the treated RC without the freeze-thaw
cycle and the content of NaOH is lower than 5%. However, the strength growth ratio becomes
negative with the increase of the freeze-thaw cycling times, and the content of 3% of NaOH is better
to obtain a higher strength growth ratio for treated RC. In fact,if the content of the NaOH is too low,
zinc stearate is still attached to the rubber, and the uncleanly surface of rubber results in the
deterioration of the adhesion between cement paste and rubber particles. If it is too high, the NaOH
may make reaction with the rubber, and the increase of the surface of caustic soda residue may
decrease the strength. The influence of the content of NaOH on strength growth ratio gradually
decrease with the increase of the freeze-thaw cycles, so the differences of strength growth ratio are
reduced for different contents of NaOH as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Strength growth ratio of concrete with pre-treated rubber particles for freeze-thaw test.
IWMCE 2018 - International Workshop on Materials, Chemistry and Engineering
310

Table 2 shows the mass growth ratio in the process of freeze-thaw test. The results show that the
mass of the freeze-thaw samples tended to increase with the increase of the cycling times. The reason
for the increase of the mass may be that the tested samples absorbed water or were even hydrated
during the freeze-thaw cycles. In order to decrease the mass growth rate, it is necessary to select
reasonable content of NaOH, in fact, the mass growth ratio is the most satisfactory for the treated RC
with a content of 3% of NaOH as shown in Table 1.
Table 2.
Mass loss rate for different recycling times for re-treated rubber concrete.
3.3 Anti-sulfate analysis
The treated RC specimen was cured 7 days in the standard curing room with a temperature of 20
2 °
C, and a relative humidity is higher than 95%, then it was taken out to soak in sulfate liquor with 5%
solubility. The strength of the specimen at different rubber mass fractions was determined, and the
strength growth ratio was also used to evaluate the anti-sulfate properties.
Figure 3 shows that the strength growth ratio for treated RC with different contents of NaOH
solution. The results show that when the rubber mass fraction is between 12% and 31%, the strength
is higher than that of the normal concrete for RC treated with the content of 10% of NaOH, and the
strength is higher than that of the normal concrete when the rubber mass fraction is about 25% for
the RC treated with the content of 5% of NaOH. The strength growth ratio decreases obviously for
the case of the content of NaOH is lower than 5%, it means that the method to treat RC with low
content of NaOH is not so efficient to improve the anti-sulfate properties.
Mass growth ratio (%)
Cycling
times
Mass fraction
for rubber
0-0%
0-1%
0-3%
0-5%
0-10%
0
0%
0
-0.43
-0.87
-0.51
-0.34
5%
0.34
-1.32
-2.22
-1.74
-0.97
15%
2.72
3.18
1.76
2.95
3.95
25%
15.64
5.46
3.67
5.09
6.38
35%
16.55
8.16
5.23
7.93
8.94
Cycling
times
Mass fraction
for rubber
25-0%
25-1%
25-3%
25-5%
25-10%
25
0%
0.53
-0.26
-0.49
-0.31
-0.15
5%
0.73
-0.57
-1.07
-0.75
-0.43
15%
5.59
5.97
3.56
4.92
6.54
25%
23.47
10.52
6.35
8.79
11.15
35%
28.44
13.25
8.74
11.27
16.12
Cycling
times
Mass fraction
for rubber
50-0%
50-1%
50-3%
50-5%
50-10%
50
0%
1.47
-0.12
-0.21
-0.23
-0.09
5%
1.64
-0.27
-0.59
-0.38
-0.21
15%
11.21
9.47
5.67
7.94
10.74
25%
33.53
16.98
8.94
13.37
18.77
35%
37.67
19.56
13.26
15.93
21.43
Experimental Study on the Strength and Durability of Concrete with Treated Rubber Particles
311
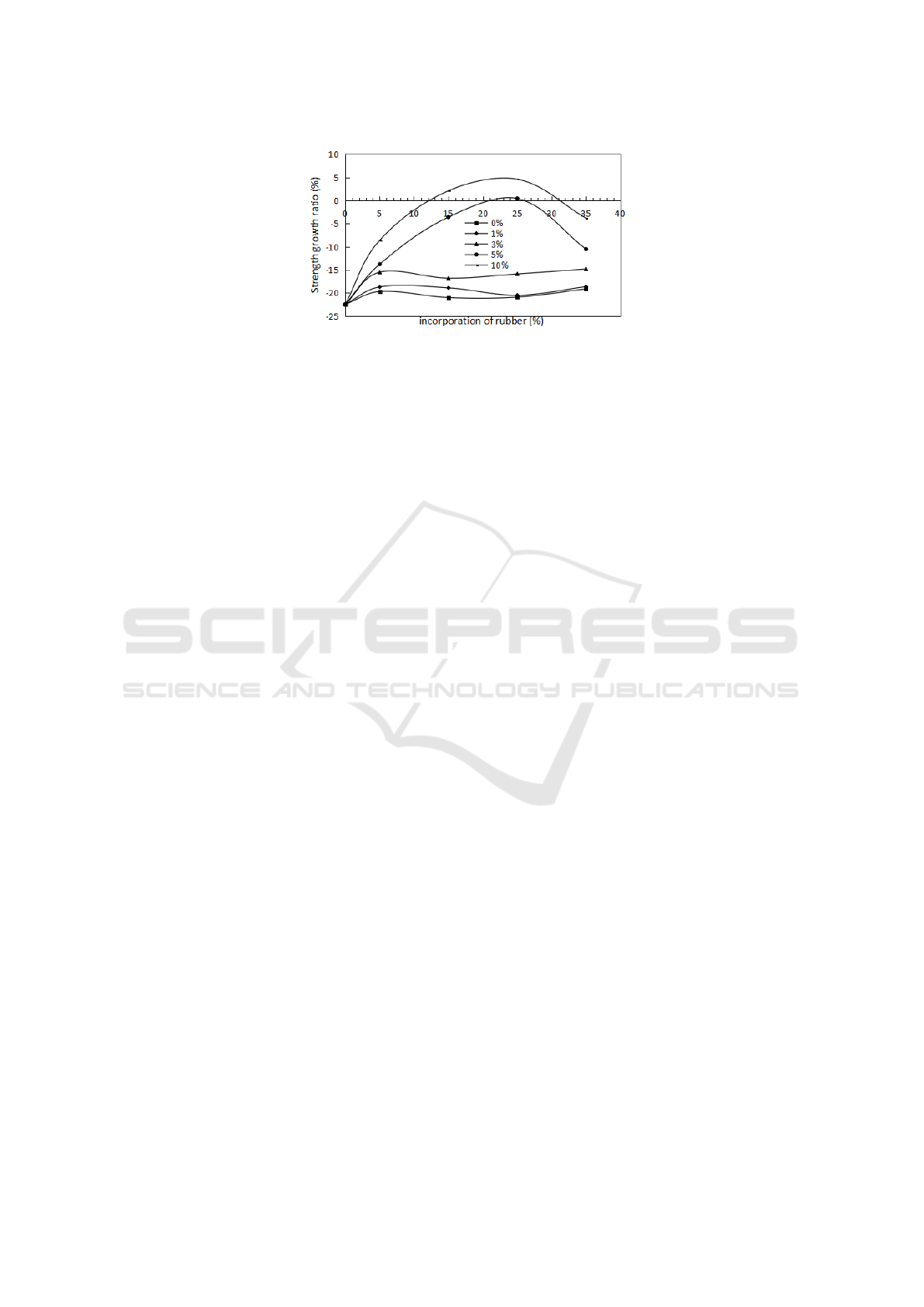
Figure 3. Anti-erosion of concrete with treated rubber particles.
4. Conclusions
The rubber particles treated with NaOH solution were used to replace part of fine aggregate in
concrete to improve the strength and durability of RC in this paper, and the following conclusions
can be obtained:
The treated RC is beneficial to improve the cube strength and axial strength for the case that the
content of NaOH is lower than 5%, and to improve the flexual strength for the case that the content
of NaOH is lower than 10%,and the optimal content of NaOH is 3%.
The strength growth ratio decreases obviously for the treated RC with higher freeze-thaw cycles,
and the content of 3% of NaOH is effective to get the lowest mass growth ratio.
The method to treat RC with low content of NaOH is not so efficient to improve the anti-sulfate
properties.
Acknowledgment
This work is financially supported by grants from the NSFC (10772047/A020206,
11172066/A020305), Foshan Science and Innovate Platform for University and Hospital
(2016AG100341), Foshan University Free Exploration Fund (2016LGZ06). Work partially supported
by Training Plan to Innovation and Enterprise of National University Students, Foshan University.
References
[1] Youssf O, ElGawady M A, Mills J E and Ma X 2014 Constr. Build. Mater. 53(0) pp522-532
[2] Youssf O, ElGawady M A, Mills J E and Ma X 2017 Acids Mater. SP (314-02)
[3] Richardson A, Coventry K, Edmondson V and Dias E and Cleaner J 2016 Prod. 112 pp599-
606
[4] Mehta P K 2001 Concr. Int. 23 (10) pp61-66
[5] Yung W H, Yung L C and Hua L H 2013 Constr. Build. Mater. 41pp665–672
[6] Thomas B S, Gupta R C and Panicker V J 2016 Journal of Cleaner Production 112 pp504-513
[7] Guo H, Shi C J, Guan X M and etc 2018 Cement and concrete composites 89 pp251-259
[8] Topçu I B and Demir A 2007 J Mater. Civ. Eng. 19 (2) pp173–178
[9] Huang B, Shu X and Cao J 2013 Constr. Build. Mater. 40 pp270-274
[10] Long G, Ma K, Xie X and Xie Y 2013 J. Build. Mater. 16 (5) pp758-762
[11] Shu X and Huang B 2014 Constr. Build. Mater. 67 pp217-224
[12] Si R Z, Guo S C and Dai Q L 2017 Construction and building materials 153 pp496-505
IWMCE 2018 - International Workshop on Materials, Chemistry and Engineering
312
