
Study on Matric Suction of Silty Clay Modified by INDUSTRIAL
Wastes
Dongxue Li
1
, Haibin Wei
2,*
, Jiangkun Jia
3
, Yangpeng Zhang
2
and Qiuqi He
2
1
Jilin Provincial Transport Scientific Research Institute,Changchun 130000, China;
2
School of Transportation, Jilin University, Changchun 130000, China;
3
China Railway 16th Bureau Group Luqiao Engineering Construction Co.Ltd., Beijing,101500,China.
Email:weihb@jlu.edu.cn
Keywords: Matric suction, soil-water characteristic curve, silty clay modified by industrial wastes,
freezing and
thawing cycle
Abstract: Northeast China is located in the seasonally frozen area. Under the influence of low temperature, the roads
are prone to serious problems. Modification of subgrade soil with industrial waste can effectively prevent
road problems. In this study, fly ash and rubber crumbs were selected to be mixed with silty clay as roadway
subgrade to prepare modified soil specimens with different dry densities. Matric suctions of the modified
soil specimens were measured and compared to those of the unmodified soil specimens. Soil water
characteristic curves for both modified and unmodified soil specimens were investigated and stability under
low temperature was studied. The test results show that the matric suction changes with the density, but the
change of the modified soil is smaller than that of the unmodified soil. The stability of the modified soil is
better especially at low temperatures.
1 INTRODUCTION
Northeast China is in the seasonally frozen area.
There is freezing and thawing of soil water in winter
and spring. The freeze-thaw cycle will make soil
moisture migrate and bring some disasters to
engineering. Subgrade soil modified by industrial
waste slag can effectively prevent road problems.
The amount of fly ash and waste rubber is very
large. By 2010, the discharge of fly ash in China had
reached 200 million tons (Jiang, 2011). In 2016,
there are almost 300 million tire wastes in China,
with a weight of more than 10 million tons, and the
tire wastes produced every year are growing at a rate
of 8- 10 percent (Xiao, 2017). These two kinds of
industrial waste used to modify silty clay can not
only realize the reuse of industrial waste but also be
used as subgrade filler.
Most of the subgrade soil is unsaturated soil. The
matric suction can well characterize the state of
water in the soil, and it also reveals the strength of
the force between water and soil particles. At
present, the research on matric suction is mainly
focused on the method of measurement, influencing
factors, and applications. ZHU Yan-bo et al. studied
the effect of different water contents, different dry
densities and grading curves on the SWCC of the
siltized intercalation of red-bed soft rock (Zhu et al.,
2013). LI Shun-qun et al. discussed the error in the
measurement of the matric suction in the axis
translation technique (LI, et al., 2016). JU Chang-
wei et al. summarized and introduced the
measurement methods of matric suction (JU and LI,
2016). Many scholars also use soil and water
characteristic curves to predict shear strength and
permeability coefficient (Pujiastuti et al., 2018; Li et
al., 2013).
From the point of view of current research, the
studies of matric suction after freeze-thaw cycles are
still few, so this paper studies the matric suction of
modified soil and unmodified soil in the normal
state and after the freeze-thaw cycles.
Li, D., Wei, H., Jia, J., Zhang, Y. and He, Q.
Study on Matric Suction of Silty Clay Modified by INDUSTRIAL Wastes.
In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Environment and Geoscience (IWEG 2018), pages 557-560
ISBN: 978-989-758-342-1
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
557

2 MATERIALS AND
EXPERIMENTAL METHODS
2.1 Basic Physical Indices of
Experimental Materials
The experimental silty clay is taken from the
homogeneous soil layer at the bottom of the
foundation pit of a large construction site in
Changchun City. Fly ash is taken from the Second
Heating power plant in Changchun. According to
the classification standard of American test materials
Association, F type fly ash is adopted in this study.
Its composition and ignition loss are shown in Table
1.
Table 1: Composition and loss on ignition of fly ash.
SiO
2
+Al
2
O
3
+Fe
2
O
3
(%)
CaO
(%)
SO
3
(%)
Mg+Ti+K
oxides (%)
Loss on
ignition
(%)
88.64 0.92 0.24 6.01 4.19
The rubber crumbs are obtained from rubber tires
scraps ground at normal temperature. This method
has the advantage of simplicity, low cost and high
conversion rate. The size of rubber crumbs used in
the experiment is between 1-2mm and the apparent
density of rubber crumbs is 1.19g/cm3.
According to the dry weight ratio of 65.3 : 32.7 :
2 (Li, 2012), soil, fly ash and rubber crumbs were
mixed. The physical parameters of modified soil are
shown in Table 2:
Table 2: The physical parameters of the modified soil.
Liquid
limit
Plastic
limit
Index
of
plasticit
y
Optimu
m water
content
Maximu
m dry
density
Modified
soil
38.33
%
24.88
%
13.45
%
15.38% 1.73g/c
m
3
Unmodifi
ed soil
34.00
%
22.40
%
11.60
%
12.10% 1.92g/c
m
3
2.2 Experimental Principle
Operation of the filter paper method is simple, and it
has the advantage of a low price and good accuracy
(Bulut, 2001). The filter paper method is based on
the hypothesis that suction in filter paper and soil are
balanced through the movement of moisture. When
the dry filter paper is put in the soil sample and
directly in contact with it, water flows from the soil
into the filter paper and reaches the balance. Then
the water content of filter paper at equilibrium is
measured. The water content in the filter paper is
related to the suction, through the calibration curve
of the filter paper (Fredlund and Rahardjo 1993).
When the filter paper is directly in contact with the
soil sample, the equilibrium moisture content of the
filter paper is representative of the matric suction of
the soil. In this paper, the filter paper method is used
to measure the matric suction, and filter paper
Whatman No.42 model is selected. The calibration
curve formulas of this type of filter paper are as
follows (ASTM International, 2010):
%)47(0779.0-327.5lg ≤=
ff
wwS
(1)
%)47(0135.0412.2lg >−=
ff
wwS
(2)
2.3
Experiment Scheme
Test soil specimens with dry densities of 1.73g/cm
3
,
1.64g/cm
3
and 1.61g/cm
3
were prepared. According
to the optimum water content, five different mass
moisture contents were chosen: 11.38%, 13.38%,
15.38%, 17.38%, 19.38% for soil samples to
determine the matric suction. In freeze-thaw cycle
test, the freezing temperature is -15
o
C during the
freezing process (Bing, 1992), the thawing
temperature is room temperature during the thawing
process, about 10
o
C.
Freeze-thaw cycle consists in freezing for 24
hours followed by melting for 24 hours. The
samples with mass moisture contents of 11.38%,
15.38%, and 19.38% experienced 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 freeze-
thaw cycles. During the freeze-thaw cycle, soil
samples were coated with preservative film to
prevent moisture loss. Matric suctions were
measured on the original and modified soils after
each freeze-thaw cycle.
3 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
AND ANALYSIS
3.1 The Results of Matric Suctions
The relationship between the matric suction and the
water content is reflected by SWCC. For modified
soil and unmodified soil, the influence of the
different water contents and dry densities were
considered. The results of the test are shown in
Table 3.
IWEG 2018 - International Workshop on Environment and Geoscience
558
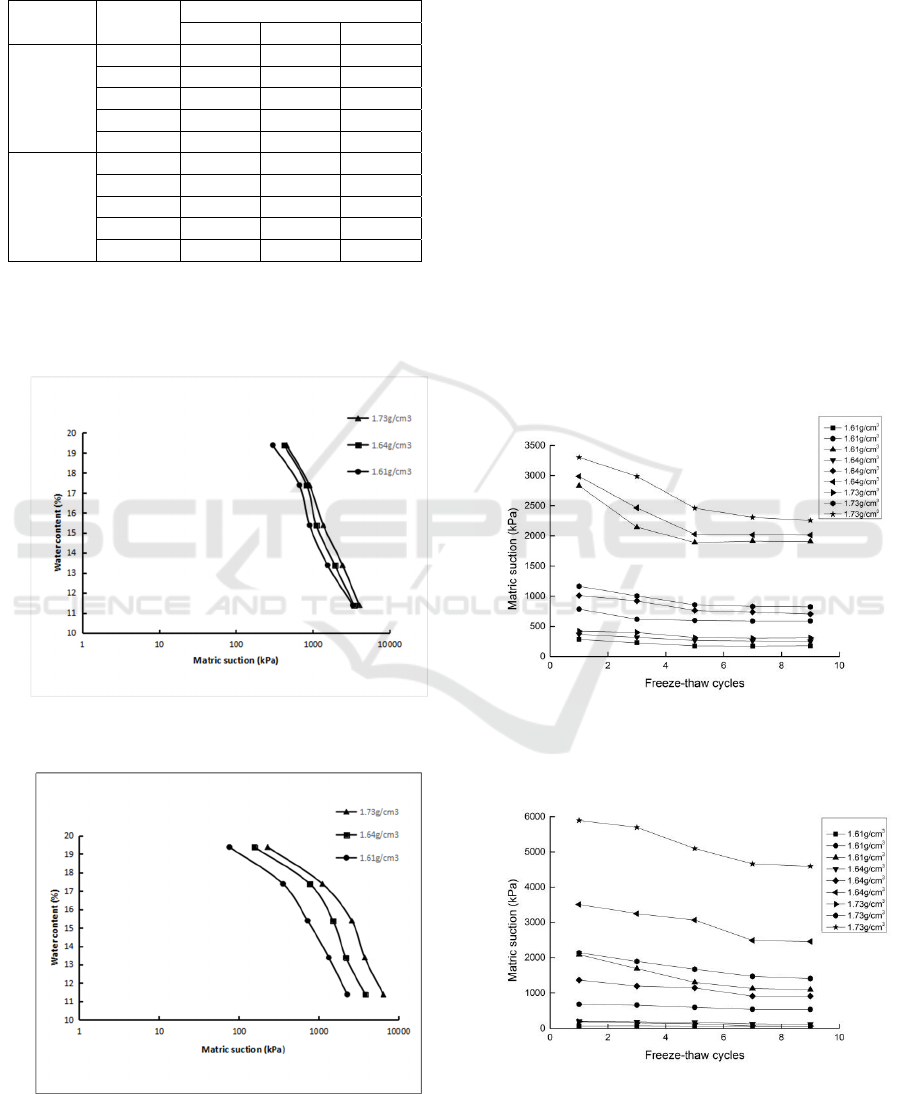
Table 3: The matric suction of the modified soil and the
silty clay.
Soil Water
content
Dr
y
densit
y
(
g
/cm
3
)
1.73 1.64 1.61
Modified
soil
11.38% 4022.44 3452.23 3309.94
13.38% 2438.33 1932.47 1554.73
15.38% 1368.77 1109.92 906.19
17.38% 902.23 832.60 668.56
19.38% 458.20 425.23 301.97
Silty
clay
11.38% 6448.63 3812.77 2278.34
13.38% 3760.99 2191.10 1334.99
15.38% 2589.54 1509.49 726.17
17.38% 1111.60 771.83 356.34
19.38% 229.41 156.32 76.02
Water content is set to Y-axis, logarithmic of the
matric suction is set to X-axis. The curves are shown
in Figures 1 and 2.
Figure 1: The soil water characteristic curves of modified
soil.
Figure 2: The soil water characteristic curves of silty clay.
Figure1 and Figure 2 show that, for the two
kinds of soils, the matric suction increases with dry
density. When the density becomes large, the soil
changes from loose condition to compact condition.
The arrangement of soil particles becomes denser,
the contact between particles increases as the space
between particles becomes smaller. It causes water
content to decrease and matric suction to increase.
The increase of dry density makes the void ratio
decrease, it is difficult for air to enter the soil, and
drainage becomes difficult. The difference between
the two kinds of soils is the changes of the matric
suctions: in the original soil, changes are much
larger than in the modified soil at different dry
densities. It may be related to the structure of the
pores.
3.2 Experimental Results of Freeze-
Thaw Cycle
Figure 3: The matric suction of the modified soil after
freeze-thaw cycles.
Figure 4: The matric suction of the silty clay after freeze-
thaw cycles.
Study on Matric Suction of Silty Clay Modified by INDUSTRIAL Wastes
559

To study the influence of freeze-thaw cycle times on
the two kinds of soils matric suction, the relationship
between freeze-thaw cycle times and matric suction
is shown in the Figures 3 and 4.
It can be seen from Figures 3 and 4, that the
matric suction of the two kinds of soils decreases
first and then tends to be stable as freeze-thaw cycle
time increases. For the modified soil, the matric
suction remains stable after 5 freeze-thaw cycles. As
for the unmodified silty clay, the matric suction
tends to be stable after 7 freeze-thaw cycles. The
effect of dry density on the matric suctions is still
obvious after freeze-thaw cycles. The matric suction
of soils at high dry density is higher than that of
soils at low dry density. The reason for this
phenomenon lies in adsorption and capillary effects
in soils. During the freezing and thawing processes,
the space between soil particles become greater, Van
der Waals' forces and electrostatic forces in the
space between soil particles decrease. So, the
adsorption and capillary effect is weakened. After
several freeze-thaw cycles, the equilibrium between
the particles is reached, the matric suction reaches a
stable state too.
4 CONCLUSIONS
For two kinds of soils, the matric suction
consistently decreases with the increase in water
content. The matric suction increases with the
increase in dry density.
It can be concluded from the SWCC that change
in the matric suction of the modified soil is smaller
than that of the unmodified soil when the density is
changing.
The matric suction of the two kinds of soils
decreases with the increase in freeze-thaw cycles
time. The modified soil stabilizes after the fifth time
freeze-thaw cycle, and the silty clay stabilizes after
the seventh time freeze-thaw cycle. The modified
soil tends to be stable quicker than the silty clay
after freeze-thaw cycles.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the National Natural
Science Foundation of China [grant number
51578263]; Transportation Science & Technology
Program of Jilin Province [grant number 2015-1-11]
and [grant number 20180201026SF].
REFERENCES
ASTM International.D5298-10 Standard test method for
measurement of soil potential (suction) using filter
papers, S. West Conshohocken:ASTM
International,2010
Bing Wenshan 1992 Road frost damage and prevention,
M. Harbin Institute of Technology press
Bulut R 2001 soil suction measurements by filter
paper[C]// ASCE 2001 CIVIL ENGINEERING
CONFERENCE. 243-261
Fredlund D G and Rahardjo H 1993 Soil mechanics for
unsaturated soils, M. Wiley
Jiang Wu Yan 2011 Application of fly ash in soil
rehabilitation and improvement. Coal Processing &
Comprehensive Utilization
JU Shangwei and LI Xiongwei 2016 Analysis and
Application on Matrix Suction Testing of Unsaturated
Soil. Journal of Changzhou Institute of Technology
Li Changyu 2012 Experimental study on mechanics
effects of fly ash soil improved by rubber particles
under freeze-thaw cycle, PhD. JiLin University
Li P, et al. 2013 Soil-water characteristic curve and
permeability perdiction on Childs & Collis-Geroge
model of unsaturated loess. Rock & Soil Mechanics
LI Shun-Qun, et al. 2016 Limitation and error analysis of
axis translation technique for measuring and
controlling matric suction. Rock & Soil Mechanics
Pujiastuti, Heni, et al. 2018 The effect of matric suction on
the shear strength of unsaturated sandy clay.
International Journal of Geomate 14.42 112-119
Xiao Yu 2017 The pollution of waste rubber is becoming
more and more serious. Waste rubber has become
black pollution.
http://news.feijiu.net/infocontent/html/20179/14/14386966
.html, 2017-09-14/2018-05-07
Zhu Y, et al. 2013 Experimental study of soil-water
characteristic curves of siltized intercalation of red-bed
soft rock. Zhongnan Daxue Xuebao 44.7 2919-2926
IWEG 2018 - International Workshop on Environment and Geoscience
560
