
Anomaly Extraction Technique of Airborne Gamma Spectrometry
Based on 2-D Wavelet
Kun Sun, Liangquan Ge*, Fei Li, Meng Wang , Xian Guan ,Yi Gu and Qingxian Zhang
The College of Nuclear Techonology and Autornation Engineering, Chengdu University of Techonglogy, Chengdu 610101,
China.
Email: glq@cdut.edu.cn
Keywords: Airborne gamma spectrometry, 2-D wavelet, anomaly extraction
Abstract: This paper uses 2-D wavelet transform to process the uranium specific activity data of 1:5000 airborne
gamma-ray spectrometry production data in a survey area in Inner Mongolia, and uses the distribution of
paleo-uranium abundance to correct the extracted anomaly areas. The experiment shows that, with small
area and high uranium ore concentration, the anomaly areas extracted by 2-D wavelet method are consistent
with the metallogenic environment. This method also appears to be insensitive to low concentration uranium
areas which may help in guiding for metallogenic prognosis.
1 INTRODUCTION
Airborne gamma-ray spectrometric survey has the
advantages of high detection efficiency, lo w cost,
and covering large areas for surface concentrations
of various gamma emitting radionuclides
(Wan et al.,
2012). At present, 80% of China's uranium deposits
were found by airborne gamma-ray spectrometric
survey (Liu et al., 2002). Due to the low intensity of
airborne gamma-ray spectrometric signals, the
signals caused by ore-bodies are easily comb ined
with other external measurement signals (reflected
informat ion on detector by lithology, soil type,
humid ity, vegetation coverage density, water area
distribution, etc.) (Ge et al., 2016, Xiong, 2016 ),
making it more difficult to extract ano malous areas,
making it more difficult to extract anomaly areas.
The method of e xtract ing anomalous information
fro m airborne gamma -ray spectrometry data is
similar to geochemical data anomalous informat ion
extraction method. In recent years, many scholars
have tried to use wavelet mu lti-scale analysis to
extract anomaly information. Gan Yuan et al.
(2013)used wavelet multi-scale analysis to filter and
denoise wavelet on field X-ray fluorescence
geochemical data
(Gan, 2013). The extracted
anomalous information a reas are s maller than those
extracted by the conventional method and are highly
consistent with actual geological background. Nan
Yan et al. (2017)applied wavelet analysis to
delineate the ano maly limit of geochemical
exploration in the Dabat area of Xin jiang(Nan et al.,
2017). The ext racted anomalous information is
consistent with the spatial distribution of known ore
sites and some extremely weak anomalies were
extracted.
As the airborne gamma-ray spectrometric survey
system is vulnerable to external factors, the collected
usable signals are easily interfered by other signals.
The wavelet t ransform has good time -frequency
characteristics and is good at handling non-
stationary signals. Traditional wavelet analysis
ignores the spatial location informat ion of survey
areas. The 2-D wavelet transform co mb ines the
spatial location information of survey areas with the
element content information, deco mposing the data
and reconstructing the low-frequency part.
According to the reconstructed data, the anomalous
informat ion in the survey area is e xt racted to
improve the accuracy of any anomaly information in
the survey area and reduce the areas of false
anomalies, which provides a basis for aiding in
prospecting.
Sun, K., Ge, L., Li, F., Wang, M., Guan, X., Gu, Y. and Zhang, Q.
Anomaly Extraction Technique of Airborne Gamma Spectrometry Based on 2-D Wavelet.
In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Environment and Geoscience (IWEG 2018), pages 283-287
ISBN: 978-989-758-342-1
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
283

2 METHODS
2.1 2-D Wavelet
The basic principles of 2-D wavelet used to extract
the anomalous information fro m airborne gamma-
ray spectrometry data are as follows. Let
2
f( , )
x y L
be a 2-D signal, x, y denote the
horizontal and vertical coordinates, and
(x,y)
denotes 2-D wavelet basis function, then 2-D
continuous wavelet definition is (Daubechies, 2011):
12
12
a;b ,b 1 2
1
( , ) , a 0; ,
x b x b
x y b b R
aa
a
(1)
Where,
12
a;b ,b
( , )
xy
is a 2-D wavelet
generating function,
a
is a scaling factor, and
12
,
bb
is displacement factors. Let
2 , * ;
j
a b n a j Z
, so 2-D
continuous wavelet transform can be discretized:
12
2
j;k ,k 1 2
( , ) 2 2 ,2
j
jj
x y x k x k
(2)
So 2-D discrete wavelet transform is:
12
f 1 2 ; ,
( ; , ) ( , ), ( , )
j k k
WT j k k f x y x y
12
2 ( , ) (2 ,2 )
j j j
f x y x k y k dxdy
(3)
The simplified formu la for 2-D wavelet
decomposition is as follows:
f( , ) ( , ) ( , ) ( , ) ( , )
H Y D
x y L x y H x y H x y H x y
(4)
Where,
( , )
L x y
and
( , )
H
H x y
,
( , )
Y
H x y
,
( , )
D
H x y
are the approximate components of the
original signal
f( , )
xy
and the detail co mponents
in the horizontal, vertical, and diagonal directions,
respectively.
Anomaly Extraction Technique
2.2 Anomaly Extraction Technique
Differences in wavelet basis functions lead to
differences in the results of different transformat ion
types. It may not be easy to accurately distinguish
the better and less preferable these extracted
anomalous information by naked eye. Therefore, the
standard deviation coefficient of variation
(hereinafter referred to as CV) can be used to
identify whether or not the optimal deco mposition
level has been reached after 2-D wavelet
decomposition.
Since the ore-bearing areas are all in the areas
with high CV
(Sun, 2009), the CV of gamma-ray
spectrometry can reflect the variation degree of the
contents of uranium, thoriu m, and potassium
contents in the survey area. Therefo re, it can be used
to study the spatial distribution of radioactive
elements, as a geological general survey and
prospecting tool.
CV is the ratio o f the samp le mean square error
to the sample mean
(Gilbert and Richardo, 1988). In
the anomaly extract ion of airborne gamma-ray
spectrometry data, the standard deviation CV
(Sun,
2009, Zhang and Xiong, 1990) is used to measure
the degree of data dispersion and to predict
metallogenetic probability. The formula is as follow:
2
1
1
()
n-1
n
i
i
XX
CV
X
(5)
Where,
X
is the mean value of an element in the
survey area;
n
is the total survey points of the
survey area;
i
X
is the element content value of a
survey point in the survey area. In a stable
geological structure, the element
content value has small fluctuation range, strong
resistance to external disturbances, and low
CV. With an inho mogeneous geological structure,
the element content value in the ore-bearing
strata has high CV, which is conducive to
discovering ore-causing information.
The 2-D wavelet deco mposition process is: First,
the wavelet decomposition is carried out in the
horizontal d irection of the data matrix; secondly,
decompose the two decomposed sub-bands along
the vertical direction; reconstruct the reconstructed
low-low frequency part and calculate its CV;
identify if there is a mutation in the CV: if it is not
mutated, iteratively deco mpose the low-low
IWEG 2018 - International Workshop on Environment and Geoscience
284
frequency part, and if it is mutated, output low-low
frequency part.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Survey Area
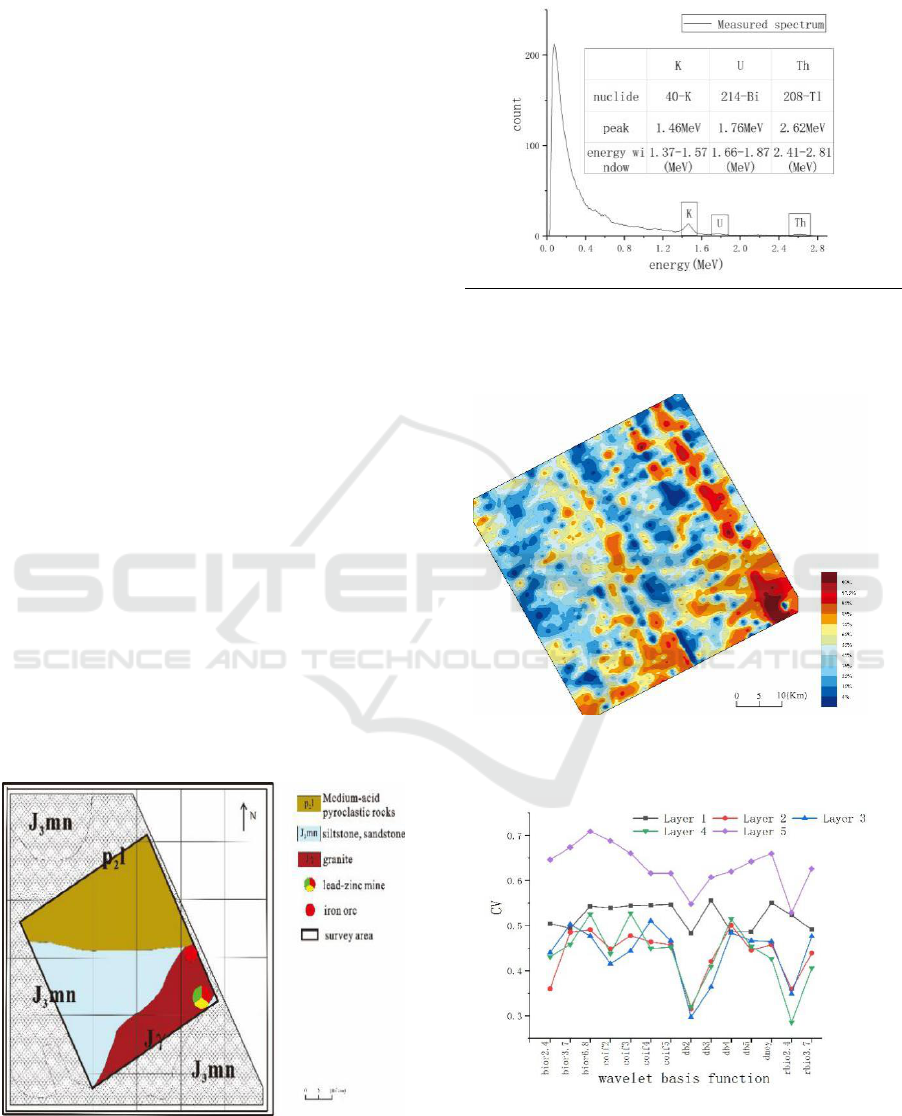
This project selects A GS863 Airborne γ
spectrometry 1:5000 data of Chengdu University of
Technology of a survey area in Inner Mongolia as a
data source for data processing. The geological map
of the survey area is shown in Figure 1. W ith five
4L NaI crystals, the AGS863 is a array NaI detectors
installed in Y-12 aircraft.The aircraft is equipped
with data co llect ion system, rad io altimeter, and
global positioning system. Its flying speed is 250
km/h and the average flying height is 180 m.
AGS863 records a data of full spectrum every
second. Full spectrum measured by γ spectrometry
is shown in Figure 2.
The survey area is approximately 1,000 square
kilometers, with a total of 21 survey lines and 6,705
survey points. The measured data was corrected by
altitude, at mospheric radon, aircraft background, and
cosmic ray background. Use Kriging to interpolate
the original data (256* 256) and draw a contour map
(shown in Figure 3). The h ighest uranium specific
activity value is 37.204(
g/
g
); the lo west value
is 0.049(
g/
g
); the average value is
3.968(
g/
g
).
Figure 1: Geological map of the survey area.
Figure 2: Actual measured full spectrum.
Figure 3: Uranium specific activity contour map.
Figure 4: Coefficient of variation after decomposition
and reconstruction of different wavelet basis functions.
Anomaly Extraction Technique of Airborne Gamma Spectrometry Based on 2-D Wavelet
285
3.2 Extraction of Uranium Elemental
Anomaly Information
This paper uses 2-D wavelet transform method to
extract anomalies and compares it with the
traditional one. Because the airborne gamma-ray
spectrometry data is discrete, the frequently-used
wavelet basis functions that can be used for discrete
wavelet transform are Biorthogonal (biorNr.Nd),
Coiflets (coifN), Daubechies (dbN), Meyer (mey r)
and ReverseBior (rbioNr.Nd) (the functions in the
modules that contain wavelet basis functions in
MATLAB can directly be called). Use the above
five discrete wavelet basis functions to decompose
and reconstruct the data, respectively, and calculate
the CV of each processed data by formula (5). The
results are shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4 shows that when decomposition level is
the same, the CV of each data possessed by different
wavelet basis functions are quite different. The CV
of data processed by the same wavelet basis function
have a negative correlation with the decomposition
level at level 1-4, and when the decomposition level
is at 5, the CV of the data reaches the maximu m;
when the decomposition level is at 1-4, the change
rate of CV is s mall and the overall trend is relatively
stable, which show that wavelet decomposition has a
small impact on the whole data.
The author uses traditional statistical method and
2-D wavelet method (wavelet basis function is
bior6.8; deco mposition level is at 5) to extract
anomalies from the data and compare the extracted
anomalies. The results are shown in Figure 5.
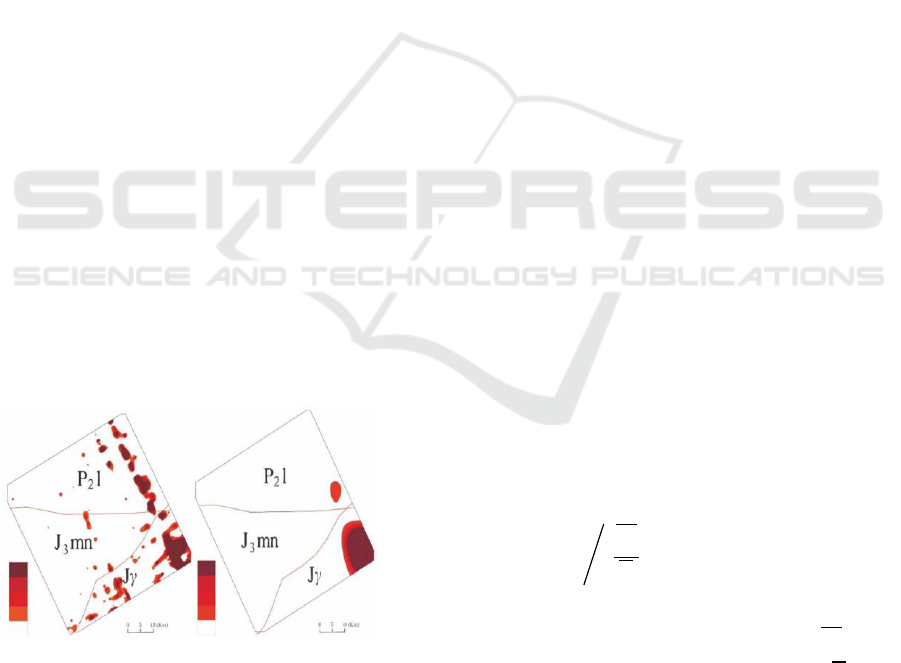
Figure 5(a): Traditional method to extract the
anomaly area. (left)
Figure 5(b): 2-D wavelet to extract the anomaly area.
(right)
As shown in Figure 5(a), the ano malous
informat ion extracted by the traditional statistical
method has a large area, and the banded anomaly
interference in formation is obvious and scattered.
The reason is that the original data does not have an
approximately normal distribution, and the high-
value point data is missing during iterative reject
phase, resulting in the anomaly threshold value
being determined only by the background value.
The advantage of the 2-D wavelet method is that
it can co mbine the element content information of
survey points with the spatial position information;
there are two ore occurrences in the survey area, one
is lead-zinc ore with high U content and one is iron
ore with low U content. In Figure 5(b), there are
only two anomalies. The central location and
anomaly shape of the anomalous areas are consistent
with the actual ore occurrences, indicating that the
results do not contain false anomalies. Since the
low-frequency parts only contain ore-bearing and
background information, and the ore-bearing
informat ion are represented by high value ano malies.
Therefore, the ano maly a reas in the figure may be
ore-bearing areas.
3.3 Verification of Uranium Elemental
Anomaly Information
The paleo-uraniu m abundance refers to the uranium
content of an area in its beginning of diagenesis. In
the initial stage of diagenesis, U and Th have the
same chemical properties and no migration occurs ;
When the later environ ment beco mes an oxidation
environment, U migrates, while the chemical
properties of Th are relatively stable and remain in
place. The uran iu m ano maly areas indicated by
paleo-uraniu m abundance are source beds. Formula
6 is the fo rmula for the calculation o f paleo-uraniu m
abundance(Dai, 2002):
u ( )
Th
G Th
U
(6)
In formu la (6):
Th
is the thoriu m content of a
certain survey point in the survey area;
Th
is the
average thorium content in the survey area;
U
is the
average uranium content in the survey area.
Using formu la (6) to calculate the paleo-uraniu m
abundance in the survey area, the result is shown in
Figure 6.
At the beginning of diagenesis, uraniu m is
mainly concentrated in granite. The main lithology
IWEG 2018 - International Workshop on Environment and Geoscience
286

in the southeastern part of the survey area is granite,
with an approximately triangular distribution. Figure
6 shows that the primary uraniu m element is mainly
concentrated in the southeast of the survey area, and
its distribution profile co incides with the profile of
the high uranium value area, indicating that there are
ore-bearing strata in this area and it has meta llogenic
conditions. Therefore, 2-D wavelet processing was
effective at locating ore-bearing units.
Figure 6: Distribution of paleo-uranium abundance.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In order to explore the advantages of 2-D wavelet
method in the extraction of ano malous information
of airborne gamma spectrometry data, comb ined
with the distribution of ancient uraniu m, an ano maly
extraction technique based on two-dimensional
wavelet method was applied to a gamma-ray survey
area. Co mpared with anomaly areas extracted
by traditional method, the anomaly areas extracted
by 2-D wavelet methods were sma ller and have a
more obvious concentration trend. These anomalous
areas were in accordance with the actual ore
occurrences and no false anomalies in the survey
area were detected. The result shows that the 2-D
wavelet methods can effectively extract the
anomalous informat ion fro m airborne gamma-ray
spectrometry, and provide a basis for aiding in
prospecting. However, This method is insensitive to
very weak ano malies . It can only extract ano malous
informat ion and somehow depends on the quality of
the original data, so it needs to be further developed.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This article was funded by the National Key R&D
Project (No.2017YFC0602105), the National
Natural Science Foundation of Ch ina (No.
41774147) , Sichuan Science and Technology
Support Program (No. 2015GZ0272)and the
Sichuan Provincia l Department of Education
Research Project (No.16ZA0085). Also thanks to
Professor Zhou Sichun, Doc. Xiong chao for his
guidance and opinions.
REFERENCES
Dai J M 2002 Discussion on characteristic Parameters of
gamma-spectrometric data Uranium Geology 1 52-55
Daubechies I 2011 Ten lectures on wavelets National
Defend Industry Press
Gan Y, Ge L Q, Wang Z, et al. 2013 The research of in-
situ XRF geochemical data processing based on
wavelet transform Nuclear Electronics & Detection
Technology 33 103-106
Ge L Q, Xiong S Q, Zeng G Q, et al. 2016 Airborne
gamma-ray spectrum detection and application BeiJing
Science Press
Gilbert and Richardo 1988 Statistical methods for
environmental pollution monitoring Van Nostrand
Reinhold Co
Liu Y H, Gu R K and Hou Z R 2002 Airborne
radiometrics survey Geophysical and Geochemical
Exploration 4 250-252
Nan Y, Lei Z Q, Xu Y, et al. 2017 Application of wavelet
Analysis to determine the lower limit of Geochemical
exploration in the Da bar area Xinjiang Gansu Science
and Technology 33 20-22+3
Sun Z R 2009 Study on usage of coefficient of variation
for statistics of magnetic Parameters of samples
Geology and Prospecting 45 65-69
Wan J H, Xiong S Q and Fan Z G 2012 The status and
prospects of airborne gamma-ray spectrometry
technology and its application Geophysical and
Geochemical Exploration 36 386-391
Xiong C 2016 The research on anomaly information
extraction method of airborne gamma-ray spectrum
survey Chengdu University of Technology
Zhang W B and Xiong S Q 1990 Airborne gamma-ray
Spectrometric variation coefficient—a useful
Parameter for interpretation Geophysical and
Geochemical Exploration 4 276-284
Anomaly Extraction Technique of Airborne Gamma Spectrometry Based on 2-D Wavelet
287
