
Sedimentary Facies of the Coal-bearing Walloon Coal Measures in
Tipton Field, Surat Basin
Yong Yang
1*
, Aifang Bie
1
, Hanyu Bie
2
, Ming Zhang
1
, and Zhaohui Xia
1
1
Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration and Development, Petrochina;
2
School of Energy Resources, China University of Geosciences (Beijing)
Email: yangyong@cnpcint.com
Keywords:
Geometry, coal ply, coalbed methane, sedimentary facies, geological model
Abstract: The Walloon Coal Measures(WCM) is the main producing formation in Tipton coalbed methane(CBM)
field in the Jurassic Surat basin of the southeast Queensland, Australia. The numerous, thin, pinching out,
merging, and splitting coal seams in the WCM show highly variable in the spatial continuity. Accurate
determination of the facies, lithological attributes and geometries is important in the CBM exploration and
development planning for Tipton field. In the paper, high resolution sequence stratigraphy is used to build
an isochronal stratigraphic framework of sublayers and coal plies by utilizing all available data from cores
and logs. The key methodology in this procession is to identified single fining-upwards cycles with
sandstone at the bottom and coal, siltstone or shale at the top. Five lithologies of coal, shaly coal, sandstone,
siltstone and shale are classified by density and gamma ray well logs. Six members, 20 sublayers and 125
single coal plies are picked and correlated for the whole WCM. The distributions and geometries of coal and
channel are analysed for each sublayer. The characteristics of the following depositional facies are
interpreted: coal swamp and swamp, major channel, minor channel, floodplain, lacustrine. A concept model
of sedimentation is reconstructed to emphasize the relationships of major facies which is essential for the
further geological modelling, potential sweet spots determining and filed development of the Tipton field.
1 INTRODUCTION
Tipton coalbed methane (CBM) field is in the central
part of Surat Basin, Queensland, Australia. It covers
an area of 200 km
2
and the structure is a southwest
dipping unicline with two near-vertical faults
developed in the north area (Figure 1). A total of 167
wells are drilled and most of them have log data
such as LSD, SSD, gamma ray. The average well
distance is about 600m.
The target formation of the Tipton field is the
Walloon Coal Measures (WCM), which is the main
coal-bearing formation and CBM producing interval
in the Surat basin (Bohacs and Sutter, 1997). WCM
is a formation of middle Jurassic underlain by the
Eurombah Formation and Hutton Sandstone and
overlain by the Springbok Sandstone (Figure 2).
Juandah and Taroom are two main sedimentary
members of WCM with Tanglooma sandstone in
between. The individual seam packages within the
Juandah coal measures are Kogan, Macalister,
Wambo and Argyle. The Taroom has two
recognized coal seams: UpperTaroom and
Condamine which is the thicker and deepest seam.
The WCM consists coal-rich mire and a fine-
grained meandering fluvial system which develops
interbedded sandstone, siltstone, carbonaceous
mudstone, shale and coal (Fielding, 1993). The coal
is low rank with the vitrinite reflectance of 0.4-0.6%
and the net coal thickness is 20-30m deposited in a
fluvial sedimentary system. Many coal plies are
developed with splitting, merging, pinching out and
show highly variable in the spatial continuity.
Moreover, not much knowledge except Tangalooma
sandstone is known about the sandstone channels in
WCM, which have much influenced on the coal beds
continuity and the behaviors of CBM.
Due to these complicated geology, the paper uses
high resolution sequence stratigraphy to build an
isochronal stratigraphic framework of sublayers and
coal plies, and identifies five lithologies to analyze
the distributions of the coal ply and sandstone. The
depositional facies including channel, floodplain,
lacustrine, coal swamp and swamp are characterized
and the concept depositional model is built to better
Yang, Y., Bie, A., Bie, H., Zhang, M. and Xia, Z.
Sedimentary Facies of the Coal-bearing Walloon Coal Measures in Tipton Field, Surat Basin.
In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Environment and Geoscience (IWEG 2018), pages 233-238
ISBN: 978-989-758-342-1
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
233
understand the coal heterogeneity and the
relationships of these major facies.
Figure 1: The structure of Tipton field.
Figure 2: WCM formation of Surat basin.
2 METHODOLOGY
This methodology constitutes a systematic and
effective workflow to delineate the characteristics of
the coal ply and sandstone, and the distribution of
the depositional facies.
Firstly, all wells in the gas field are investigated,
including core data analysis, depth shifting, logs
normalization, lithology and facies interpretation.
Then the ply and sandstone are correlated and the
isochronal stratigraphy framework is built. The
correlation is based on the fining-up sequence cycle,
in which the sandstone bodies are the fluvial
channels at the base then the flooding plains of
siltstones upwards and then the development of the
lacustrine clays and coal swamps. The roof and floor
of the coal plies are manually picked in well section
in order to descript the splitting and merging of the
coal plies in areal and vertical directions. The
boundaries of the sandstone are also picked in order
to better improve channel description quality.
Based on the core descriptions, photographs and
logs of all wells, lithologies and sedimentary facies
are studied to describe the fluvial depositional
system in the gas field. The horizontal distributions
of the coal ply and sandstones are mapped. The
geometry parameters such as the coal thickness, the
area of coal distribution, the width, orientation,
amplitude, wavelength of the channel belts are
studied.
Then finally, the concept depositional model is
generated in which channel, floodplain, lacustrine,
coal swamp and swamp are integrated to describe
the interrelationships of these facies and to improve
the understanding of swamp heterogeneity in fluvial
system.
3 WCM THREE-ORDER
CORRELATION AND
ISOCHRONAL
STRATIGRAPHIC
FRAMEWORK
Correlation within the WCM package are complex
with an absence of marker beds and significant
lithological variations across small aerial distances
(Zhou, 2017). Individual seams are generally not
easy to be correlated due to the very high frequency
of seam pinches, swells, coalescence and
truncations.
For WCM isochronal correlation, a three–order
cycle correlation methodology is used to complete
the work guided by sequence stratigraphy theory.
The correlations in three-order cycle are made on the
basis of log comparison, using similar coal seams to
correlate over short distances and fining upward
IWEG 2018 - International Workshop on Environment and Geoscience
234

packages to correlate over longer distances. The first
order is the correlation of wells between coal
members, and then the sublayers. The third order is
the correlation of wells of single coal ply and
sandstone within each sublayer.
For the coal member division, the best markers
are the Macalister and Condamine which are
considered massive and relatively continuous
(Hamilton, 2014). There is often a gamma baseline
shift between the Macalister and Wambo seam
packages, with an increase in gamma response in the
Wambo. The Tangalooma sandstone at the base of
Argyle can also be regarded as a marker for its
relative lateral continuity.
The Kogan package which is the uppermost of
WCM generally contains one to three coal seams.
The Macalister package generally consists of one or
two well-developed seams and the highest
percentage of coal with a number of smaller
stringers. The Wambo generally consists of thin,
poorly correlatable coal seams. The Argyle package
usually consists of one or two major coaly intervals
with banded coals and muds, and Tangalooma
sandstone is at the base of Argyle which may be
continuous and consists of individual sand lenses in
some area. The Upper Taroom package is generally
a thick zone of thin coal seams, and forms a
relatively thick and continuous single seam at the
base. The Condamine is occasionally present as a
well-developed single seam up to 10m thick.
Sublayer is the general result of one fluvial
decrease period. The sandstone bodies are the fluvial
channels at the base then the flooding plains of
siltstones upwards and then the development of the
lacustrine clays and coal swamps. For sublayer
correlation, the typical single fining upwards cycle
with coal, clay or siltstone at the top and sandstone
at the base. The total of 20 sublayers are picked and
correlated for the whole WCM.
A ply refers to an individual depositional coal
seam and often quickly splits, merges or pinches out
laterally due to the sedimentary complexity. A total
of 125 coal plies, 54 sandstones are divided and
correlated in all 20 sublayers of the six members.
Figure 3 shows the plies correlation in sublayer3 of
Wambo member. Four fining upwards cycles (in red
triangular) are identified with the normalized density
and gamma ray logs. In each cycle sandstones are
divided and plies are picked for correlation. Three
sandstones are picked and the only lowest seems
continuous. The six correlated coal plies show the
high degree changing of lateral heterogeneity.
From members, sublayers to plies, the three-
order sequence stratigraphy correlation framework
are built for the whole WCM in Tipton field.
Figure 3: Coal ply and sandstone correlation.
4 COAL AND SANDSTONE
DISTRIBUTION
Based on the isochronal stratigraphic framework, the
thickness of each ply in each sublayer at well points
are summarized. The main thickness of coal plies is
about 0.5m, and only a few coal plies have the
thickness larger than 5m in WCM of Tipton field
(Figure 4). The horizontal thickness surfaces of each
ply are mapped with the coal ply thickness point
data. From these surfaces the maximum coal ply
thickness and the areal coal area can be picked. Thus
the correlation between coal ply thickness and the
extension area is established (Figure 5). It can be
seen that the coal seam area increases with the ply
thickness.
Figure 4: Histogram of coal ply thickness.
Sedimentary Facies of the Coal-bearing Walloon Coal Measures in Tipton Field, Surat Basin
235
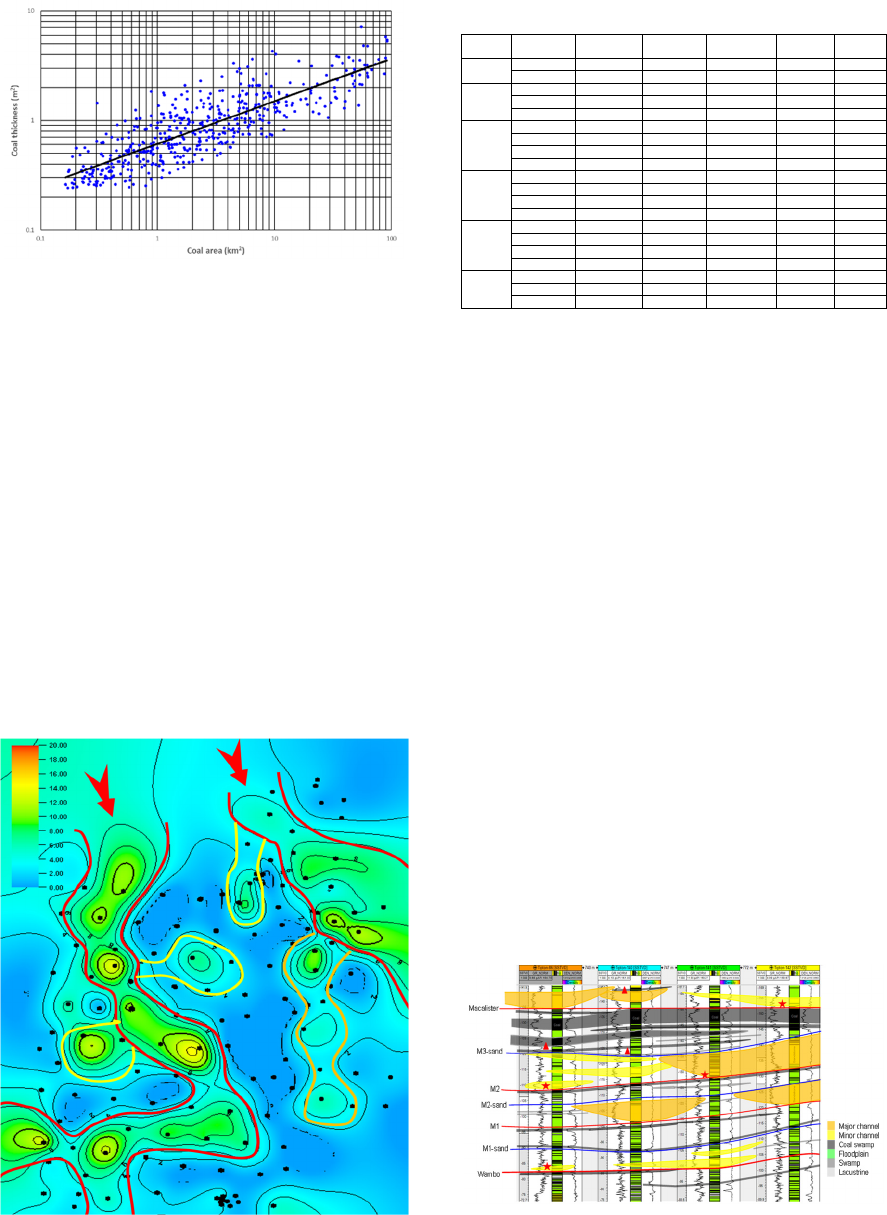
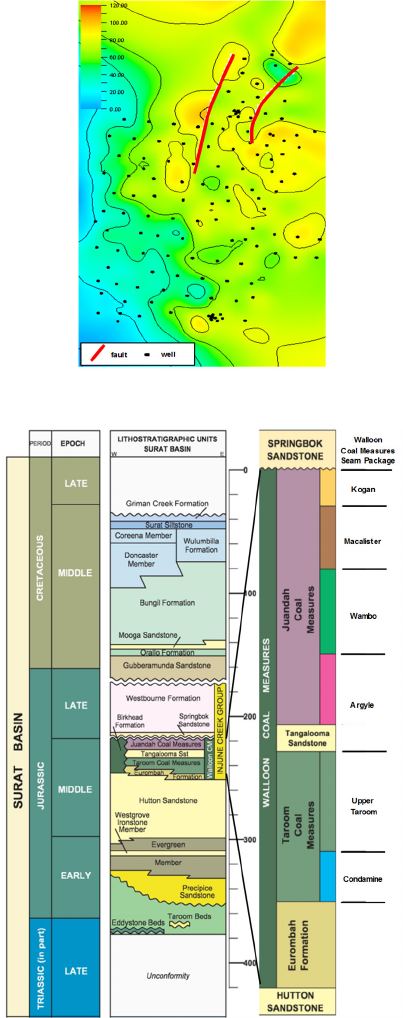
Figure 5: Relationship between coal area and ply
thickness.
The sandstone thickness surfaces are also created
using the thickness from well points. From these
surfaces the channel belts can be identified. Figure 6
is the thickness surface of M1-sand. The red lines
show the major channel, the brown lines the minor
channel and yellow lines the crevasse splay. The red
arrows are the provenance direction. Then the key
parameters such as the amplitude, orientation, width
and wavelength of the channel belts can be obtained.
Table 1 is the parameter summary of major
sandstones in each sublayer of Tipton field. The
main orientation of the channel is from north to
south, and the width is 700- 1500m. The channel
amplitude is 800-1900m, and the wavelength is
1400-4000m. These channel geometry parameters
are important inputs for the facies object modelling
in the future research.
Figure 6: The sandstone thickness surface of M1-sand.
Table 1: The parameters of the channels of each sublayer
Memb
e
r
Sand
name
Orientation
Amplitude
(m)
Wavelength
(m)
Width
(m)
Thickn
ess (m)
Kogan
K2-sand
N
E, E 1000 1800
1000-1500
3-12
K1-sand
N
W, N 1200-1800
1900-4000
1200-1500
3-20
Macalist
er
M3-sand
N
W, N 1000-1200
2000-3000
1000-1200
2-15
M2-sand
N
1200-1500
2500-2700
1000-1400
2-10
M1-sand
N
, NW 1100-1300
1800-2700
1300-1500
5-20
Wambo
W4-sand
N
, NW 900-1000
1900-2000
1000
2-10
W3-sand
N
1000 2400
800
4-10
W2-sand
N
, NW, NE 1000 2400-2600 1200 2-12
W1-sand
N
E, NW, N 1000 2200-2400 900-1200 4-15
Argyle
A4-sand
N
E, NW 1000 2000-2200 1000-1200 3-15
A3-sand
N
E, N 1000 2000-2600 800-1200 4-12
A2-sand
N
E, N 800-900 1900-2200 700-900 4-12
A1-sand
N
W, N 800-1500 2000-2100 700-900 3-16
Upper
Taroom
T4-sand
N
W, N 1000-1900 1800-3000 900-1000 4-17
T3-sand
N
1000-1300 1600-2100 1000-1300 3-16
T2-sand
N
800-1000 2200-2500 800-1000 2-16
T1-sand
N
W,NE 900-1200 1900-2400 1000-1200 4-16
Condam
ine
C3-sand
N
900-1000 2300-2600 1100-1200 4-16
C2-sand
N
, NE 1000 1400-2000 800-1200 2-13
C1-sand
N
, NE 800-900 2400 1100-1200 1-10
5 MAJOR FACIES FEATURES
AND GEOLOGICAL CONCEPT
MODEL
The calibrated facies features of coal-bearing fluvial
system are summarized by combination of core
sample data, lithology log, mud log description,
lithology report and normalization logs (Hoffman,
2009). Six depositional facies are interpreted as
major channel, minor channel, floodplain, coal
swamp, swamp and lacustrine. The lithologies of
coal, shaly coal, siltstone and shale are
approximately corresponded the facies of coal
swamp, swamp, floodplain, lacustrine, respectively.
The sandstone is for the facies of major channel and
minor channel considering the thickness (Martin,
2013). Major channel thickness is usually large than
5m. Note that some thick crevasse splays could have
been interpreted as minor channel. Figure 7 is the
well section interpreting the distribution of the facies
between wells. The red star is the eroded coal by
channel, and the red triangular is the coal overlain on
the abandoned channels. The coal plies severely vary
in lateral with the splitting, merging, pinching out, or
erosion by channels.
Figure 7: Geological concept model of coal-bearing
environment.
IWEG 2018 - International Workshop on Environment and Geoscience
236
5.1 Coal Swamp and Swamp
Coal swamp and swamp are deposited in the
flooding plain. Coal swamp was relative pure coal
and swamp was the coal with shaly or siltstone
which may be more influenced by major or minor
channel system than coal swamp. The coal swamp
facies formed sheet-like deposits which rarely
exceeded 3m in thickness and usually ranged from
0.1 to 2.0m. They are usually underlain by shallow
water, and in some instances they are interbedded
with each other to form coal seams which may
occasionally exceeded 5m in thickness. Channel
system usually has great influence on the geometry
of the coal swamp and swamp (Stuart, 2014).
Usually the coal seams are eroded by the channels,
and coal can also deposit in the abandoned channels.
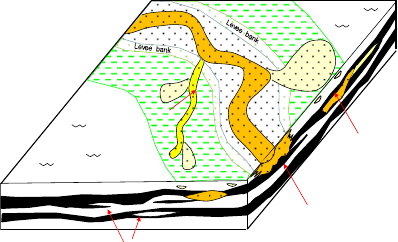
5.2 Channel
Channel deposits in WCM of Tipton field are
dominated mostly by sandstones which form long
belts tens of kilometers long from the north
direction, with typically 700- 1500m wide, mostly in
1000-1200m width and 2- 20m thick, although they
may occasionally exceed these dimensions (Shields
and Esterle, 2015). Major channels usually has the
thickness larger than 5m and sandstone is
dominating. Minor channel refers to the thickness
larger than 2m and sandstone is major. In Tipton
field the sandstone in both channels is generally fine
grained, and sometimes medium to coarse
sandstones may present. The major and minor
channels may include crevasse splays and levee
bank with relatively fine sandstone, which are
difficult to separate them from channels.
5.3 Floodplain
The floodplain is the background facies including
commonly fine-grained siliciclastic rocks such as
siltstone, mudstone, shale. Even levee bank and
crevasse splay which are not easy to separated are
also included in the floodplain facies. Sometimes
thin and isolated shaly coal is also included in some
places in the Tipton field.
5.4 Lacustrine
Dark, gray shale, claystone or siltstone in shallow
water are the main lithologies in the lacustrine. The
sedimentation rates and energy are low, and the
sediments generally occur as sheets which ranged
from a few centimeters to a few meters in thickness.
The organization of the major facies of the WCM
depositional environment is summarized in Figure 8,
which is a simplification and synthesis of geological
concept facies models. Major channels of variable
sinuosity are the main pathways of sediment
dispersal across the floodplain. These major
channels feed a hierarchy of minor channels,
crevasse splays and levee bank, depositing
sediments in floodplain. Sediments infilling the
shallow water, abandoned channel systems and
floodplain enable conditions to be established in
which coal could form and develop.
Figure 8: Geological concept model of coal-bearing
environment.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The isochronal stratigraphic framework of sublayers
and coal plies in WCM of Tipton field is built using
high resolution sequence stratigraphy, and the
geometries, distributions and interrelationships of
the coal plies and channels are obtained to better
reveal the lithology heterogeneity and continuity. A
number of sedimentary facies have been identified
and geological concept model is built which would
enhance the understanding of the depositional
environments of Tipton field.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank the support of
Arrow Energy and Department of Asia and Pacific
E&P, RIPED, Petrochina.
Lacustrine
Floodplain
Floodplain
Lacustrine
Major channel
Minor channel
Crevasse splays
Coal eroded by channel
Coal in abandoned channel
Coal pinch out and split
Sedimentary Facies of the Coal-bearing Walloon Coal Measures in Tipton Field, Surat Basin
237
REFERENCES
Bohacs K and Sutter J 1997 Sequence stratigraphic
distribution of coaly rocks: fundamental controls and
paralic examples. AAPG Bull 81 (10) 1612-1639
Fielding C R 1993 The middle jurassicWalloon Coal
Measures in the type area, the rosewood Walloon
coalfield, SE Queensland. Aust. Coal Geol 9 4-15
Hamilton S K, Esterle J S and Sliwa R 2014 Stratigraphic
and depositional framework of the Walloon Subgroup,
eastern Surat Basin, Queensland. Aust. J. Earth Sci.
61(8) 1061-1080
Hoffman K L, Totterdell J M, Dixon O, Simpson G A,
Brakel A T, Wells A T and McKellar J L 2009.
Sequence stratigraphy of jurassic strata in the lower
Surat Basin succession, Queensland. Aust. J. Earth
Sci. 56 461-476.
Martin M A, Wakefield M, MacPhail M K, Pearce T and
Edwards H E 2013 Sedimentology and stratigraphy of
an intra-cratonic basin coal seam gas play: Walloon
Subgroup of the Surat Basin, eastern Australia. Pet.
Geosci. 19 21-38.
Shields D and Esterle J 2015 Regional insights into the
sedimentary organisation of the Walloon Subgroup,
Surat Basin, Queensland. Aust. J. Earth Sci.62 949-
967.
Stuart J, Moundney N P,McCaffrey W D, Lang S and
Collinson J D 2014. Prediction of channel connective
and fluvial style in the flood basin successions of the
Upper Permian Rangal Coal Measures (Queensland).
AAPG 98(2) 191-212.
Zhou F, Shields D, David T, Tyson S and Esterle J 2017
Understanding the geometry and distribution of fluvial
channel sandstones and coal in the Walloon Coal
Measures, Surat Basin, Australia. Marine and
Petroleum Geology 86 573-586
IWEG 2018 - International Workshop on Environment and Geoscience
238
