
Review of the Research Status and Progress of Ground-Based GNSS
Meteorology
Qiuying Guo
*
, Xuxiang Wu and Wengang Sang
College of Surveying and Geo-informatics, Shandong Jianzhu University, Fengming Road, Jinan 250101,P.R. China.
Email: qyguo@sdjzu.edu.cn
Keywords
: GNSS meteorology, atmospheric water vapour, tomography, data assimilation
Abstract:
The distribution of water vapor in troposphere is very uneven and has a strong sense of temporal and spatial
variation. The weather forecast requires accurate temporal and spatial information of the atmospheric
humidity field. The atmospheric water vapor information collected by traditional meteorological
observation methods has lower temporal-spatial resolution and higher observation cost. Using GNSS to
obtain atmospheric water vapor information has great potential of high quality, high temporal and spatial
resolution, low cost, all weather conditions and real-time monitoring. GNSS meteorology has an important
application value for atmospheric monitoring, extreme weather forecast and regional climate research. This
paper summarizes the state and progress of several respects of ground-based GNSS meteorology including
GNSS atmospheric vapor tomography, GNSS-derived data water vapor assimilation and GNSS
meteorological applications. The strategies and methods for GNSS tomography are summarized. And the
development and application prospects of the Multi-GNSS (GPS/Beidou/Glonass/Galileo) meteorology are
also discussed.
1 INTRODUCTION
The content of water vapor in the atmosphere is a
key parameter affecting the accuracy of weather
forecast. It is very important for the regional weather
forecast, especially for the accurate nowcasting. It is
also an important indicator for studying the long-
term climate change. Therefore dynamic monitoring
of atmospheric vapor content and real-time
constructing vertical distribution of the water vapor
field will play an important role in improving the
accuracy of weather forecast and modeling
atmosphere. The atmospheric water vapor
information collected by traditional meteorological
observation methods (radiosonde, radiometer) has
lower temporal-spatial resolution and higher
observation cost. The lack of four dimensional (4D)
distribution information of water vapor affects the
precision of the initial humidity field and the
accuracy of the numerical weather forecast.
Therefore it is a research focus in the field of
meteorology currently to find effective methods for
real-time acquisition of high precision atmospheric
vapor content and construct a real-time monitoring
system.
The propagation delay of GNSS satellite signal
through the atmosphere is related to the content of
water vapor in the troposphere. So the zenith
tropospheric delay (ZTD) can be inversed using
GNSS observations of the ground station. The ZTD
is devided into hydrostatic or dry component (ZHD)
and wet component (ZWD). The ZHD can be
calculated accurately according to Saastamoinen
model using the precise surface pressure data. Then
the ZWD can be obtained by subtracting ZHD form
ZTD. Finally, the ZWD can be converted to the
precipitable water vapor (PWV) by a ratio value Π,
which is related to the weighted mean temperature
T
m
(Bevis et al., 1992). So the PWV of GNSS signal
transmission route can thereby be calculated. And
the PWV is very important for weather forecasting
and extreme weather events monitoring.
Furthermore the 4D water vapor distribution can be
obtained by tomography when the density of the
GNSS stations available on the ground is sufficient.
GNSS water vapor tomography has the potential to
provide PWV fields with high temporal and spatial
Guo, Q., Wu, X. and Sang, W.
Review of the Research Status and Progress of Ground-Based GNSS Meteorology.
In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Environment and Geoscience (IWEG 2018), pages 199-206
ISBN: 978-989-758-342-1
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
199
resolution. And the PWV fields can make the 4D
temporal and spatial changes of water vapor
understood in more detail and more favorable for
monitoring and early warning storm disasters.
Therefore GNSS has become a very effective tool
for the study of meteorology currently
(Flores et al.,
2000;
Manning et al., 2014; Wang et al., 2016).
In recent years, using GNSS for meteorological
detection has become an important component of
World Meteorological Organization (WMO) new
global upper air observing system in the 21 century.
The application superiority of atmospheric sounding,
weather change monitoring and numerical weather
forecast using GNSS observation data makes GNSS
meteorology become a completely new and highly
potential field.
2 RESEARCH STATUS OF
GROUND-BASED GNSS
METEOROLOGY
Since 1990s, people have begun to use satellite
navigation theory and technology sensing the Earth's
atmosphere. A new method to measure the content
of atmospheric water vapor using satellite
navigation signal started from the inverse problem
of noise processing for signal atmospheric delay of
satellite navigation, which provides new technical
support for better monitoring unfavourable weather
and climate change. Ground-based GPS
meteorology was early proposed by Bevis M. et al.
(1992) to sense atmospheric water vapor and support
weather forecast (Bevis et al., 1992). The GNSS
reference station network has been established in
many countries in the world in recent years. There
are global International GNSS Service (IGS) and
national/regional tracking station network on the
space scale. IGS is the most widely distributed and
the largest GNSS reference network in the world.
The number of global IGS tracking stations has
exceeded 500 by the end of January 2017. Among
them about 200 stations are multi-system GNSS
continuous operation reference station (MGEX).
Also some satellite ground-based augmentation
systems have been built in the world in recent years,
such as American StarFire with about 100 stations
(Jiang, 2017). Also, HxGN SmartNet claims to be
the world’s largest Continuously Operating
Reference Stations (CORS) network with more than
4,000 reference stations covering the majority of
developed countries, which continues to provide
trusted GNSS data worldwide
(https://hxgnsmartnet.com/). In addition, many
countries and private organizations have built their
own CORS networks. According to incomplete
survey, there are more than 4000, 5000, 1300 CORS
stations in America, China and Japan respectively.
Europe and Australia all have more than 1000
CORS stations. All these CORS stations provide
very favorable conditions for GNSS ZWD/PWV
estimation. However, the distribution of these CORS
stations is uneven at present and many governmental
agencies and private organizations still do not make
GNSS CORS data available to the public. So there is
a need for policies on data sharing and collaboration
among the different organizations that operate
GNSS stations.
As the coverage area of the ground GNSS station
network is greatly increased, the algorithm for
obtaining the tropospheric zenith wet delay (ZWD)
has also been developed and improved. So the
accurate water vapor information can be obtained
with high temporal and spatial resolution. GNSS
tomography is such a technique to reconstruct
detailed information of water vapor over the
interested area using the slant wet delay (SWD)
observations. Currently, GNSS tomography
atmospheric water vapor information is one of the
research focus in GNSS meteorology.
To make a forecast we need to know the current
state of the atmosphere conditions. The accuracy of
the water vapor field in the lower atmosphere is
particularly important for the forecast of extreme
weather (such as storms). The emergence and
evolution of many extreme weather conditions are
very rapid. The sampling rate of traditional water
vapor observation methods is too low so that the
information of water vapor change in extreme
weather can not be captured in time. While GNSS
tropospheric products and tomographic data can
provide a reliable source of data with high spatial
and temporal resolution. Research shows that
assimilating GNSS ZTD/ZWD/PWV can effectively
improve the initial atmospheric humidity field and
have a positive effect on strong precipitation
forecast (Boniface et al., 2009;
Zeng et al., 2014).
The assimilation of the GNSS observations is a
relatively new and very promising approach to
improve the short-term forecasts. Therefore
assimilation of GNSS tropospheric products and
tomographic data to improve the extreme weather
IWEG 2018 - International Workshop on Environment and Geoscience
200
forecast has become another research hotspot in the
field of GNSS meteorology.
In the following sections, we introduced the
research status of ground-based GNSS meteorology
from the following aspects: GNSS water vapor
tomography, GNSS-derived water vapor data
assimilation and meteorological applications of
GNSS-derived water vapor.
2.1 GNSS Water Vapor Tomography
A lot of research and test work has been done on
GNSS tomography 3D water vapor distribution in
the past 20 years, especially in Europe and America.
Bevis M. et al. (1992) presented early in 1992 that
dense GPS networks could be used to sense the
vertical distribution of water vapor. Since Flores A.
et al. (2000) first proved the feasibility of the 4D
tropospheric tomography technology using GPS
slant wet delays by experiment, many researchers in
the geodesy and meteorology fields have carried out
the related research. Many experiments have proved
that the water vapor field obtained by GNSS has
good consistency with the traditional meteorological
observation methods and also proved the
effectiveness of the study of atmospheric state by
GNSS tomography (Flores et al., 2000;Bastin et al.,
2005;Song et al., 2006). The research contents on
GNSS tomography mainly involve voxel division of
tomographic area, tomography algorithm,
optimization of tomography parameters, applications
of GNSS tomography in the field of meteorology
and advantages of multi-constellation GNSS
tomography.
Bastin S. et al. (2005) proved the 3D water vapor
field obtained by GPS tomography using numerical
simulation for the first time and studied the
interaction between the regional sea breeze and the
topography using data sets provided by GPS
tomography for the description of the water vapor
variability. Song S. et al. (2006) obtained 3D
structure of water vapor information over Shanghai
area by GPS tomography technique using GPS slant
water vapor retrieved from Shanghai GPS network
and improved numerical forecasted wet field
obviously. Wang W. et al. (2011) carried out GPS
water vapor tomography experiments using three
algebraic reconstruction techniques on Shanghai
GPS network and discussed the range of relaxation
factor and the initial value of iteration for the
reconstruction algorithm. He L. et al. (2015)
analyzed eight algebraic reconstruction algorithms
and discussed various problems of GPS vapor
tomography with respect to constraint condition,
initial value, optimal relaxation factor and iteration
termination condition.
However, due to many influencing factors (such
as satellite constellation, geometric distribution of
GNSS stations, voxel division), the coefficient
matrix of the tomographic equation is often sparse
and severely deficient, which causes GNSS
tomography can not be solved directly. So there are
still some problems to be solved on ground-based
GNSS tomography water vapor distribution, such as
solutions to the ill-posed tomography equations,
reasonable density of stations, optimization of voxel
division and the optimal settings of tomography
parameters. In addition, the quality of the water
vapor field obtained by GNSS tomography is related
to many factors, such as the priori value of water
vapor field, the number of slant path tropospheric
delay observation, weighting scheme of
observations, spatial resolution of a tomographic
region and the parameter settings of tomography
algorithm (e.g. the stop criteria of iterative
reconstruction algorithms) (Wang and Wang,
2011a;Bender et al., 2011;Wang and Wang,
2011b;He et al., 2015;Yu et al., 2016;Xia and Ye,
2017;Yao and Zhao, 2017;Chen and Liu.,
2014;Möller, 2017). Bender M. et al. (2011) found
by studying Germany ground-based GNSS station
network that the spatial coverage of the atmosphere
by slant paths can change very fast as the GNSS
satellite constellation varies and a uniform quality of
the reconstructed fields can therefore not be
expected. Möller G. (2017) studied the mathematics
formulation of ill-conditioned, inverse problems on
GNSS tomography equations. And the research
showed that the GNSS tomography solutions are not
only sensitive to the observation error and the
change of observation geometry but also sensitive to
the solution scheme and the parameter settings,
which caused by the ill-conditioned GNSS
tomography equations.
Review of the Research Status and Progress of Ground-Based GNSS Meteorology
201
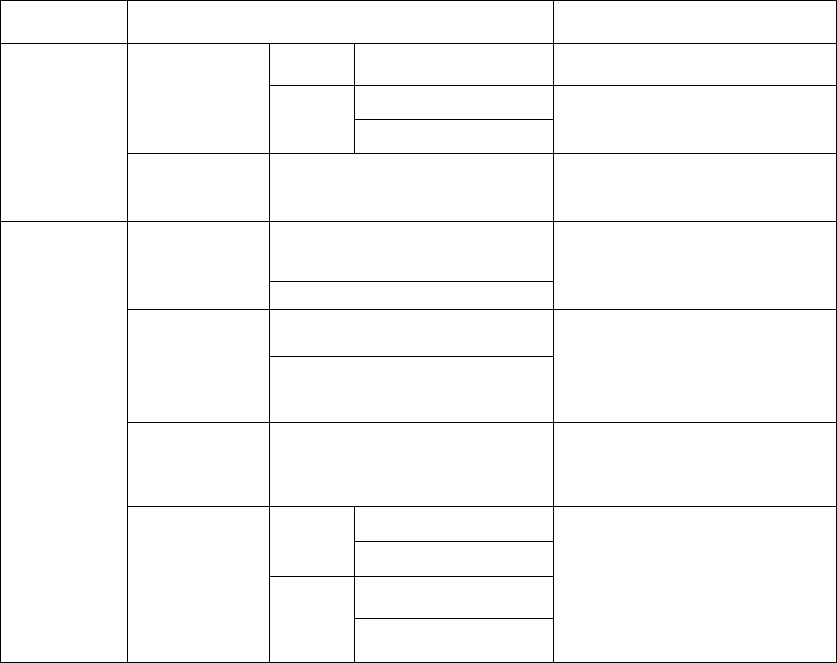
Table 1: Summary of strategies and methods for GNSS tomography.
Research
content
Research strategies and methods Scheme or characteristic
Optimization of
voxel division of
tomography
Vertical
stratification
Even Equidistant spacing
Unconsistent with actual vertical
distribution of water vapor
Uneven
Uneven spacing
Better reflect vertical variation of
water vapor in troposphere
Exponential spacing
Horizontal
resolution
Inhomogeneous, Commonly
(10-50km)×(10-50km)
According to the density of the
ground GNSS stations
Solutions to
tomography
equations
Non-iterative
reconstruction
algorithm (NIRA)
Truncated singular value
decomposition (TSVD)
Directly inverse;
Need to determine optimal threshold
for singular values and regularisation
parameters
Tikhonov regularization (TR)
Iterative
reconstruction
algorithm
(IRA)
Algebraic reconstruction technique
Avoiding inversion problem;
High stability and reliability;
Need to determine relaxation factor
and stop criteria
Multiplicative algebraic
reconstruction technique (MART)
Combined
reconstruction
algorithm
NIRA+IRA
Solutions obtained by TSVD or TR
are used as initial value of IRA, which
can provide high quality initial value
for IRA.
Classical
constrained
solution
H
orizontal
constraints
Horizontal smoothing
Directly inverse;
Adding constraints; Inappropriate
constraints may debase the accuracy
of results.
Gauss weighted function
Vertical
constraints
Decrement based on
exponential function
Radiosonde observation
Most of the aforementioned research mainly aim
to improve the precision and reliability of GNSS
tomography solutions. Table 1 gives the summary of
different approaches. GNSS tomography has the
potential of providing 4D water vapor field with
near real-time and high temporal-spatial resolution,
which can be used for numerical weather forecast,
extreme weather event monitoring and climatology
research. Despite with more than 10 years of
development, GNSS tomography atmospheric water
vapor technology still faces many challenges. There
are many factors affecting GNSS tomography
results. For example, the slant path delay can
provide local changes related to atmospheric
information and is considered to be a promising
value of meteorological observation, but the
precision of slant path water vapor in the region at
low altitude is still low (Wang et al., 2016;
Möller,
2017). So the accurate estimation of the slant path
water vapor needs further study. The weighted mean
temperature T
m
is an important parameter for
calculating the atmospheric water vapor. A detailed
study of precise determination of T
m
needs further
development. Moreover, there exists the problem of
precision instability of GNSS tomography results.
With the significant progress of BeiDou and
Galileo systems, as well as updating Glonass, the
integrated multi-GNSS may improve water vapor
tomography (Bender et al., 2010;Wang et al.,
2014;Zhao et al., 2018;Dong and Jin, 2018). Bender
M. et al (2010) estimated the impact of GPS, Galileo
and GLONASS data on the GNSS tomography by
simulation which showed that the spatial coverage
of the atmosphere with slant paths is highly
improved by combining observations from two or
three satellite systems. But observations in the lower
part of the atmosphere, e. g, below 3 km, are still
rather sparse. Zhao Q. et al (2018) used multi-GNSS
IWEG 2018 - International Workshop on Environment and Geoscience
202
(GPS, GLONASS and BDS) data to validate the
tomographic results derived from various multi-
GNSS combined strategies and compared with
radiosonde data. Tomography experiments showed
that multi-GNSS observations can increase the
accuracy of 3D wet refractivity reconstruction but
not as well as was expected when using currently
available techniques. Dong Z. et al (2018) obtained
3D water vapor tomography results using multi-
GNSS data from Wuhan CORS and the reliability of
tomographic water vapor density reconstructed by
combining multi-GNSS is significantly enhanced
when compared to the GPS-only system.
Above mentioned study shows that the number
of satellite rays used has been almost doubled or
tripled when multi-GNSS observations were used in
the tomographic model, but the percentage of empty
voxels did not decreased as much as was expected.
The possible reason was that the spatial resolution of
the tomographic model was not improved as was
expected, which can be addressed by increasing the
spatial density of ground-based GNSS stations. In
summary, GNSS water vapor tomography
technology is still in the process of research. In fact,
the water vapor in the atmosphere of 4D variation
characteristics are very complex. And there is a lack
of analysis of the fine 4D structure of the
atmosphere on the medium and small scale in
operational applications. Therefore more research is
needed to improve the accuracy and reliability of
GNSS tomography solution.
2.2 GNSS-Derived Water Vapor Data
Assimilation
The data assimilation technique is a vital part of
numerical weather forecasting. Europe and the
United States have began research in the related
fields of data assimilation of GNSS tropospheric
products since 2000 (Bennitt and Jupp, 2012).
During the 2000-2001 years, some European
Research Group successfully implemented and
confirmed the concept of ground-based GNSS
meteorology. In the following European Union
project (E-GVAP, 2005-2017, http://egvap.dmi.dk),
the fifteen European countries participated in the
campaign of the European GPS meteorology and
began to be used in actual production. Currently,
near real-time tropospheric products provided
through E-GVAP have been used in the assimilation
of many numerical weather prediction (NWP)
models. Now GNSS receiver network with real-time
retrieval of PWV has been running in Europe and
the United States and successfully applied to
weather forecast, such as American GPS/MET and
European E-GVAP.
The study of GNSS meteorology for the last 20
years showed that assimilation of GNSS precipitable
water can effectively improve the quality of the
initial atmospheric humidity and has a positive
effect on improving the performance of strong
nowcasting precipitation forecast (Bennitt and Jupp,
2012;Mahfoufet al., 2015;Lindskog et al.,
2017;Zhong et al., 2017;Guerova et al., 2016). The
research contents on GNSS data assimilation mainly
involve improvement of the initial conditions for
NWP using GNSS-PWVs, assimilation algorithm,
assimilation impacts of ZTD/ZWD/SWD/PWV and
wet refractivity data obtained by GNSS tomography
using various schemes. In the current study, a 3-
dimensional variational data assimilation (3D-Var)
scheme was mainly used for data assimilation. The
European Centre for Medium-Range Weather
Forecasts (ECMWF) has pioneered work on
assimilation methods such as 4D-Var (Zhong et al.,
2017) And many questions on the ground-based
GNSS data assimilation need further study, such as
the methods to effectively assimilate the PWVs into
the NWP model, estimation of observation error,
adjustment of the initial field, determination of the
background error, selection of assimilation
algorithm and analysis of the impact of the GNSS
data assimilation on NWP models. There are still
many unresolved problems related to the GNSS data
assimilation. Therefore there's a lot of space for
research on how to effectively assimilate GNSS
tropospheric products and tomography data into the
operational system of the numerical weather forecast.
The research on GNSS meteorology in recent
years was mainly on retrieving high temporal and
spatial PWV and analyzing relationship between
water vapor and precipitation events (Guerova et al.,
2016;Lu et al., 2016;Yu et al., 2017;Zheng et al.,
2018). While the work on data assimilation
algorithm of GNSS tropospheric products is
relatively few. Also little has been done in the past
to use GNSS reprocessed troposphere products for
data assimilation in climate models. This field of
research has however seen starting some recent
initiatives. The European Reanalysis project, in
which the U.K. Met Office take part, will be used to
promote the data assimilation of ZTDs/PWVs in
climate re-analysis. Recently, the European Union
Commission carried out a new research project
Review of the Research Status and Progress of Ground-Based GNSS Meteorology
203
“GNSS4SWEC” running from 2013 to 2017. The
research fields of the project include GNSS
advanced processing techniques, GNSS for severe
weather monitoring and GNSS for climate
monitoring (http://gnss4swec.knmi.nl).
It has become a new hotspot of GNSS
meteorology research to assimilate GNSS
tomography results improving the initial field of the
numerical weather forecast model and the quality of
nowcasting. The new generation of high resolution
weather prediction model requires high resolution
input data and observation data. With the
improvement of the resolution of weather forecast
model, it becomes more and more important to
initialize of the mesoscale atmospheric phenomena
using high spatial and temporal resolution
observations. Therefore GNSS data assimilation is a
very promising approach to improve the quality of
the short-term weather forecast, especially for
extreme weather events, such as heavy rainfall.
2.3 Meteorological Applications of
Gnss-Derived Water Vapor
Meteorological applications of GNSS-derived water
vapor mainly involves the following aspects:
disaster monitoring, weather forecasting and climate
monitoring. High precise and high temporal-spatial
resolution PWV data is the important information
for disaster monitoring (such as torrential rain,
thunderstorm, typhoon, dense fog). A lot of research
has been done on the nowcasting of disastrous
weather using GPS-PWV (Poli et al., 2008;Manning
et al., 2012;Yao et al., 2017;Liang et al., 2015;Choy
et al., 2013). Poli P. et al. (2008) discuss the effect
of GNSS-derived data on NWP by using European
ground-based GNSS-ZTD data introduced into the
Météo-France global forecasting system. They
reported that the benefits of including such data
were most apparent in improved predictions of
temperature and wind, and especially, in superior
quantitative precipitation forecasts over France.
Boniface K. et al. (2009) evaluated the impacts of
assimilating GPS data on the precipitation forecast
on Mediterranean heavy rainfall forecasting.
Manning T. et al. (2012 ) presented a case study
based on the analysis of an extreme convective super
cellstorm in the Victorian region during March 2010
using GPS tomography and CORS network in
Australia. The study concluded that GPS
tomographic wet refractivity profiles showed an
excessive increase as a response to supercell
thunderstorm formation.
A number of experimental analysis on GNSS-
PWV data for nowcasting of disastrous weather
shows that the ground-based GNSS-PWV has the
same accuracy as radiosonde and radiometer and
high temporal-spatial GNSS-PWV data plays a
significant role in monitoring severe weather.
Assimilating PWV data can improve the initial
humidity field of NWP mode and improve the
accuracy of the numerical weather forecast.
Moreover, GNSS is not only used to sense the
precipitation but also to detect the wind and clouds.
Climate is defined as the average weather
conditions at a place usually over a period of years
as exhibited by temperature, air pressure, humidity,
precipitation, winds, sunshine and clouds. So GNSS
is also a promising climate monitoring tool capable
of providing accurate, long-term, and consistent data
for climate studies. The applications of GNSS-
derived water vapor in climate monitoring need
further studies.
3 DEVELOPMENT AND
APPLICATION PROSPECTS
At present, GNSS is mainly used for tropospheric
water vapor monitoring and weather forecast.
Actually, GNSS meteorology also have better
prospects for development and application. With the
ground-based GNSS observing networks
continuously densified, GNSS will be an important
technical means for monitoring the total and vertical
distribution of atmospheric water vapor along with
upper wind measurement and climate change
monitoring. GNSS will play a more important role
in medium and small scale weather analysis,
numerical weather forecast, disastrous weather
service and global climate change monitoring. In
addition, GNSS data supporting meteorological
applications mainly use GPS single constellation
system and observations of GPS ground reference
station currently. With the development and
integration of multi-constellation GNSS
(GPS/Beidou/Glonass/Galileo) system, the number
of GNSS observations will be greatly increased.
Moreover, with the rapid growth of the number of
GNSS reference stations, the rapid development of
mobile surveying system integrated with
GNSS/inertial navigation carried by vehicle, ship-
borne and unmanned aerial vehicles, the available
IWEG 2018 - International Workshop on Environment and Geoscience
204
GNSS observations will further increase, which will
also promote the development of GNSS
meteorology. Fostered by these developments,
advanced processing strategies are necessary to
exploit the full potential of future GNSS systems for
describing the physical state of the low atmosphere.
Other potential applications like estimating cloud-
base height should also be explored. So there has
great research potential in the fields of ground-based
GNSS meteorology.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work is supported by the Shandong Provincial
Natural Science Foundation, China
(ZR2017MD029), the Technology Project Plan of
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development
of the People’s Republic of China (2014-K8-070)
and Shandong Provincial Department of Housing
and Urban Rural Construction Technology Project
Plan (2017-R1-004). The authors greatly appreciate
the editor and the anonymous reviewers on this
manuscript.
REFERENCES
Bastin S, Champollion C, Bock O, et al. 2005 On the use
of GPS tomography to investigate water vapor
variability during a Mistral/sea breeze event in
southeastern France Geophysical Research Letters 32
L05808
Bender M, Dick G, Ge M, et al. 2011 Development of a
GNSS water vapour tomography system using
algebraic reconstruction techniques Advances in Space
Research 47 1704-1720
Bender M, Stosius R, Zus F, et al. 2010 GNSS water
vapour tomography-expected improvements by
combining GPS, GLONASS and Galileo observations
Advances in Space Research 47(5) 886-897
Bennitt G, Jupp A 2012 Operational assimilation of GPS
zenith total delay observations into the Met Office
numerical weather prediction models Monthly
Weather Review 140 (8) 2706-2719
Bevis M, Businger S, Herring T A, et al. 1992 GPS
meteorology: Remote sensing of atmospheric water
vapor using the global positioning system Journal of
Geophysical Research Atmosphere 97 15787-15801
Boniface K, DucrocqV, JaubertG, et al. 2009 Impact of
high-resolution data assimilation of GPS zenith delay
on Mediterranean heavy rainfall forecasting Annales
Geophysicae 27 2739-2753
Chen B, Liu Z 2014 Voxel-optimized regional water
vapor tomography and comparison with radiosonde
and numerical weather model Journal of Geodesy 88
691-703
Choy S, Wang C, Zhang K, et al. 2013 GPS sensing of
precipitable water vapour during the March 2010
Melbourne storm Advances in Space Research 52
1688-1699
Dong Z, Jin S 2018 3-D water vapor tomography in
Wuhan from GPS, BDS and GLONASS observations
Remote Sensing 10(1) 62 DOI: 10.3390/rs10010062
Flores A, Ruffini G and Rius A 2000 4D tropospheric
tomography using GPS slant wet delays Annales
Geophysicae 18 223-234
Flores A., Ruffini G, Rius A 2000 4D tropospheric
tomography using GPS slant wet delays Annales
Geophysicae 18 223-234
Guerova G, Jones J, Douša J, et al. 2016 Review of the
state of the art and future prospects of the ground-
based GNSS meteorology in Europe. Atmospheric
Measurement Techniques 9 5385-5406
He L, Liu L, Su X, et al. 2015 Algebraic reconstruction
algorithm of vapor tomography[J]. Acta Geodaetica et
Cartographica Sinica 44 (1) 32-38
Jiang W 2017 Challenges and opportunities of GNSS
reference station network Acta Geodaeticaet
Cartographica Sinica 46(10) 1379-1388
Liang H, Cao Y, Wan X, et al. 2015 Meteorological
applications of precipitable water vapor measurements
retrieved by the national GNSS network of China
Geodesy and Geodynamics 6 (2) 135-142
Lindskog M, Ridal M, Thorsteinsson S, et al. 2017 Data
assimilation of GNSS zenith total delays from a
Nordic processing centre Atmospheric Chemistry &
Physics 17(22) 1-22
Lu C, Li X, Ge M, et al 2016 Estimation and evaluation of
real-time precipitable water vapor from GLONASS
and GPS GPS Solutions 20(4) 703-713
Mahfouf J, Ahmed F, Moll P, et al 2015 Assimilation of
zenith total delays in the AROME France convective
scale model: A recent assessment. Tellus A: Dynamic
Meteorology and Oceanography 67 (1) DOI:
10.3402/tellusa.v67.26106.
Manning T, Rohm W, Zhang K, et al. 2014 Determining
the 4D Dynamics of Wet Refractivity Using GPS
Tomography in the Australian Region Springer Berlin
Heidelberg 139 41-49
Manning T , Zhang K , Rohm W, et al. 2012 Detecting
severe weather using GPS tomography: an Australian
case study Journal of Global Positioning Systems 11
(1) 58-70
Möller G 2017 Reconstruction of 3D wet refractivity
fields in the lower atmosphere along bended GNSS
signal paths. Ph.D dissertation,Vienna University of
Technology
Poli P, Pailleux J, Ducrocq V, et al. 2008 Weather report:
meteorological applications of GNSS from space and
on the ground InsideGNSS 3(8) 30-39
Song S, Zhu W, Ding J, et al. 2006 3D water-vapor
Review of the Research Status and Progress of Ground-Based GNSS Meteorology
205
tomography with Shanghai GPS network to improve
forecasted moisture field Chinese Science Bulletin 51
(5) 607-614
Wang W and Wang J 2011a Ground-based GPS water
vapor tomography based on algebraic reconstruction
technique Journal of Computer Applications 31 (11)
3149-3151
Wang W and Wang Jiexian 2011b Ground-based GPS
water vapor tomography based on algebraic
reconstruction technique Journal of computer
applications 31(11) 3149-3151
Wang W, Song S, Wang J, et al 2016 Distribution
Analysis of Multi GNSS Slant Delay sand Simulated
Water Vapor Tomography in Yangtze River Delta
Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica 45 (2) 164-
169
Wang X, Wang X, Dai Z, et al. 2014 Preliminary results
of tropospheric wet refractivity tomography based on
GPS/GLONASS/BDS satellite navigation system
Advances in Atmospheric Sciences 31 355-362
Xia P, Ye S A 2017 Troposphere tomography technique
based on combined reconstruetion algorithm Journal
of Geodesy and Geodynamics 37(9) 928-932
Yao Y, Shan L, Zhao Q 2017 Establishing a method of
short-term rainfall forecasting based on GNSS-derived
PWV and its application Scientific Reports 8 12465
DOI: 10.1038 /s41598-017-12593-z
Yao Y, Zhao Q 2017 A novel, optimized approach of
voxel division for water vapor tomography.
Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics 129 (1) 57-70
Yu C, Penna N, Li Z 2017 Generation of real-time mode
high-resolution water vapor fields from GPS
observations Journal of Geophysical Research
Atmosphere 122 2008-2025
Yu S, Wan R, Fu Z 2016 Application of algebraic
reconstruction technique on the GNSS water vapor
tomography Geomatics and Information Science of
Wuhan University 41 (8) 1113-1117
Zeng M, Zhang B, Zhou J, et al. 2014 Quantitative
evaluation for GPS/PWV data assimilation in heavy
precipitation events Journal of the Meteorological
Sciences 34 (1) 77-86
Zhao Q, Yao Y, Cao X, et al. 2018 Accuracy and
reliability of tropospheric wet refractivity tomography
with GPS, BDS, and GLONASS observations
Advances in Space Research
DOI:10.1016/j.asr.2018.01.021
Zheng F, Lou Y, Gu S, et al. 2018 Modeling tropospheric
wet delays with national GNSS reference network in
China for BeiDou precise point positioning Journal of
Geodesy 92 545
Zhong J, Guo Y, Zhang J 2017 A study of quality control
and assimilation of ground-based GPS ZTD in North
China Acta Meteorologica Sinica
75 (1) 147-164
IWEG 2018 - International Workshop on Environment and Geoscience
206
