
Study on the Purification Process of Arsenic High Iron Wastewater
from Zinc Smelter
Haoen Zuo, Jiankang Wen
*
, Biao Wu, Xinglan Cui, He Shang and Wencheng Gao
National Engineering Laboratory of Biohydrometallury, General Research Insitute for Nonferrous Metals, Beijing 10080,
China.
Email: kang3412@126.com.
Keywords: Wastewater; reducing agent, purification, efficiency, complex salt flocculant
Abstract:
Arsenic high iron wastewater was produced by sulfated roasting-water leaching process from the zinc
smelting industry, high contents of total iron, zinc ion and sulfate ion, were contained, a certain amount of
arsenic ion, copper ion and cadmium ion were also involved. With strict environmental protection, the
comprehensive utilization of wastewater has great economic significance, it is one of the most important
direction that the preparation of iron-salt flocculant with wastewater. It is necessary to pretreat and purify
firstly. In this paper, the sample comes from Chihong Inner Mongolia, China. The concentrations of total
iron, sulfate ion and zinc ion are 24.18 g/L, 91.31 g/L and 5.54 g/L, respectively. The effect of reducing
agent proportion, temperature, stirring speed on the purification of arsenic ion, copper ion, cadmium ion was
researched. The optimal conditions are: reducing agent proportion of 1% of iron powder, 2% of zinc powder,
temperature of 60 ℃, and stirring speed of 800 rpm. Under the conditions, the efficiency of arsenic ion,
copper ion and cadmium ion all reached 99.99%. The concentrations of total iron, sulfate ion and zinc ion in
the wastewater after purification are 55.23 g/L, 126.25 g/L and 39.00 g/L, respectively, which provided the
precondition for the subsequent preparation of iron-salt flocculant.
1 INTRODUCTION
Arsenic high iron wastewater was produced by
sulfated roasting-water leaching process from the
zinc smelting industry(Fu and Wang, 2011)(Zhao et
al., 2012). The main features of this type of
wastewater was high iron content, which was
generally up to 30-60 g/L; strong acidity, pH value
between 1-4; sulfate ion mass concentration up to
thousands of milligrams per liter; at the same time,
contains trace amounts of arsenic ion, copper ion,
cadmium ion and so on(Ozverdi, 2006)(Tang, 2010).
Arsenic high iron wastewater treatment methods
were neutralization precipitation method, sulfide
precipitation method, ion exchange method, iron
reduction method and biological flocculation
method(He et al., 2013; Huisman, 2006; Yang et al.,
2014; Huo et al., 2009; Greenleaf et al., 2006; Liu,
2016). Among them, the industrial application was
still extensively used in the neutralization
precipitation method, which has the advantages of
low cost and simple process The main problem was
the large amount of slag, secondary pollution
problem(Meng and Geng, 2013)(Gao and Sheng,
2015).
The use of arsenic high iron wastewater for
preparation of iron and zinc complex salt flocculant
has good industrial application prospects(Busetti et
al., 2005; Jong and Parry, 2003; Song, 2016).
However, the resource utilization of the kind of
wastewater was limited for arsenic ion, copper ion,
cadmium ion. To prepare iron and zinc complex salt
flocculant by using the wastewater, firstly, it was
necessary to purificate(He et al., 2012)(Li et al.,
2010). In this paper, arsenic high iron wastewater
was used as research object, which come from
Chihong Smelting Plant in In Nei Mongol Province,
China. Iron powder and zinc powder were used as
reduing agent, arsenic ion, copper ion, cadmium ion
and other impurities were purified. Different factors
on the efficiency of arsenic ion, copper ion,
cadmium ion were researched, which included
adding proportion of reducing agent, reaction
temperature and stirring speed.
Zuo, H., Wen, J., Wu, B., Cui, X., Shang, H. and Gao, W.
Study on the Purification Process of Arsenic High Iron Wastewater from Zinc Smelter.
In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Environment and Geoscience (IWEG 2018), pages 189-193
ISBN: 978-989-758-342-1
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
189
2 MATERIAL AND METHODS
2.1 Material
The arsenic high iron wastewater was obtained from
Chihong Smelting Plant in In Nei Mongol Province,
China. The chemical multi-elemental analysis was
detected by ICP-OES, the product model is Agilent
725-ES. The results are shown in Table 1. The
sample contains 46.35 mg/L cadmium ion, 453.74
mg/L arsenic ion, 260.5 mg/L copper ion, 91310
mg/L sulfate ion, 5540 mg/L zinc ion, 24180 mg/L
total iron.
2.2 Experimental Method
Purification experiment was performed in 500 mL
beaker containing 200 mL solution. The content of
arsenic ion, cadmium ion, copper ion, total iron, zinc
ion, and sulfate ion in the solution was measured by
ICP-OES.
(1) Effect of reducing agent proportion
The reactor was set to temperature 60 ℃, time 4
h, stirring speed 800 rpm. The addition amount of
the reducing agent was 3%(ω/ν) of iron, 2%(ω/ν) of
iron and 1%(ω/ν) of zinc, 1.5%(ω/ν) of iron and zinc,
1%(ω/ν) of iron and 2%(ω/ν) of zinc, 3% (ω/ν) of
zinc.
(2) Effect of stirring speed
The reactor was set to temperature 60 ℃, time 4
h, iron 2% (ω/ν) and zinc 1% (ω/ ν). The stirring
speed was 400 rpm, 600 rpm, 800 rpm, 1000 rpm.
(3) Effect of temperature
The reactor was set to time 4 h, stirring speed
800 rpm, reducing agent iron 2%(ω/ν) and zinc
1%(ω/ν). The temperature was 20 ℃, 40 ℃, 60 ℃,
80 ℃.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Effect of Reducing Agent
Proportion
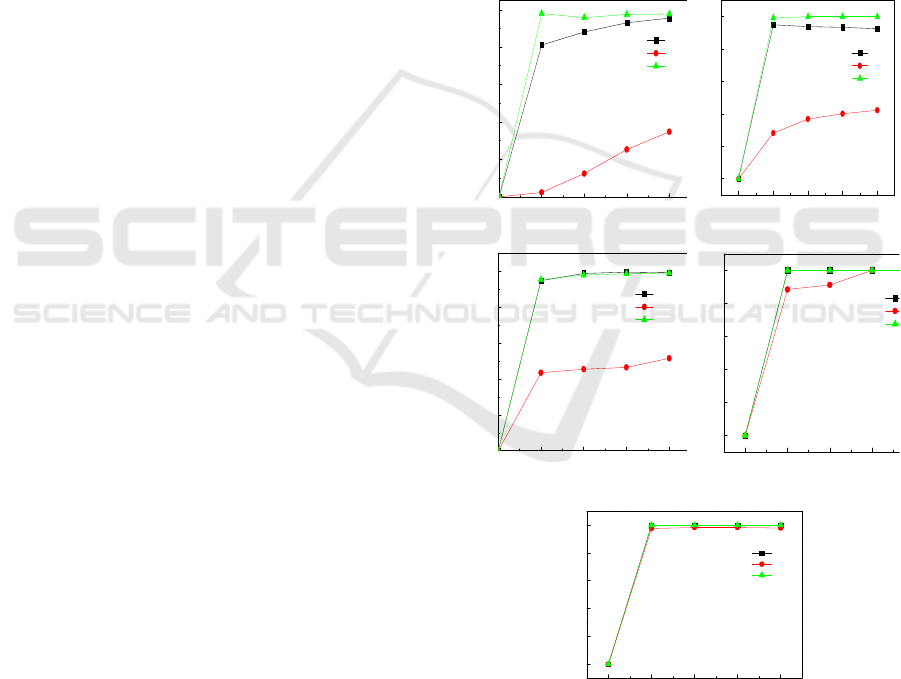
Figure 1 shows the efficiency of arsenic ion, copper
ion, and cadmium ion under different reducing agent
proportion. As shown in Figure 1(a)(b)(c)(d)(e), the
efficiency of arsenic ion, copper ion and cadmium
ion increase firstly then remain stable. Under the
condition of iron powder 3%, copper ion efficiency
was 98.03% in the first hour, finnaly, arsenic ion
and cadmium ion efficiency were 95.64%, 34.81%.
Adding 3%(ω/ν) iron powder has good removal
effect on copper ion and arsenic ion, however
removal effect on cadmium ion was poor with
efficiency of only 34.81%. Under the condition of 2%
(ω/ν), iron powder added with 1% (ω/ν) zinc powder,
the copper ion efficiency was less affected, and the
copper ion efficiency reached 99.24% in first hour, it
increased by 1.21 percentage points compared to
iron 3%, and the addition of zinc powder accelerated
the efficiency of arsenic ion, the efficiency of
arsenic ion was basically identical, the efficiency of
cadmium ion was 42.23%, which was obviously
higher than that without zinc powder, Zinc have a
good impact on the removal of cadmium ion.
01234
0
20
40
60
80
100
(a)
Iron 3%
Removal
efficiency
/
%
Time/h
As
Cd
Cu
12345
0
20
40
60
80
100
R
emova
l
e
ffi
c
i
ency
/%
Iron 2%
Zinc 1%
As
Cd
Cu
Time/h
(b)
0
20
40
60
80
100
Removal
efficiency
/
%
Iron 1.5%
Zinc 1.5%
3
4
As
Cd
Cu
Time/h
1
2
(c)
0123
0
20
40
60
80
100
Removal
efficiency/%
I
Z
Time/h
(d)
01234
0
20
40
60
80
100
Removal efficiency/%
(e)
Zinc 3%
As
Cd
Cu
Time/h
Figure 1: Arsenic ion, copper ion and cadmium ion
efficiency with different iron and zinc addition ratios.
(a) iron powder 3% (b) iron powder 2%, zinc powder 1%
(c) iron powder, zinc powder 1.5%d) iron powder 1%,
zinc powder 2% e) zinc powder 3%.
IWEG 2018 - International Workshop on Environment and Geoscience
190

Table 1: Chemical multi-elemental analysis of arsenic high iron wastewater (concentration, mg/L).
As
3+
Ca
2+
Cd
2+
Cu
2+
TFe K
+
Mg
2+
Na
+
SO
4
2-
Zn
2+
453.74 0.48 46.35 260.5 24180 0.07 0.05 0.02 91310 5540
As shown in Figure 1 (c)(d)(e), the efficiency of
copper ion and arsenic ion have little impact with
the increase of zinc powder addition, copper ion and
arsenic ion efficiency reached 99.99% in first hour,
and the efficiency of cadmium ion was shown an
increasing trend. While the amount of zinc powder
added was 1.5% (ω/ν), the efficiency of cadmium
ion was 51.67%. The addition of 2%(ω/ν) zinc
powder of cadmium ion efficiency reached 99.99%
in the third hour. Cadmium ion efficiency got faster
under the condition of 3% zinc, it reached 99.99% in
the first hour.
As a result, while reducing agent was only iron
powder, arsenic ion and copper ion efficiency was
good, cadmium ion efficiency was poor. With the
increase addition of zinc powder, copper ion
efficiency was less effected, arsenic ion efficiency
can be accelerated to a certain extent. However,
cadmium ion efficiency was effected greatly, the
final efficiency reached 99.99%.
In the selection of addition of iron and zinc
powder, due to the industrial price of zinc is much
more expensive than iron, and combined with the
follow-up preparation of iron-zinc composite salt
flocculant, the agent proportion was iron 2% (ω/ν),
zinc 1% (ω/ ν), the reaction time was 3 h
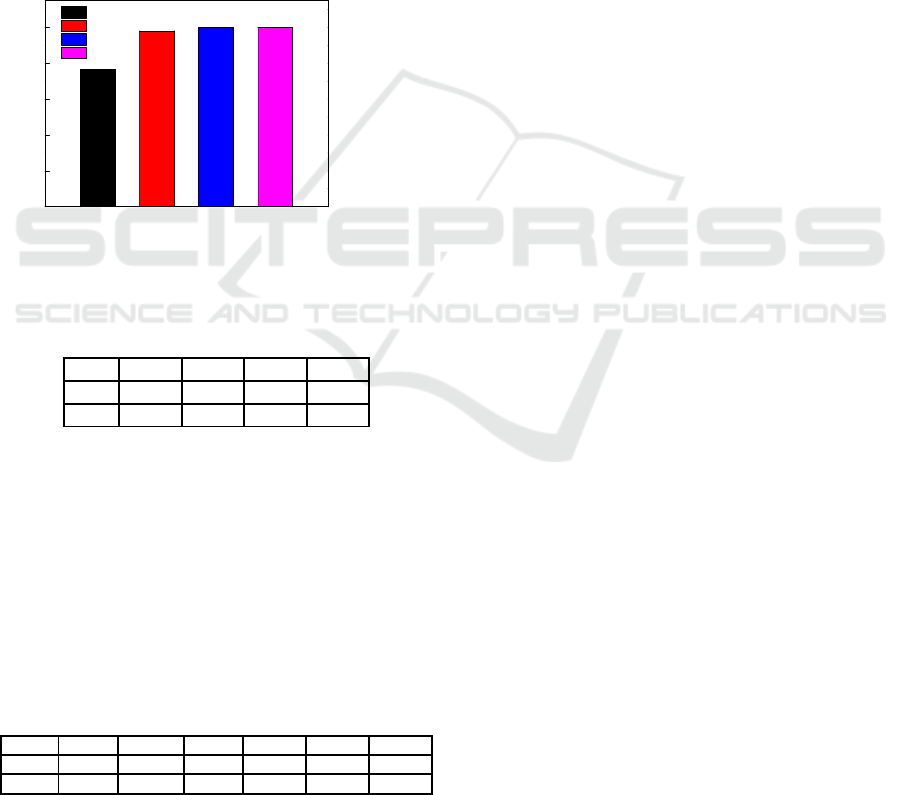
3.2 Effect of Stirring Speed
The effect of stirring speed on the efficiency of
cadmium ion was shown in Figure 2. As can be seen
from Figure 2, with the increase of stirring speed,
the efficiency of cadmium ion was gradually
increased. After the stirring speed was increased to
800 rpm, the cadmium ion
efficiency reached
99.99%. The effect of stirring speed on the
efficiency of copper ion and arsenic ion was shown
in Table 2. It can be seen from that the stirring speed
has little effect on the efficiency of copper ion and
arsenic ion. The increase of stirring speed increased
the removal of cadmium ion, but had no obvious
effect on the efficiency of copper ion and arsenic ion.
In summary, stirring speed was 800 rpm.
Table 2: Effect of stirring speed on copper ion and arsenic
ion efficiency (efficiency/%).
400 rpm 600 rpm 800 rpm 1000 rpm
Cu
2+
99.99 99.99 99.99 99.99
As
3+
99.99 99.99 99.99 99.99
0
20
40
60
80
100
1000
800
600
Cd
2+
removal efficiency/%
400 rpm
600 rpm
800 rpm
1000rpm
400
Stirring speed/rpm
Figure 2: cadmium ion efficiency with different stirring
speed.
The chemical elemental analysis of the purified
solution was shown in Table 3. It can be seen from
Table 3 that the total iron concentration of the
purified solution was significantly increased from
initial iron concentration of 24.18 g/L to final of
45.25 g/L. And the concentration of zinc ion was
31.07 g/L, which was significantly higher than the
initial 5.54 g/L. It was worth noting that the content
of arsenic ion, copper ion, and cadmium ion was
lower after purifying, which meets the National
standards.
Table 3: Chemical multi-element analysis of the purified
solution (concentration, mg/L).
TFe SO
4
2
-
Zn
2
+
Cu
2
+
As
3
+
Cd
2
+
Initial 24180 91310 5540 260.5 453.73 46.35
Final 45250 120090 31070 0.0001 0.0001 0.0001
3.3 Effect of Temperature
The effect of reaction temperature on cadmium
ion removal rate was shown in Figure 3. As was
seen from Figure 3, cadmium ion efficiency
increased with the increase of reaction temperature.
When the reaction temperature was 20 ℃, the
Study on the Purification Process of Arsenic High Iron Wastewater from Zinc Smelter
191
efficiency of cadmium ion was only 76.49%. When
the temperature was increased to 40 ℃, the
efficiency of cadmium ion was increased to 98.12%.
After the temperature was increased to 60 ℃, the
efficiency of cadmium ion reached 99.99%.
The influence of reaction temperature on copper
ion
and arsenic ion efficiency was shown in Table 4.
It can be seen from Table 4 that the reaction
temperature has little effect on the efficiency of
copper ion and arsenic ion. The increase of reaction
temperature increased the removal of cadmium ion
by iron powder and zinc powder, but had no obvious
effect on the removal of copper ion and arsenic ion.
In summary, the reaction temperature was selected
60
0
20
40
60
80
100
Cd
2+
removal efficiency/%
20 ℃
40 ℃
60 ℃
80 ℃
20
40
60
80
Temperature/℃
Figure 3: Cadmium ion efficiency with different
temperature.
Table 4: Effect of temperature on copper ion and arsenic
ion efficiency (efficiency/%).
20 ℃ 40 ℃ 60 ℃ 80 ℃
Cu
2+
99.99 99.99 99.99 99.99
As
3+
99.99 99.99 99.99 99.99
The chemical multi-elemental analysis of the
solution after purification at 60 °C was shown in
Table 5. It can be seen from Table 3 that the
concentration of total iron, zinc ion and sulfate ion
in purified solution were respectively 55.23 g/L,
39.0 g/L and 126.25 g/L. It was worth noting that the
content of arsenic ion, copper ion and cadmium ion
in the purified solution was relatively low, which
also meets the National standards.
Table 5: Chemical multi-element analysis of the purified
solution(concentration, mg/L).
TFe SO
4
2
-
Zn
2
+
Cu
2
+
As
3
+
Cd
2
+
Initial 24180 91310 5540 260.5 453.73 46.35
Final 55230 126250 39000 0.0001 0.0001 0.0001
4 CONCLUSIONS
Adding iron powder as reductant without zinc,
arsenic ion, copper ion efficiency was good, the
removal rate reached 99.37%、99.17%, however,
cadmium ion removal rate was poor, the removal
rate of only 51.67%. cadmium ion removal rate can
be greatly improved by adding zinc powder , which
reached 99.99% under the condition of 1% zinc;
The best purification conditions are: iron powder
1%, zinc powder 2%, reaction temperature 60 ℃,
stirring speed 800 rpm. Under this condition, arsenic
ion, copper ion, cadmium ion content comply with
national emission standards;
After purification, the concentrations of total
iron, sulfate ion and zinc ion were 55.23 g/L, 126.25
g/L and 39.00 g/L, respectively, which provided the
precondition for the subsequent preparation of iron
and zinc complex salt flocculant.
REFERENCES
Busetti F, Badoer S, Cuomo M, et al. 2005Occurrence and
Removal of Potentially Toxic Metals and Heavy
Metals in the Wastewater Treatment Plant of Fusina [J].
Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research 44(24)
9264
Fu F, Wang Q 2011 Removal of heavy metal ions from
wastewaters: a review[J] Journal of Environmental
Management 92(3) 407
Cao X L, Sheng Y X 2015 Research Progress in
Biological Treatment of Wastewater Containing
Sulfate Heavy Metals[J] Environmental Science and
Technology s2 181
Greenleaf J E, Lin J C, Sengupta A K 2006 Two novel
applications of ion exchange fibers: Arsenic removal
and chemical-free softening of hard water[J].
Environmental Progress 25(4) 300
He Y C, Li X Z, Zhou Q J. 2013 Practice of treatment of
copper-containing acidic wastewater by sulfide
precipitation method[J] Sulfuric Acid Industry 06 51
He Z, Li Y, Yu G, et al. 2012 Preparation of polyferric
aluminum sulfate from pyrite wastewater treatment
sludge[J] Chinese Journal of Environmental
Engineering 6(7) 2437
Huisman J L S G 2006 Biologically produced sulphide for
purification of process streams, effluent treatment and
recovery of metals in the metal and mining industry.[J]
Hydrometallurgy 83 56
Huo J X, Guo Y, Wang Z 2009 Review and Prospect of
Arsenic (III) Water Treatment Technology[J]
Environmental Science and Technology 11 102
Jong T, Parry D L 2003 Removal of sulfate and heavy
metals by sulfate reducing bacteria in short-term bench
IWEG 2018 - International Workshop on Environment and Geoscience
192

scale upflow anaerobic packed bed reactor runs[J].
Water Research 37(14) 3379
Li Y, Xu M X, Lin C M 2010 Process for preparing iron
black pigment from pyrite wastewater[J] Chemical
Industry and Engineering Progress 29(1) 168
Liu Z C 2016 Research on resource utilization technology
of pickling waste liquid in iron and steel enterprises [D]
Xiangtan: Xiangtan University
Meng B, Zhai C Z 2013 Research progress in the
treatment of arsenic-containing wastewater by
microbial treatment[J] Water Treatment Technology
39(11) 5
Ozverdi A E M 2006 Cu
2+
, Cd
2+
and Pb
2+
adsorption from
aqueous solutions by pyrite and synthetic iron
sulphide.[J] J. Hazard. Mater 137 626
Song J 2016 Preparation and properties of novel organic-
inorganic flocculants [D] Tianjin: Tianjin Polytechnic
University
Tang Z Y 2010 Study on wastewater treatment of heavy
metals and arsenic [D] Lanzhou: Lanzhou University
Yang Z C, Zhu L J, Liu R P, et al. 2014 Treatment method
and economic evaluation of strong acid high
concentration arsenic wastewater[J] Journal of
Environmental Engineering 06 2205
Zhao J Y, Wang J S, Zheng J 2012 Current Status of
Treatment and Disposal Technology of Arsenic-
Containing Wastewater and Waste Slag[J] Journal of
Beijing Normal University(Natural Science) 48(3) 287
Study on the Purification Process of Arsenic High Iron Wastewater from Zinc Smelter
193
