
Characteristics of Heavy Metal Enrichment of Vegetation
Rhizosphere Sediment in Intertidal Salt Marsh of Minjiang River
Estuary
Yonghong Wu
The Geography Science Department of MinJiang University, Fuzhou 350108, China.
Email: shuangyun2626@163.com.
Keywords: Minjiang River estuary, intertidal wetland, vegetation rhizosphere sediments, heavy metals
Abstract: In order to investigate the characteristics of heavy metal elements enrichment in the rhizosphere sediments
of different vegetation types, several cores of the rhizosphere sediments (0~20 cm) were collected from
different vegetation types zone in intertidal wetland of Langqi Island, the Minjiang estuary. The results
demonstrate that heavy metals have obvious enrichment at the depth of 2 cm in the sediment surface in the
rhizosphere of Spartina alterniflora, Scirpus mariqueter and Phragmites australis. Heavy metals also showed
obvious accumulation at the depth of 10~12 cm in the rhizosphere sediments of Scirpus mariqueter and
Phragmites australis, while Spartina alterniflora did not show this feature. The content of heavy metals in
the rhizosphere sediments of Scirpus mariqueter reached its lowest value at the depth of 16 cm, then
increased with depth. It is speculated that the adsorption of heavy metals by the roots of Scirpus mariqueter
mainly concentrates at the depth of 16 cm. Pearson correlation analysis was conducted on the changes of
heavy metal in sediments under different vegetation, shows that obvious positive correlation is observed
between Cu, Fe, Mn, Pb and Zn, indicating that they have similar sources and may have a certain
relationship with human activities. However, Cr, Sr is more likely to come from natural sources. The
enrichment of Rb, Zr may be influenced by the selective adsorption of different plant roots or other
environmental factors.
1 INTRODUCTION
The coastline of China is long and has developed a
broad muddy coast (tidal flats). The tidal flats are
affected by many factors such as cyclical tide and
vegetation growth, which cause significant changes
in redox conditions, organic matter degradation, and
microbial activity (Wang et al., 2012). Changes in
these factors have an important impact on the
accumulation, change and migration of heavy metals
in sediments. The estuary tidal flats are affected by
the two-way currents of rivers and seas. They have
complex hydrodynamic actions and frequent
changes in erosion and siltation. They are typical
environmental fragile zones and sensitive zones and
are highly susceptible to sudden events such as
severe weather and storm surges (Yu et al., 2009).
When the sediment is disturbed, heavy metal
elements will be released into the environment and
cause secondary pollution (Wang et al., 2005). Tidal
flats sediments as potential sources of heavy metals
may contaminate the surrounding aquatic ecosystem
and may be toxic to aquatic organisms (Wang et al.,
2012). More importantly, heavy metals can be
absorbed by aquatic organisms, and thus enter the
food chain, transfer to the superior nutrition layer,
and become a potential source of toxicity to humans
(Ke and Wang, 2012). Therefore, the accumulation
and cycling of heavy metals have been a concern for
tidal flats in estuarine ecosystems (Reboreda and
Caçador, 2007; Duarte et al., 2010; Koretsky et
al.,2007).
The Minjiang River estuary is a strong tide
estuary that develops submarine deltas and forms a
broad muddy coast. In recent decades, the exotic
species Spartina alterniflora has rapidly spread and
Wu, Y.
Characteristics of Heavy Metal Enrichment of Vegetation Rhizosphere Sediment in Intertidal Salt Marsh of Minjiang River Estuary.
In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Environment and Geoscience (IWEG 2018), pages 99-104
ISBN: 978-989-758-342-1
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
99

is bound to affect the tidal flat wetland ecosystem of
the Minjiang River estuary. At present, there are few
reports on the characteristics of the heavy metal
accumulation in the tidal flat wetland of the
Minjiang River estuary and its relationship with
environmental factors. In this paper, the
characteristics of heavy metal accumulation in the
rhizosphere sediments of different vegetation types
in the Minjiang River estuary are studied. It will not
only contribute to the development of resources and
environmental remediation in the Minjiang River
estuary, but also provide scientific theoretical basis
for the conservation, maintenance and restoration of
the tidal flat wetland ecosystem in the Minjiang
River estuary.
2 MINJIANG RIVER ESTUARY
TIDAL FLAT WETLAND
OVERVIEW
The Minjiang River is the largest river in Fujian
province and originated in Wuyi Mountain in
western Fujian. The basin area is 60,992 km
2
,
accounting for about one-half of the total area of
Fujian Province. The Minjiang River estuary is an
important material distribution center, and it is also
the seat of Fuzhou city, the provincial capital of
Fujian and plays an important role in the economic
development of Fujian Province. The Minjiang
River estuary is a strong tide estuary that develops
submarine deltas and forms a vast muddy coast. The
tidal flat wetland is affected by the regular half-day
tide, and the tidal creek system develops, forming a
typical tidal flat salt marsh. From land to sea, it can
be divided into high tidal flats, medium tidal flats
and low tidal flats. The tidal flat vegetation is
dominated by Phragmites australis, Spartina
alterniflora and Scirpus mariqueter. Phragmites
australis mainly grow on high tidal flats. Spartina
alterniflora and Scirpus mariqueter grow on
medium tidal flats. The vegetation growth density
gradually decreases from high tidal flats to low tidal
flats. Phragmites australis and Scirpus mariqueter
are the primary vegetation in this area, and Scirpus
mariqueter is a unique salt herb in China. Spartina
alterniflora is a perennial salt marsh plant native to
the Atlantic coast of the United States, and it has
superior reproduction and diffusion capabilities.
Since it was introduced in 1979, it has rapidly
spread in coastal areas of China. At present, from
the north of Liaoning province to the south of
Guangdong province, the invasion area of Spartina
alterniflora has reached 56,000 hectares, which
poses a serious threat to the conservation of
biodiversity and ecological security in tidal flats.
3 SAMPLE COLLECTION AND
EXPERIMENTAL METHODS
3.1 Sample Collection
In October 2015, six columnar samples of plant
rhizosphere sediments were collected from a typical
vegetation zone in the Dongtan of Langqi island
using a PVC pipe about 8 cm in diameter (Figure 1).
The length of the column sample was 20-25 cm, and
2 of them were located in a typical Phragmites
australis growing area, 2 of them are located in the
Spartina alterniflora growing area, 2 of them are
located in the Scirpus mariqueter growing area, but
the latter has a sporadic distribution of Spartina
alterniflora. The samples were packaged in
polyethylene bags and placed vertically and returned
to the laboratory for separation. The columnar
samples were divided according to 0~1 cm, 1~2 cm,
2~4 cm, 4~6 cm, 6~8 cm, 8~10 cm, 10~12 cm,
12~14 cm, 14~16 cm, 16~18 cm and 18~20 cm.
Figure 1: Location map of the study area and sampling sites.
IWEG 2018 - International Workshop on Environment and Geoscience
100

3.2 Experimental Methods
In this study, the contents of Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb, Zn,
Rb, Sr, Zr, Cr in the rhizosphere sediments of the
tidal flat vegetation in the Minjiang River estuary
were tested and analyzed. The heavy metal of the
sample was measured using XRF-1800 scanning X-
ray fluorescence spectrometer. The sample was
dried in an oven at 40°C for 72 hours and then fully
ground using an agate mortar. After sifting through a
100-mesh sieve, 2~4 g of the sample were placed in
a polyethylene disk and samples with an inside
diameter of approximately 30 mm and an outside
diameter of approximately 40 mm are produced at
pressure of 37.5 t. This method selected standard
water system deposition materials (GSD-9, China
Stream Sediment Reference Material) as the control
standard (Wu et al., 2015).
4 CHARACTERISTICS OF
HEAVY METAL
ACCUMULATION IN
RHIZOSPHERE SEDIMENTS
OF TIDAL FLAT VEGETATION
4.1 Enrichment Characteristics of
Heavy Metals in Rhizosphere
Sediments of Phragmites Australis
The vertical variation of heavy metal in the
rhizosphere sediments of Phragmites australis is
obvious (Figure 2). Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb, Zn, Sr, Zr
and Cr are significantly enriched at the depth of 2
cm, after that, the content of heavy metal decreases
with depth. However, the enrichment of Rb at the
depth of 2 cm is not significant. All of the 10
elements were significantly enriched at 10-12 cm,
and at the depth of 6 cm, there are low content.
Below 12 cm, the contents of Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb, Zn,
Rb, Sr, and Cr decreased significantly with depth.
However, the Zr does not decrease with depth below
12 cm. Rb and Sr are enriched at the depth of 16 cm,
and Fe, Mn, Ni, Zn and Cr also reflects this feature
but not significant. With the exception of Cr, the
enrichment of the other 9 elements at the depths of
10-12 cm was significantly stronger than that at the
depths of 2 cm.
Figure 2: Distribution profiles of heavy metal
concentrations in the rhizospheric sediments of
Phragmites australis.
4.2 Enrichment Characteristics of
Heavy Metals in Rhizosphere
Sediments of Scirpus Mariqueter
The vertical variation of heavy metal elements in the
rhizosphere sediments of Scirpus mariqueter was
similar to that of Phragmites australis at 0-12 cm
depth (Figure 3). At the depths of 2 cm and 12 cm in
the sediments, there was significant heavy metal
enrichment. Below 12 cm, the content of heavy
metal decreases with depth. However, below 16 cm,
the contents of Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb, Zn, Rb, Sr and
Zr showed a gradually increasing with depth. The
content of Cr reached the lowest value at the depth
of 6 cm, and then it increased significantly with
depth, reached the highest value at the depth of 14
cm. Afterwards, it showed a decreasing trend until it
reached the depth of 18 cm, and then it showed a
tendency to increase with depth.
Figure 3: Distribution profiles of heavy metal
concentrations in the rhizospheric sediments of Scirpus
mariqueter.
Characteristics of Heavy Metal Enrichment of Vegetation Rhizosphere Sediment in Intertidal Salt Marsh of Minjiang River Estuary
101

Figure 4: Distribution profiles of heavy metal
concentrations in the rhizospheric sediments of Spartina
alterniflora.
4.3 Enrichment Characteristics of
Heavy Metals in Rhizosphere
Sediments of Spartina Alterniflora
The vertical variation of heavy metal in the
rhizosphere sediments of Spartina alterniflora was
significantly different from that of Phragmites
australis and Scirpus mariqueter. The heavy metal
were significantly enriched at the depth of 2 cm, and
then decreased with depth (Figure 4).
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
5.1 Key Features of Enrichment of
Heavy Metals in Rhizosphere
Sediments of Tidal Flat Vegetation
The vertical variations of heavy metal in the
rhizosphere sediments of different vegetations in the
tidal flats are similar, and they are significantly
enriched at the depth of 2 cm. It is more obvious in
Spartina alterniflora and Scirpus mariqueter. The
heavy metal accumulation in the rhizosphere
sediments of Phragmites australis and Scirpus
mariqueter was significant at the depth of 10~12 cm,
while Spartina alterniflora did not show this feature.
At the depth of 12 cm, the heavy metal decreased
significantly with depth. This change is also
reflected in previous studies. For example, in the
study of tidal flat sediments on the south bank of
Tivoli in New York, the three heavy metal elements
were significantly enriched at the depths of 13~15
cm. At the depth of 18~20 cm, the content of heavy
metal decreases rapidly with depth, reaching the
background value at about 50 cm (Gaboury et al.,
1999; Wang et al., 2002).
The rhizosphere of plants has an important
adsorption effect on heavy metal elements. During
the plant growing season, heavy metal in sediments
of the tidal flats was significantly reduced. Relative
to plant leaves and stems, plant roots have the
highest concentrations of heavy metals (Wang et al.,
2002). The content of heavy metals in the
rhizosphere sediments of the three plants of the
Minjiang River estuary were significantly enriched
at the depth of 2 cm, which may be due to the fact
that heavy metals in surface sediments are less
affected by the absorption of plant roots. The roots
of Scirpus mariqueter are concentrated below the
depth of 10 cm (Wang et al., 2012), and the heavy
metals in the surface sediments are less affected by
the absorption of plant roots, resulting in higher
heavy metal content at the depths of 2 cm and 10~12
cm, and a minimum of heavy metal content at
depths of 16 cm. Later, as the depth increases, it
shows a gradual increase. It can be inferred that the
adsorption of heavy metals by the roots of Scirpus
mariqueter is mainly concentrated at the depth of 16
cm. The roots of Phragmites australis are mainly
concentrated at 20~80 cm below the surface (Wang
et al., 2012). It has less adsorption of heavy metals
on surface sediments, which may lead to more
obvious enrichment of heavy metals at 10~12 cm
than that of Scirpus mariqueter. From 12 to 20 cm,
heavy metal gradually decreased with depth,
indicating that the adsorption of heavy metals by the
roots of Phragmites australis gradually increased.
The contents of heavy metals in the rhizosphere
sediments of Phragmites australis and Scirpus
mariqueter have a significant low value at the depth
of 6 cm. This phenomenon is not caused by the
adsorption of plant roots. The specific mechanism
needs further research. Roots of Spartina alternifolia
are more developed and a longer growing period
than Phragmites australis and Scirpus mariqueter
(Li et al., 2009). Its adsorption capacity for heavy
metals is also stronger. This feature may lead to
significant adsorption of Spartina alterniflora to
heavy metals in sediments at the depths of 10~12 cm.
As a result, Spartina alterniflora did not show
similar characteristics of heavy metal enrichment to
those of Phragmites australis and Scirpus
mariqueter.
IWEG 2018 - International Workshop on Environment and Geoscience
102
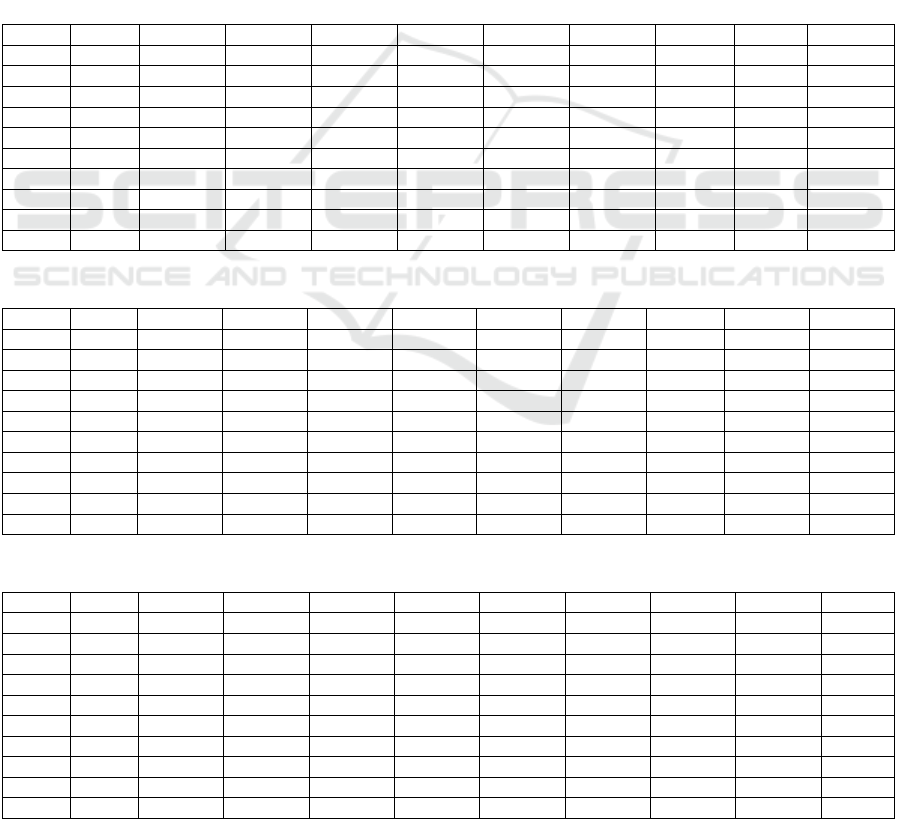
5.2 Correlation Analysis
Pearson correlation analysis was conducted on the
heavy metal of different vegetation rhizosphere
sediments (Table 1, Table 2, Table 3). The results
showed that Cu, Fe, Mn, Pb, and Zn were strongly
correlated in the rhizosphere sediments of the three
plants, it can be speculated that these five elements
have similar sources. There is no obvious correlation
between Cr, Sr and other elements, and Cr, Sr are
more likely to come from natural sources, such as
atmospheric deposition, changes in geochemical
composition, etc. The results of this study are in
good agreement with previous studies. Studies on
the surface sediments of Shanghai no residential
island have also confirmed that the sources of Cu,
Pb, and Zn are related to the effects of human
activities, and Cr is more likely to come from
natural source (Yang et al., 2011). Ni is an iron-
friendly elements that may be affected by changes in
Fe. Rb and Zr have no good correlation with other
elements in the rhizosphere sediments of Phragmites
australis. However, in the rhizosphere sediments of
Spartina alterniflora, Rb and Zr have a good
correlation with other elements. In the rhizosphere
sediments of Scirpus mariqueter, Rb and Zr also
showed some correlation with other elements. This
may be due to the effect of selective adsorption of
heavy metals by different plant roots or other
environmental factors. The specific mechanism
needs further investigation and verification.
Table 1: Correlation analysis of heavy metal elements in the rhizosphere sediments of Phragmites australis.
C
u
Fe Mn Ni Pb Z
n
Rb S
r
Z
r
C
r
C
u
1 .906
**
.830
**
.665
*
.762
**
.900
**
.755
**
.459 .030 .345
Fe 1 .905
**
.887
**
.726
*
.982
**
.581 .505 .183 .649
*
Mn 1 .798
**
.624
*
.851
**
.608
*
.608
*
.173 .421
Ni 1 .449 .886
**
.365 .388 .302 .818
**
Pb 1 .744
**
.550 .567 .451 .262
Z
n
1 .549 .424 .238 .627
*
Rb 1 .679
*
.145 .044
S
r
1 .397 .228
Z
r
1 .227
C
r
1
Table 2: Correlation analysis of heavy metal elements in the rhizosphere sediments of Scirpus mariqueter.
C
u
Fe Mn Ni Pb Z
n
Rb S
r
Z
r
C
r
C
u
1 .954
**
.941
**
.856
**
.833
**
.979
**
.824
**
.342 .622
*
-.007
Fe 1 .954
**
.892
**
.839
**
.980
**
.790
**
.295 .705
*
.179
Mn 1 .770
**
.732
*
.953
**
.729
*
.175 .523 -.002
Ni 1 .929
**
.883
**
.807
**
.404 .804
**
.267
Pb 1 .866
**
.704
*
.333 .899
**
.112
Z
n
1 .759
**
.275 .690
*
.050
Rb 1 .687
*
.578 .122
S
r
1 .357 .291
Z
r
1 .299
C
r
1
Table 3: Correlation analysis of heavy metal elements in the rhizosphere sediments of Spartina alterniflora.
C
u
Fe Mn Ni Pb Z
n
Rb S
r
Z
r
C
r
C
u
1 .986
**
.975
**
.981
**
.946
**
.992
**
.968
**
.731
*
.909
**
.207
Fe 1 .980
**
.990
**
.954
**
.996
**
.954
**
.745
**
.924
**
.192
Mn 1 .971
**
.947
**
.983
**
.907
**
.702
*
.921
**
.168
Ni 1 .933
**
.988
**
.957
**
.784
**
.910
**
.175
Pb 1.961
**
.909
**
.731
*
.977
**
.294
Z
n
1 .956
**
.740
**
.924
**
.211
Rb 1 .783
**
.892
**
.125
S
r
1 .724
*
.183
Z
r
1 .215
C
r
1
Characteristics of Heavy Metal Enrichment of Vegetation Rhizosphere Sediment in Intertidal Salt Marsh of Minjiang River Estuary
103

6 CONCLUSIONS
Through the analysis of the changes of heavy metal
in the rhizosphere sediments of different vegetations
on the tidal flats of the Minjiang River estuary, it is
found that the heavy metals in the rhizosphere
sediments of Phragmites australis, Scirpus
mariqueter and Spartina alterniflora were
significantly enriched at the depth of 2 cm. In the
rhizosphere sediments of Phragmites australis and
Scirpus mariqueter, heavy metal is also enriched at
the depth of 10~12cm.
Because the root system of Spartina alternifolia
is more developed than those of Phragmites
australis and Scirpus mariqueter, and it has a
stronger adsorption capacity for heavy metals in
surface sediments. It resulted in the fact that
Spartina alterniflora did not show similar heavy
metal accumulation to those of Phragmites australis
and Scirpus mariqueter at the depths of 10~12 cm.
The content of heavy metals in the rhizosphere
sediments of Scirpus mariqueter was the lowest at
the depth of 16 cm, and then shows increasing with
depth. It is inferred that the adsorption of heavy
metals by the roots of Scirpus mariqueter is mainly
concentrated at the depth of 16 cm.
The correlation analysis of the 10 heavy metal
elements indicates that there are strong correlations
among Cu, Fe, Mn, Pb, and Zn. It can be speculated
that they have similar sources and may have a
certain relationship with human activities. Cr, Sr is
more likely to come from natural sources. Rb, Zr
may be significantly affected by the selective
adsorption of different plant roots or other
environmental factors.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported by Minjiang University
Science and Technology Key Project of Fujian
Province of China (MYK17014), Young and
Middle-aged Teacher Education Research Project of
Fujian Province of China
(JT180403).
REFERENCES
Duarte B, Caetano M and Almeida P R 2010
Accumulation and biological cycling of heavy metal in
four salt marsh species, from Tagus estuary (Portugal)
Environment Pollution 158 1661
Gaboury B, William C N and Michael L 1999 Source and
history of heavy metal contamination and sediment
deposition in Tivoli south bay, Hudson river, New
York Estuaries 2 167
Ke Pan and Wang WenXiong 2012 Trace metal
contamination in estuarine and coastal environments in
China
Science of the Total Environment 421-422 3
Koretsky C M, Haveman M and Beuving L 2007 Spatial
variation of redox and trace metal geochemistry in a
minerotrophic fen Biogeochemistry 86 33
Li Bo, Liao Chengzhang and Zhang Xiaodong 2009
Spartina alterniflora invasions in the Yangtze River
estuary, China: An overview of current status and
ecosystem effects Ecol Engineer 4 511
Reboreda R and Caçador I 2007 Halophyte vegetation
influences in salt marsh retention capacity for heavy
metals Environment Pollution 146 147
Wang An-bao, Chen Manrong and Qu Haiyun 2005
Inductively coupled plasma atomic emission
spectrometry analysis of heavy metal contaminants in
tidal flat sediments. Environmental Chemistry 3 346
Wang Yong-hong, Zhang Jing and Shen Huanting 2002
Review of accumulation features study of heavy metal
in sendiment of tidal flat Advance in Earth Sciences 1
69
Wang Yongjie, Zheng Xiangmin and Zhou Limin 2012
Spatial and seasonal variation of acid volatile sulfide
(AVS) and its influence factors in intertidal salt marsh
of Yangtze River estuary Geochimica 2 158
Wang Yong-jie, Zhou Limin and Zheng Xiangmin 2012
Influence of Spartina alterniflora on the mobility of
heavy metals in salt marsh sediments of the Yangtze
River Estuary, China Environmental Science and
Pollution Research 3 593
Wu Yonghong, Zheng Xiangmin and
Zhou Limin 2015
Variation of elements in sedimentary and
paleoenvironment indicators during the last 8000 years
in Taihu Lake Journal of Salt Lake Research 1 16
Yang Hong, Wang Xiang and Li Naijiang 2011 Heavy
metal distribution and pollution assessment in the
surface sediments of Shanghai no residentis lands
Marine Environmental Science 1 24
Yu Ruilian, Wang Lijuan and Hu Gongren 2009
Distribution of acid-leachable heavy metals in
intertidal sediments from Quanzhou Bay
Environmental Chemistry 5 739
IWEG 2018 - International Workshop on Environment and Geoscience
104
