
Errors in Representation Translation in Solving Problems Related to
Number Sense of Pre-Service Math Teachers
Tatik Retno Murniasih
1,2
, Cholis Sa’dijah
2
, Makbul Muksar
2
and Susiswo Susiswo
2
1
Department of Mathematics Education, Universitas Kanjuruhan, Jl. S. Supriadi No. 48, Malang, Indonesia
2
Department of Mathematics Education, Universitas Negeri Malang, Jl. Semarang No. 5, Malang, Indonesia
tretnom@unikama.ac.id, {cholis.sadijah.fmipa, makbul.muksar.fmipa, susiswo.fmipa}@um.ac.id
Keywords: Number Sense, Pre-service Math Teachers, Representation, Translation.
Abstract: This research aims to describe errors in the representation translation ability in solving problems related to
number sense of the pre-service math teachers. The representation translation process used the Lash model
and focused on the representation translation of symbols, written language, and pictures. The research
subject was chosen according to their ability, and the result was 3 people with low ability, 4 people with
average ability, and 3 people with high ability. Based on the research result, the errors were mostly found in
the representation translation of decimal symbols into written language representation and fraction symbols
representation. It was easier for the pre-service math teachers to understand the representation translation of
pictures into written language representation and symbol representation. It is recommended for further
researches to study about the obstacles in representation of problems which are related to number sense.
1 INTRODUCTION
Number sense is important in learning mathematics.
Number sense is related to intuitive feeling and the
ability to be flexible when working with numbers
(Howden, 1989; NCTM, 1989). Number sense is
used as the basis in the concept of measurement,
geometry, algebra, and data analysis (Purnima et al.,
2014). Number sense is also used to develop
mathematical ability at school (Cochran and Dagger,
2013). Furthermore, number sense also influences
the performance in mathematics because people who
do mathematic calculation through algorithm do not
learn mathematics yet (Chattopadhyay et al., 2017).
From the description above, number sense ability is
important in building mathematic ability.
In many levels, number sense ability is very low.
Number sense ability in Junior High School is very
low in all grades (AK kaya, 2016). The number
sense performance of students aged 12-13 years-old
is weak (Purnima et al., 2014). According to
Sa’dijah (2013), many Junior High School students
have low number sense. Based on the research
conducted on mathematics students, the result is that
their number sense ability is low and they face
difficulties in doing representation translation (Ali,
2014). Therefore, there is a lot of chance to review
the representation translation about number sense
done by the pre-service math teachers.
A lot of researchers tried to analyze the errors in
representation translation process. Pre-service
teachers’ ability in doing representation translation
from mathematical notation (operation and brackets)
into problem statement is low (Isik, 2012). The
representation translation process from verbal into
graphic is not easy because it needs more than one
translation process, such as symbolic, schematic,
equation, and numeric (Rahmawati et al., 2017). The
ability to use mathematics flexibly in daily situation
is being more emphasized, yet to solve a problem,
representation translation from verbal description
and interpreting it into other representation is needed
(Usman, 2015). The difficulties in bridging these
representations and changing one representation into
other representation are the causes of the difficulties
in mathematical representation (Yerushalmy, 1997).
Therefore, further review on the errors in
representation translation about number sense is
needed.
Some researchers have used the representation
translation model. Janvier model (1987) used the
following representation translation: formulation,
tables, verbal descriptions, graphs, and object. Lesh
et al. model (1987) used the representation
translation: verbal symbols, written symbols,
Murniasih, T., Sa’dijah, C., Muksar, M. and Susiswo, S.
Errors in Representation Translation in Solving Problems Related to Number Sense of Pre-Service Math Teachers.
In Proceedings of the Annual Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities (ANCOSH 2018) - Revitalization of Local Wisdom in Global and Competitive Era, pages 393-399
ISBN: 978-989-758-343-8
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
393
manipulatives, pictures, and real world stuations,
which can be used to solve mathematical problems.
According to Pal (2014), real life experiences
representation, concrete models and diagrams, oral
language and symbols are needed to solve number
sense problems. The representation translation about
number sense problem in this research uses Lash et
al. (1987) representation translation model which
has been adapted: a) symbolic, b) written language,
and c) pictures. Based on these descriptions, the
aims of this research to describe errors in the
representation translation ability in solving problems
related to number sense of the pre-service math
teachers.
2 METHOD
This research reveals the errors in representation
translation of pre-service math teachers when
solving problems related to number sense. The
representation translation process is focused on the
symbolic, written language, and pictures
representation translation. The adapted Lash et al.
(1987) representation translation model can be seen
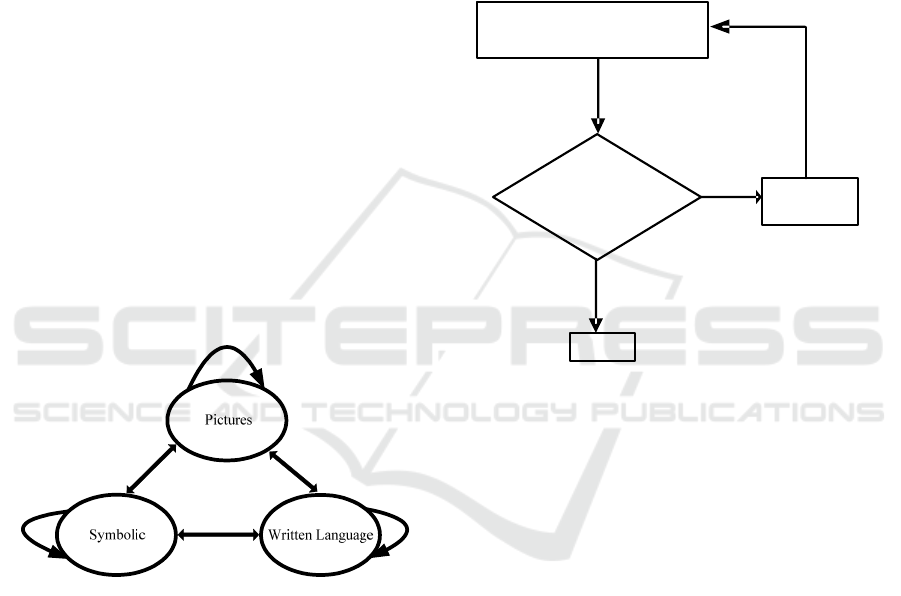
in the following Figure 1.
Figure 1: Representation Translation Model (Lash et al.,
1987).
In particular, this research describes the errors in
representation translation about number sense for
pre-service math teachers. The researchers wanted to
explain about the translation process from one
representation into other representation. This
research was conducted using qualitative data.
Qualitative research can explain, interpret, and
classify the obtained data (Yahia, 2006). This is
descriptive explorative research because the
researchers wanted to obtain detailed data naturally
about the process of representation translation in
number sense problems for the pre-service math
teachers.
The subject of this research was 10 pre-service
math teachers, which consisted of 3 people with low
ability (X1, X2, and X3), 4 people with average
ability (X4, X5, X6, and X7), and 3 people with high
ability (X8, X9, and X10). These pre-service math
teachers were given two problems in number sense.
Their results were examined. If they did the
representation translation correctly, their results
would not be analyzed. However, if they did not do
the representation translation correctly, their results
would be analyzed. The steps of choosing the
research subject can be seen in Figure 2 below.
Yes
Analyzed
No
Pre-service teachers are given
the number sense problems
Is the representation
translation correct?
Not a subject
Figure 2: Choosing the Research Subject.
The instruments used in this research were:
question sheets, recording tools, interview guidance,
and field notes. The question sheet were given to
find out the process of representation translation in
number sense done by the pre-service math teachers.
The question sheets were developed by the
researchers with the help from advisors and then
were validated by experts. There were two recording
tools, those were picture and voice recorder. The
interview was conducted to reveal the process of
representation translation in number sense of the
pre-service math teachers. The field notes were
notes made by the researchers when observing the
pre-service teachers solving the problems and
answering the researchers’ question in the interview.
The data analysis process was begun with
examining the result of the pre-service teachers,
recordings, field notes, and interview. The errors in
representation translation made by the pre-service
teachers were then analyzed. Qualitative analysis
was used to observe their concept understanding that
they had learned (Ghosh, 2015). The recordings
were used to further examine the representation
ANCOSH 2018 - Annual Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities
394
translation errors. The research procedure was
divided into several stages. In the preparation stage,
we prepared the learning tools and conducted a pre-
test. Based on this pre-test, we found that the
representation translation process in number sense
was still a problem for the pre-service math teachers
in Malang. In the data collecting stage, a camera was
used as a recording tool. To further understand about
the representation translation process in number
sense done by the pre-service teachers, an interview
was conducted to the selected subjects after they
finished solving the problems. These recordings
were then transcript. The data analysis stage was
done by reducting the data and illustrating diagrams
of representation translation in number sense
problems.
Instruments validation was made before
conducting this research. The validation was made
by 2 experts: 1 mathematics expert and 1 learning
expert. The criteria of the instruments validation can
be seen in Table 1.
Table 1. Validation Result Criteria (Akbar and Sriwiyana,
2011).
Standard
Criteria
Category Explanation
86% – 100% Very valid
Can be used without
revision
70% – 85% Valid
Can be used with
mino
r
revision
60% – 69% Not valid Unuseable
0% – 59%
Very not
valid
Cannot be used at all
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Based on the validation from validator 1, the score
achieved was 84% and 88% from validator 2. Next,
find the mean of the scores that was 86%. Thus, the
instruments used were in very valid category, hence
could be used without revision.
After the instruments were validated, they were
ready to be used for this research. The researchers
gave the question sheets to the pre-service math
teachers. If the answer of the representation
translation in number sense from the pre-service
teachers was correct, it would not be used as the
research subject. If the answer was incorrect, it
would be used as research subject. There were two
problems in the question sheet: a) 1 problem about
decimal symbols representation that had to be
translated into written language representation and
fraction symbols representation, and b) 1 problem
about picture representation that had to be translated
into fraction symbols representation and decimal
symbols representation.
The description of the results of the pre-service
math teachers who made errors in representation
translation is as follows.
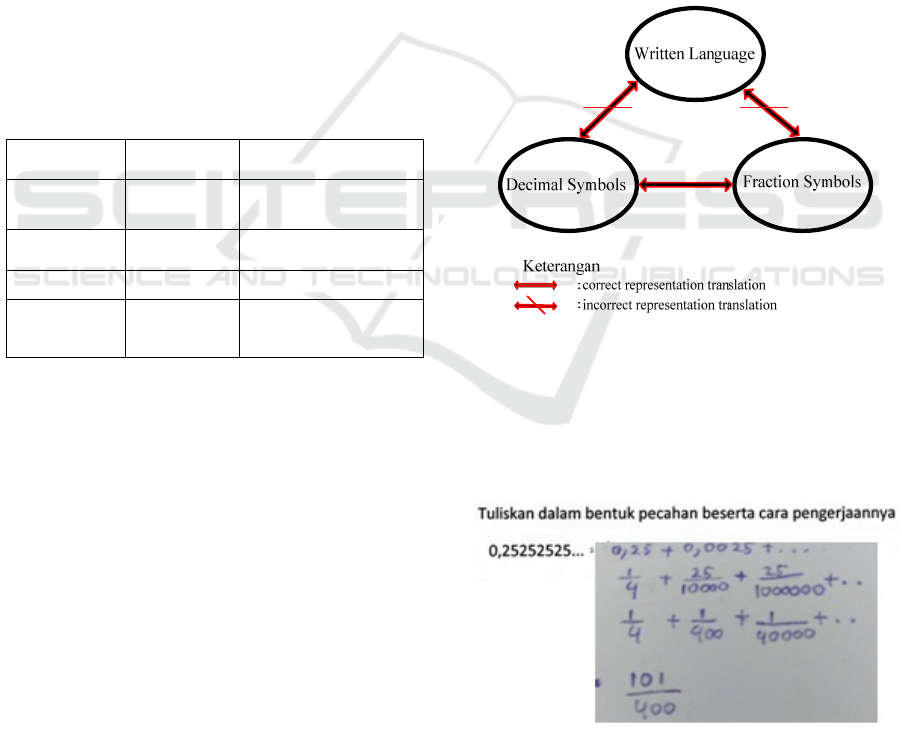
3.1 Result of Pre-Service Teacher X1
In the procedure of solving the first problem, pre-
service teacher X1 could translate the decimal
symbols representation into fraction symbols, but the
final answer was incorrect. Pre-service teacher X1
made an error in translating the decimal symbols
representation into written language and fraction
symbols representation (Figure 3).
Figure 3: Representation Translation on the First Problem
of Pre-Service Teacher X1.
The result of pre-service teacher X1 on the first
problem (Write down the fraction along with the
steps) can be seen in Figure 4 below.
Figure 4: Answer on the First Problem of Pre-Service
Teacher X1.
Errors in Representation Translation in Solving Problems Related to Number Sense of Pre-Service Math Teachers
395
Pre-service teacher X1 did not solve the second
problem, so the answer could not be analyzed.
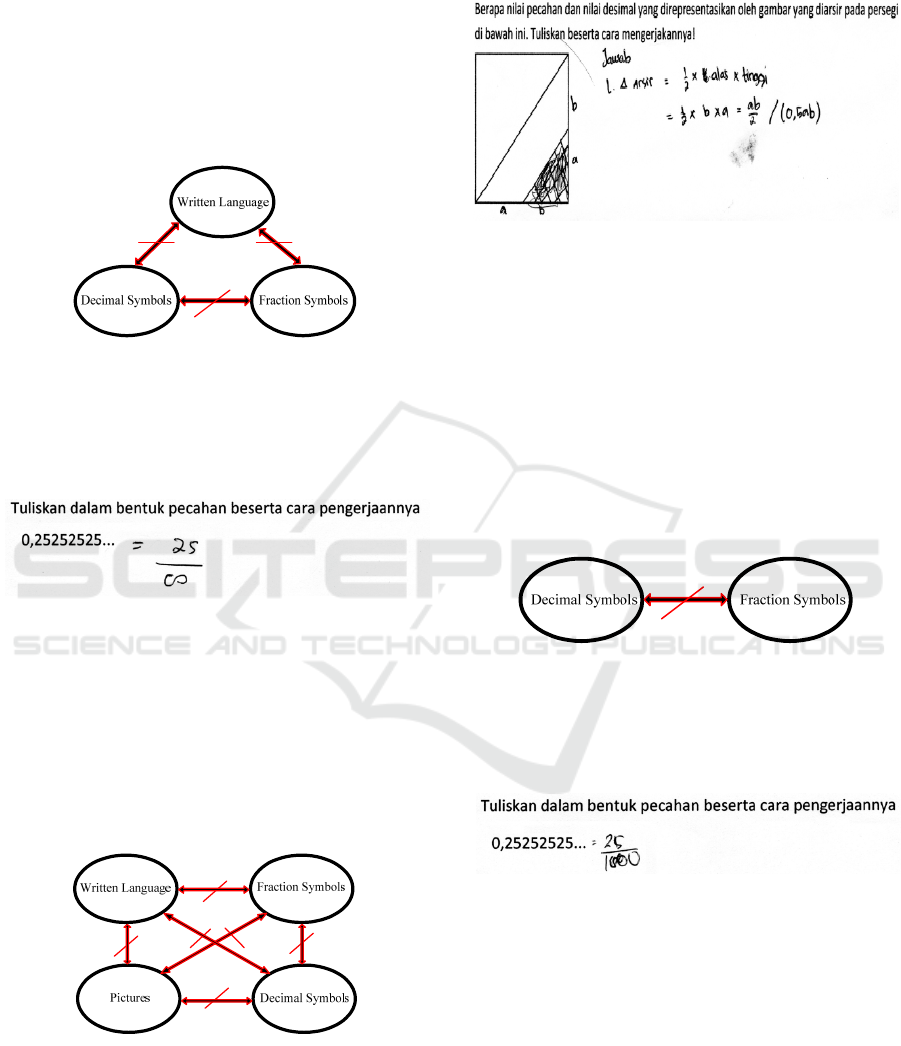
3.2 Result of Pre-Service Teacher X2
On the first problem, pre-service teacher X2 made
an error in translating the decimal symbols
representation into written language representation
and fraction symbols representation (Figure 5).
Figure 5: Representation Translation on the First Problem
of Pre-Service Teacher X2.
The result of pre-service teacher X2 on the first
problem can be seen in Figure 6.
Figure 6: Answer on the First Problem of Pre-Service
Teacher X2.
On the second problem, pre-service teacher X2
made an error in translating the pictures
representation into written language representation,
fraction symbols representation, and decimal
symbols representation (Figure 7).
Figure 7: Representation Translation on the Second
Problem of Pre-Service Teacher X2.
The result of pre-service teacher X2 on the
second problem (Find the value of fraction and
decimal represented by the shaded region of the
square below. Write down along with the steps!)
can
be seen in Figure 8.
Figure 8: Answer on the Second Problem of Pre-Service
Teacher X2.
3.3 Result of Pre-Service Teacher X3
On the first problem, pre-service teacher X3 made
an error in translating the decimal symbols
representation into written language and fraction
symbols representation. Pre-service teacher X3 did
not translate the written language representation but
directly made incorrect representation translation of
decimal symbols representation into fraction
symbols representation instead (Figure 9).
Figure 9: Representation Translation on the First Problem
of Pre-Service Teacher X3.
The result of pre-service teacher X3 on the first
problem can be seen in Figure 10.
Figure 10: Answer on the First Problem of Pre-Service
Teacher X3.
Pre-service teacher X3 did not solve the second
problem, so the answer could not be analyzed.
3.4 Result of Pre-Service Teacher X4
On the first problem, pre-service teacher X4 did not
translate the written language representation. Pre-
service teacher X4 directly translated the decimal
symbols representation into fraction symbols
representation incorrectly (Figure 11).
ANCOSH 2018 - Annual Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities
396
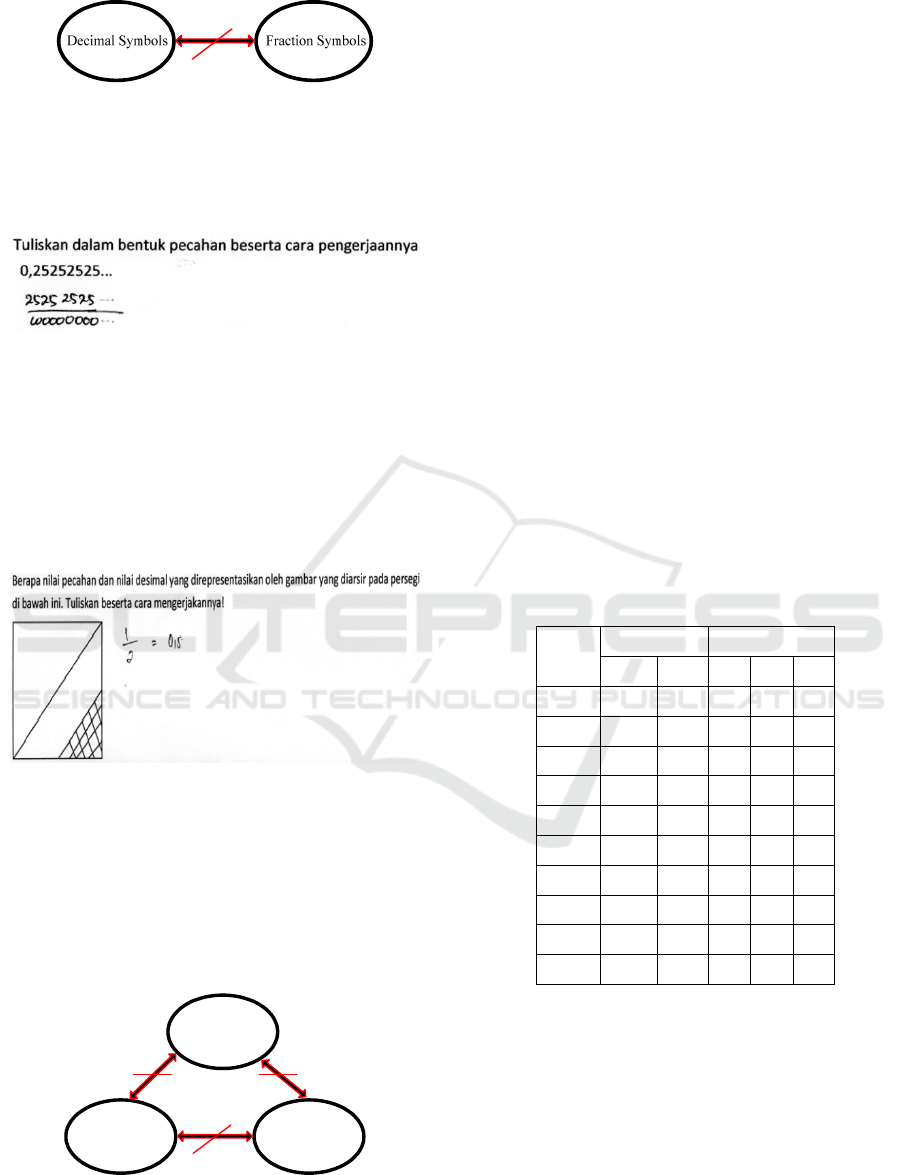
Figure 11: Representation Translation on the First
Problem of Pre-service Teacher X4.
Figure 12 shows the result of pre-service teacher
X4 on the first problem.
Figure 12: Answer on the First Problem of Pre-Service
Teacher X4.
3.5 Result of Pre-Service Teacher X5
Pre-service teacher X5 did not solve the first
problem, so the answer could not be analyzed.
Meanwhile the answer of pre-service teacher X5 on
the second problem can be seen in Figure 13.
Figure 13: Answer on the Second Problem of Pre-Service
Teacher X5.
In Figure 14, we can see that on the second
problem, pre-service teacher X5 did not translate the
written language representation, but directly
translate the pictures representation into fraction
symbols representation and decimal symbols
representation incorrectly.
Pictures
Fraction Symbols
Decimal Symbols
Figure 14: Representation Translation on the Second
Problem of Pre-Service Teacher X5.
The result of the pre-service teachers for the first
problem is: a) 4 people answered incorrectly (X1,
X2, X3, and X4), b) 3 people did not answer (X5,
X6, and X7), and c) 3 people answered correctly
(X8, X9, and X10). There are 4 incorrect answer on
the first problem which can be analyzed. The result
of the pre-service teachers for the second problem is:
a) 2 people answered incorrectly (X1 and X5), b) 2
people did not answer (X2 and X3), and c) 6 people
answered correctly (X4, X6, X7, X8, X9, and X10).
There are 2 incorrect answer on the second problem
which can be analyzed.
In general, the representation translation on the
first and the second problems of the pre-service
math teachers can be seen in Table 2. Based on
Table 2, for the first problem, 70% of the pre-service
teachers were not able to translate the decimal
symbols representation into written language
representation and fraction symbols representation.
On the second problem, the result was 40% of the
pre-service teachers were not able to translate the
pictures representation into written language
representation, fraction symbols representation, and
decimal symbols representation.
Table 2: Representation Translation of Pre-Service Math
Teachers.
Name
Problem 1 Proble
m
2
a b a b c
X1 x x x x x
X2 x x x x x
X3 x x x x x
X4xx
√
√
√
X5 x x x x x
X6xx
√
√
√
X7xx
√
√
√
X8
√
√
√
√
√
X9
√
√
√
√
√
X10
√
√
√
√
√
Notes:
a = representation translation of written language
b = representation translation of fraction symbols
c = representation translation of decimal symbols
√ = pre-service teacher can do the representation
translation correctly
x = pre-service teacher cannot do the representation
translation correctly
The pre-service teachers could not do the
representation correctly because they did not
understand the problem well. This is in line with the
Errors in Representation Translation in Solving Problems Related to Number Sense of Pre-Service Math Teachers
397

opinion from Hapsah, et al. (2017), which stated that
the incorrect problem understanding will lead to
incorrect representation. Errors in understanding the
problem also cause the modelling process from one
representation into other representation to be
incorrect (Murniasih, 2016). After understanding the
problem, the right strategy is needed to solve the
problem (Risalah, et al., 2016).
The researchers conducted an interview with the
pre-service teachers who made errors in doing the
representation translation in number sense problems.
The interview was not conducted on all of the pre-
service teachers, but it was classified based on the
characteristics of errors from the answers. From
each group, one person was chosen to be
interviewed. 3 subjects was chosen for the interview,
namely X1, X2, and X5. A break was given in every
interview so that the subjects could give the
complete answer. This is in line with the opinion
from Juairiyah et al. (2014). Based on the interview
with subject X1 on the first problem, subject X1 was
able to translate the decimal representation into
fraction representation, but he found difficulties in
finding the final answer. Subject X1 was confused
because the addition was infinite, so he could not
write down the final answer. Subject X1 stated that
the denominators were distinct, thus he did not know
how to add them. On the second problem, subject
X1 stated that he was confused because the area was
unknown; therefore, he could not find the final
answer. Based on the interview with X2, on the first
problem, subject X2 did not know the procedure;
therefore, he directly gave the incorrect final answer.
On the second problem, subject X2 stated that the
area was unknown, so he could not find the final
answer. Based on the interview with X5, on the first
problem, subject X5 could not solve the problem
because he forgot the steps. The researchers asked
whether he had done similar problem before, and he
answered that he had, but he could not recall the
steps at all. On the second problem, subject X5
stated that he had difficulties with fractions. Based
on the interviews, we can see that the learning for
the pre-service teachers is still not effective.
Ineffective learning is the cause of the students’
inability to solve non-routine problems (Whittle and
Pacaya, 2007; Heath, 2010; Wright, 2016).
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the result and discussion, the
representation translation in number sense is still a
problem for the pre-service math teachers. The pre-
service math teachers made more mistakes in
translating the decimal symbols representation into
written language representation and fraction symbols
representation. On the other hand, they made less
mistakes in translating the pictures representation
into written language representation, fraction
symbols representation and decimal symbols
representation. Further research are recommended to
study about the obstacles in representation.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to express our gratitude to all parties
who had helped us in completing this article:
Universitas Kanjuruhan which sponsored us
financially; Prof. Dr. Cholis Sa’dijah, M.Pd, M.A. as
advisor I; Dr. Makbul Muksar, S.Pd., M.Si. as
advisor II; Dr. Susiswo, M.Si. as advisor III; and
State University of Malang for providing us with a
comfortable place to study and learn.
REFERENCES
AK kaya, R., 2016. An Investigation into the Number
Sense Performance of Secondary School Students in
Turkey. Journal of Education and Training Studies.
Vol. 4, No. 2.
Ali, P., 2014. Assessing Developmental Students’ Number
Sense: A Case Study. NADE Digest. Volume 8. Issue
1.
Chattopadhyay, K. N., Sarkar, K. C., Koner, S., 2017.
Number Sense of High School Students: An
Assessment. International Research Journal of
Interdisciplinary and Multidisciplinary Studies
(IRJIMS). Volume-III. Issue-V.
Cochran, Dagger. 2013. Taking the Guesswork Out of
Computational Estimation. The Mathematics
Educator. Vol. 23, No. 1.
Ghosh, B., 2015. Project based Learning to Support
Enterprise Business Analytics Education - The Role of
Cross Functional Groups to Enhance Cognitive
Outcomes. In Proceedings of the 7th International
Conference on Computer Supported Education.
Volume 2: CSEDU, 5-13, Lisbon, Portugal.
SCITEPRESS.
Hapsah, D. S., Susiswo, Nusantara, T., 2017. Kesalahan
Representation Matematis Siswa da Scaffolding pada
Pemecahan Masalah Luas Daerah Biandg Datar.
(Online) available at: http://karya-
ilmiah.um.ac.id/index.php/disertasi/article/view/61237
Heath, B., 2010. What Do the Signs Say? APMC 15 (1).
ANCOSH 2018 - Annual Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities
398

Howden, H., 1989. Teaching Number Sense. Arithmetic
Teacher. 36(6), 6-11.
Isik, C., 2012. The Analysis of the Problems the Pre-
Service Teachers Experience in Posing Problems
about Equations. Australian Journal of Teacher
Education. Vol. 37: Iss. 9
Janvier, C., 1987. Representations and Understanding:
The Notion of Function as an Example, In C. Janvier
(Ed.) Problems of Representations in the Learning
and Teaching of Mathematics. New Jersey: Lawrence
Erlbaum Associates.
Juairiyah; As’ari, A.R.; Muksar, M. 2014. Penggunaan
Number Sense dalam Pembelajaran Matematika untuk
Meningkatkan Hasil Belajar Trigonometri Siswa Kelas
X SMAN Negeri 7 Barabai. (Online) available at:
http://library.um.ac.id/ptk/index.php?mod=detailandid
=67755.
Lash, R., Post, T., Behr, M., 1987. Representations and
Translations among Representations in Mathematics
Learning and Problem Solving, In C. Janvier (Ed),
Problems of Representation in the teaching and
Learning of Mathematics (pp. 33-40). Hillsdale,
NJ:Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Murniasih, T. R., 2016. Penggunaan Media Manipulatif
Untuk Meningkatkan Pemahaman Konsep Siswa Pada
Teorema Pythagoras. Prosiding Seminar Pendidikan
Matematika Pascasarjana Universitas Negeri Malang.
NCTM, 1989. Curriculum and Evaluation Standarts for
SchoolMathematics, Author. Reston, VA.
Pal, M., 2014. Making Conceptual Knowledge
Connections to Clear Misconceptions in Fractions in
Primary Classrooms. IOSR Journal of Research and
Method in Education (IOSR-JRME). Volume 4, Issue
2 Ver. IV, PP 12-18.
Purnima, Y. W., Kowiyah, Alyani, F., Assiti, S. S., 2014.
Assessing Number Sense of Indonesian Elementary
School Students. International Education Studies. Vol.
7, No. 8.
Rahmawati, D., Purwanto, Subanji, Hidayanto, E., Anwar,
R. B., 2017. Process of Mathematical Representation
Translation from Verbal into Graphic. IEJME -
Mathematics Education. Vol. 12, No. 4.
Risalah, D., Nusantara, T., Sutawidjaja, A., Susiswo,
Irawan, E. B., Musa, 2016. Case Study Spatial
Reasoning in Student Junior High School Solve
Problems Geometri. IOSR Journal of Mathematics
(IOSR-JM). Volume 12, Issue 6 Ver. V. 58 – 61.
Sa’dijah, C., 2013. Kepekaan Bilangan Siswa SMP
Melalui Pembelajaran Matematika Kontekstual yang
Mengintegrasikan Keterampilan Berpikir Kreatif.
Jurnal Pendidikan and Pembelajaran (JPP)., Vol. 20,
No. 2.
Usman, A. I., 2015. Secondary School Pre-Service
Mathematics Teachers’ Content Knowledge of
Algebraic Word Prblem in Nigeria. European Journal
of Science and Mathematics Education. Vol. 3, No. 4.
Whittle, Pacaya, M., 2007. Meaningful Maths: Teaching
Map Skills. APMC 12 (3).
Wright, P., 2016. Social Justice in the Mathematics
Classroom. London Review of Education. Volume 14,
Number 2.
Yahia, I. B., 2006. B2C Virtual Communities: Typology
And Associated Benefits - An Exploratory Qualitative
Study. In Proceedings of the International Conference
on e-Business. Volume 1: ICE-B, 235-241, Setubal,
Portugal. SCITEPRESS.
Yerushalmy, M., 1997. Designing Representations:
Reasoning about Functions of Two Variables. Journal
for Research in Mathematics Education. 27 (4), 431-4.
Errors in Representation Translation in Solving Problems Related to Number Sense of Pre-Service Math Teachers
399
