
Does Problem-Based Learning Work on Presentation Skills?
Supri Wahyudi Utomo
1
, Moh. Ubaidilla
2
, Soetarno Joyoatmojo
1
, Sri Yutmini
1
and
Nunuk Suryani
1
1
Sebelas Maret University, Jl. Ir. Sutami 36A, Surakarta, Indonesia
2
Universitas PGRI Madiun, Jl.Setia Budi 85, Madiun, Indonesia
supriu@unipma.ac.id, mohubaidillah@unipma.ac.id, soetarno486311@gmail.com
Keywords: Presentation skills and problem-based learning.
Abstract: Presentation skills are seen as an important ability that must be mastered by university students to prepare
them for the work-place. Another purpose of university education aside from improving knowledge and
achievement is preparing the students for the real competitions and succeed in their career. This research
aimed to empirically prove whether problem-based learning method has its effect on students’ achievement
and presentation skills. This research used descriptive qualitative method while quota sampling technique was
used to select the subject. The data were analyzed by using structural equation modeling (SEM) with partial
least squares (PLS) while the students’ performance was measured descriptively. The result showed that
problem-based learning method gave a significant effect on students’ presentation ability which therefore
improve their achievements. Students developed independent learning habit through their Problem-Based
Learning experience which gave significant impact on the content and mastery of their presentation material
although the discussions session didn’t run well due to the text dependency of the participants.
1 INTRODUCTION
Presentation is a technique commonly used by
students and teachers to practice their knowledge and
teaching skills. Yalcin and Yalcin (2010: 480-486)
state that in the 21st century, the presentation method
had become the important requirement in daily life
related to social and individual needs. Presentation is
often used by teacher to measure the students’
mastery and understanding of the material as well as
to measure their communication skills. This is very
essential especially for those students majoring in
education as they are being prepared to deliver the
knowledge to their future students.
Recent studies have emphasized on the use of
Problem-Based Learning to improve students’
understanding on learning material. Some studies
have also mentioned on the effect of Problem-Based
Learning on students’ independent learning, problem
solving ability and teamwork. However, combining
all the aspect of learning above is another important
thing. All aspect mentioned can be seen clearly
through students’ ability in presentation skills. Harun,
Yusof, Jamaludin and Hassan (2012: 233-242) said
that: In the problem-based learning models, the
students are trained to do independent learning,
become useful in their group to solve the real
problems through context and independent learning.
This is in line with Magsino (2014: 1-5) and Jalani
and Sern (2015: 153-163) who stated that students
who taught with problem-based learning get wider
knowledge and understand the concept deeper than
those who taught with teacher-centered learning
model.
A problem-based learning is used by the teachers
to improve students’ motivation and creativity in the
learning process. Walton and Matthew in Alrahlah
(2016: 155-161) and Phungsuk, Viriyavejakul, and
Ratanolarn (2017: 297-306) also state that problem-
based learning had been introduced and develop as an
important part of learning to improve students’
ability, knowledge, and attitude which is the essential
part of the curriculum and encourage students to
question and examine on the area, object, people,
book, proof, and information. The process of
Problem-Based Learning encourage students to
present their study arrange the materials and present
the result of their study in a form of presentation.
Presentation is a form of evaluation which
become an important part of learning process that
enable teacher to evaluate the students’ knowledge,
and understanding of the materials as well as other
abilities such as communication, teamwork, group
discussion and problem solving. This skill is however
286
Utomo, S., Ubaidilla, M., Joyoatmojo, S., Yutmini, S. and Suryani, N.
Does Problem-Based Learning Work on Presentation Skills?.
In Proceedings of the Annual Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities (ANCOSH 2018) - Revitalization of Local Wisdom in Global and Competitive Era, pages 286-289
ISBN: 978-989-758-343-8
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

less observed by researchers. Levasseur, Dean, and
Pfaff in De Grez, Valcke, and Beringgs (2010: 1786-
1789.), stated that oral presentation skill recognized
as a major professional skill, but the learning process
and skill about the presentation is ever researched by
another researcher.
This research is aimed to evaluate the students’
ability in presentation. This is very important to
understand the effect given by Problem-Based
Learning method in students’ understanding and
mastery of the material through presentation. Other
skills promoted by the use of PBL in teaching and
learning such as communication, teamwork and
group discussion can also be analyzed through
presentation easily.
2 METHOD
This research is carried out by descriptive method,
which describes the application of the problem-based
learning to develop students’ achievement and
presentation skill. The subjects of the research are 45
sample students of the Accountant Education Study
program out 0f 96 student who are taken by quota
sampling technique. The overall students initially
have quite low of presentation abilities and most are
using monotonous slides and paper based
presentation. Their ability in mastering the material
was very poor and their presentation was not
interesting and alive.
2.1 Measurement of Variables
The measurement of problem-based learning
collisions is 3 dimensions and 18 indicators are
learning independence with the indicator code
KMB1, KMB2, KMB3, KMB4, KMB5, KMB6 and
KMB7, Learning Motivation with MOB8, MOB9,
MOB10, MOB11, MOB12, MOB13 indicator code,
and teamwork with code indicator KRT14, KRT15,
KRT16, KRT17, KRT18.
The measurement of presentation capacity is 12
indicators with the code KRT15, KRT16, KRT17,
KRT18, PRE19, PRE20, PRE21, PRE22, PRE23,
PRE24, PRE25, PRE26, PRE27, PRE28, PRE29,
PRE30.
2.2 Data Analysis Technique
The technique of analyzing the questionnaire data is
using structural equation modeling (SEM) analysis
with partial least squares (PLS) or smartPLS 2 tools,
to know the effect of problem-based learning model
on presentation ability. The reason for using SEM
analysis is, because of the latent and the first order
and second order constructs.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Evaluation of Measurement Model
(Outer Model)
Outer model is a step to know the validity and
reliability that connects with latent variables. To see
the validity is measured by using outer loading and
AVE. Requirements to meet validity must be above
0.50. Measuring the outer loading if there is one
invalid indicator that is PRE20 on variable Ability
presentation. On the AVE measurement, all contracts
and dimensions meet the criterion of the criterion of
0.5 is declared valid.
Measurement reliability using composite
reliability with criterion 0.7. The result of smartPLS
shows that all the constants and dimensions have met
the requirements, so it is declared reliable all the
constants and dimensions. Here are the AVE tables
and composite reliability.
Table 1: AVE and composite reliability.
AVE
Composite
Reliability
KMB
0,661662
0,931455
KRT
0,699493
0,92076
MOB
0,65102
0,917911
PBL
0,619589
0,966893
PRE
0,56497
0,933663
Source: Results of Data Processing SmartPLS 2 (2018).
3.2 Model Structure (Inner Model)
The structural model is evaluated by using R-square
(R²) for the dependent construct, and the T-test as
well as the significance of the structural path
parameter coefficients. R² can be used to assess the
effect of independent latent variables on latent
dependent variables whether they have substantive
results. In Table R-Square shows that the lowest R-
Square 0.049065 is included in the weak category and
the highest 0.945921 is included in the stable
category.
Does Problem-Based Learning Work on Presentation Skills?
287
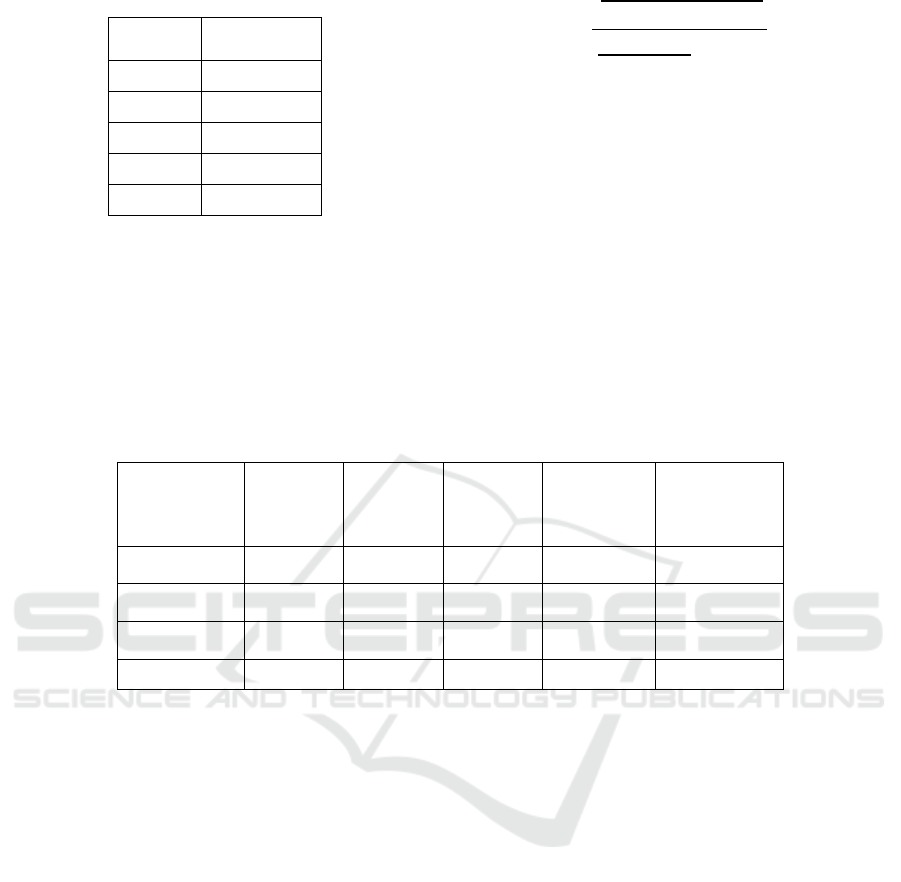
Table 2: R-Square.
R Square
KMB
0,945921
KRT
0,913484
MOB
0,928598
PBL
PRE
0,049065
Source: Results of Data Processing SmartPLS 2 (2018).
3.3 Evaluation of the Goodness of Fit
The result of the calculation of goodness of fit values
is 0.67340033 above the 0.50 criteria, so that the
research model is categorized fit. Here is the result of
the goodness of fit calculation with the formula:
3.4 Significance Test
In the Path Coefficient tables can be seen that the
problem-based learning model (PBL) to Presentation
Capability (PRE) with the value of T-statistics
14.855864 above 1.96 or 5% significant, and the
coefficient up to 0.221506 that shows the positive
numbers. It shows that the constraint of problem-
based learning has a positive effect on the
presentation skills.
Table 3: Path coefficients (Mean, STDEV, T-Values).
Original
Sample
(O)
Sample
Mean (M)
Standard
Deviation
(STDEV)
Standard
Error
(STERR)
T Statistics
(|O/STERR|)
PBL -> KMB
0,972585
0,972489
0,001775
0,001775
547,829967
PBL -> KRT
0,955764
0,955544
0,002888
0,002888
330,887144
PBL -> MOB
0,963638
0,963682
0,002072
0,002072
465,040043
PBL -> PRE
0,221506
0,227078
0,01491
0,01491
14,855864
Source: Results of Data Processing SmartPLS 2 (2018).
The result showed that the implementation of
Problem-Based Learning has a good impact on
Students’ presentation skill. Students’ ability in
constructing materials for presentation is quite good,
although improvement is needed. Students’ ability of
presentation is also improved quite significant.
However, there are some aspects that need further
improvement namely mastery of the materials and
readiness in responding the participants’ questions.
4 DISCUSSION
Problem-Based learning develops student’s
independent learning as they are faced to real life
problem to be solved. This is in line with Harun,
Yusof, Jamaludin and Hassan (2012: 233-242) who
stated that in PBL, students are trained to be
independent, effectively function in group work to
solve the real problem, therefore it motivates students
to learn contextually and independently. Supporting
the idea are Jalani and Sern (2015: 153-163) who
stated that students who are taught by using PBL are
able to obtained a wider knowledge and deeper
understanding of the concept compares to those
taught by using Teacher-Centered Learning.
The result also showed that students’ ability in
presentation is also improve significantly especially
in term of preparing the materials. This is essential as
preparing presentation is needed to give precise
information which makes it well accepted by listener.
Simona (2015: 69-74) says that to increase students'
awareness, preparing and providing the good
academic presentation, technique, and business based
on the rule, clear structure, uses language list and
supported by technology which can give success
contribution on their future career is highly essential.
The ability of presentation can be evaluated from
two kind points such as the ability to make the
material presentation (slide form as a document
presentation) and the ability when they do the
presentation. Goto and Kashihara (2016: 1285 –
1293) says that recently was happen increases usage
document presentation that consists of the slide as
ANCOSH 2018 - Annual Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities
288

learning content. The result showed that students’
ability in preparing a good and precise material has
improved significantly.
The similar result is found in the students’ ability
to present the material. This is in line with Levasseur,
Dean, and Pfaff in De Grez, Valcke and Berringgs
(2010: 1786-1789) that the ability of oral presentation
is recognized as the main professional skill. The result
shows that students’ ability in oral presentation has
improved compared to their previous result.
However, there are some skills that didn’t show
any improvement namely the material mastery and
ability to give quick response to every question.
Students are mostly still depend on the text in
presenting their material. Although the slide content
is quite effective and represent the materials, most of
them still used the text to refer to the answer given by
participants.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The result of the research shows that problem-based
learning model has significant influence towards the
students’ achievement. It is also able to develop
students’ presentation skill, in terms of the material
development and presentation performance. Students
are able to develop deeper understanding of the
material and present the material fluently. However,
students’ mastery of the material during the
presentation is still hasn’t improved. In addition, the
students are still unable to give quick responses
toward the questions given by participants and have
to refer to their text to find the answer.
REFERENCES
Alrahlah, A., 2016. How effective the Problem-Based
Learning (PBL) in dental education: A critical review.
The Saudi Dental Journal, 28, 155-161.
De Grez, L., Valcke, M., Beringgs. 2010. Student response
system and learning oral presentation skills. Procedia-
Social and Behavioral Sciences, 2, 1786-1789.
Goto, M., Kashihara, A., 2016. Understanding presentation
document with visualization of connections between
presentation slides. Procedia Computer Science, 96,
1285 – 1293.
Harun, N. F., Yusof, K. M., Jamaludin, M. Z., Hassan, A.
H. S., 2012. Motivation in problem-based learning
implementation. Procedia-Social and Behavioral
Sciences, 56, 233-242.
Jalani, N. H., Sern, L. C., 2015. Efficiency comparisons
between example-problem-based learning and teacher-
centered learning in the teaching of circuit theory.
Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 204, 153-
163.
Magsino, R. M., 2014. Enhancing higher order thinking
skills in a marine biology class through problem-based
learning. Asia Pacific Journal of Multidisciplinary
Research, 2, 1-5.
Phungsuk, R., Viriyavejakul, C., Ratanaolarn, T., 2017.
Development of a problem-based learning model via a
virtual learning environment. Kasetsart Journal of
Social Science, 38, 297-306.
Simona, C. E., 2015. Developing presentation skills in the
English language courses for the engineering students
of the 21st century knowledge society: A
methodological approach. Procedia Social and
Behavioral Sciences, 203, 69-74.
Yalcin, A., Yalcin, N., 2010. How to get best result from a
presentation? How to increase effectiveness of a
presentation? Procedia Social and Behavioral
Sciences, 9, 480–486.
Does Problem-Based Learning Work on Presentation Skills?
289
