
Strategy Increases Informal Trader Investment Discovered
Traditional Market in Medan City
Ahmad Kholil and Hubbul Wathan
Politeknik Negeri Medan, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Kampus USU, Jl. Almamater No. 1, Kota Medan, Sumatera Utara
20155 Indonesia
ahmadkholil@polmed.ac.id, hbwathan@polmed.ac.id
Keywords: Informal, tradears, strategy, SWOT.
Abstract: From the results of in-depth interviews with the seven related parties, it is concluded that the factors that
influence the informal income of Traders around the Traditional Market in Medan City. Different from other
reports and the informal sector or more often known by informal traders is increasing in number. The presence
of informal traders that continue to grow and increase also occurred in the city of Medan. Informal traders in
Medan City are mostly around traditional markets. This study aims to formulate a strategy in optimizing the
income of informal traders around the traditional market in Medan City. This research is expected to provide
benefits in optimizing revenue for informal traders and PD Pasar Medan city. The informal sector as a term
is usually used for a number of small-scale economic activities. The informal sector is considered as a
manifestation of the situation of employment growth in developing countries, so those entering these small-
scale activities in the city, primarily aim to seek employment and income rather than profit. Since those
involved in the sector generally come from low-income, low-educated, unskilled and predominantly
immigrant dominions, it is clear that they are not capitalists seeking profitable business and are not
businessman as they are known in general.
1 INTRODUCTION
The informal sector or more often known by informal
traders is increasing in number. The presence of
informal traders that continue to grow and increase
also occurred in the city of Medan. Informal traders
in Medan City are mostly around traditional markets.
North Sumatra as one of the most developed
provinces outside Java. As an area that is one of the
destinations of migrants from various regions, the
informal sector dominates the main job status in the
trade sector. In Table 1. It can be seen that 63.83% or
about 3.87 million people work in the informal sector,
while for the formal sector only about 36.28% or 2.19
million.
The informal sector as a term is usually used for a
number of small-scale economic activities (Alma,
2001). The informal sector is considered as a
manifestation of the situation of employment growth
in developing countries, so those entering these
small-scale activities in the city, primarily aim to seek
employment and income rather than profit. Since
those involved in the sector generally come from low-
income, low-educated, unskilled and predominantly
immigrant dominions, it is clear that they are not
capitalists seeking profitable business and are not
businessman as they are known in general.
The presence of informal traders that continue to
grow and increase as well as in the city of Medan,
most informal traders depend their lives on the
existence of traditional markets. However, the current
development of traditional markets is very
insignificant and even declining because of the
difficulty of structuring and managing the places that
cannot attract merchants to sell goods on the available
spots in traditional markets.
One of the problems in the development of
traditional markets in Medan is the difficulty of
arranging informal traders who prefer to sell in the
street stands that causes inconvenience of buyers and
traffic of vehicles that are hampered by trading
activities. Informal Traders who basically have
limitations in venture capital, expertise and
knowledge of the existing rules become a problem
that has to be taken care of. Some alternative that can
be done is expected to overcome the existing
problems.
Kholil, A. and Wathan, H.
Strategy Increases Informal Trader Investment Discovered Traditional Market in Medan City.
In Proceedings of the Annual Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities (ANCOSH 2018) - Revitalization of Local Wisdom in Global and Competitive Era, pages 275-285
ISBN: 978-989-758-343-8
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
275
The Medan City Government has been trying to
accommodate informal traders' demand by providing
areas for local markets, but informal traders are not
willing to sell their goods in the provided place
because the places are seen as not being strategic.
The SWOT Matrix is an important matching tool
to help decision makers develop 4 (four) types of
strategies. The four types of strategies are SO
Strategy, WO Strategy, ST Strategy, and Strategy ST.
In this matrix, using key success factors for internal
and external environments is a difficult part so good
judgment is required. The usefulness of the SWOT
matrix is to formulate a feasible alternative strategy
to implement, not to choose or determine which
strategy works best. So not all strategies are
developed in the SWOT. Table 1 shows the informal
merchant SWOT matrix PD Pasar Kota Medan as a
manager of traditional markets experienced problems
with store occupancy rate, kiosks and stall selling
under 80%.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Understanding the Informal Sector
The paper size must be set to A4 (210x297 mm). The
informal sector is generally defined as a sector
comprised of small business units that produce,
distribute goods and services with the ultimate goal
of creating employment and income for themselves
respectively as well as in their efforts is greatly
limited by capital and skills factors (Sinungan, 1988).
Meanwhile, according to Hadionoto (1996) who
stated that the choice of the informal sector is an
answer to the low education and skills possessed by
street children. The investment required for this
sector is relatively low and does not require special
skills or skills requirements.
2.2 Characteristics and Examples of
the Informal Sector
The informal business sector has only a small and
narrow scope of economic enterprises, since the
informal business sector is carried out by people who
may not be capitalized. In fact, the actors in the
informal sector can only borrow merchandise from
large entrepreneurs, then sell in their own way
without a neat sales organization. The sellers of
newspapers and magazines in big cities often borrow
the merchandise they sell, after the merchandise is
sold, and then they pay it off. The following describes
the characteristics of the informal sector:
• Has no business permit.
• Capital is not too large, relatively small.
• The number of workers involved is not too much
• In running the business does not require formal
education, special skills but only based on the
will or experience. The technology used is very
simple.
• Less understanding of how to manage finances.
• Business hours are not regular.
• The scope of his business is small.
• The type of business that is usually done in the
form of: craftsmen, trade and simple services.
• Production results tend to lower middle
segment.
The Characteristics of the Informal Sector is
different from the formal sector, in summary in Table
1 it can be seen the difference between the two
sectors.
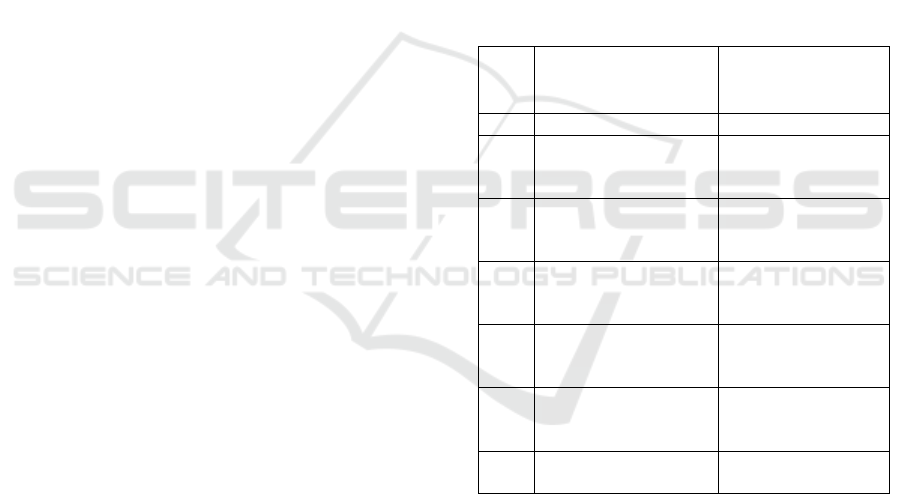
Table 1: Formal and informal character sector.
Source: Hadionoto, 1996.
Some examples of businesses in the informal
sector are:
• Street Traders
Street vendors we can meet on the street or in
the village. Street vendors in peddling
merchandise using carts, tables with tents as a
place to take shelter.
• Wholesalers
The traders are the ones who peddle goods by
thrusting goods to prospective buyers. Goods
offered are lightweight and portable goods such
as mineral water, newspapers, cigarettes,
No Informal character
sector
formal character
sector
1 Easy to access Difficult to access
2 depending on local
resources
depending on
external resources
3 family ownership
system
company ownership
system
4 operate in small cases
operates in large
numbers
5 technology is adaptive
using imported
technology
6 skills can be obtained
from outside
requires skill from
school
7 unorganised protected
ANCOSH 2018 - Annual Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities
276
candies, tissues, and others. These traders we
encounter at street intersections in urban
markets, at bus stops, at terminals, on buses, on
trains, and at stations.
• Grocers
Merchants who sell their goods from door to
door and from one place to another. They use
motorcycles, cars, carts, and others to carry
around. And they sell daily necessity.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
3.1 Types of Research
The research was conducted in traditional market
managed by PD Pasar Kota Medan. In each
traditional market there are informal traders. The type
of research in this study is action research, a study
conducted to obtain practical findings or for the
purposes of operational decision making. Because the
purpose is for operational decision making in order to
develop new skills or new approaches (Sinulingga,
2011).
Population is the whole subject of research that
includes all elements that exist within the research
area (Arikunto, 2006). The population in this study
consists of the competent parties provide information
about informal traders who sell around the traditional
market managed PD Pasar Medan namely:
• The Director of Operational of PD Pasar Kota
Medan
• Chairman of Traditional Traders Association of
Medan City
• Vice Chairman of Traditional Traders
Association of Medan City
• Chairman of Traditional Market Traders
Cooperative Medan City.
• Chairman of Association of Street Traders
(APKLI) Medan City
• Vice Chairman of APKLI Medan City
• Secretary of APKLI Medan City
3.2 Data Collection Technique
Data were obtained from in-depth interviews with the
seven specified parties. Interviews were conducted
separately, then the researchers formulated the
interview results coupled with supporting documents.
3.3 Data Analysis
Data and information obtained from seven parties
related to informal traders and traditional market
operations managed by PD Pasar Kota Medan, were
collected and then analyzed by using environmental
analysis that is an analysis of internal environment of
company which produce strength and weakness and
also external environment of company which
generate opportunities and threats (Rangkuti, 2008).
SWOT is an acronym for Strengths, Internal
Weakness, and Opportunities and Threats from the
company's external environment. The SWOT
analysis is based on the assumption that an effective
strategy maximizes the strengths and opportunities
and minimizes the weaknesses and threats of a
company (Umar, 2004).
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
From the results of in-depth interviews with the seven
related parties, it is concluded that the factors that
influence the informal income of Traders around the
Traditional Market in Medan City, from the aspect of
opportunities and threats include:
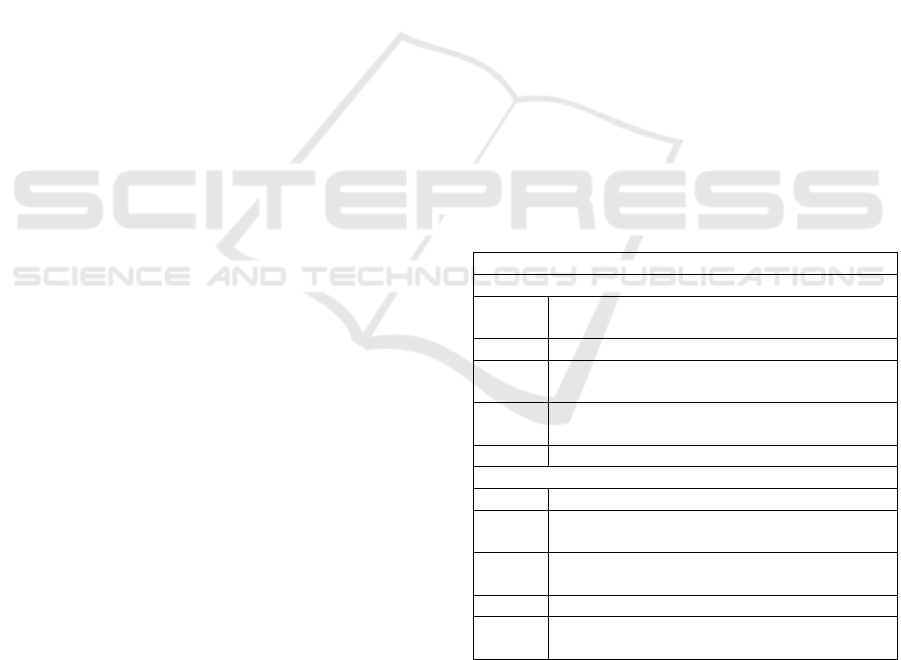
Table 2: External factors affecting income informal traders
around traditional market in Medan city.
External Factors
(Opportuinty)
1
Regulations of a provisional rule of
g
overnment
2 Growing Informal Sector in North Sumatra
3
Increase your visit to the city of Medan for
sho
pp
in
g
in traditional markets
4
Flexibility of Informal Trade in the
market
p
lace
5 Flexibilit
y
in the world of strate
g
ic tradin
g
(
Threat
)
1 The eviction and control can happen anytime
2
Lots of malls or plazas, self-catering, and
minimarkets are continuall
y
bein
g
added.
3
Information technology makes it easy to find
and choose between online media
4 Com
p
etition faced b
y
fellow informal traders
5
Illegal charges and threats of bullying that
reduce the income of informal traders
Source: Data Processing Results, 2018.
4.1 Factors Included in Opportunities
The following describes the explanation of each
external factor that affects the income of informal
traders around the traditional market in Medan City.
Strategy Increases Informal Trader Investment Discovered Traditional Market in Medan City
277

4.1.1 Traditional Government Regulations
in Favor of Traditional Markets (O
1
)
Development and fostering of informal traders in
traditional markets is fully supported by the
government, as evidenced by the government's role in
Government Regulation No. 32 Year 1998 on Small
Business Development and Development related to
the role of government in developing and developing
small-scale enterprises in the informal sector in order
to play a role in realizing the economy national level
that is getting better and balanced based on economic
democracy in Indonesia. Further supported by
Presidential Regulation no. 112 of 2007 on the
arrangement and fostering of traditional markets,
shopping centers and modern stores. This regulation
regulates technically the division of business between
traditional markets, shopping centers and modern
stores. In some provisions of the article, the
Presidential Regulation provides very clear on the
location and terms of establishment, building area,
hours of operation, provision of goods, licenses, and
guidance and supervision for traditional markets,
shopping centers and modern stores. This regulation
is made with the objective of protecting and
developing small business as well as efforts to
develop small business in order to move forward and
develop.
Related issues of public interest and national
interest are basically the spirit of nationalism of
policy makers. One of the tasks of the government is
to seek the strengthening of the economy from within
so that domestic business actors or informal traders
can compete with outsiders. Strengthening the
economy is by conducting guidance to informal
traders (UMKM) to innovate in order to compete with
foreign business actors.
It is said that informal traders because some of
them are not clear the status of their business.
Certainly influenced by various factors that actually
harm not just one party. Government support has not
been fully realized, especially in this class (Siregar
and Hidayat, 2012).
4.1.2 The High Growth of the Informal
Sector in North Sumatra (O
2
)
Based on data from the Central Statistics Agency of
North Sumatra noted that according to the main
employment status in February 2016, the population
working on formal activities amounted to 2.19
million people or 36.18 percent. While working on
informal activities amounted to 3.87 million people
or 63.82 percent. From these data shows the high
growth of Informal Traders in North Sumatra.
Improved economic conditions are an opportunity for
informal traders to increase their income through a
viable strategy. Business opportunities and high
public interest spending are the drivers of the growth
of the informal sector in Medan. The number of
public spaces and traditional markets in Medan City
make informal traders freely to sell. The high interest
of consumers to shop in the informal sector keeps
informal traders on hold and will continue to grow
every year (www.medantribunnews.com).
The high interest of shopping in the community to
the area of Medan is a fresh breeze for a trader to
continue to develop his business. In the future there
are more and more traders, including the informal that
comes up with the variety of products they offer. The
way to have an optimal income is to improve the
quality in running the business.
4.1.3 Increased Consumer Visits Outside the
City of Medan to Shop in Traditional
Markets (O
3
)
The city of Medan as the capital of North Sumatra
Province becomes the attraction for the surrounding
community to buy various types of products for
resale. Traditional markets managed by PD Pasar
Kota Medan some of them are Small and Medium
Micro Enterprises in the form of big shops or
wholesalers who act as suppliers to various stores or
informal Traders both within and outside the city of
Medan (www.analisadaily.com).
Enthusiastic people who come from outside the
city of Medan on the scope of North Sumatra who are
accustomed to direct shopping to Medan within a
certain time with a variety of needs to be traded back
in the place of origin or to meet personal
consumption. Usually the type of community with
this type has its own assessment criteria that regard
Traders in the city of Medan both Formal and
Informal have their own uniqueness that they do not
find elsewhere. This has become a valuable value for
traders because it has been able to create a good
impression even for people outside the city of Medan.
The position of Medan as the capital of the
province makes Medan a place of transit. Even in
some big cases such as meetings, competitions, and
performances the city of Medan has greater
opportunity to be chosen than other cities. This can
certainly be a valuable opportunity when Traders can
work together to build a good image at all times to the
buyer. Such as the management of convenient
shopping places and the placement of traders in a
structured way.
ANCOSH 2018 - Annual Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities
278

4.1.4 Informal Trader's Flexibility in
Following Market Demand (O
4
)
The flexibility of informal traders in adjusting market
demand with goods or products sold encourages an
increase in the informal sector in Medan City. The
price of goods and products are cheap because
unencumbered traders with leasing of premises and
business licenses, make consumers choose to buy
goods through informal traders. The service to meet
the consumer directly in selling the products and
goods becomes a separate value owned by informal
traders. Its flexible existence makes it easy for
consumers to find informal traders in public places in
Medan City.
The main characteristic of Informal Traders
presence is unrestricted and always depends on the
conditions that make the sector more responsive to
adapt. But the impact on income that becomes erratic
each time will make an adaptation.
4.1.5 Flexibility in Finding a Strategic Place
of Trade (O
5
)
Place becomes one of the biggest factors for a trader
to determine success. Informal Sectors that do not
have fixed stalls will make it easier to move around
in accordance with their own needs without any
personal harm. Moving is a step toward finding new,
unbound and new opportunities for new profits. If this
continues to happen it will reduce the market
atmosphere and confuse the already comfortable
consumer.
4.2 Factors Included in the Threat
In addition to the factors included in the
opportunities, external factors included in the threat
criteria are described below.
4.2.1 Evictions and Controls that can
Happen Anytime (T
1
)
Evictions by local governments to informal traders
are a very common threat. The existences of informal
traders who sell not in place become the main reason
for evictions. Evictions are always carried out in a
way that is not feasible and continually cause unrest
for both buyers and informal traders who are in the
point of location. The importance of proper direction
and planning is the best solution to discipline while
protecting informal traders. We know that Informal
Traders is a sector of MSME which with its
empowerment will prosper regional income and
trader itself. Evictions will cause traders to move
suddenly without preparation even in conditions that
are not ready. Not only informal traders, buyers and
others involved can also feel the impact of evictions.
The government is experiencing a dilemma in this
case, traditional markets managed by local
governments are revitalized to provide comfort, but
informal traders increasingly, thereby reducing the
entirety.
4.2.2 The Number of Malls or Plazas,
Supermarkets, and Minimarkets
Continues to Grow (T
2
)
The growth of various shopping centers such as
plazas and minimarkets poses a serious threat to
informal traders as well as to traditional markets. The
location is very strategic and close to the traditional
markets to give impact to upper middle class to shop
for basic needs no longer in traditional markets. So as
to impact the declining income for informal traders
who peddle merchandise in traditional markets. The
comfortable market atmosphere is able to maintain
the visitors is different from the traditional Market
with a solid nuance.
Plus the existence of shopping system with only
capitalize internet network plus direct delivery
facility to the address of course greatly facilitate the
life of urban special community today. This is
certainly a serious threat due to the lifestyle of today's
society that prioritizes comfort so as to put aside
many other factors.
4.2.3 Information Technology that Allows
Consumers to Choose and Buy Goods
through Online Media (T
3
)
Informal Traders are accustomed to only maximizing
product promotion when they have shown the product
in place that they live at that time with consumers who
are also in the same place. It is unfortunate that a
merchant sells an attractive product but because the
place is always on the move, the buyer becomes not
fixed.
Various online shopping applications are growing
in Indonesia. The easiness and convenience afforded
to consumers is a significant advantage. Various
features, visual products and variety of products
offered make the customers interested in buying.
4.2.4 Competition Faced by Informal
Traders (T
4
)
It is easy to be an informal trader, making the
emergence of informal traders an enormous amount.
This indirectly makes the competition among
Strategy Increases Informal Trader Investment Discovered Traditional Market in Medan City
279

informal traders increasingly tight. The absence of an
institution or organization that accommodates
informal traders leads to non-partnership and
business sharing.
4.2.5 There are Illegal Levies and Thuggery
Threats that Reduce Informal
Merchant Revenues (T
5
)
The existence of informal traders is increasingly and
cannot be controlled because of certain parties that
protect. The existence of a dominant youth
organization as a party given rights in parking
management, it becomes an indirect threat to the
existence of informal traders in the form of illegal
levies and the threat of thuggery.
Resident traders also encourage their families to
become informal traders. This is because as long as a
formal trader who obeys the demand of market
managers it is not a guarantee in business security.
Issues such as overpriced rent, unhealthy places,
inconvenient comforts and regulations encourage
merchants to opt into Informal Traders.
Giving access to credit or loans to raise capital is
also very difficult to access by informal traders in
traditional markets. This is because due to
complicated procedures and credit requirements,
bureaucratic, and so on. Based on the research, the
percentage of capital used as much as 86.8% is its
own capital. In addition, relatively small capital
becomes the main reason why informal traders cannot
afford to open a shop or sell at a place that has been
provided PD Pasar Kota Medan.
The following describes the factors influencing
the non-optimal income of informal traders around
the traditional market in Medan City from the internal
environment side, which is shown in Table 3.
Table 3: Internal factors affecting informal traders'
revenues around the traditional market in Medan City.
Internal Factors
(Strenght)
1 Small Relative Capital
2 Item Prices Cheape
r
3 It can be found by heart that it does not require
special skills
4 Can be easier to make the job easie
r
5 Advantages can be instantly enjoyed
Weakness
(Weakness)
1 Limitations in terms of business developmen
t
2 Rental prices for expensive venues
3 Lack of ability in accessing materials or
merchandise from suppliers
4 he ability to take advantage of a less than optimal
smartphone
5 Informal traders lack protection and security.
4.3 Factors Included in Strength
4.3.1 Relatively Small Capital (S
1
)
To build Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs)
through the informal sector does not require large
capital. With the capital roughing informal traders
can sell products and goods to consumers they meet.
This small capital resulted in a short turnover of
capital so that they would not be difficult to resume
trading the next day. These advantages resulted in not
a few people willing to pursue the profession of
informal traders’ background even though the income
generated is also not large.
4.3.2 Cheaper Goods Price (S
2
)
With relatively small capital accompanied by a
quantity of goods that do not make much informal
traders can more freely move position from one place
to another where this factor is one side advantageous
because of reduced costs that should be charged by
taxes and retribution in trading environment. The
absence of additional costs, making the price of goods
and products.
Offered by informal traders will be cheaper than
the prices found in kiosks or other stores. When in
fact the price of goods that are cheaper will have an
impact on consumer interest, but the condition of laps
that do not settle sometimes can divert the existence
of consumers.
4.3.3 Can Be Established by Anyone and
Does Not Require Special Skills (S
3
)
Being an informal trader does not need any special
background so it is the right choice for anyone who
wants to trade without big risk. This encourages the
growth of informal traders every year. The informal
sector is very important to note in order for rapid
growth to be balanced with proper handling. Positive
economic growth is expected by society that is not
causing any problems either environmentally or
socially in the future.
4.3.4 Can Absorb Labor More Easily (S
4
)
The large number of people in both big and small
cities creates many labor force. Not all labor forces
have a chance to work in the formal sector. Especially
for people with a background of regular education,
certainly prefer the direction of the informal sector
that is more dynamic. The informal sector can absorb
the workforce by providing space to keep working not
in idle predicates. These entrepreneurs will work on
ANCOSH 2018 - Annual Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities
280

small business fields with limited capital and do not
require any special managerial skills. Empowerment
may be able to develop a business of an informal
trader to enable a trader expand his business that
absorbs other labor.
4.3.5 Profits Can Be Directly Used (S
5
)
With an effort that passes only a few cycles and does
not require a special recording certainly will make it
easier for people who cultivate this field to manage
the money in and out of something that is needed. If
not careful, the business can be a loss and vice versa.
In these circumstances awareness of a more serious
trade is needed. The goal is for the traders the still be
able to sell every day without complaining about the
limited capital that is often due to incorrect
management.
4.4 Factors Included in Weaknesses
4.4.1 Limitations in Terms of Business
Development (W
1
)
Constraint many traders experienced in the informal
sector mainly is limited capital, especially working
capital. With the status of work that does not have
official permission, making informal traders
difficulties in getting additional capital and
constrained in developing its business due to limited
funds. Access to credit or loans to increase capital is
very difficult to access by informal traders in
traditional markets. Due to complicated, bureaucratic
procedures, credit requirements, and so on. Based on
the research, the percentage of capital used as much
as 86.8% is his own capital. A relatively small capital
is the main reason why informal traders can not afford
to open a store or sell at a place that has been provided
by PD Pasar. Yet by helping merchants to increase
revenues will certainly affect the prosperity of the
market and local revenue.
4.4.2 Rental Price of Expensive Place to Sell
(W
2
)
Informal traders complain about the expensive cost of
shop and kiosk rental. Meanwhile, sales turnover is
not too high, in addition to competition among
informal traders. Thus, price competition must occur
to attract customers.
Informal traders initially only sell in narrow
alleys. Along with the high cost of selling places,
informal traders start selling along the buyer's traffic
area. However, this move turned out to make the
market more uncomfortable, and eventually the
buyers became reluctant to shop in traditional
markets.
4.4.3 Lack of Ability to Access Raw
Materials or Merchandise from
Suppliers (W
3
)
The ability to access merchandise from suppliers is
also a disadvantage of informal traders. This is
certainly due to the low bargaining power of informal
traders to suppliers, because they buy small amounts
of data. Another problem is the procurement of raw
materials (e.g., too far, expensive, and not always
available), lack of expertise in certain types of
production techniques (e.g. skilled or expensive
designers / designers), and lack of management
expertise. Next is a keen competition and low
communicating ability, including their access to
facilities that should be available but difficult to
communicate. This is certainly comparable to that of
fixed traders who are superior in access so as to know
informal sector traders are lagging behind. This is
certainly due to the low bargaining power of informal
traders to suppliers, because they buy small amounts
of data. Another problem is the procurement of raw
materials (e.g., too far, expensive, and not always
available), lack of expertise in certain types of
production techniques (e.g. skilled or expensive
designers / designers), and lack of management
expertise. Next is a keen competition and low
communicating ability, including their access to
facilities that should be available but difficult to
communicate. This is certainly comparable to that of
fixed traders who are superior in access so as to know
informal sector traders are lagging behind.
4.4.4 Improper Marketing Communication
Skills (W
4
)
Competition in business is not only in terms of quality
and price, but also in services after sales and product
appearance. With various limitations, ranging from
limited funds, skills, to difficulty to obtain good
quality raw materials, making many informal traders
and home industries in Indonesia difficult to improve
the quality of their products in order to compete in the
domestic and export markets. Especially when they
have to deal with the lack of security guarantees and
the difficulty of maintaining the place of business
they run as informal traders. In addition, in promoting
merchandise also does not utilize communication
tools such as smartphones that now have become the
basic necessities in communicating. Various
applications that can be a means of promotion are not
put to good use.
Strategy Increases Informal Trader Investment Discovered Traditional Market in Medan City
281

4.4.5 Informal Traders Lack Protection and
Security (W
5
)
The presence of Informal Traders is not really
something that the Government expects. Due to its
status as a temporary trader still known for its
incompetence and difficulty in management, it affects
the difficulties of informal traders getting help from
the government. Therefore, the Government hopes
that they will not only become informal traders but
become permanent traders who are able to contribute
to contribute later. Thus, there is a gap in the
relationship between the market government and
Informal Traders.
4.5 SWOT Matrix Compilation
This matrix is used to identify strengths and
weaknesses within the company's internal
environment, while opportunities and threats in the
company's external environment (Rangkuti, 2008).
Analysis of the strengths and weaknesses that exist in
the internal environment is primarily directed towards
key success factors. So with this analysis it is hoped
that there will be a way to develop and utilize
strengths and support or reduce weaknesses in order
to exploit opportunities and reduce threats (David,
2006).
4.6 Strategy Application
From all proposed alternative strategies obtained
from the analysis of IE Matrix, and SWOT Matrix,
then grouped into 4 (four) strategic applications as
shown in Table 6.of 4 (four) quadrants namely:
1) S-O Strategy
• Establish Cooperatives for informal traders
that make it easier for them to borrow
Business Capital.
• Develop a market concept as an economic
corridor or a tourist market by improving
hygiene and adding facilities or
infrastructure for informal traders.
2) S-T Strategy
• Establish cooperation with financial
institutions in informal merchant financing.
• Establish cooperation between merchants
and suppliers with consideration of high
liquidity from informal traders.
• The leadership of the PD Market builds
partnerships with private traditional market
managers, to deal with illegal levies and
thuggery, which is a facilitator for informal
traders.
3) W-O Strategy
• Provide assistance in the form of payment
relief installment place official trade with
process easy and fast.
• Joining the merchant's cooperative to
develop faster and legal business.
• Placing CCTV in various strategic locations,
as a form of supervision to informal traders
who do not occupy predetermined areas.
4) W-T Strategy
• Involving SOEs in the form of CSR
programs to informal traders aimed at
providing network-building skills with
suppliers and capital assistance for business
leases.
• Enhanced the ability of informal traders by
optimizing smartphone functionality
• Informal merchant cooperatives build
partnerships with private traditional market
managers.
• Pemko Medan encourages mall or plaza
owners to provide special areas for informal
traders on a certain day or time.
4.7 Discussion
Informal traders and traditional markets should be
taken seriously by the government. The government
should consider the sustainability of traditional
markets and informal traders by maintaining fair
competition between traditional markets and modern
markets. Among them is regulating the balance
between the number and location of the modern
market. The modern market must be placed
somewhat away from traditional markets and the
numbers are limited, not to the traditional markets
surrounded by modern markets / mini markets. This
restriction is to maintain the continuity of small
traders who are in many traditional markets.
The existence of the informal sector in the
national economic development system has shown its
role significantly. In addition to toughness, ease of
substitution and business flexibility, the informal
sector also promises a pretty good economic outlook.
It is proper that the sector is developed in harmony,
serious and polite.
The most important form of urban informal sector
to foster is the Informal Traders. Along with growth
in other cities, the efforts of informal traders can also
be dynamic and growing. It can be seen from
Informal Traders activities that provide promising
prospects if the government delivers special attention
and makes some form of regulation in the context of
coaching and development. The Informal Traders'
ANCOSH 2018 - Annual Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities
282

business flexibility is very likely to evolve over time.
The government is expected to raise the presence of
Informal Traders as partners as well as provide
flexibility in the business. Legally, legal guarantees
are also needed for the business they undertake to
avoid being misused by many parties.
The difficulty of obtaining loans in business
development often shows the stigma of the
relationship between the Informal Traders and the
relevant government. Business protection and capital
that should be accessible, not least felt by small
traders. This situation is often followed by repeated
evictions which further encourage inconsistencies in
various situations and parties. Background with a
modest education shows the ability to communicate
and manage their own capital that is sometimes not
fully structured. Naturally the application of business
rarely reveals innovation and follows the times as
competitors do.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND
SUGGESTION
5.1 Conclusions
From the results of the discussion, the factors that
lead to informal sales revenues around traditional
markets are not optimal because limitations in
business improvement, the rental price of expensive
places to sell on traditional markets, lack of ability to
access raw materials and merchandise from suppliers,
lack of ability to use communication technologies
such as smartphones, lack of protection and security,
confiscation by security, the number of malls or
plazas, supermarkets, and minimarkets continues to
grow also information technology that allows
consumers to choose and buy goods and competition
faced by informal merchants.
5.2 Suggestion
From the conclusion, it is advisable: PD Pasar Kota
Medan and Koperasi Informal Traders conduct a
partnership to provide a place to sell on the upper
floors of traditional markets for informal traders with
cheaper rental system, but with restrictions on
duration of rent for example for 6 (six) months, and is
not allowed to be extended by informal traders the
same, allowing other informal traders to take turns
using the area. PD Pasar Kota Medan performs
detailed and complete data collection on informal
traders in order to mapping the potential of each
informal trader that can be fostered through
partnership with Informal Traders Cooperative.
Cooperate between PD Pasar Medan and Dinas
Pemuda and Sport and Gardening Agency to arrange
informal traders not to sell in areas passed by motor
vehicles. For example the parking area football
stadium that can be used for informal traders selling
from morning until noon with the system open-close
stall, so that the area used back clean in the afternoon.
Provide convenience in terms of capital to develop
business so that more and more traders are not
worried about competing with modern competitors so
that businesses are able to grow and able to open jobs
that can be felt others. Conducting management
related to the laying of kiosks or stalls of traders
according to the goods sold. After the placement is
done, regulation should be made to do the mutual help
of the market as well as the mapping of homogeneous
selling locations in the form of lists listed in various
corners of the market in order to facilitate the
consumers find the required seller. Sanctions are also
required against merchants who are unable to meet
the rules and maintain cleanliness. And issued a
regulation ban on street sales in addition to stalls.
Pemko Medan and Dinas Kopeasi UMKM in
cooperation with the Department of Parks as the
manager of Football Stadium, so that the stadium
parking area can be used for the place of selling.
Informal traders are given a special place in the
stadium parking area from morning until noon,
because stadium activity usually does not exist at that
time. If it is past the deadline traders are expected to
leave the place selling, and clean the place of business
to return clean and does not interfere with the interests
of others.
REFERENCES
Alma, B., 2001. Manajemen pemasaran dan pemasaran
jasa. Alfabeta, Bandung.
Arikunto, S., 2006. Prosedur penelitian; Sebuah
pendekatan praktek. Rineka Cipta, Jakarta.
David, C. R., 2006. Manajemen strategis. Salemba Empat,
Jakarta.
Hadionoto, K., 1996. Perencanaan pengembangan
destinasi pariwisata. UI Press, Jakarta.
Http://medan.tribunnews.com/2017/05/08/jelang-bulan-
suci-ramadan-beberapa-pasar-tradisional-sudah-
naikkan-harga-ayam-potong, diakses pada tanggal 26
Januari 2018
Http://harian.analisadaily.com/kota/news/puluhan-
pedagang-informal-pelataran-pasar-petisah-
ditertibkan/19055/2014/04/04, diakses pada tanggal 26
Januari 2018
Strategy Increases Informal Trader Investment Discovered Traditional Market in Medan City
283

Peraturan Pemerintah No. 32 Tahun 1998 tentang
Pembinaan dan Pengembangan Usaha Kecil.
Peraturan Presiden No. 112 tahun 2007 tentang penataan
dan pembinaan pasar tradisional, pusat perbelanjaan
dan toko modern.
Rangkuti, F., 2008. Analisis SWOT teknik membedah kasus
bisnis. Gramedia Pustaka Utama, Jakarta.
Sinulingga, S., 2011. Metode penelitian, USU Press,
Medan.
Sinungan, M., 1998. Produktivitas; Apa dan bagaimana.
Bumi Aksara, Jakarta.
Siregar, T. N. M., Hidayat, P., 2012. Pasar tradisional di
Kota Medan. Jurnal Ekonomi dan Keuangan, 2(6), 22.
Umar, H., 2004. Strategic management in action. Gramedia
Pustaka Utama, Jakarta.
ANCOSH 2018 - Annual Conference on Social Sciences and Humanities
284

APPENDIX
Appendix 1: Matrix SWOT informal traders around the traditional market in Medan City.
(Strengths) S (Weaknesses) W
1. Capital is relatively small
2. The price of the Goods is
cheaper
3. Can be established by anyone
and does not require any special
skills
4. Can absorb labor more easily
5. Direct benefits enjoyed
1. Limitations in business development
2. The rental price of the place is
expensive
3. Lack of ability to access raw materials
and merchandise from suppliers
4. Lack of ability to use communication
technology such as smartphones
5. Lack of protection and security..
(Opportunities) O Strategy S – O Strategy W – O
1. Government regulation in
favor of traditional markets.
2. The high growth of the
Informal Sector in North
Sumatra
3. increasing of Population and
increasing of consumer visit
outside Medan City
4. Informal Trader's flexibility
in following market demand
5. Flexibility in finding a
strategic place of trade.
1. Establish cooperatives for
informal traders that make it
easier for them to borrow
capital business
(S
1.
S
2
.O
3
.O
4
.O
5
)
2. Developing the concept of a
market as an economic corridor
or a tourist market by
improving cleanliness and
adding facilities or
infrastructure for informal
traders (S
4.
S
5
.O
3
.O
4
.O
5
)
1. Provide assistance in the form of
payment relief mortgage official place
with easy and fast process. (W
2
.O
4
)
2. Joining a merchant's cooperative to
develop faster and legal business
(W
5
.O
4
.O
5
)
3. Placing CCTV in various strategic
locations, as a form of supervision to
informal traders who do not occupy
predetermined areas. . (W
6
.O
4
)
(
Threats
)
T Strate
gy
S
–
TStrate
gy
W
–
T
1. Confiscation by Security
2. The number of malls or
plazas, supermarkets, and
minimarkets that continue to
grow.
3. Information technology that
allows consumers to choose
and buy goods.
4. Competition faced by
informal merchants
5. There are illegal levies and
thuggish threats that reduce
informal merchant revenues
1. Building cooperation with
financial institutions in
informal merchant financing
(S
2
.T
4
)
2. Establish cooperation between
merchants and suppliers with
consideration of high liquidity
from informal traders. (S
2
.T
6
)
3. The leadership of the PD
Market builds partnerships
with private traditional market
managers, to deal with illegal
levies and thuggery, which is a
facilitator for informal traders
(S
3
.T
1
.T
6
)
1. Involving BUMN in the form of CSR
programs to informal traders aimed at
providing network-building skills with
suppliers and capital assistance for
business leases (W
2
.T
3
.T
4
.T
5
)
2. Improvement of informal merchant
capabilities by optimizing smartphone
functionality ( W
5
.T
3
)
3. Informal merchant cooperatives
establish partnerships with private
traditional market managers (
W
1.
W
6
.T
1
.T
5
)
4. Pemko Medan encourages mall or
plaza owners to provide special areas
for informal traders on a certain day or
time.
(
W
5
.T
2
)
Strategy Increases Informal Trader Investment Discovered Traditional Market in Medan City
285
