
Risk Profile And Corporate Governance On Company Performance
In The Banking Industry
Adistyana Damaranti, Iman Harymawan, and Mohammad Nasih
Department of Accounting, Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia
adistyanadamaranti@gmail.com, harymawan.iman@feb.unair.ac.id
Keywords: Capital, Corporate Governance, Earnings, Loan to Deposit Ratio, Non-Performing Loan, Return On Assets,
Risk Profile.
Abstract: The purpose of this research is to identify and analyze the connection between the risk profile and
performance of public banks on the Indonesian Stock Exchange for the years 2012–2015. This research uses
a quantitative method and a purposive sampling technique with a sample population of 128. The results
show that Non-Performing Loan and Loan to Deposit Ratio have a significant and negative effect on Return
on Assets, while Net Open Position has no significant effect on Return on Assets. The conclusion that taken
from this research is that the performance of a bank is dependent on how the bank manages its performing
loans and its liquidity.
1 INTRODUCTION
The banking sector has become an intermediary
institution that plays an important role in the
financial system of society. Bank health is an
important aspect that must be understood. To keep
the banks in a good health, supervision is undertaken
by the Financial Services Authority (OJK), which
requires banks to conduct self-assessment on their
own health levels and take effective remedial
measures.
Basically, the banking policy issued and
implemented by the Financial Services Authority
aims to create and maintain the health of banks,
either individually or consolidated. The health or
financial and non-financial conditions of a bank are
in the interests of all relevant stakeholders, owners,
managers, bank users, and governments.
Along with the banking needs in terms of facing
global challenges, Bank Indonesia has made
improvements to its method of appraising bank
health. Bank Indonesia considers that the previous
method of appraisal, CAMELS (Capital, Assets
Quality, Management, Earning, Liquidity, and
Sensitivity Market), was less able to assess bank
health, so it changed the bank health rating method
to RGEC (Risk Profile, Good Corporate
Governance, Earnings, and Capital), either
individually or consolidated, as of January 2012,
with the issuance of Bank Indonesia Regulation
No.13 / 1 / PBI / 2011 (Setyaningsih & Herawati,
2013). The difference between RGEC and CAMELS
lies in the assessment of risk profile and good
corporate governance. Risk profile assessment is a
new appraisal relating to the level of bank
soundness, while corporate governance, which used
to be part of management’s assessment of the
CAMELS method, is now a standalone component
of the RGEC assessment (Dincer, H., Gencer, G.,
Orhan, N., & Sahinbas, K, 2011; Hardikasari, E.,
Hardikasari, E., & Pamudji, S, 2011).
RGEC is associated with a health rating
assessment that focuses on risk assessment. In the
risk profile, there are eight aspects of risk that are of
concern in the assessment of the bank’s RGEC
method of health risk: credit risk, market risk,
liquidity risk, operational risk, legal risk, strategic
risk, compliance risk, and reputation risk
(Permatasari & Nuswantara, 2012).
The first part of this paper will examine the
effect between risk profile, represented by Non-
Performing Loan (NPL), Net Open Position (NOP),
and Loan to Deposit Ratio (LDR), and Return on
Assets, representing the Earnings Appraisal Factor.
As we know, risk profile is one of the four factors
for appraising bank health.
The second part of this paper will examine Good
Corporate Governance, represented by components
of the board of commissioners, audit quality, and the
composition of independent commissioners, with
316
Damaranti, A., Harymawan, I. and Nasih, M.
Risk Profile And Corporate Governance On Company Performance In The Banking Industry.
In Proceedings of the Journal of Contemporary Accounting and Economics Symposium 2018 on Special Session for Indonesian Study (JCAE 2018) - Contemporary Accounting Studies in
Indonesia, pages 316-322
ISBN: 978-989-758-339-1
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Return on Assets representing the Earnings
Appraisal Factor. Additionally, Good Corporate
Governance is one of the four factors for appraising
bank health.
2 HYPOTHESIS DEVELOPMENT
Credit risk arises from the failure of the debtor
and/or other parties to fulfil obligations to the bank.
Credit risk is generally found in all banking
activities, the performance of which depends on the
performance of the counterparty, the issuer, or the
borrower. In managing bank credit risk in Indonesia,
Bank Indonesia issued Regulation No.13 / 1 / PBI /
2011, which required banks in Indonesia to conduct
bank rating assessments using the RGEC method.
The RGEC method includes the rating of bank
health by assessing bank credit risk. According to
the RGEC method, the effect of credit risk can be
measured by the Non-Performing Loan (NPL) ratio,
which measures the ability of the company in
managing non-performing loans that are
substandard, doubtful, or loss-making (Eng, 2013).
Based on Bank Indonesia Regulation No.13 / 1 / PBI
/ 2011, banks have provisions that the NPL should
be less than 5%. The lower the NPL ratio in the
bank, the better the bank will be in managing the
non-performing loans, and the better the bank rating
in the risk profile factor. In some previous studies, a
small credit risk brings good bank performance
(Sabir Muhammad, Ali Muhammad, Habbe Hamid,
2012; Eng, 2013). Based on the description above,
the first hypothesis for this research is as follows:
H1: Non-Performing Loan negatively affects
Return on Assets.
Market Risk arises in the balance sheet position
and administrative accounts, including derivative
transactions, due to changes in market conditions,
and the risk of change of option price. According to
Bank Indonesia Regulation No.13 / 1 / PBI / 2011,
market risk includes foreign exchange risk arising
from foreign exchange transactions. Net Open
Position (NOP) is one of the instruments set by Bank
Indonesia in assessing foreign exchange risk to be
covered by bank capital. The purpose of the NOP
ratio measurement is for bank security from forex
risk (hedging risk), mitigation of bank/customer
support speculation, managing the bank’s forex
assets (maintaining balance of sources and use of
funds), as a tool for Bank Indonesia to monitor bank
health and to manage the stability of the rupiah. The
lower the NOP ratio of the bank the better, since the
foreign exchange risk is lower so the foreign
exchange risk can be covered by bank capital. In
some previous studies, a small market risk resulted
in good bank performance. Based on the description
above, the second hypothesis for this research is as
follows:
H2: Net Open Position positively affects Return
on Assets.
Liquidity risk is assessed on a bank’s ability to
settle its short-term liabilities. According to Bank
Indonesia Regulation No.13 / 1 / PBI / 2011, in the
assessment of bank soundness by the RGEC method,
liquidity risk can be measured by the Loan to
Deposit Ratio (LDR) ratio, which measures the
bank’s ability to repay the withdrawal, which the
depositors do by relying on credit as liquidity. Banks
with good LDR quality have a small risk, are able to
pay their short-term liabilities, or are able to manage
their liquidity. The lower the LDR ratio, the better
the bank’s liquidity risk; a lower liquidity risk
reflects the bank’s ability to manage its liquidity
well. In previous studies, a small liquidity risk
results in good bank performance (Sabir
Muhammad, Ali Muhammad, Habbe Hamid, 2012).
Based on the description above, the third hypothesis
for this research is as follows:
H3: Loan to Deposit Ratio negatively affects
Return on Assets.
Corporate governance can be described as a set
of relationships between the board of
commissioners, directors, shareholders, and other
stakeholders of a company. This relationship
establishes a system that regulates and controls the
company concerned. Corporate governance can also
be assessed by the RGEC method implemented by
Bank Indonesia Regulation No.13 / 1 / PBI / 2011.
The board of directors is responsible for the
operation of the company in accordance with the
intent and purpose of the company. Bank Indonesia
requires each bank to have at least three directors.
The composition of the board of directors in
accordance with the standards of the Bank Indonesia
Regulation will affect the rating of a bank. In Dedu
& Chitan’s (2013) study, the composition of the
board of directors that meets the standards will have
an effect on the performance of the bank. Based on
the description above, the fourth hypothesis for this
research is as follows:
H4: The size of the Board of Directors has a
positive effect on Return on Assets.
Audit quality is a form of good corporate
governance. In accordance with Bank Indonesia
Regulation No.13 / 1 / PBI / 2011, corporate
governance is assessed by the RGEC method. Audit
quality reflects good corporate financial reporting,
Risk Profile And Corporate Governance On Company Performance In The Banking Industry
317

with good audit quality expected to increase trust
among users such as investors, creditors, or
customers. The audit quality in this study is reflected
by auditors of the Big Four public accounting firms
and the non-Big four public accounting firms, as the
auditor’s influence in generating audit quality is
measured by how many public accounting firms
conduct an audit of a bank that has gone public. In
some previous studies, the quality of a good audit
will affect the performance of the company (Sari,
2010). Based on the above description, the fifth
hypothesis for this study is as follows:
H5: Audit quality positively affects Return on
Assets.
An independent board of commissioners is
responsible for and authorized to oversee
management action, and it advises management if it
is deemed necessary. Independent commissioners
may not have financial, management, share
ownership, and/or family relationships with other
members of the board of commissioners, directors,
and/or other controlling shareholders or relationships
that may affect their ability to act independently.
According to Bank Indonesia Regulation No.13 / 1 /
PBI / 2011, the composition of the board of
commissioners shall consist of independent
commissioners and commissioners, with a minimum
composition of 50% of the total members of the
board of commissioners required to be independent
commissioners. In Noverio & Dewayanto’s (2011)
study, the control of independent commissioners
influenced the bank’s performance. Based on the
description above, the sixth hypothesis for this
research is as follows:
H6: Percentage of the Indepndent Board of
Commissioners have a positive effect on Return
on Assets.
3 DATA
3.1 Samples
The population in this research is banking
companies that have gone public on the Indonesian
Stock Exchange (BEI) during the period 2012–2015.
Sampling in this research was carried out by a
purposive sampling method, with the aim of
obtaining a representative sample with four criteria:
[1] banks that have gone public and are listed on the
Indonesian Stock Exchange; [2] banks that have
published financial statements regularly during the
period 2012-2015; [3] banking companies whose
shares are actively traded on the Indonesian Stock
Exchange for the four periods of the research; [4]
banking companies that were not in the process of
delisting during the period of observation.
Based on the list of samples above, the
researchers used a sample of 32 commercial banks.
The list of 32 bank samples was observed for four
periods (2012 to 2015). Consequently, there was 128
sets of data.
3.2 Variables
This study uses risk profile and corporate
governance as independent variables and bank
performance as measured by Return on Assets
(ROA) as a dependent variable. Risk profile is
defined as credit risk, market risk, and liquidity risk,
in accordance with a quantitative measurement of
risk profile regulated in Bank Indonesia Regulation
Number 13/1 / PBI / 2011. Corporate governance is
defined as the composition of the board of directors,
the quality of the audit, and the components of the
board of commissioners. The following is an outline
of the six independent variables in this study:
1. Credit risk is the risk of failure of the debtor in
fulfilling the bank’s liabilities (Sabir
Muhammad, Ali Muhammad, Habbe Hamid,
2012; Eng, 2013), measured by the Non-
Performing Loan (NPL) ratio.
2. Market risk is the risk that occurs due to foreign
exchange transactions, which can be measured
using the Net Open Position (NOP) ratio.
3. Liquidity risk is the risk of possible loss due to
the inability of the bank to meet the obligations
due. Liquidity risk can be measured using the
Loan to Deposit (LDR) ratio.
4. Board size (BOARDSIZE) is the total number of
board directors and commissioners. In this study,
the Board of Commissioners is one of the
measurement variables of corporate governance.
5. Audit quality is used to detect and report material
errors in financial statements. The quality of
audit in this study is measured by the company
using the services of Big Four public
accountancy firms or non-Big four public
accountancy firms (Sari, 2010). In this study, the
quality of audit is measured by how many public
accounting firms audit the listed banks in the
period 2012-2015. We define Big Four auditors
if they are in the top four in term of number of
clients in banking industry within the sample
period. Audit Quality (AQ) is the second
measurement variables of corporate governance
in this research.
JCAE Symposium 2018 – Journal of Contemporary Accounting and Economics Symposium 2018 on Special Session for Indonesian Study
318

6. The third governance variable is percentage of
independent commissionaire (INDCOM).
INDCOM is the total number of independent
commissioners scaled by total number of board
commissioners. Independent commissioners in
the company have duties and responsibilities
related to quality control information contained
in the financial statements (Utama & Musa,
2011).
The control variables used in this study are the
ratio of Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) and firm
size. CAR is one of the ratios used in the health
rating assessment based on Bank Indonesia
Regulation Number 13/1 / PBI / 2011 in the RGEC
method of Capital Bank assessment, while firm size
is measured by net total assets log (Astutik &
Djazuli, 2014).
4 Empirical Analysis
4.1 An Overview of Subject and Object
Research
The research subjects used are banking companies
listed on the Indonesian Stock Exchange during the
period 2012–2015, i.e. banking companies that meet
the predetermined criteria of sampling. Banking is
part of the financial sector of the Indonesian Stock
Exchange. Since the issuance of Bank Indonesia
Regulation No.13 / 1 / PBI / 2011, bank health is
expected to have a more representative assessment
method. If the bank has a good bank health rating,
then it will have a good performance (Leventis, S.,
Dimitropoulos, P. E., & Anandarajan, A, 2012).
Bank performance can be measured by using
earnings in the rating of the bank soundness RGEC
method. In this study, the authors use the variable
Return on Assets in measuring the earnings of a
bank. Good or bad performance of the bank will
affect the users of financial statements. A good bank
soundness should have a good overall level of the
four existing assessments, namely Risk Profile,
Good Corporate Governance, Earnings, and Capital.
The object of this research is the effect of risk
profile and corporate governance on the
performance of banks that go public in BEI, as
regulated in Bank Indonesia Regulation No.13 / 1 /
PBI / 2011, based on the RGEC method (Risk
Profile, Good Corporate Governance, Earnings,
Capital). In this study, the authors measure the risk
profile with the variables Non-Performing Loan,
Loan to Deposit Ratio, and Net Open Position.
Corporate governance is measured by the
composition of the board of directors, the quality of
the audit, and the components of the board of
commissioners. The author uses company size and
Capital Adequacy Ratio as control variables.
As presented in Table 1, Return on Assets
(ROA) of the sample companies obtained an average
of 1.773. This means that the average sample
company is able to get a net profit of 1.773% of the
total assets owned by the company in one period.
The median for ROA is 1.71, with the median
indicating a mean value. The maximum value of
6.41 means that the highest ROA from a sample
company is 6.41% of total assets owned by the
company in one period, while the minimum value of
ROA is 5.37% of total assets.
Table 1: Descriptive Statistics
Variable Mean Median Min Max
ROA 1.773 1.71 -5.37 6.41
NPL 2.451 2.11 0.21 9.95
NOP 1.669 1.115 -10.72 9.61
LDR 82.89 82.24 0 112.54
BOARDSIZE 7.085 6 3 11
AQ 0.765 1 0 1
INDCOM 0.578 0.571 0.461 0.733
CAR 16.95 16.5 10.05 26.56
SIZE 17.57 17.403 15.063 20.593
The Non-Performing Loan sample obtained an
average of 2.451. This reflects the risk of failure of
the debtor in fulfilling the bank’s obligation of
2.451%. The median for Non-Performing Loans is
2.11, where the median indicates a median value.
The maximum value of 12.28 means that the highest
Non-Performing Loan of the sample company can
reach 9.95, while the minimum value of Non-
Performing Loan is 0.21.
With respect to Net Open Position, the sample
companies obtained an average of 1.669. This
reflects the risks arising from foreign exchange
transactions of 1.669%. The median for Net Open
Position is 1.115, where the median indicates a mean
value. The maximum value of 9.61 means that the
highest Net Open Position of the sample company
can reach 9.61, while the minimum Net Open
Position value is -10.72.
Loan Deposits to Ratio of the sample company
obtained an average of 82.89. This reflects the risks
arising from foreign exchange transactions of
82.89%. The median for Loan Deposits to Ratio is
82.24, where the median indicates a median value. A
maximum value of 112.54 means that the Loan
Deposits to the highest Ratio of the companies
Risk Profile And Corporate Governance On Company Performance In The Banking Industry
319
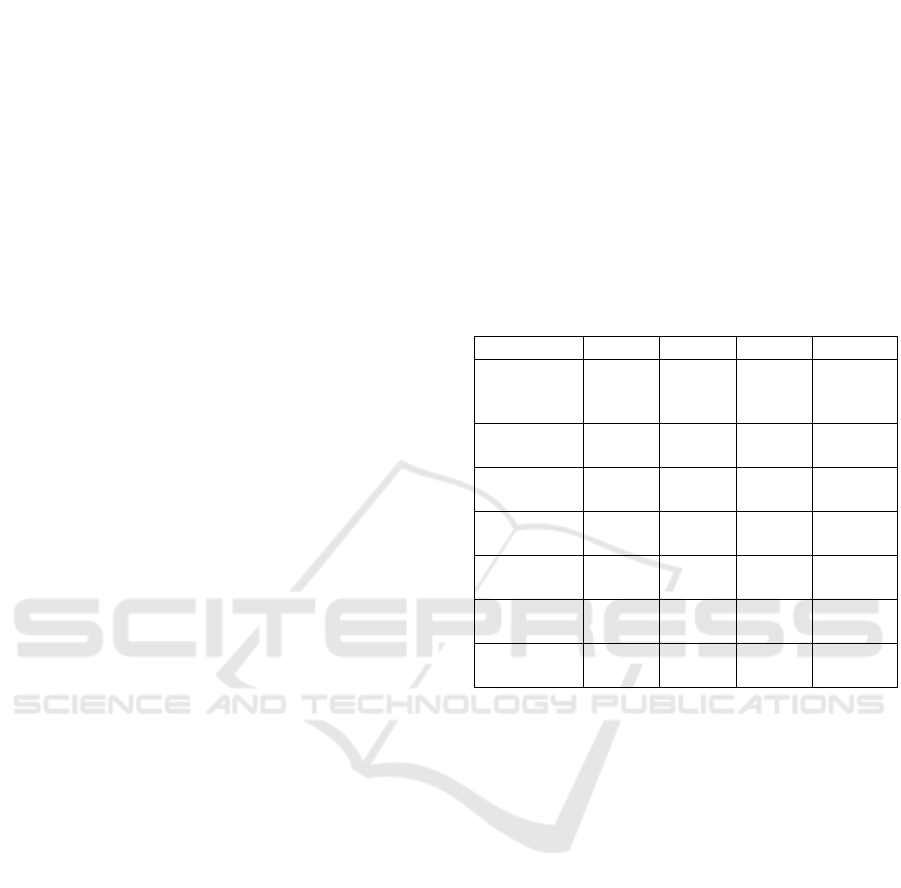
sampled can reach 112.54, while the minimum value
of Loan Deposits to Ratio is 0.
Based on the results of the data processing in
Table 4.2, the components of the board of
commissioners of the sample companies obtained an
average of 7.085. This reflects the components of
the board of commissioners of bank companies
reaching 7.085%. The median for the board
component is 6, where the median represents the
mean value. The maximum value of 3 means that the
highest audit quality of the sample company can
reach 3, while the minimum value of the
commissioner’s component is 12.
The audit quality of the sample companies
obtained an average of 0.765. This reflects the audit
quality of bank companies reaching 0.765%. The
median for the composition of the board of
commissioners is 1, where the median denotes the
middle value. A maximum value of 11 means that
the highest audit quality of the sample company can
reach 11, while the minimum value of audit quality
is 3.
The board of directors, defined as IC2 in the
table, is calculated by the total composition of the
board of directors coupled with the number of
components of the board of commissioners divided
by the total of both. The total IC2 of the sample
firms obtained an average of 0.578. This reflects IC2
reaching 0.578%. The median for the composition of
the board of directors is 0.571, where the median
indicates a mean value. The maximum value of
0.733 means that the highest IC2 of the companies
sampled can reach 0.733, while the minimum value
of IC2 is 0.461.
The Capital Adequacy Ratio of the sample
companies obtained an average of 16.95. This
reflects CAR reaching 16.95%. The median for the
composition of the board of commissioners is 16.5,
where the median denotes the middle value. The
maximum value of 26.56 means that the Capital
Adequacy Ratio of the sample company can reach
26.56%.
With respect to size, the sampled companies
obtained an average of 17.57. This reflects the
company’s size reaching 17.57%. The median for
the composition of the board of commissioners is
17.403, where the median denotes the median value.
The maximum value of 20,593 means that the
highest company size of the sampled companies is
20,593, while the minimum value of 15,063 firm
size is 15,063.
4.2 Model Analysis and Evidence of
Hypotheses
This study used multiple linear regression analysis
techniques to test the hypotheses that were built. A
multiple linear regression test using software
STATA version 14 was used to examine the
relationship between the variables. The independent
variables are reflected by three variables, namely
proxy risk profile to Non-Performing Loan, Loan to
Deposit Ratio, and Net Open Position.
Table 2: Results of regression of risk profile on
performance
Variables [1] [2] [3] [4]
NPL -
0.266
***
(
-3.65
)
-
0.267***
(
-3.76
)
NOP -0.098
*
(
-1.77
)
-0.100*
(
-1.94
)
LDR -0.017
*
(-1.92)
-0.020**
(-2.44)
CAR 0.103
**
(2.53)
0.123
***
(2.92)
0.112
***
(2.65)
0.092**
(2.30)
SIZE 0.330
*
(
1.87
)
0.277
(
1.52
)
0.273
(
1.50
)
0.367**
(
2.14
)
CONSTANT -5.703
*
(
-1.93
)
-6.371
**
(
-2.08
)
-4.131
(
-1.26
)
-3.140
(
-1.02
)
R-squared
No obs
0.389
128
0.339
128
0.342
128
0.432
128
Corporate governance is proxies by the size of
board commissionaire, the audit quality, and
percentage of independent commissionaire. The
dependent variable used by the author is the
measurement of company performance (ROA). For
control variables, the author used the Capital
Adequacy Ratio (CAR) and company size.
Regression analysis was used to determine the
direction of the relationship between independent
variables and the dependent variable, whether each
independent variable is positive or negative, and to
predict the value of the dependent variable if the
value of the dependent variable increases or
decreases.
Based on Table 2 model 1, the regression of the
NPL variable has a negative and significant
association to ROA (t-value -3.65). In model 2, we
find that NOP has a negative and significant
association to ROA, with significance equal to 10%
(t-value -1.77). In model 3, the LDR variable has a
negative and significant association to ROA, with a
significance level of 10% (tvalue -1.92). These
JCAE Symposium 2018 – Journal of Contemporary Accounting and Economics Symposium 2018 on Special Session for Indonesian Study
320
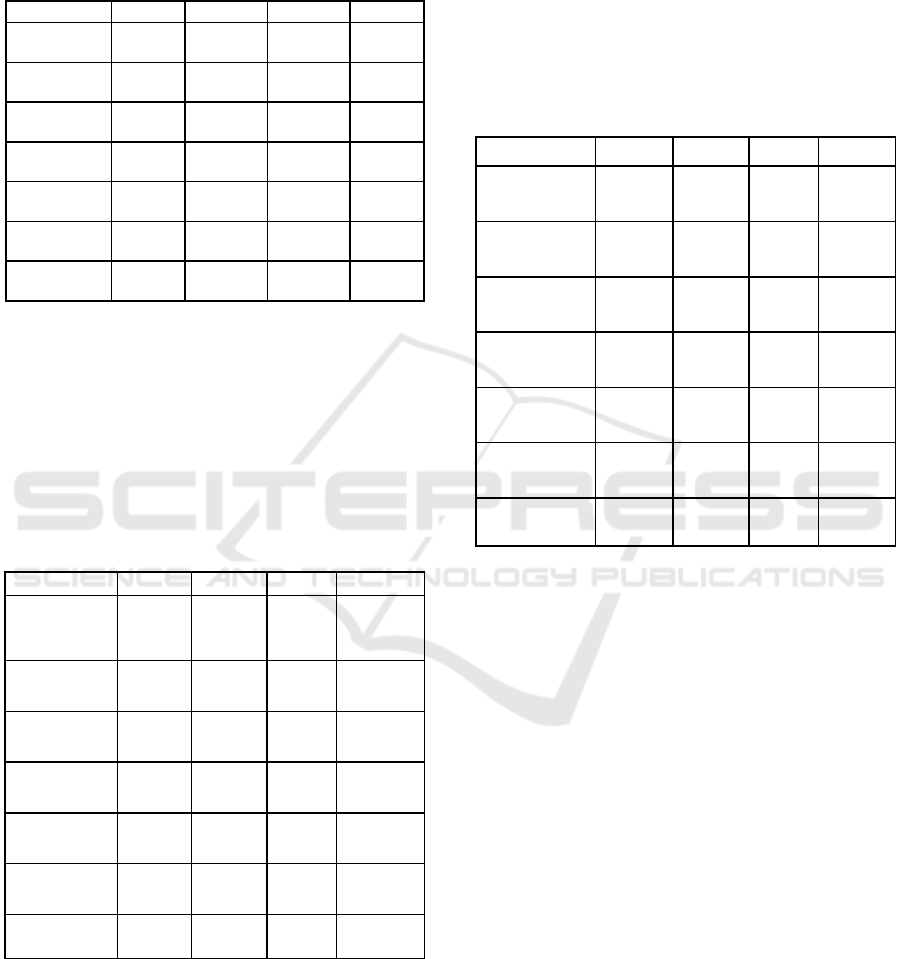
results are remain significant when we run in model
4.
Table 3: Results of regression of corporate governance on
performance
Variables [1] [2] [3] [4]
BOARDSIZE 0.270**
(2.26)
0.155
(1.35)
AQ
0.020
(0.06)
-0.169
(-0.51)
INDCOM
-2.083
(-0.76)
-2.643
(-1.03)
CAR 0.103**
(2.53)
0.123***
(2.92)
0.112***
(2.65)
0.092**
(2.30)
SIZE 0.330*
(1.87)
0.277
(1.52)
0.273
(1.50)
0.367**
(2.14)
CONSTANT -5.703*
(-1.93)
-6.371**
(-2.08)
-4.131
(-1.26)
-3.140
(-1.02)
R-squared
No obs.
0.389
128
0.339
128
0.342
128
0.432
128
Table 3 presents the results of regression of
corporate governance variables on performance. In
model 1, the coefficient of COMSIZE has apositive
and significant associations to performance (t-value
2.26). In models 2 and 3, we find no significant
associations between AQ and INDCOM to
performance.
Table 4: Results of robust regression of risk profile on
performance
Variables [1] [2] [3] [4]
NPL -
0.266
**
(
-2.00
)
-
0.267***
(
-2.69
)
NOP -0.098
(-1.25)
-0.100*
(-1.70)
LDR -0.017
*
(-1.89)
-0.020
(-1.64)
CAR 0.103
**
(2.51)
0.123
***
(2.74)
0.112
**
(2.36)
0.092**
(2.17)
SIZE 0.330
*
(1.76)
0.277
(1.51)
0.273
(1.41)
0.367*
(1.97)
CONSTANT -5.703
*
(-1.67)
-6.371
*
(-1.75)
-4.131
(-1.02)
-3.140
(-0.79)
R-squared
No obs
0.389
128
0.339
128
0.342
128
0.432
128
Table 4 presents results of robust regression of
risk profiles on performance. Consistent with OLS
regression results, we find that NPL, NOP, and LDR
are negatively correlated to performance. However,
the result for NOP is insignificant.
Table 5 shows the results of robust regression of
corporate governance variables on bank
performance. The findings confirm the OLS
regression results that BOARDSIZE is positive and
significantly associated to ROA. With regards to
audit quality and percentage of independent
commissionaire, we find no significant association
to bank performance.
Table 5: Robust regression result of corporate governance
on performance
Variables [1] [2] [3] [4]
BOARDSIZE 0.270
*
(1.95)
0.155
(1.14)
AQ 0.020
(0.05)
-0.169
(0.41)
INDCOM -2.083
(-0.71)
-2.643
(-0.87)
CAR 0.103
**
(2.51)
0.123
***
(2.74)
0.112
**
(2.36)
0.092**
(2.17)
SIZE 0.330
*
(1.76)
0.277
(1.51)
0.273
(1.41)
0.367*
(1.97)
CONSTANT -5.703
*
(-1.67)
-6.371
*
(-1.75)
-4.131
(-1.02)
-3.140
(-0.79)
R-squared
No obs
0.389
128
0.339
128
0.342
128
0.432
128
In model 4, regression of the KDK variable has a
positive influence, with significance to ROA equal
to 10% (t count: 1.95). This model has a positive
control variable, i.e. CAR, with a significance level
of 5% (t arithmetic: 2.51) and SIZE with a
significance level of 10% (t count: 1.76). In models
5 and 6, the regressions of the KA and IC2 variables
have no effect on ROA. In model 7, the NPL has a
negative effect, with a strong significance to ROA of
1% (t count: -2.69), the NOP has a significant
negative effect on the ROA of 10% (-1.70), and
LDR, KDK, KA, IC2 have a significant influence on
ROA.
5 CONCLUSION
This study aimed to determine the effect of the
independent variables Non-Performing Loan, Net
Open Position, and Loan to Deposit Ratio on Return
on Assets in banking companies in Indonesia listed
on the Indonesian Stock Exchange during 2012-
2015. The variables used in this study were Non-
Risk Profile And Corporate Governance On Company Performance In The Banking Industry
321

Performing Loans, Net Open Position, and Loan to
Deposit Ratio, Board of Directors composition,
Board of Commissioner components, Audit Quality,
Size, Capital Adequacy Ratio, and Return on Assets.
Based on the analysis of the research results, the
following conclusions can be drawn:
a. Regression test results show that risk profile
variables measured using Non-Performing Loan
and Loan to Deposit Ratio have a significant and
negative effect on Return on Assets. This means
that, when the values of the Non-Performing
Loan and Loan to Deposit ratios of the company
increase, the Return on Assets will decrease, and
vice versa; if the Non-Performing Loan and Loan
to Deposit ratios are down, then Return on
Assets will experience an increase; however, the
Net Open Position has no effect on Return on
Assets, meaning that when the value of the Net
Open Position of a company experiences an
increase, then Return on Assets has no effect.
b. The result of the regression test shows that
corporate governance variables measured using
Components of Board of Commissioners have a
significant and positive effect on Return on
Assets, while Audit Quality and Board of
Directors Composition have a non-significant
positive effect on Return on Assets.
REFERENCES
Astutik, P., & Djazuli, A. 2014. Influence of Bank Health
Level according to Risk Based Bank Rating on
Financial Performance (Study on Sharia Bank in
Indonesia). Jurnal Ilmiah Mahasiswa FEB, 3(1).
Central Bank of Indonesia. Central Bank of Indonesia
Regulation No. 13/ 1/ PBI/ 2011 about Assessment of
Commercial Bank Rating.
Dedu, V., & Chitan, G. 2013. The influence of internal
corporate governance on bank performance-an
empirical analysis for Romania. Procedia-Social and
Behavioral Sciences, 99, 1114-1123.
Dincer, H., Gencer, G., Orhan, N., & Sahinbas, K. 2011. A
performance evaluation of the Turkish banking sector
after the global crisis via CAMELS ratios. Procedia-
Social and Behavioral Sciences, 24, 1530-1545.
Eng, T. S. 2013. Effect of NIM, BOPO, LDR, NPL and
CAR against ROA of International and National Bank
Go Public period 2007-2011. Jurnal Dinamika
Manajemen, 1(3).
Hardikasari, E., Hardikasari, E., & Pamudji, S. 2011. The
Influence of Corporate Governance Implementation
on Financial Performance in Banking Industry listed
in Indonesia Stock Exchange (BEI) year 2006-2008.
Universitas Diponegoro.
Leventis, S., Dimitropoulos, P. E., & Anandarajan, A.
2012. Signalling by banks using loan loss provisions:
the case of the European Union. Journal of Economic
Studies, 39(5), 604-618.
Noverio, R., & Dewayanto, T. 2011. Analysis of the
Auditor’s Quality Impact, Liquidity, Profitability and
Solvency on Going Concern Audit Opinion on
Manufacturing Companies listed on Indonesia Stock
Exchange. Universitas Diponegoro.
Permatasari, I., & Nuswantara, D. A. (2012). Information
Content Analysis on New Regulation of Commercial
Banks’ Health: A Study on Indonesian Case. Paper
presented at the International Conference on
Management (online), (www.internationalconference.
com.my, accessed on 20 Mei 2013).
Sabir Muhammad, Ali Muhammad, Habbe Hamid. 2012.
Analysis on the Influence of Bank Health Ratio on
Financial Performance of Sharia Bank and
Conventional Bank in Indonesia. Jurnal IISn Vol. 1
no.1.
Sari, I. 2010. The Influence of Good Corporate
Governance Mechanism on National Banking
Performance (Study on Banking Companies listed in
Indonesia Stock Exchange period 2006-2008).
Universitas Diponegoro.
Setyaningsih, N. R., & Herawati, T. 2013. Influence of
Bank Health Level on Profit Change (Study on Sharia
Bank in Indonesia year 2010-2012). Jurnal Ilmiah
Mahasiswa FEB, 2(2).
Utama, C. A., & Musa, H. 2011. The Causality between
Corporate Governance Practice and Bank
Performance: Empirical Evidence from Indonesia.
Gadjah Mada International Journal of Business,
13(3).
JCAE Symposium 2018 – Journal of Contemporary Accounting and Economics Symposium 2018 on Special Session for Indonesian Study
322
