
The Social Media Perception and Reality – Possible Data Quality
Deficiencies between Social Media and ERP
Mirona Ana-Maria Popescu
1
, Mouzhi Ge
2
and Markus Helfert
3
1
Faculty of Entrepreneurship, Business Engineering and Management, University Politehica of Bucharest, Romania
2
Faculty of Informatics, Masaryk University, Czech Republic
3
School of Computing, Dublin City University, Ireland
Keywords: Data Quality, ERP, Social Media, Business Intelligence Solutions.
Abstract: With the increase of digitalisation, data in social media are often seen as more updated and realistic than the
information system representations. Due to the fast changes in the real world and the increasing Big Social
media data, there is usually certain misalignment between the social media and information system in the
enterprise such as ERP, therefore there can be data deficiencies or data quality problems in the information
systems, which is caused by the differences between the external social media and internal information
system. In this paper, underpinned by the work of ontological data quality from Wang and Wand 1996, we
investigate a set of data quality problems between two representations - Social Media and ERP. We further
discuss how ERP system can be improved from the data quality perspective.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays -in the area of big data- data exploration
and social media are offering a constant data feeds
that represent real world phenomes. Based on the
social media data, data analysis has begun to be part
of the social media system. These can be observed as
a reflection of the real world. At the same time, data
in social media is often seen as more realistic than the
real world representation. Facebook's organic reach is
steadily decreasing, so a system should have the
pressure to create content that is relevant to their
consumers. In this paper we examine the variation
between real world and its representation in social
media.
Over the last decade, many researchers and
practitioners have emphasised the importance of data
quality (Ge and Helfert 2007). Data quality has
become a critical concern to the success of
organisations. Numerous business initiatives have
been delayed or even cancelled, citing poor-quality
data as the main reason (Ge et al 2017). Ge et al. 2017
further point out that despite the sizeable body of
literature available, relatively few researchers have
tackled quantifying the conceptual definitions. The
literature provides numerous definitions and
taxonomies of data quality dimensions analysing the
problem in different contexts. Also, literature
provides us with numerous case studies, investigating
data quality in practice. Research as well as industrial
discussions (such as Gartner 2017) with practitioners
identified that firms may lose upwards of 10% of
revenues due to poor operational data, together with
other serious consequential effects relating to tactical
decision making and strategy generation. A report
from The Data Warehouse Institute estimated that
data quality problems costs US business $600 billion
a year (5% of the American GDP) in postage, printing
and staff overhead costs alone, whilst the majority of
the senior managers in those companies affected
remained unaware (Ge and Helfert 2013).
Wand and Wang (1996) have developed a data
quality model based on the differentiation between
internal and external view. The external view is
concerned with reflection of real world facts. In
contrast, the internal view addresses the construction
and operation necessary to attain the required
functionality in information systems, given a set of
requirements which reflect the external view.
Underpinned by this model, therefore, social media
can be seen an external view of the real world. The
internal view can be described as an information
system that combines data collection, storage
management tactics and analytical tools to provide
comprehensive and competitive process of planning
and decision-making in an organization. The entire
198
Popescu, M., Ge, M. and Helfert, M.
The Social Media Perception and Reality – Possible Data Quality Deficiencies between Social Media and ERP.
DOI: 10.5220/0006788801980204
In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2018), pages 198-204
ISBN: 978-989-758-298-1
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

organizational context requires rigorous planning,
standardization of procedures and optimization of
existing resources.
In this paper, we demonstrate the propositions,
using one of the typical information systems,
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP). ERP platform
enables companies to improve the most important
metric: sales, profits, costs, quality of products and
services, customer satisfaction. Promoting improved
organizational performance, it plays a crucial role in
the production and processing of knowledge
management. Improvements are seen in
organizational activities, decisions, products,
services, processes and relationships, which will lead
to improved organizational performance.
Furthermore, implementing Business Intelligence
Solutions in ERP will help the processing of
knowledge management, research and development
by extracting information already processed by the
other information systems implemented by the
organization.
Due to the fast changes in the real world -reflected
via Big Social media data-, there is always a
misalignment between the representation in social
media and the enterprise information system such as
ERP. Caused by the difference between the social
media and internal information system, there are
usually data deficiencies or data quality problems in
the information systems.
Underpinned by the work on Data Quality from
Wand and Wang (1996), we examine with this paper
the various viewpoints between two representations,
on the one hand side ERP and on the other side the
view offered by Social Media. In this paper, we
expand this ontological concept with the perception
Social Media can provide, in form of a social media
create “reality” or perception. We then propose a set
of data quality deficiencies resulting from an
ontological view on information system. To identify
a set of criteria for a real-world system to be properly
represented by an information system. Based on this,
they identify possible representation deficiencies that
can occur during system design and data production.
The remainder of the paper is organized as
follows: Section 2 conducts a literature review on
social media and information systems. Section 3
discusses some typical social media system from the
digital marketing perspective. Section 4 provides and
overview on the ERP system. Based on Section 3 and
4, section 5 summarises possible data deficiencies
between social media and ERP systems.
2 RELATED WORK
Wamba (2017) developed a theoretical model to
determine if the internal and external factors have a
role in adopting social media in an organisation. The
model is examined utilizing cross-sectional
information gathered from various working
environments in various geographic districts. The
outcomes reveal the presence of particular selection
practices for various gatherings inside the general
example. These discoveries sustain the
implementation of social media into a workspace.
Carr (2017) analyses the impact of Social Media
on an enterprise and how it can be utilized to
accomplish generous business execution upgrades.
Jinno (2017) outlines the consequences that consists
in actualizing endeavour asset arranging adequacy
from the viewpoint of execution strategy and
operational viability. With ERP Systems,
organizations can institutionalize their business forms
and oversee them all the more viably and
productively. Irani (2017) outlines online
networking/Web 2.0 in building information sharing
abilities. Restrictions and further research into the
utilization of online networking/Web 2.0 are
discussed. Dezdar (2017) describes the innovation
factors and hierarchical factors. It conceptualize an
incorporated connection between ERP execution
benefits, ERP venture factors, ERP framework
factors, and hierarchical factors in a single model.
The examination demonstrated that ERP framework
quality, ERP seller support, and client preparing and
instruction had positive association with client
fulfilment and ERP usage benefits appropriately.
Alimam (2017) gives another point of view, one
that underpins the claim that economical views are
important. Aloini (2016) studies the evolution of ERP
systems from a social point of view and also a
collaborative one by taking into account the
suitability. There highlight the advantages and
impediments and proposed a framework. He et al.
(2016) provides the perspective to organizations in
order to improve their strategies regarding social
media. ERP systems have an impact on the absorptive
capacity of a firm, except the e-commerce ones. The
existence of social media is strong related to this
capacity. It is based on the work by Loukis (2016).
Leonardi (2015) outlines the significance of a data
rich informal community to the production of
information. It is based through firms' web-based
social networking activities. Lam (2016) discusses
the hypothetical and administrative ramifications
from the point of view of operations administration.
The paper describes three interrelated objectives. It
The Social Media Perception and Reality – Possible Data Quality Deficiencies between Social Media and ERP
199

gives a hypothetical structure, in light of the idea of
affordances, to estimate the potential ramifications of
online networking use for sorting out. Second, it
surveys existing grant via web-based networking
media and arranging, featuring web-based social
networking dispersion, utilize, and its suggestions for
hierarchical procedures of correspondence,
coordinated effort, and learning sharing. Third, it
depends upon the affordance viewpoint and existing
grant with a specific end goal to express a motivation
for future research via web-based networking media
and arranging, pushing for an enhancement of the
marvels under examination and for more noteworthy
assorted variety and inventiveness in the
methodological methodologies.
3 SOCIAL MEDIA - EXTERNAL
VIEW
3.1 Google
We are experiencing a technological trend heading
towards total personalization. That is why the
expression 'data is more important than gold’ is
becoming more and more valid. Not only social
networking messages or site banners are personalized
by remarketing campaigns, but also searches on
Google. Newsletters display dynamic parts based on
people's behaviour, and more recently, websites adapt
to the context of the visit. Provides multiple audience
creation and usage capabilities, easily managed from
either Google Analytics or Google Adwords, tracking
data from multiple people's platforms - Youtube,
Gmail, Search, or the Display Network (GDN).
Google Announces Attribution, a platform for a
concept that promises to revolutionize digital
reporting, identifying the effectiveness of each digital
touch used by people in online businesses. It is more
than obvious that if a social network did not directly
generate a desired action on the site, certainly this will
influence that action indirectly.
3.2 Facebook
It provides access to very detailed data about people
and their interaction in the social network, create
audiences with those who have seen videos on
Instagram, with those who have interacted with the
Facebook page, or subscribers to the newsletter, see
messages specific to people who have dropped out of
the order book page or another step in the shopping
process. Provides the most accurate segmentation of
subscribers, and if brands automate 'customer care'
processes between email marketing platforms and
CRM applications, their subscribers receive more
relevant and smarter messages for their automatically
sent interests without human intervention.
It can be determined by a mix of human behaviour
and the process of purchasing a product / service
offered by a particular brand. Digital budgets should
be determined by these factors and not by the
calculated availability of profit, as is often the case.
Digital instruments, channels, banners, and figures
are the means by which we interpret human
behaviour. Therefore it is essential to match as best as
possible specific messages to the audiences.
However, without having data about the people we
are following, it is almost impossible to find out what
they intend to do. Using data is a tactic that draws us
close to the essence of marketing. Thus, we have
considered social media as an external view and the
relationship between this external view and ERP is
described as follows.
Figure 1: External view from Social Media.
4 ERP SYSTEM - INTERNAL
VIEW
An ERP system requires a large data volume to track
precisely the process undertaken by a company and
offers a financial report, as well as gives a proper
program to its development. Each progression in a
business procedure expects clients to enter or refresh
information in an ERP system. This is highlighted in
Figure 2.
ERP system allows the company to organize and
pursue investments in research and development
projects. Thus, ERP for commercial field could
underlie the entire process of decision management in
the company, where it will be implemented, it can
provide managers the most effective way to analyse
different scenarios and achieve the most efficient and
effective products and services through investments
in market research on customer preferences, in order
ICEIS 2018 - 20th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
200

Figure 2: Information Organisation in ERP.
to support the ideals of corporate social responsibility
and investment in research on developing new
products and services according to the real needs of
the market at the present time, inspired by market
research conducted.
Entering information in a convenient and exact
way is usually done by users of the ERP system. This
procedure of gathering information is frequently
manual, tedious, where mistakes can occur. Since
ERP underpins end-to-end forms, more information
is expected to guarantee accuracy. For instance, to
make a client record in ERP, it is not enough to set
the economic component of the client record and it is
needed also the sell part, the repository, the
commerce, and so on. As the entered data volume
grows the number of possible errors increases. These
glitches, appear later in the process, can cause
enormous damages and lie at the base of numerous
information quality issues in the company.
Since each procedure has a budgetary effect, all
information quality issues in the long run stream
down to the accounting department group. The data
that come from consumers into the ERP helps the
company to understand the needs of the clients and
the actions that should be developed. Data that comes
from consumers about the company or its services /
products is an essential factor in its development as a
brand and in consolidating its position on the market.
The review indicates an assessment of a product,
service or location, or an artistic creation by a person
who has found a particular interest in the subject.
Some critical analysis does not necessarily require
specialist training for the evaluator. Reviews and
comments by users who bought the product are the
most important source of information from those who
have bought and used the product. Based on the
review, we are able to provide quality information
that can be composed by respecting the following
rules:
To know where and for whom the review is
written.
To show the writer’s point of view as clear as
possible. A review of product should under no
circumstances end in a vague, indefinite note,
and it must reveal the writer’s position that
remains in the mind of the reader (liked or not)
but not in an explicit way, but from the weight of
those pluses or minuses.
The written information should be original.
To write smart (but reasonable, not to make
smart).
Not to praise or accuse for free.
Accept the possibility of differences of opinion.
Provides the context in which the review
appears: if it is part of a wider research, a hobby
or a contest, an express request from someone
interested in reactions etc.
Express the writer’s opinion. The review itself is
a way of reflecting, ordering someone’s thoughts
and weighing the pluses and minuses to finally
make a conclusion.
A form of rating: the specificity of the review is
that at the end of it you are allowed - even
indicated - to give a note after your own
evaluation system.
5 DATA QUALITY DEFICIECIES
BETWEEN SOCIAL MEDIA
AND ERP
Integrating the components of social media with ERP
systems were considered of critical importance in
comparison with combining social media websites
with ERP. The retail marketing and reputation
management are influenced by the advantages given
when integrating social media in ERP systems. The
capacity to incorporate with outer web-based social
networking devices on the general population web
does not weigh intensely on the determination
procedure for ERP. However, the appropriation of
web-based social networking capacities to
incorporate cooperative and correspondence
capabilities is seen with significance yet isn't viewed
as a noteworthy influencer. There are two essential
advantages of social usefulness installed in ERP; to
streamline and convey inside the undertaking and also
to record business process-es to help lean activities.
Data quality can impact the competitiveness and
economic activity that refers to the value of the
relationship with the data with quality and the success
of a business. To further highlight the focus of this
The Social Media Perception and Reality – Possible Data Quality Deficiencies between Social Media and ERP
201
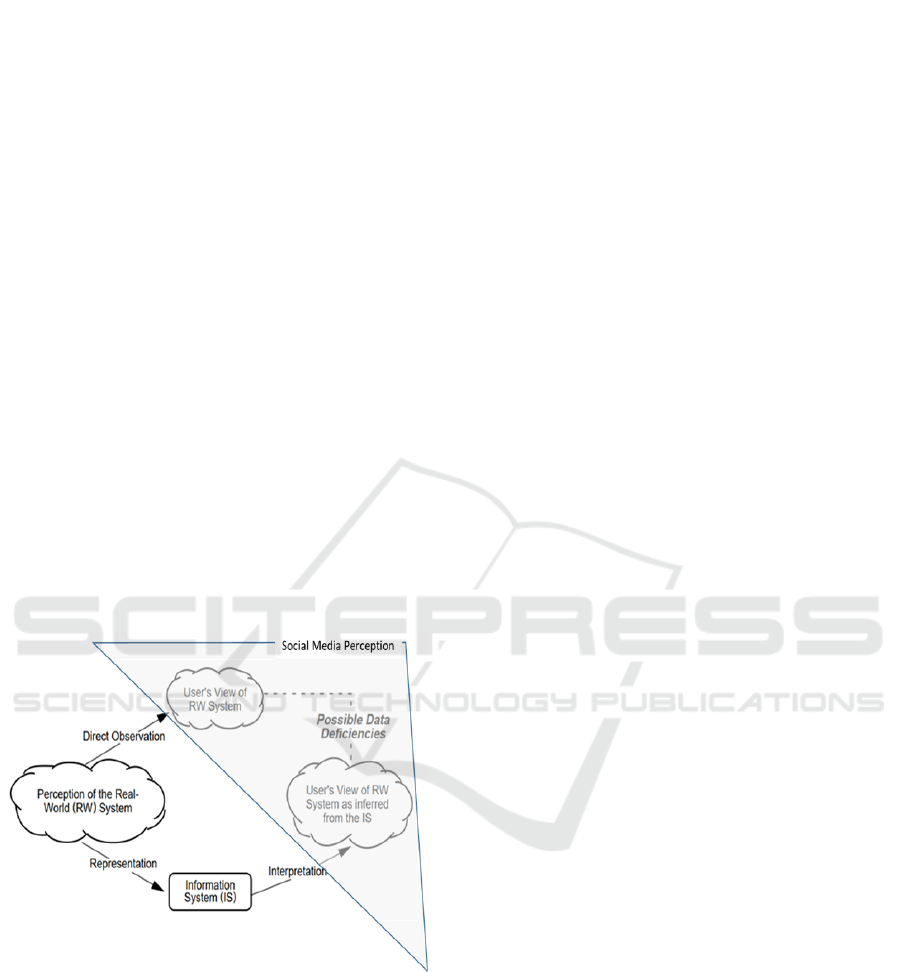
paper, we have demonstrated the social media
perception and the representation from ERP system in
Figure 3. Wand and Wang (1996) further detailed
four types of representing a real-world system, which
are interpreted as follows:
Proper Representation: The representation of a
real-world system (we consider it as Social
Media in this paper) is based on the mapping
each of its valid states to at least one valid state
that corresponds to the information system and
vice versa.
Incomplete Representation: The mapping from
Social Media to ERP must be thorough (i.e., each
of the states in RW is mapped to IS) in order to
represent a real-world system by using an ERP.
Ambiguous Representation: If there is more than
one real-world state mapped into the same state
of the information system, then the
representation is not right and the information is
not enough in order to assume which of the
Social Media state is expressed.
Meaningless States: It is not mandatory that
the mapping from Social Media to ERP be
thorough concerning ERP. In any case, when this
circumstance exists, there are legitimate states in
ERP that cannot be mapped back to a state in
Social Media.
Figure 3: Social Media perception (adapted from Wand and
Wang 1996).
By considering the four types of possible data quality
problems proposed in Wand and Wang in 1996. We
have found a set of data quality problems that are
caused by the misalignment between social media and
ERP systems as shown in table 1 in the appendix. We
found that data quality management in ERP is not just
about fixing data or improving quality within a single
business application or process, but also about taking
a more expansive and forward-looking enterprise-
wide approach. This should involve addressing
cultural issues, initiating both short and long term
process and procedural improvements by a step-by-
step, incremental approach, whilst ensuring that the
data conforms to appropriate specifications or
requirements.
It can be seen that there cannot be a “one size fits
all” remedy to embedding organisational
improvements in ERP systems, but rather to identify
appropriate solutions to fit individual situations and
circumstances. One accepts that data quality
problems are not created intentionally by people, but
more by the failure of the surrounding processes
whether these are system related or individual related
involving lack of education, training, personal
developments or purely the person being placed in a
position for which they are not suited. This research
has major practical implications which leads to a
further key theme, that of aligning robust theoretical
and academic concepts, within the operating
environment of a real-life ERP, in order to implement
sustainable data quality improvements. It is also
recognised that research in this specific area may
have implications for other functional sectors where
process improvements programmes can be applied.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we have validated the ontological data
quality view that are proposed by Wand and Wang in
1996, where data quality deficiencies are caused by
the misalignment between real-world perception and
information system representation. In order to study
this misalignment, we have instantiated the real-
world perception as social media, which can be
considered as reflection of the real world. On the
other hand, information system representation is
illustrated by the ERP system.
Based on the observation of the differences
between social media and ERP systems, we have
concluded a table that contains possible data duality
deficiencies that are caused by misalignment between
Social Media and ERP. Based on the results, this
paper has also discussed the indications of data
quality management in ERP systems. As a future
work, we plan to further investigate how to
improvement the data quality in the ERP systems, and
how to proactively prevent possible data quality
deficiencies.
ICEIS 2018 - 20th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
202

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported, in part, by Science
Foundation Ireland grant 13/RC/2094 and co-funded
under the European Regional Development Fund
through the Southern & Eastern Regional Operational
Programme to Lero - the Irish Software Research
Centre (www.lero.ie)
REFERENCES
Alimam, Mayla, Emmanuel Bertin, and Noel Crespi
(2017). ITIL perspective on enterprise social media.
International Journal of Information Management 37.4:
317-326.
Aloini, Davide, Riccardo Dulmin, Valeria Mininno, and
Alessandro Spagnesi (2016). Benefits and barriers of
social/collaborative ERP systems: a state of the art and
research agenda. In Strengthening Information and
Control Systems, pp. 171-184. Springer.
Carr, Peter (2017). Whole Enterprise Social Media for
Business Performance. Phantom Ex Machina. Springer
International Publishin. 25-35.
Dezdar, Shahin (2017). An integrative model for realising
benefits from enterprise resource planning
implementation. International Journal of Business
Information Systems 24.4: 423-451.
He, Wu, Xin Tian, Yong Chen, and Dazhi Chong (2016).
Actionable social media competitive analytics for
understanding customer experiences. Journal of
Computer Information Systems 56, no. 2: 145-155.
Ge, Mouzhi, Helfert, Markus (2007), A review of
information quality research—develop a research
agenda, International Conference on Information
Quality 2007, MIT USA, pp. 76-91,
Ge, Mouzhi, O’Brien, Tony, Helfert, Markus (2017)
Predicting Data Quality Success - The Bullwhip Effect
in Data Quality. Perspectives in Business Informatics
Research. BIR 2017. Lecture Notes in Business
Information Processing, vol 295. Springer.
Ge, Mouzhi, & Helfert, Markus. (2013). Cost and Value
Management for Data Quality. In Handbook of data
Quality (pp. 75-92). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Gartner (2017) How to Overcome the Top Four Data
Quality Practice Challenges.
Irani, Zahir, Amir M. Sharif, Thanos Papadopoulos, and
Peter ED Love (2017). Social media and Web 2.0 for
knowledge sharing in product design. Production
Planning & Control 28, no. 13: 1047-1065.
Jinno, Haruna, Hiromichi Abe, and Kayo Iizuka (2017).
Consideration of ERP Effectiveness: From the
Perspective of ERP Implementation Policy and
Operational Effectiveness. Information 8.1: 14.
Knight, S, Burn, J. (2005) Developing a Framework for
Assessing Information Quality on the World Wide
Web, Informing Science 8(5).
Lam, Hugo KS, Andy CL Yeung, and TC Edwin Cheng
(2016). The impact of firms’ social media initiatives on
operational efficiency and innovativeness. Journal of
Operations Management 47: 28-43.
Leonardi, Paul, and Emmanuelle Vaast (2016). Social
media and their affordances for organizing: A review
and agenda for research. Academy of Management
Annals.
Loukis, Euripidis, Spyros Arvanitis, Niki Kyriakou, Anna
Famelou, Michail Marios Chatzianastasiadis, and
Foteini Michailidou (2016). ERP, e-Commerce, Social
Media and Absorptive Capacity of Greek Firms: An
Empirical Investigation. In Proceedings of the 20th
Pan-Hellenic Conference on Informatics, p. 26. ACM.
Teegalapally, Vivek, Kiran Dhote, Vamsi S. Krishna,
Shubham Rao (2016), Survey on Data Profiling and
Data Quality Assessment for Business Intelligence.,
International Research Journal of Engineering and
Technology, 3 (11).
Wamba, Samuel Fosso, Mithu Bhattacharya, Laura
Trinchera (2017), and Eric WT Ngai. Role of intrinsic
and extrinsic factors in user social media acceptance
within workspace: Assessing unobserved
heterogeneity. International Journal of Information
Management 37, no. 2: 1-13.
Yeoh, William, and Aleš Popovič, (2016), Extending the
understanding of critical success factors for
implementing business intelligence systems, Journal of
the Association for Information Science and
Technology 67.1: 134-147.
Wand, Yair, and Wang, Richard Y. (1996) Anchoring data
quality dimensions in ontological
foundations. Communications of the ACM, 39 (11):
86-95.
The Social Media Perception and Reality – Possible Data Quality Deficiencies between Social Media and ERP
203
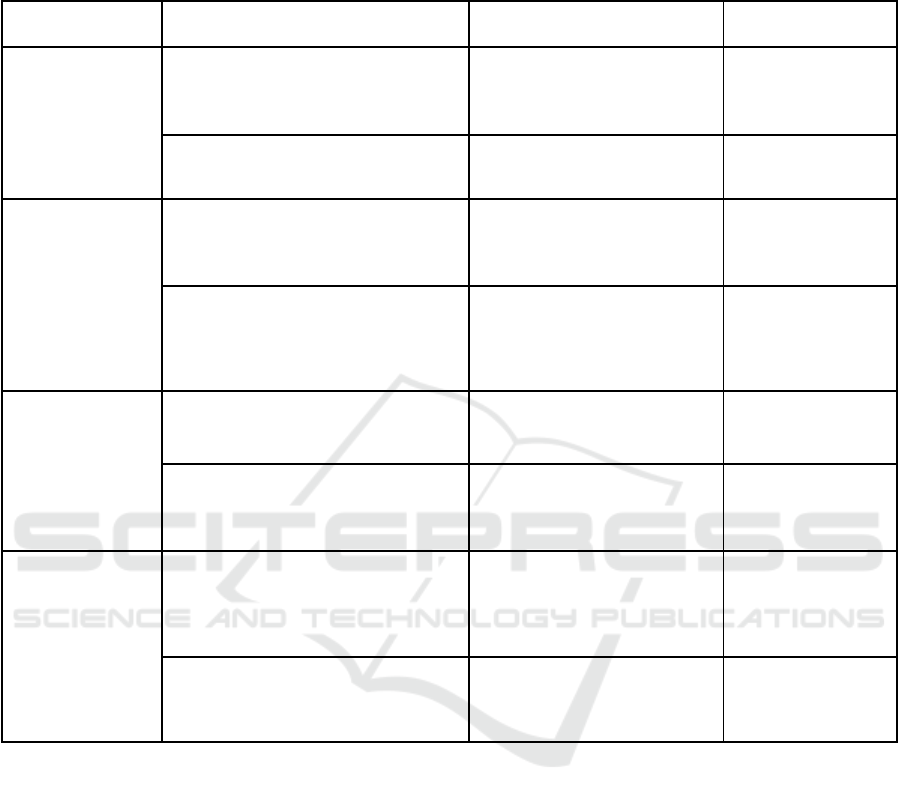
APPENDIX
Table 1: Possible Data Quality Deficiencies between Social Media and ERP.
DQ Deficiencies
Perception of Social media
Representation in ERP
Possible Data quality
problems
Incomplete
Representation
The user would rely more on the reviews
from the other users to choose this product,
which is more important than the product
description itself
Only included the essential
information about the product
Missing the reviews
The user relies on the product’s
description, relevant for his decision to
acquire or not the product.
This information may consist of
functionalities, features.
Missing data regarding
the product
Ambiguous
Representation
The product has a description based on
vague phrases or their construction is not
precise and the customer is not able to
understand what the product offers.
The description made by the
company’s specialists has multiple
meanings or the content is not
precisely.
Data with various
meanings and
imprecise.
The quality of the product is described
very equivocal. The customer remains
with a lot of questions unanswered.
There is offered information about
the product’s characteristics, but
the terms used are too complex or
they are giving the text different
connotations.
The quality data is
unclear.
Meaningless
Representation
The product description does not match to
the product itself or has no relevance for it
in the customer’s opinion.
The description was mismatched
by the system or the person in
charge of writing it.
The description of a
product is linked to
another product.
The product’s price is not an amount of
money that will confuse the customers and
make him even think that the company
which is selling it is not a serious one.
There are displayed strings or
special characters.
Data in a wrong format.
Proper
Representation
The customer finds all the information
needed about a product.
The customer’s reviews are
available next to the product and
the description of it is complete and
detailed reaching all the important
point.
The good communication and data
transmission between the suppliers and the
sellers give the actual availability of a
product to satisfy the customer.
The status regarding the product
availability is always up to date
ICEIS 2018 - 20th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
204
